lcd screen power consumption price
Today, people use TVs to stream the latest shows and movies in excellent picture quality. But televisions are doing more than providing entertainment value. Your television draws power every second it"s on, which means you should consider your TV power consumption every time you pay your electric bill. How much power does a TV use? Continue reading to learn how much electricity a TV uses across the different types of television sets available.
With these variables in mind, you can better determine how much energy a TV uses over a set period. First, you should learn more about the different types of televisions and how much power they draw. Please remember that the following wattages listed are generalized since every TV is different. Use the following information to get closer to understanding your TV"s power consumption.
LED stands for "light-emitting diode." LED TVs use this technology to provide excellent picture quality with low power consumption. Today, most consumers use LED TVs to watch movies, tune in to their favorite shows and play the latest video games. Most LED screens range from around 30 to 60 inches, but recently, people have started buying larger LED TVs reaching upward of 85 inches. LED technology allows for these massive screen sizes, thanks to their inexpensive design and efficient energy performance.
A 32-inch LED TV will consume around 50 watts of electricity. On the other end of the size spectrum, you can expect a 50-inch or larger LED TV to consume 100 watts at the most, with many modern LED TVs using much less energy. Compared to plasma, LCD and OLED TVs of similar sizes, you"ll find LED TVs are significantly more efficient, which makes them a popular product.
LCD screens use tiny lights called pixels that manipulate the colors of green, blue and red to create moving images. These pixels get the electrical power needed to emit light using liquid crystals, which is where the term LCD comes from. LCD TVs grew in popularity during the late "90s and early 2000s because the technology allowed the TVs to be slimmer, letting people mount their televisions on walls for the first time.
Besides these advantages, LCD TVs also provided consumers with a more energy-efficient television option over the outdated cathode-ray tube variety. However, they are slightly less energy-efficient than LED TVs of similar sizes. A 30-inch LCD TV uses about 60 watts of electricity. Larger LCDs like a 50-inch model will use around 150 watts.
Plasma TVs use a different type of technology than LEDs and LCDs. Plasma is an electricity-conductive gas. As the plasma receives energy, the particles begin moving and colliding which causes the release of light photons. This technology allows plasma TVs to have a slim form factor like LEDs, but plasmas differ considerably from LED TVs in their wattage used.
Plasma TVs produce incredible images with deep blacks and crisp color contrast, but they use a lot of energy in the process. In 2009, the California Energy Commission banned the sale of TVs that do not meet efficiency standards when powered on and displaying a picture. To put this information into perspective, a 42-inch plasma TV can consume nearly 500 watts of electricity. This level of energy use puts plasma TVs in a similar realm of power consumption as that of many household refrigerators.
OLED stands for "organic light-emitting diode" and is one of the latest progressions in television technology. Many viewers agree that OLED TVs provide the best picture quality available, but they do this at the expense of slightly increased power consumption over their LED predecessors.
For perspective, a 65-inch OLED TV will consume nearly 120 watts of electricity compared to a 65-inch LED, which will use close to 90 watts. It may seem like a minuscule difference at first, but this increase in energy consumption will add up over your TV"s lifetime.
Using an energy-efficient TV can help lower your monthly energy bills and reduce your carbon footprint. Often, modern TV packaging will display how much energy the TV uses in a year under a specific set of parameters. If you want to be even more energy-conscious, you can buy Energy Star-certified TVs that can help keep your TV power consumption low while still giving you excellent picture quality.
The Sceptre E185BV-S LED TV is the option for you when you want to save as much as possible on your energy bill. With its low weight and portable design, you can easily move it around your house for use in the living room, bedroom or guest room. Plus, its size makes it a viable option as a desktop computer monitor, so you can use it for work and leisure. Here are some of the specs.Screen size: 18 inches
For a TV that doesn"t sacrifice image quality for excellent energy efficiency, choose the VIZIO D40-D1. It has a refresh rate of 60 Hz with 1080p resolution, so you know you"re getting outstanding picture quality without cranking up the energy usage. Here are some things to note about the VIZIO D40-D1.Screen size: Ranges from 24 to 50 inches
If you"re an informed consumer who cares about your energy consumption and monthly bills, you may be searching for ways to reduce your carbon footprint. At EnergyBot, we can help lower your energy bill by pairing you with the lowest-cost energy provider in your area. Getting started with our process is easy, and the results could keep more in your pocket every month.

