bad tv lcd panel symptoms made in china

The difference between a LED TV and a LCD TV is that they are both LCD TV’s except one has LED stripes and the other has CCFL Backlights- (Florescent Tubes). I used a Philips Magnavox Emerson LG TV when testing these repaird, but they should work on other TV brands that are similar. Before you do any Repair, check to see if you are still under warranty, or are covered by a recall of your TV!!
If your Plasma or LCD/LED or CCFL/LCD TV or monitor has stopped working, or is displaying one of the following symptoms, then it *may* need some new capacitors in the power supply board or a replacement board
-Upon three unsuccessful start up attempts the TV locks itself in protection mode and needs to be disconnected from AC for 30-40 seconds before power attempts can be restore-Display Locks after 10 minutes–
1) the front green LED of your TV comes and stays on for 20-30 seconds, then turns off for 1-2 seconds and then keeps cycling like that, but the display never comes;
2) the display comes on for a brief few seconds, then the TV shuts off; in some models the display may not even come on, but still the relay clicking on and off and the green power LED activation and shutdown can be easily observed.
A model number is needed to determine the unlock procedure, but most likely you will need a remote to unlock most TV’s. Below is a common lock procedure.
Choose On to disable all the buttons on the front of the TV. FPA Lock On will appear on the TV screen each time you press buttons on the front of the TV. You can still operate the TV with the remote control. You can still use the POWER button on the front of the TV, but only to turn off the TV (not on). Set FPA Lock to Off to cancel this feature so you can use the buttons on the front of the TV again.
3. Press and hold each of the remaining buttons on the TV, one at a time, for about five seconds, and then release. DO NOT use the buttons on the remote control - only use the buttons on the TV itself.
6. The TV should start automatically scanning for active channels from your input signal source. Make sure you have a good signal (antenna or cable or satellite).
If the TV still does not display anything, try the menu button on the TV and see if you can access the menu. If not, try using the remote control’s menu button.
If the TV is still locked and will not respond to any commands from the front panel control buttons or the remote control unit, it is apparently locked in a failure or diagnostic mode, and would probably have to be diagnosed and repaired by a reputable TV repair facility. Good luck.
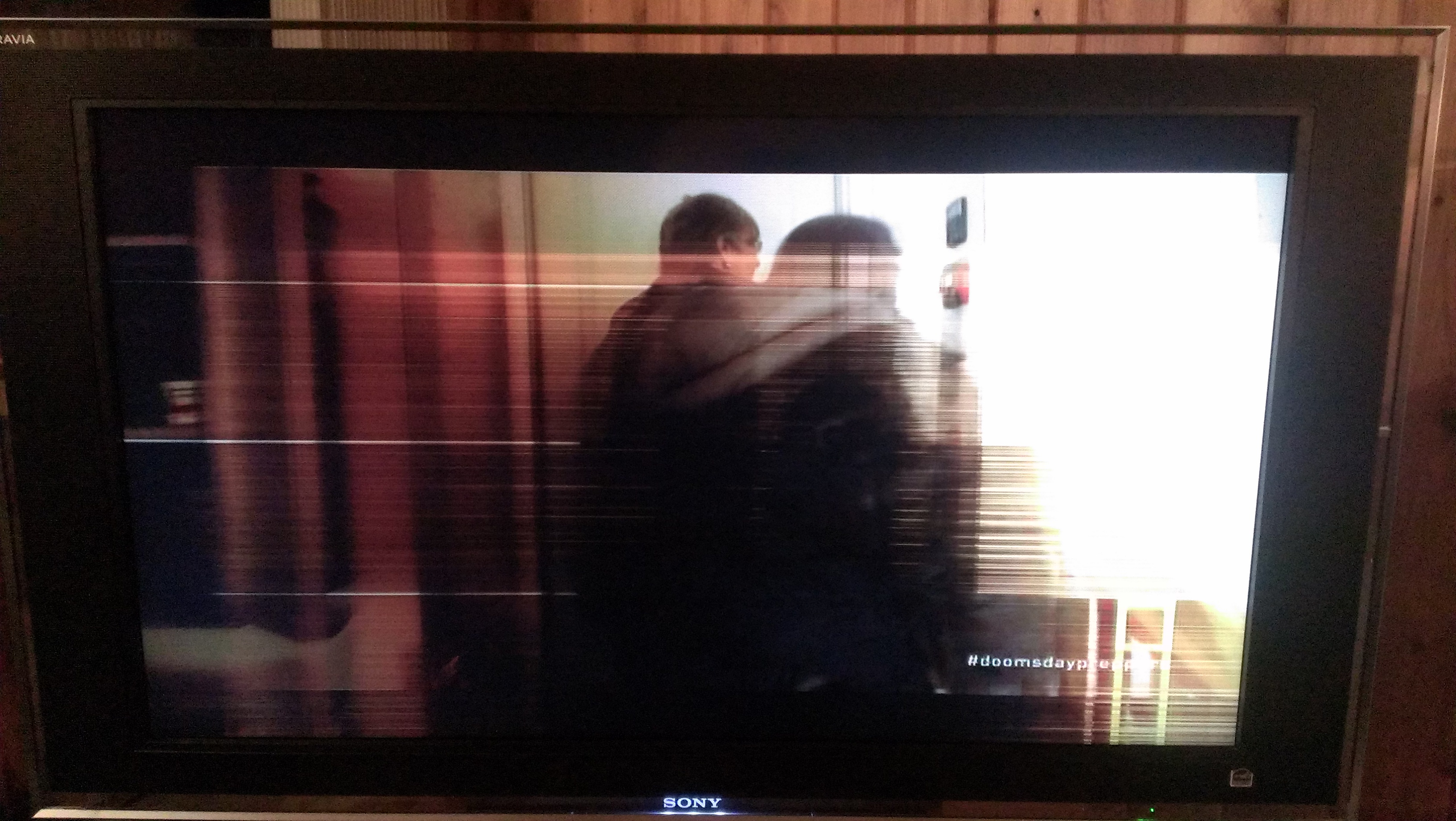
If it is a thin vertical line that appears on certain video resolution/image then it is normal and is indicated in the users manual under troubleshooting. If the line is almost half the screen, it could be a problem with the cable connection between the LCD panel and logic board, or the LCD panel itself. Try reseating the cable first if it’ll solve the problem. I’ve done similar issue in the past. Reseating the cable worked for a couple of months till eventually the LCD panel is the problem. Replacing the LCD panel is quite costly and impractical.
If the lines are there all the time or intermittent but in the same location it is an indication of a bad panel. The panel driver can also be the cause of this symptom.
If the lines/bars are across the OSD Menu, and all the video signal inputs also same result, that means the TV LCD Panel is defective Most of the time this symptom is caused by a bad LCD Panel 95%. You can try refitting LVDS Cable or replacing Main Board capacitors or replacing Main Board—5%
Bad news unfortunately, their are two possible causes for what you have described, one would be a fault with the picture drive pcb ( Power Control Board ), and the other is physical damage to the LCD cell matrix, (screen).
There’s videos on how to fix this. It has to do with putting foam, in between panel frame and screen, which applies pressure to solder joints, which then completes the circuit- Contact my10cents, for better explanation.
Big Black Bar on bottom of TV Screen– If the bar that appears in the bottom is showing the energy saving logo, HDMI, Dolby surround and pc mode capabilities look into your remote.
Is the OSD menu affected as well? If yes then possibility could be the LCD Panel or the t-con board. Since you have replaced the t-con board then possibility is the LCD panel. There could be also a possibility of mainboard where upgrading the firmware could restore the picture. If the OSD menu is not affected then the LCD panel is good.
If the lines are across the OSD menu then chances is very high the LCD panel is the cause of the problem otherwise it can be due to bad T-con board or even Mainboard. Have you tested on the OSD menu to see if the lines are really across the menu?
White Lines– There are several possibilities that can cause white lines on an lcd screen. One would be high temperature on the logic board. Logic board drives the LCD panel and when it overheats can cause this display problem. One solution would be to clean the vent holes around the TV. One possibility that I have experienced myself servicing is a bloated capacitor on the power supply board. The worst possibility is a defective LCD panel, which is costly to repair, and sometime more practical to buy a new TV set.
Do you get blue screen when using x-box or DVD, VCR? Have you tried to reset cable box if you have one? Reset TV. Check all cable connections? Try these first.
Do you use the Set top box for cable channels? If yes then try connecting through HDMI and see if you can see the TV. Also do you get blue screen when using x-box or DVD, VCR?
What made you decide to change the mainboard? I ask because if the MENU does not appear, then this indicates a problem elsewhere within the TV. Also, did you check for any swollen, or bulged capacitors on the power supply board?
There are several problems that could cause this problem. It could be the connection from the T-Con board to the panel, try wiggling these cables around and see if the picture comes up even for a second. The Mainboard or it’s cables are not the issue in my opinion. The isdsue is either going to be a bad capacitor, faulty output from the power supply to the T-Con board, a bad connection from T-Con to panel, or the T Con or the panel itself are faulty.
Basic things you can do is to check the connections. If you have a cable box, check the video connections. And while doing that, unplug the TV and the cable box from the AC outlet for it to reset. These are the most likely cause of a blue screen
Most of the new TVs display a blue screen when theres no signal for it to lock on. Try unplugging it for about 5-10 minutes and see if that clears up the problem. Why? Because they have microprocessors in em (computer chips) and just as like with any other operating system, they can hang up or crash. This isnt an uncommon problem with todays TV sets. Unplugging it for awhile resets the microprocessor (in other words, it causes it to re-boot when you plug it in again).-
It could be the connection from the T-Con board to the panel, try wiggling these cables around and see if the picture comes up even for a second. The Mainboard or it’s cables are not the issue in my opinion. This is due to either a bad capacitor, faulty output from the power supply to the T-Con board, a bad connection from T-Con to panel, or the T Con or the panel itself are fault. Also, it’s possible the A/V receiver’s Video On feature was turned off by an electrical surge or something else.Turn the Video feature back to On and suddenly that bad blue screen was gone.