The power consumption of computer or tv displays vary significantly based on the display technology used, manufacturer and build quality, the size of the screen, what the display is showing (static versus moving images), brightness of the screen and if power saving settings are activated.
Click calculate to find the energy consumption of a 22 inch LED-backlit LCD display using 30 Watts for 5 hours a day @ $0.10 per kWh. Check the table below and modify the calculator fields if needed to fit your display.
Hours Used Per Day: Enter how many hours the device is being used on average per day, if the power consumption is lower than 1 hour per day enter as a decimal. (For example: 30 minutes per day is 0.5)
LED & LCD screens use the same TFT LCD (thin film transistor liquid crystal display) technology for displaying images on the screen, when a product mentions LED it is referring to the backlighting. Older LCD monitors used CCFL (cold cathode fluorescent) backlighting which is generally 20-30% less power efficient compared to LED-backlit LCD displays.
The issue in accurately calculating the energy consumption of your tv or computer display comes down to the build quality of the screen, energy saving features which are enabled and your usage patterns. The only method to accurately calculate the energy usage of a specific model is to use a special device known as an electricity usage monitor or a power meter. This device plugs into a power socket and then your device is plugged into it, electricity use can then be accurately monitored. If you are serious about precisely calculating your energy use, this product is inexpensive and will help you determine your exact electricity costs per each device.
In general we recommend LED displays because they offer the best power savings and are becoming more cheaper. Choose a display size which you are comfortable with and make sure to properly calibrate your display to reduce power use. Enable energy saving features, lower brightness and make sure the monitor goes into sleep mode after 5 or 10 minutes of inactivity. Some research studies also suggest that setting your system themes to a darker color may help reduce energy cost, as less energy is used to light the screen. Also keep in mind that most display will draw 0.1 to 3 watts of power even if they are turned off or in sleep mode, unplugging the screen if you are away for extended periods of time may also help.

Before we get into the details of power consumption, let"s explain how we test for power consumption. We plug the TV into a Kill-A-Watt meter which measures the wattage. We display our checkerboard test pattern in SDR after calibration with local dimming disabled, and we record the power consumption. This is supposed to give an idea of everyday usage, but since everyone"s consumption is different, it"s simply an estimate. As for the max consumption, we set the TV in HDR with the checkerboard pattern, which sets the brightness to the max and enables local dimming, and we record the wattage in this situation.
Now that we have that out of the way, let"s talk about power consumption. Most modern TVs don"t take up much power as technologies such as LED and OLED have brought television power usages down a fair margin. Gone are the days of inefficient CRTs and plasma sets that could run up electricity costs by a good amount or even overheat.
Along with developments in technology that have allowed for more energy-efficient TVs, other new advances need more power, like HDR, which requires TVs to get brighter. Larger TV sizes are also becoming more popular, so they need more power than smaller TVs, even if they use the same technology. However, even then, TVs still don"t require a whole lot of power to function, and they won"t be burning a hole into your wallet when you get your utility bill.
TVs that require more power also get hotter. For most 4k TVs, this isn"t too much of a problem, but we"ve noticed 8k TVs get hot. If you have a TV that gets hot, it"s best to avoid placing it in a hot room and allow for good air ventilation around it. This shouldn"t be much of a problem in the winter because it may actually help heat your room, but you can end up spending more on air conditioning to cool it down in the summer. Then again, most 4k TVs won"t get hot enough to make a big difference in the winter or summer.