Repair/Solution: Change the cable box to a fixed resolution. OR have the customer install the latest TV firmware which can be located at your TV Brand Customer Support
Your power board needs serious help–If you want to repair you have to replace Switching Mosfets, disc capacitors and of course the main fuse, Rectifier Diodes and most of the time the transformer–Costly–Easier to replace Power Board–There is a chance the strike come through the cable line, so it’s possible the Main Board needs repair–That’s a small chance though, but I thought I’d let you know–Replacing power board should repair your TV. During a lightning storm, electrical power surges is induced to the transmission line eventually end to our household appliances. Our TV sets, computers are the most susceptible. For the TV set, the basic cure is to leave the TV unplug from the AC outlet for it to discharge and reset
5. wait another 30 seconds and some type of picture should appear—If that does not work–Unplug TV for 10 minutes and then hold power button on TV for 60 seconds–Plug in and turn on.
Unplug TV– On TV, hold the power button down while pushing and holding each button for a few seconds. After going through all buttons, (on TV) then plug TV back in and it should power up–
When the TV, has no Picture or Sound. Led turns from red to (Blue or Green). It means the Main Board has sent out the start up signal to the PSU (Power Supply) Board.
Now we need to know if PSU Board has all the correct output voltages. This means checking the secondary side output voltages of Power Board. Probable causes are the Power Supply, the T-Con board, Main Board or the LCD panel itself has failed.
No Picture/Sound The person who looked at my TV, stated that the high voltage power supply needs to be replaced. He explained that I have a low voltage supply which is why the power button is lit once pressed, and a high voltage supply which needs to be replaced.
You will have to go into the TV and check for capacitors or burn marks or cracked solder around the pins–Main board could be IC’s, or regulators–Panel–Disconnect panel and see if your TV stay’s on—
The flashing green light indicates a fault on the power board inside your TV. This will be due to a faulty component like a capacitor or voltage regulator. Faulty electrolytic capacitors on the power board are the most common cause of this problem. These capacitors will often leak and stop working as the TV set gets older,but could also be caused by the Main Board or the inverter board. (LCD TV ONLY) So we will have to take a look inside and maybe do some circuit testing and a visual of your boards-
In a dark room take a flashlight and at an angle shine it on the screen and see if you can see any movement. If you can see movement or see your menu then its backlight failure. If totally black screen with sound then its T-Con board. So if you see movement on a led screen, then it’s your LEDs inside the panel. If on a LCD TV you see movement and lamps are not turning on, replace inverter. If with a LCD TV your lamps turn on, with no picture replace T-Con Board.
Plasma is the most durable in terms of panel failure. LED/LCD is terrible for panel failure. (But every model gets bad apples. Samsung LED/LCD panels die frequently. LG panels are a lot more reliable.) Overall I’d say plasma is more reliable, and even if it fails, in most cases plasma is repairable, LED/LCD is expensive to repair and often difficult to troubleshoot.
A blurry image on a high-definition LCD TV is typically the result of a mismatch between the TVs resolution capabilities and the resolution of the signal that is coming from connected devices, such as a DVD player or satellite TV receiver. Typically, blurry pictures result when a peripheral device connects to the TV through non HD cables and jacks.

Ever had your TV showing nothing but a black screen even if the audio was working? Unfortunately, that’s a common issue with low/middle-end LCD/LED TVs these days… Even more frustrating, this issue often comes from a rather tiny and cheap component that can be easily replaced. Most common issues are:
One of my relatives had this exact symptom happening all of a sudden. This problem on low-end TVs often occurs within the first couple years. As the repair costs for that kind of TV is pretty low, considering repairing it yourself might be a good idea!
That implies disassembling the TV to access the backlight which is between the LCD screen in the front and the boards in the rear. In my case, with a Samsung F5000, I had to process as follows:
First we have to remove the back housing to reveal the boards (from left to right: main board, T-CON, power supply) and disconnect the LCD panel from the T-CON board.
Note: Older TVs have neon tubes for backlight, which is thicker and less exposed to this kind of failure. LED backlight is the most common thing these days, but do not mistake an LED TV with an OLED TV. The first one is a classic LCD panel with a LED backlight, whereas the second is an OLED panel that doesn’t need any backlight as it is integrated in each pixels (making the spare parts much more expensive by the way).
For starters I’ll go with the third one, just to make sure there is no other issues with the TV, but afterwards it’s better to replace the LED with a new one, otherwise you might notice a darker spot on the image.
Once we have by-passed the LED, we can power the TV on. Careful! High voltage (200-300v) runs through the TV when plug, so be very careful how you handle it so you don’t electrify yourself!
Now we just need to unplug the TV, replace the LED with a new one and put everything back together. Just to be sure, we should power the TV back on and check that everything is fine.
There might be a lot of other root causes for similar symptoms, a black screen often looks like something very serious and therefore expensive to repair, but this case is the perfect example that taking some time to look for the root cause can sometime lead to a good surprise: here a 1$ fix!

Troubleshooting CRTs versus LCDs begins with similar steps, but diverges due to the differing natures of the two display types. The first troubleshooting steps are similar for either display type: power down the system and display and then power them back up; make sure the power cable is connected and that the outlet has power; verify that the signal cable is connected firmly to both video adapter and display and that there are no bent pins; verify that the video adapter is configured properly for the display; try the problem display on a known-good system, or try a known-good display on the problem system; and so on. Once you"ve tried the "obvious" troubleshooting steps, if the problem persists, the next step you take depends on the type of display. The following sections cover basic troubleshooting for CRTs and LCDs.
Check the obvious things first. Verify that the CRT is plugged in (and that the receptacle has power), the video cable is connected to the video card, the computer and CRT are turned on, and the brightness and contrast settings are set to the middle of their range. If none of these steps solves the problem, your CRT, video card, or video cable may be bad. Check the suspect CRT on a known-good system or a known-good CRT on the problem system.
The CRT may need to be degaussed. A CRT that sits in one position for months or years can be affected even by the earth"s very weak magnetic field, causing distortion and other display problems. Exposing a CRT to a strong magnetic field, such as unshielded speakers, can cause more extreme image problems. Many modern CRTs degauss themselves automatically each time you cycle the power, but some have a manual degauss button that you must remember to use. If your CRT has a manual degauss button, use it every month or two. The degaussing circuitry in some CRTs has limited power. We have seen CRTs that were accidentally exposed to strong magnetic fields, resulting in a badly distorted image. Built-in degaussing did little or nothing. In that case, you can sometimes fix the problem by using a separate degaussing coil, available at RadioShack and similar stores for a few dollars. We have, however, seen CRTs that were so badly "magnet burned" that even a standalone degaussing coil could not completely eliminate the problem. The moral is to keep magnets away from your CRT, including those in speakers that are not video-shielded.
If your LCD displays no image at all and you are certain that it is receiving power and video signal, first adjust the brightness and contrast settings to higher values. If that doesn"t work, turn off the system and LCD, disconnect the LCD signal cable from the computer, and turn on the LCD by itself. It should display some sort of initialization screen, if only perhaps a "No video signal" message. If nothing lights up and no message is displayed, contact technical support for your LCD manufacturer. If your LCD supports multiple inputs, you may need to press a button to cycle through the inputs and set it to the correct one.
Unlike CRTs, where increasing the refresh rate always reduces flicker, LCDs have an optimal refresh rate that may be lower than the highest refresh rate supported. For example, a 17" LCD operating in analog mode may support 60 Hz and 75 Hz refresh. Although it sounds counterintuitive to anyone whose experience has been with CRTs, reducing the refresh rate from 75 Hz to 60 Hz may improve image stability. Check the manual to determine the optimum refresh rate for your LCD, and set your video adapter to use that rate.
First, try setting the optimal refresh rate as described above. If that doesn"t solve the problem and you are using an analog interface, there are several possible causes, most of which are due to poor synchronization between the video adapter clock and the display clock, or to phase problems. If your LCD has an auto-adjust, auto-setup, or auto-synchronize option, try using that first. If not, try adjusting the phase and/or clock settings manually until you have a usable image. If you are using an extension or longer than standard video cable, try connecting the standard video cable that was supplied with the display. Long analog video cables exacerbate sync problems. Also, if you are using a KVM switch, particularly a manual model, try instead connecting the LCD directly to the video adapter. Many LCDs are difficult or impossible to synchronize if you use a KVM switch. If you are unable to achieve proper synchronization, try connecting the LCD to a different computer. If you are unable to achieve synchronization on the second computer, the LCD may be defective. Finally, note that some models of video adapter simply don"t function well with some models of LCD.
Not all analog video cards synchronize perfectly with flat panels. The gray Shutdown screen exaggerates the problem, so don"t worry if very tiny movements are visible after you"ve adjusted clock and phase as well as possible. After you"ve set the clock and phase controls for the best image possible on the gray screen, cancel Shutdown and the image should be optimized.
Your video card is supplying a video signal at a bandwidth that is above or below the ability of your LCD to display. Reset your video parameters to be within the range supported by the LCD. If necessary, temporarily connect a different display or start Windows in Safe Mode and choose standard VGA in order to change video settings.