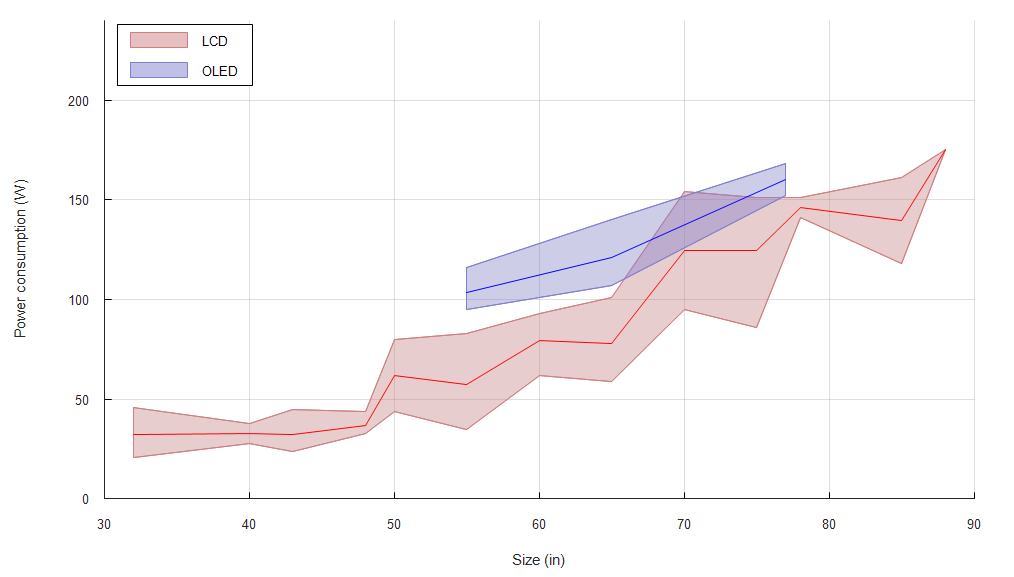
As you can see in this chart plotting TVs from 2016 and 2017, there"s a definite link between size and power consumption. Some features, such as full-array local dimming, are more costly, both to build and use. They require more LEDs than standard direct-lit and edge-lit type LCD TVs, but this isn"t represented in the chart. OLEDs have been consistently more power-hungry than the average LED models. In both cases, it"s not a ton of power, especially compared to older plasma TVs that often consumed twice as much as even the hungriest LEDs and OLEDs.
This chart above is a bit old now, so don"t look at the data points, but the trends still apply under our latest Test Bench 1.6 with 2020 and 2021 TVs. Out of our 4k TVs that we"ve tested, the TVs that require the most power in SDR are generally OLEDs. Seven of the ten most power-hungry TVs are OLEDs, and the three LEDs in the top 10 are 65, 75, and 85 inches. Larger TVs still require more power than smaller ones, which is expected. We noticed another trend with the Max Power Consumption: the 4k TVs that require the most power are also some of brightest, which are all LEDs. Even if you get an LED TV, it doesn"t mean it will need less power than OLED if you constantly watch HDR content at its max brightness.
Another trend we notice is that 8k TVs require a lot more power than 4k TVs. This makes sense because 8k TVs have four times the pixels as 4k TVs, so they need more energy to power. When testing 8k TVs at their max consumption power, they often get too hot to touch, which we rarely notice with 4k TVs.
Not only does consumption scale with size, but it also almost perfectly scales with brightness. As you can see above, raising your brightness from minimum progressively leads to higher consumption and inevitably higher costs. Reducing the brightness to the 50% setting instead of max doesn"t exactly halve the energy use, but that"s mostly because other parts of the TV also consume some energy.
Lower the backlight setting. The backlight is by far the biggest drain on your power, and the lower you can get your backlight, the less power your TV will consume. Placing your TV in a dark or dimly lit environment will help you avoid needing a bright backlight.
A lot of TVs have a “Quick Start” feature. This usually means that they stay in standby mode when you press the power button instead of shutting off completely. Turning these features off can help, but some models also allow you to hold the power button on the remote to shut down completely.
Most TVs today feature a light sensor that can adjust the TV"s brightness to the room. Instead of having the TV constantly run at a static brightness, this feature can help reduce consumption by lowering the brightness when it isn"t needed. However, some people may not enjoy this because it constantly changes the brightness.
If you often fall asleep in front of the TV at night, make use of its sleep timer feature. This greatly reduces consumption since you"re not leaving the TV on when you"re not watching it.
Power consumption varies from TV to TV and with the type of content you watch. However, there"s a trend that larger, brighter, and 8k TVs require the most power to function. OLEDs also tend to have slightly higher energy consumption than LEDs, but not if you"re using a bright LED TV and watching HDR content. You can use our power consumption calculator above to give you an estimate of how much you"ll be spending on electricity annually, but it all depends on the type of content you watch.

While we can’t keep your kids away from Paw Patrol, at Power Wizard, we can help you make sure you have an electricity rate that is so low, you will want to watch TV all day long!
The electricity usage of your flat-screen TV can vary widely depending on the size. The level of technology also makes a difference, but size has a larger impact on electricity usage.
No, flat-screen TV’s do not typically use a lot of electricity. They only use a small fraction of energy compared to other appliances and electronics.
TVs with improved technology use energy more efficiently than older models. However, newer TVs usually have larger screens so they might require more power.
Even with larger screens that consume more energy than older models, the flat-screen TV in your home still only makes up for about 5% of all of the total electricity that you use each month.
Power Wizard shops around for an electricity plan highly suited for you based on your personal usage needs. This ensures that you’re not overpaying for your electricity.
When you become a Power Wizard member, we continuously monitor the marketplace for better deals and will let you know if one becomes available so we can help you switch.
However, as previously mentioned above, your TV doesn’t consume much electricity when compared to other appliances in your home. There might be better ways to cut savings than downgrading your TV screen size.
She used Power Wizard to shop around for a better electricity plan and ended up saving a ton of money each month without having to change her lifestyle.

There are an estimated 120 million TVs in households across the U.S. But while televisions are among the most commonly owned and used appliances, they actually account for a small portion of your monthly electricity usage. As TV technology advances and screens getter bigger and higher definition, one thing remains constant: TVs are remarkably energy efficient.
According to US Energy Information Administration, the average cost of electricity in the U.S. is 13 cents/kWh. However, this number can vary depending on your electricity supplier. Today, people in some states have the power to shop for their electricity and find cheaper rates.
The first step to lowering your TV costs is watching less TV. The good news is that there are lots of other benefits of limiting your TV consumption. Here are some of our favorite alternative activities to watching TV:
For guaranteed savings on your annual electricity cost, join a community solar project in your area. Perch will help match you to a local solar farm—you"ll support the operations of that farm so that it can generate and contribute as much clean, solar energy to the overall grid. You don"t directly receive electricity from the solar power you"re supporting, but thanks to government incentives, you"ll get credits toward your own utility bill. Essentially, you"re being rewarded with discounts on your own electricity because you"re enabling solar generation and development in your state.

The meter then multiplies the voltage and current values to get the amount of power being used. This power is given in units of kilowatts or watts. These units and the time your devices have been used decide your electricity bill for the month.
Given this data, your TV will be consuming 100x8x30 = 24,000 units per month in watts. Convert this to kilowatts, and your TV consumes 24 kilowatts of power per month. This unit is then multiplied by the cost per unit, which, at the time of writing, is 12 cents on average in the US. Based on these calculations, you would have to pay somewhere around 24x0.12 = $2.88 per month.
Although this number might look small, not every television is built the same, and different TV sets consume different amounts of energy. This energy consumption is based on the technology, size, and of course, your ability to stay glued to the TV while binge-watching a show.
Television sets using cathode ray tubes are bygones. Given their bulky size, television sets using CRT technology were replaced by LCD panels in the early 2000s. That said, with the rise in retro gaming, it"s safe to say that you might have a huge CRT display hooked to your gaming machine if you love playing Contra in the way it"s supposed to be played.
Although the CRT offers a great gaming experience with no input lag and no visible motion blur, these television sets using CRT technology can take up a lot of power to display those crisp images. In fact, a 24-inch CRT TV can draw up to 120 watts of power. To put things into perspective, an LCD of the same size only uses 50 watts of power which is less than half compared to the bulky CRT sets.
That said, the cost of running a plasma TV is high. In terms of power consumption, a 30-inch plasma screen can consume 150 watts, with 60-inch screens hogging over 500 watts. Due to this high-power consumption and issues of permanent burn, plasma TVs also lost popularity and were replaced by LCD technology. Also, the state of California banned plasma TVs power-hungry demands in 2009.
When it comes to TV technology, there is nothing that comes close to LCD. With over 284 million units shipped in 2019, LCD technology dominates the industry, and for good reason.
Offering great picture quality while consuming low power, LCD TVs provide the best of both worlds. In terms of power consumption, a 32-inch set consumes 70 watts of power, while a full-blown 60-inch set uses 200 watts.
In terms of technology, both LED and LCD TVs use the same display technology. That said, as the name suggests, LED TVs use Light Emitting Diodes for backlighting compared to cold-cathode fluorescent lamps, which are used in LCDs.
Due to this difference in backlighting technology, LED television sets offer better contrast ratios and viewing angles. Not only this, but due to the use of less power-hungry LEDs, the power consumption of LED TVs is much lower when compared to LCDs. In terms of numbers, a 40-inch LED tv consumes 50 watts of power, while the LCD consumes 100 watts.
Compared to LCD and LED technologies that use backlights along with Liquid Crystal Displays, OLED TVs use organic light-emitting diodes, emitting light when electricity is applied. Due to this, an OLED TV offers the best contrast ratios and great picture quality.