This occurs when you run an LCD at other than its native resolution. For example, if you have a 19" LCD with native 1280x1024 resolution but have your display adapter set to 1024x768, your LCD attempts to display those 1024x768 pixels at full screen size, which physically corresponds to 1280x1024 pixels. The pixel extrapolation needed to fill the screen with the smaller image results in artifacts such as blocky or poorly rendered text, jaggy lines, and so on. Either set your video adapter to display the native resolution of the LCD, or set your LCD to display the lower-resolution image without stretching the display (a feature sometimes referred to as display expansion), so that pixels are displayed 1:1, which results in the lower resolution using less than the entire screen.
This is a characteristic of LCDs, particularly older and inexpensive models, caused by defective pixels. Manufacturers set a threshold number below which they consider a display acceptable. That number varies with the manufacturer, the model, and the size of the display, but is typically in the range of 5 to 10 pixels. (Better LCDs nowadays usually have zero dead pixels.) Nothing can be done to fix defective pixels. Manufacturers will not replace LCDs under warranty unless the number of defective pixels exceeds the threshold number.
Some people claim that leaving the unit powered off for a day or two will "erase" a persistent after-image. Others suggest leaving a neutral gray screen (like the one used for phase adjustment) up on the screen to "equalize" the display. I dunno. FWIW, I"ve seen this problem on older Samsung panels but never on the Sony or NEC/LaCie panels I use.
Again, this is a characteristic of LCDs, particularly older and inexpensive models. The after-image occurs when the display has had the same image in one place for a long time. The after-image may persist even after you turn the display off.
Transistor-based pixels in an LCD respond more slowly than the phosphors in a CRT. The least-expensive LCDs exhibit this problem even with slow image movement, as when you drag a window. Better LCDs handle moderately fast image movement without ghosting, but exhibit the problem on fast-motion video. The best LCDs handle even fast-motion video and 3D gaming very well. The only solution to this problem is to upgrade to an LCD with faster response time.
Modern flat screen TV"s have a known problem with capacitors going bad. If your LCD or LED TV won"t turn on, or makes repeated clicking sounds, there is a very good chance that you can save hundreds of dollars doing this simple repair yourself.
I know, I know. You"re thinking, "Tinker inside my LCD HDTV. Are you crazy?" No, I"m not crazy. This is a repair almost anyone can do and this fix will work for any TV.
You sit down and get comfortable, ready to watch your favorite TV show or movie. You turn on your TV and...nothing! Unsure if you hit the power button, you try again...again, nothing! But you do notice a clicking sound emanating from your TV.
HDTV"s aren"t cheap. Most of us have to save, or at least be prepared to spend $800-$1000 on new one. Heck, I"m sure many of you don"t savor the idea of spending a few hundred on repairs.
I have good news. This repair is actually quite simple, and with only a few basic tools and about 20 bucks, you can have your TV working in less than an hour.
The bad News. If your TV is physically damaged in any way, been dropped, has a broken screen or gotten wet then this repair isn"t for you. But if your TV was working one day but not the next, read on.
After unplugging everything on the TV, you will need to remove the stand. If your TV was wall mounted you will need to remove the TV from the wall, and remove the mounting bracket from the back of the TV.