That being said, OLEDs consume more power when compared to LEDs as they have billions of organic light-emitting diodes, and electricity needs to be supplied to each one of the organic elements. In terms of power consumption, a 60-inch OLED TV consumes 107 watts on average, while an LED TV of similar dimensions consumes 88 watts.
Now that we have a basic understanding of the different technologies of TVs in the market, we can look at how much electricity your TV uses depending on its type. As you might expect, different types of TV tech consume different amounts of power.
The data given above depicts the average power consumption for a particular technology. For accurate power ratings, look at the power rating sticker on your TV or go to your TV manufacturer"s website to find accurate power consumption data.
Once you have the power consumption details for your TV, you can multiply it with your usage and the cost per unit to get an idea of how much electricity your television is consuming.
Your TV wakes up as soon as you click on the power button on your remote control, but how does it capture a signal from the remote when it looks like it"s not working?
It is due to these features that your television draws power from the grid even when it’s in standby mode, and this power consumption is known as vampire power draw.
Although the power consumption of a TV is in the range of 0.5 to 3 watts when in standby mode. It’s important to note that power consumption increases exponentially when smart wake-up features are enabled on smart television sets.
According to MUO Review Editor James Bruce, vampire devices consume way more power than you expect when in standby mode. Therefore, if you have a smart TV at home and love playing content using your favorite wake words, remember that this functionality comes at a price.
On average, a TV consumes 108 kilowatts of energy in a year when smart wake features are disabled. That said, this number increases to 191 kilowatts when smart features are enabled—increasing power consumption by 76.8 percent.

A home without a TV set is more the exception than the rule in the U.S. Many households even have a couple or more. Well, watching TV is one way to relieve stress and boredom, so we can’t blame you if you have a TV in every room. But if you aim to lower your energy consumption, it will be a good idea to find out how many watts a TV use. In that way, you can limit your TV viewing to see a reduction in your electric bill.
How much electricity a TV set uses depends on several factors, such as your TV’s size, age, and the like. In general, a television’s power consumption falls between 80 and 400 watts. So if electricity costs $0.13 per kWh in your area and you leave your set on 5 hours a day, expect your viewing to add around $7.13 a month to your energy expenses.
However, as we said, how much electricity a TV consumes varies. A 24-inch 2080p model will use far less power than a 75-inch 4K QLED one. So if you want to save electricity, knowing the factors that affect your TV’s energy consumption will help with your goal.
Cathode-ray tube (CRT) models: These types were the only models you could find for the longest time. Their energy consumption is around 60 to 100 watts per hour. ACRT TVconsumes about 2-3 watts an hour in standby mode.
LCD models: The size of the panel determines how much power an LCD TV consumes. The median model has a 32-inch panel size, with an electricity consumption ranging between 40 and 55 watts. In sleep mode, this type uses up a minuscule 1W per hour.
LED TVs: Being more energy-efficient, the power consumption of LED TVs is 40% lower on average than other models. Compared to LCD TVs of the same size, one with an LED panel uses up around 50 watts per hour powered up and only 0.3 watts in sleep mode.
Plasma TVs: These models aren’t as energy-efficient as LCD or LED types. The average electricity consumption of a 30-inch TV is around 150 watts per hour. In sleep mode, the plasma TV consumes about 0.5 watts.
You’ll need three essential pieces of information if you want to calculate your TV’s power consumption. These include your unit’s wattage, hours of TV use, and the electricity rate in your area. Use the following formulas to find out how much you pay for your TV viewing.
TV models in the market have wattages between 80 to 400 watts. So let’s say you have a 50-inch LED TV with a rated power of 100 watts, and you use it for 12 hours a day.
Before the invention of the different models, only the size of a cathode-ray tube TV determined how much energy the unit consumed. Advances in technology created various models, some of which are more power-efficient than others. Nowadays, how many watts a TV consumes depends on several factors aside from its size. So if you want to know how many watts a TV use, you’ll need to look at the model.
The older your TV set, the higher its electricity consumption. For example, the energy usage of a 32-inch CRT model stands at 150 watts, on average. Compare that with a newer LED TV of the same size, which is between 40-55 watts and a maximum of 70 watts per hour.
Aside from the reduced power consumption of newer models, upgrades in technology also led to better picture quality. So it’s not just a matter of how many watts your unit consumes but also the viewing pleasure it brings.
The second most significant factor determining how many watts a TV consumes is its size. For example, a LED model 15-inch TV needs only around 15 watts to operate. In contrast, one with a 50-inch panel uses 50 watts an hour. This proves that the size of your TV affects how much power your home draws from the grid. In fact, each upgrade in size will increase the watts your set uses due to the resolution enhancement of the unit.
The display technology used in your TV will affect its power usage and hence, your electricity bill. An LCD and LED TV are comparable when it comes to energy efficiency. Older CRT and plasma screens are substantial energy drains compared to newer screen types. CRT and plasma TVs use around three times more electricity than their LCD and LED counterparts. If you have a TV set using the older technologies, switching to an LCD or LED set can help lower your electricity bill.
Knowing some important terms will allow you to calculate your appliance’s power usage correctly. This will significantly aid your efforts to lower your home’s total energy consumption. These essential terms are the following:
All TV sets have corresponding wattages, which vary depending on the factors we’ve mentioned. If you want to know the wattage of your flat-screen TV, for example, look at the back of your appliance. You’ll usually find a small silver sticker detailing the technical specifications of your unit. These specifications include the wattage, input voltage, and the like.
Undoubtedly, a CRT TV drains more electricity than its LED counterpart. Screen size notwithstanding, the older technology is less energy-efficient, making the old tube a power hog.
A CRT set can use up a whopping 400 watts depending on the screen size and other factors. Plasma screens come second in terms of energy usage at about 150 watts, followed by LCDs which suck up 165 watts of power. LED TVs are the most energy-efficient, as they use up only 155 watts.
Although TV sets aren’t the top energy users in a home, they still consume electricity, and this power consumption can significantly add to your total electricity usage. Thus, they can potentially increase your monthly electric bill. However, you won’t have to give up one of your sources of entertainment to see some savings on your utility expenses. Reducing the amount of power your set draws is the key to your goal.
The backlight drains the most power among your television’s components. Lowering the backlight level will also reduce your set’s energy consumption. Installing your device in a dimly lit environment will lessen your need for a bright backlight. Modern units usually come with a built-in light sensor. Turn it on to automatically optimize your set’s brightness setting.
Turning off your TV set is the best way to reduce its power consumption. Better yet, pull the plug off the socket. The energy consumed by even a 100-inch TV falls to zero if it’s disconnected from a power source. This may seem like a no-brainer, but many people leave their sets on all the time. They may use it for some background noise or don’t even notice it running. Make a conscious effort to power down your set to see some savings on your electricity bill.
You likely have several components connected to your TV. Examples of these are your home entertainment system and gaming consoles. These devices may remain on standby mode without your knowledge, making them continually use electricity. Like with your television, make sure you completely turn off all the accessories attached to it. Using a smart power stripmakes it easier to cut off the power for these devices.
Just because an appliance isn’t powered on doesn’t mean it’s not drawing energy from the grid. Electronics usually have a standby mode setting. In such a state, they continue to consume electricity. Standby power will use about 2.5% to 5% of electricity. The amount may be small but it can add up, especially if you leave all your appliances in this mode. So turn off your set completely when it’s not in use. For greater convenience, you can plug your TV into a smart power strip which turns off devices that are not in use.
The “always-on” feature on your set lets you enjoy viewing ease older generations never dreamed of. Imagine being able to turn on your TV by voice command to a smart speaker. The downside? This feature adds to the set’s electricity usage. You can lower your appliance’s energy consumption by almost 50% by turning off this feature, especially if it’s an Energy Star model.
The best location for your TV depends on your viewing habits. In general, install it in a lighted room to save on the screen brightness. However, if you prefer a theater-like ambiance, place the set in a dimly lit room and adjust the contrast, setting the brightness control to low.
Electronics that remain plugged in continue using electricity even when they’re not running. There’s even a term for the power consumed by electronics that draw electricity. It’s called vampire energy. To prevent wasting electricity, pull the plug off the socket. Alternatively, you can use a smart power strip. You can save around 5 watts by using this technique.
A smart TV is an excellent investment when it comes to reducing your power bills. It has many features that can help lower its power use. Better yet, get an Energy Star-certified model. Appliances with this seal indicate that they consume less electricity (by about 30%) than conventional models. They may cost more upfront, but you can get back your investment through the savings on your utility expenses.
Next to the old CRT models, plasma TVs consume the most electricity among the newer screen types. Their picture quality may be terrific, but eco-friendly, they’re not as they need more power to operate. The higher energy usage may not be enough to show a dramatic spike in your electricity bill, but the small amount adds up. OLED and LED TVs are better alternatives.