The TV sits on top and inside the stand, so it wont just flop over when you remove the stand screws, but it"s always safer to have a friend hold the TV upright as you remove the screws from the stand. Then each of you grab a side and carefully lay it flat on a carpeted surface.
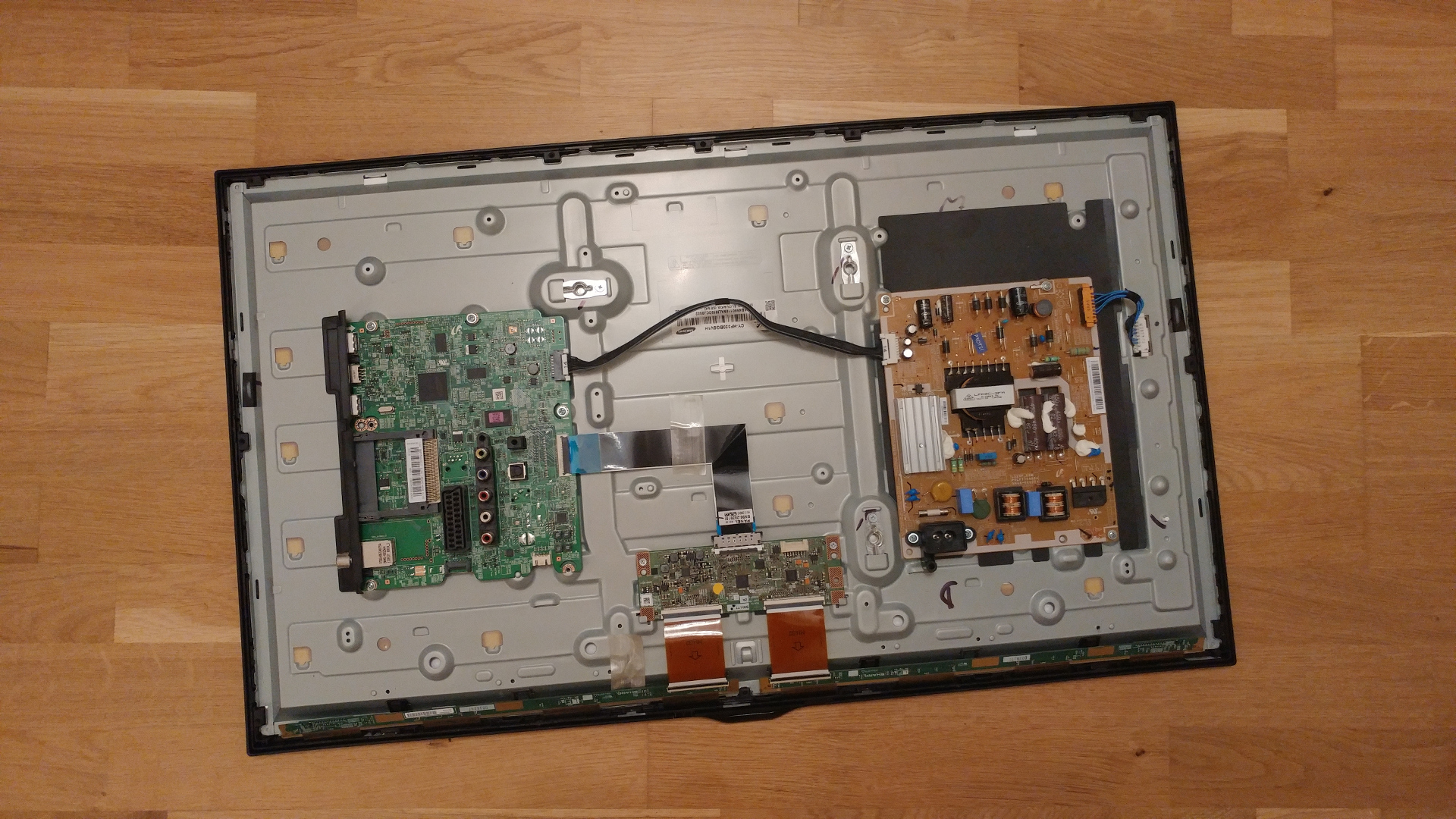
Above is a a picture of the back side of a typical TV. The left picture is my LG 42LN5300 and the right picture is my Samsung LN46A550, but all TVs are similar. Remove all of the screws along the outer edge of the back casing. There can be anywhere from 10 - 16 of these screws.
Then identify the "power board". Every TV is a little different, but the power board will have can shaped capacitors and is the board that the main power from the plug goes to first. On this Samsung TV I put a green rectangle around the power board that we will be working on..
The other "green" board is the "logic board", this is the computer that runs the TV. Repair of the board is beyond the scope of this article. (But it"s most likely not the problem)
Remove the screws holding the power board to the TV chassis. Most boards will have 6 screws holding them down, as does the one shown in the picture. But look it over there could be more or less.
This TV repair focuses on the small "can shaped" Aluminum ElectrolyticCapacitors.These capacitors come in many colors and sizes but are easy to find on any power board. Not only are these the most likely cause of your problem, but bad ones are simple to find and simple to replace. In most instances you will be able to visually identify the bad capacitors. You don"t need any special skills in electronics or testing.
Capacitors do not always show visible signs of failure. But, if you see either of the 2 signs above on your board, you can be confident that you"re close to fixing your TV. If you don"t see these signs of failure, but your TV had the tell-tail clicking sound, you still can be fairly certain the steps below will fix your TV.
On power board pictured above, I have indicated which capacitors you should be examining for signs of failure. These Capacitors are Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitors, and are the most likely cause of your problem. The capacitors with the green arrows are the most likely candidates for being bad, but the blue arrow are other capacitors to examine.
The pictures above are actual closeups of my TV"s board. Notice how the blue capacitors in the foreground are bulging. These are the capacitors I will replace. All other capacitors look OK. If you can find replacements for all 4 of these capacitors, and any others that show visual signs of going bad, I recommend replacing them all while your in here.
Now that you"ve identified the capacitors that look bad, turn the board over and carefully identify exactly which points on the board are the wire leads from the these capacitors.
So I took my tv apart and I think I found the problem can you please verify for me? Pictures attached. I think one of the big CAPACITOR is bad and leaking on the bottom of the board is brown.
I have a Samsung LN-T4066F that keeps clicking like it"s trying to turn on, but won"t. It"s plugged into a surge protector so I just turn that off to make it stop. Every few hours, I turn the switch on the surge protector and once in a while the TV turns on! Can it be the capacitors?More CommentsPost Comment

Samsung Display will stop producing LCD panels by the end of the year. The display maker currently runs two LCD production lines in South Korea and two in China, according to Reuters. Samsung tells The Verge that the decision will accelerate the company’s move towards quantum dot displays, while ZDNetreports that its future quantum dot TVs will use OLED rather than LCD panels.
The decision comes as LCD panel prices are said to be falling worldwide. Last year, Nikkei reported that Chinese competitors are ramping up production of LCD screens, even as demand for TVs weakens globally. Samsung Display isn’t the only manufacturer to have closed down LCD production lines. LG Display announced it would be ending LCD production in South Korea by the end of the 2020 as well.
Last October Samsung Display announced a five-year 13.1 trillion won (around $10.7 billion) investment in quantum dot technology for its upcoming TVs, as it shifts production away from LCDs. However, Samsung’s existing quantum dot or QLED TVs still use LCD panels behind their quantum dot layer. Samsung is also working on developing self-emissive quantum-dot diodes, which would remove the need for a separate layer.
Samsung’s investment in OLED TVs has also been reported by The Elec. The company is no stranger to OLED technology for handhelds, but it exited the large OLED panel market half a decade ago, allowing rival LG Display to dominate ever since.
Although Samsung Display says that it will be able to continue supplying its existing LCD orders through the end of the year, there are questions about what Samsung Electronics, the largest TV manufacturer in the world, will use in its LCD TVs going forward. Samsung told The Vergethat it does not expect the shutdown to affect its LCD-based QLED TV lineup. So for the near-term, nothing changes.
One alternative is that Samsung buys its LCD panels from suppliers like TCL-owned CSOT and AUO, which already supply panels for Samsung TVs. Last year The Elec reported that Samsung could close all its South Korean LCD production lines, and make up the difference with panels bought from Chinese manufacturers like CSOT, which Samsung Display has invested in.

If your TV isn’t working properly, there are still a few things to consider before you give up on it. Generally, you’ll have a few warning signs that things are not exactly right.
Of course, sometimes, the TV is beyond repair and you should replace it instead. If the screen is broken or the TV doesn’t turn on no matter what you do (or if the sound stopped working completely), it’s time to check out a new set.
The difference is that stuck pixels usually happen because of a problem with a transistor; they often have different colours and are usually just simply out of place. If it is a dead pixel, then the TV should be sent for repairs, as, unfortunately, the issue is a difficult one to fix.
If the colours on your screen appear distorted, then your TV might be malfunctioning. Traditionally, this issue tends to occur gradually, meaning that you might not notice any difference at first. This is due to the common factor that one colour tends to weaken at a time; therefore, no obvious changes happen overnight.
If your screen starts to display bars and lines, this tends to indicate that there is an issue with a connector. This can occur when something magnetic has been placed near the TV and, in turn could mess with the picture quite considerably, even potentially de-magnetising the screen.
The issue can be due to cables that have become loose inside the screen as well, which is an easy fix, although it may require a professional because the TV may have to be opened.
You may be able to do something about this by adjusting the levels of brightness and contrast on your TV and playing different types of content to see if the problem goes away. You can also enable your TV’s Pixel Shift feature; when this feature is turned on, images on the screen move a bit to vary the pixels used. Pixel Shift is often included in modern sets and might clean out the phantom image.
This issue could occur if the signal received is a digitised standard (480p), as there’s a discrepancy between the resolution and the display. It’s also worth noting that the digital signal your TV receives can be affected by weather conditions as well, so the image can appear fuzzy and glitchy.
However, the good news is that, when this happens to modern televisions, there is a high chance of it being fixed, so you can still enjoy your TV for a long time.
If the TV is on but the picture is faded on some areas of the screen, it’ll be difficult for you to actually enjoy the content. You may try to ignore the stain-like mark but there is no denying that this will impact your experience. Faded spots are not that rare and can be accompanied by other serious issues, like your image fading to black after you’ve turned the TV on.
We offer repairs as well as a vast range of products so, if you find that your current TV is well past its sell-by date, be sure to browse our amazing
Television is a very intimate object in our daily lives. It not just entertains and informs us about the happenings around us, but it also helps unite families at several houses as we binge on our favourite movies and TV shows together. And despite it being the age of hand-held gadgets, there are still enough people around who prefer television to mobile. No doubt, it feels terrifying when your beloved TV gets a cracked screen.
Though a cracked TV screen is not something that happens so often. But when it happens, not any random mechanic should be assigned the task of repairing it. Instead, only the experts who know the job in and out should be called upon.
Besides, here’re some important things and suggestions, directly from our experts, you must go through before moving ahead on cracked tv screen repair
Firstly, the question is how TV screens can get cracked. Well, there are umpteen reasons to cause this. In most cases, it is accidentally damaged. Your child kicking or hitting at a ball that, unfortunately, lands up at the heart of the TV! Or, the television, placed precariously at the edge of a table, tips over and develops a crack! And at times, you may drop it while either moving or installing it. So it’s advisable to place your TV out of kids’ reach, and you had better not allow kids to play balls in that room. Also, its installation and movement (from one place to another) should be immaculately done, preferably with the help of trained professionals.
Now, the next question is what if your TV screen does get cracked? Is it the end of the story (as some internet articles seem to claim) or you can still get it repaired successfully?
Access the Damage: When a TV screen cracks, there could be several levels of severity and you could be dealing with anything from a completely dead screen to small lines in the picture, and no-picture, no-sound to poor picture quality.
Check Your TV Warranty: A feasible thing to do here is, bring out the papers and check if the TV is still within the warranty period. If yes, then all you need to do is to take the TV to the authorized service centre (Please, make sure to contact the guys only at an authorised service centre to get genuine services). Most probably, you will earn a free repair or a paid repair or a replacement (depends on the reason behind the damage and the sub-clauses in the warranty contract from your TV manufacturer/supplier).
Get A Professional, Authorized Repair:Taking your TV to a professional, authorized service center is your best choice to get your TV screen back to life. If you spot any such issue in your Synix TV screen, walk down to your nearest Carlcare service center immediately. Our trained TV technicians will check it thoroughly and give proper detail of the damage, as well as providing a cost-effective repairing. We are skilled in fixing cracked TV screen of various brands. In case your TV is not a recent purchase and the warranty period has lapsed, we ensure you the best repair at the best prices, combined with authentic and professional advice from our experts.
TV experts at Carlcare can determine the extent of the damage to give it a fix that’s needed. A minor crack may not be difficult to repair and may not be all that expensive. A slightly deeper crack or multiple cracks may be irreparable or may require replacement. In either case, you can rest assured that we will never misguide you but assist you with the best of our intentions.

2. #Confirm whether the VAA is normal (normally about 17V). If abnormal, disconnect the RP32 to confirm whether it is caused by DC/DC loop or X-side COF: disconnect RP32, if the VAA is normal, the COF is bad, CO must be changed; COF can be Disconnect one by one to determine which NG disconnects RP32, VAA NG, try to change UP1; at the same time, confirm whether the continuity of the surrounding triode is OK.
4. #Press the LCD glass side of the panel, if the vertical lines disappear or reappear, it can be judged that the cause of poor contact, OM checking should be able to find the poor contact.
The above is the full text of LCD screen failure repair guide, we hope it is helpful to you. If you need to buy LCD and find a reliable LCD supplier, we suggest you to read our other great blog – How to find a reliable LCD supplier.
Founded in 2014, VISLCD is a professional LCD supplier. We provide LCD modules, touch LCD and customized LCD in various sizes with stable quality and competitive price. Welcome to contact us for any LCD demand, thank you.

The current situation of children"s screen time from the toddler years to adolescence is extremely severe. Studies have shown that a large proportion of very young children living in Australia were exposed to screens for >2 h per day and that 40% of infants aged under 18 months used screens for longer than the time specified in the current recommended guidelines (4). The average daily screen time of preschool children in the United States was found to be as high as 4.1 h, and more than half of children had a daily video time >2 h (5). The Active Healthy Kids Global Alliance surveyed children and youth in 42 countries across 6 continents (representing 60% of the world"s population) (6). These findings of children and youth revealed that 62% of 13-year-olds and 63% of 15-year-olds watched over 2 h of television per day on weekdays and weekends (6). The US and European countries as well as Asian countries face this problem. A study in Japan reported that 29.4% of children aged under 18 months and 24.5% of children aged under 30 months watched TV for more than 4 h a day (7). In China, a study involving 27,200 children aged 3–6 years showed that the average daily screen time of preschool children was 1.81 h and that the percentage of children who had >1 h/d of screen time was 62.4% (8). A survey of 20,324 kindergarten children aged 3–4 years in 2018 showed that the average screen time of preschoolers in Shanghai was 170.2 min/day and that 78.6% of children had an average screen time of more than 1 h per day (9). The latest study in Shandong Province in China in 2019 found that the average daily screen time of 2,131 children aged 4–6 years was over 1.5 h. Research has also explored the age of children"s first exposure to electronic devices. The average age is 2.25 years, and the youngest age at first exposure to electronic devices is 3 months (0.25 years). Studies have also analyzed the screen time of children in different age groups. The average daily electronic screen time of children aged 4–5 years is 1.52 ± 1.24 h. The two results above both exceed the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommendations (10).
Wu X demonstrated that screen time might be correlated with some autistic-like symptoms (25), but few studies focused on the correlation between screen time and the developmental levels of children with ASD. Therefore, our study compares the screen time of TD children with that of children with ASD to determine whether children with autism have a longer screen time. Then, we explored the correlation between the screen time and the autistic symptoms and development quotients (DQs) of children with ASD.
After the children completed the Gesell Developmental Schedule, the evaluator investigated the children"s screen time. In our study, screen time measures the total amount of time that the children were exposed to various electronic screens, such as watching TV, using computers, playing games, and using mobile phones, during the week before the survey