Many TV brands and models now come with the energy-saving mode. The feature may be called by different names, such as eco-mode, or it may be part of an Ambient Light Detection selection. But it serves the same purpose, which is to save electricity consumption. Find out if your set is equipped with this feature and use it as much as possible. Not only will yousave money on your bill, but you’ll also reduce your home’s carbon footprint.
Although other factors come into play that can affect the TV’s power consumption, size is a major consideration. That’s because it takes more electricity to power a large screen than a small one. For example, a 30-inch LED TV uses between 50 and 60 watts, while a 42-inch one consumes between 80 and 100 watts.
Appliances that have a standby mode consume electricity even when turned off. This energy use is called vampire power. Computers and equipment related to computer use (i.e., modems, routers, etc.) rank first in the list of appliances that use vampire energy. Instant-on TVs come next.
The answer to how many watts a TV consumes depends on a few factors, such as screen size, type, model, and set’s age. Even your TV use affects your unit’s energy usage. Plenty of screen time significantly drives up your monthly electricity bill. If you aim to shrink your monthly electricity bill, there are some measures you can employ. These include buying a smart TV, lessening your TV use, and following our tips for reducing your appliance’s power usage. Some homeowners even opt to power their sets using solar panels.
In the end, it’s not just about saving money on your energy costs but also about helping the environment. By lowering your home’s electricity consumption, you join the efforts to lessen the greenhouse gas emissions that warm the planet and accelerate global warming.

That"s the primary reason I stopped widely testing TV power consumption a couple of years ago (plasmas are the exception; I still test consumption by those). Simply put, TV manufacturers have done a good-enough job of managing TV power that the operating cost became negligible. And once people realize how cheap even the biggest TVs are to run, energy use largely stops being a factor in the purchasing decision.
Of course, there"s a bit more to it than that. I like to think of the Energy Guide number as the minimum it"ll cost to run the TV. It"s determined using the default picture settings, which are often (especially on plasma TVs) dimmer than what people end up using at home. Since most TVs" default picture settings incorporate a room lighting sensor, watching in a bright room may in turn automatically make the image brighter and thus use more power.
But even if you double the figures on the Energy Guide label, even the largest, least efficient TVs still cost less per month than a decent lunch. The most power-hungry TV I"ve recently tested, Panasonic"s 65-inch TC-P65VT50, costs about $81 per year, or $6.77 per month. And that"s after calibrating the picture so it"s suitable for viewing in moderate lighting.
Here"s a list of various recent TVs we measured for power use after calibration. They appear in order of how much they cost in electricity, assuming the same per-kWh cost and usage as the Energy Guide labels.
Are you still concerned about how much juice your next TV will use? Here are a few tips on how to keep the power bills very slightly lower, and do something to help the environment, while you watch TV.
Buy an They use one-half to one-quarter the power of a comparably sized plasma. Some LEDs are more efficient than others; Energy Star"s Most Efficient designation for the most miserly.
Watch with a dimmer picture. Light output is the largest factor in how much power a given TV uses. Try turning down the backlight control or engaging the power-saver setting.

1. * With electricity expense calculating, you can monitor which appliance cost the highest energy and how much your standby appliances cost. In this way, you can determine how to low your power consumption.

So, how does e-paper stand up? Can the technology make up for these LED/LCD roadblocks, or is it just hype?Ise-ink paper the most energy-efficient digital signage out there?
✓ Energy usageE-paper displays only use power when you change what’s on the display or when the wireless display pushes over WiFi for new updates. In fact, an e-paper low-power display can use merely0.008% of the power an LCD display requiresin a day. The ultra-efficient technology hardly makes a dent in your electricity bill. What’s more, the low power consumption allows these devices to run on battery power, lasting months between charges.
✓ Long-livedWhile a baseline LCD might be cheaper upfront, e-paper devices make up the difference in longevity. With such low refresh requirements, electronic ink displays are dormant most of their lives. This inactivity greatly increases the lifespan of the devices, resulting in an ultra-low failure rate and incredible longevity.
✓ EffectiveElectronic paper displays are just that — digital paper. As with paper, these displays reflect light in the environment off of the surface of the display. The result is a glare-free experience, improving screen readability in any setting. What’s more, electronic ink displays function perfectly in a wide range of temperatures, thriving from 32°F to 122°F (0°C to +50°C) and working in more extreme conditions.
✓ Long-term costContrary to LED and LCDs, e-paper displays cost substantially less in the long run. The initial purchase price is about equal to a high-quality LCD display made of sustainable materials, but that’s where the similarities end. E-paper technology uses very little energy, keeping utility costs down. The displays require no installation, aside from the two minutes it takes to mount them on a surface. Their low refresh rate gives them an unparalleled lifespan, keeping replacement costs negligible.
✓ SustainableAs far as power consumption goes, e-paper displays are naturally more sustainable than LED or LCDs. Therefore, e-paper technology has a small carbon footprint in comparison. Many top-of-the-line e-paper devices are made of quality, sustainable materials that are reusable or recyclable, making e-paper the most environmentally-friendly display technology on the market.

If you are wondering how much power does my TV consumes in a month, and whether your wife watching TV all day long is increasing your electricity bill or is it something else, then this article is for you. In this article we will see how to calculate power consumption of a TV
Most LED TV’s has rated power between 60 watt to 150 watt. Generally speaking larger the screen size higher is the rated power. A 100 watt TV running for 12 hours everyday will consume 1200 watt hours = 1.2 kWh (units) of electricity in a day and 36 kWh of electricity in the entire month.
There are few terms which you should know to correctly calculate power consumption of any television and understand the results. These are as follows:
Watt (W) : Just like you measure your height in feets and inches, your weight in kilogram or pounds, in the same way wattagea.k.awatt is the unit of measurement of power. For example a 10 watt led bulb, 150 watt television. 1 kilowatt = 1000 watt To know more you can read this blog.
To calculate power consumption of your TV (or any device for that matter) you need to know three things viz., wattageof your TV, operational hrs and electricity tariff.
Most TV available in the market has wattage from 80 watt – 400 watt, this value depends on the size of the TV (32 inch inch, 44 inch, 56 inch and so on) and type of TV (CRT, LCD, LED, QLED, Plasma and so on).
For our calculation lets say you have a50 inchLED TV from Samsung that has a rated power of 100 wattand you use it everyday for 12 hrs, then how much electricity will you get for using it?
The below TV power consumption calculator will do all the calculations for you, just type the wattage of your TV, operational hours and electricity tariff and you are good to go.
The above calculate result will have 5 % – 10 % error and everytime you use your TV your setup box, speakers or something else is also hooked up which also consumes power hence, if you want to calculate your TV exact power consumption then use a Kill A Watt Meter.
To use a Kill A Watt meter to calculate the power consumption of your television, first connect the TV plug to the Kill A Watt meter and then plug the Kill A watt meter in your wall socket.
Size of TV : Larger the size of the TV, higher is the power consumption. A 15 -inch LED TV screen consumes as low as 15 watt, which brings your daily costs down to a negligible number. Whereas a typical size 30-inch LED TV, consumes about 50 watt of power. So the size of your TV screen has direct impact on your electricity bill.
Screen type: LCD screens have nearly the same power profile as LED’s, while CRT and plasma screens typically use about three times as much energy as their energy efficient LED cousins. If you are still using CRT or plasma then switch to LED you will see a massive reduction in your electricity bill.
You already have a good TV an don’t want to buy a new energy efficient one then follow these simple tips to reduce your TV power consumption. Mind you none of thee will drop your electricity bill by 30-40% but will surely help you save some money.
Lower the backlight setting : The backlight is by far the biggest drain of your power, and the lower you can get your backlight, the less power your TV will consume. Placing your TV in a dark or dimly lit environment will help you avoid needing a bright backlight.
Turn OFF TV accessories : Turn OFF all the system connected to your TV when you are not using it. Example, home theater, DVD or blue ray player, PlayStation. They all consume power in standby mode.
To calculate power consumption of a TV all you have to do is multiply it’s rated power (watt) by the operational hours. And to calculate electricity bill in a month for using the TV you have to multiply the power consumed by your TV in a month (kWh) with your electricity tariff (Rs/kWh).
To save electricity make sure you go use energy efficient TV like LED, LCD, QLED and not CRT, Plasma TV, turn of the TV and all it’s accessories when not in use (not in standby mode) and change the brightness to an optimal level and switch off always turn on features like voice control.

Many appliances continue to draw a small amount of stand-by power when they are switched "off." These "phantom loads" occur in most appliances that use electricity, such as televisions, stereos, computers, and kitchen appliances. Most phantom loads will increase the appliance"s energy consumption a few watt-hours, and you can use a monitor to estimate those too. These loads can be avoided by unplugging the appliance or using a power strip and using the switch on the power strip to cut all power to the appliance.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey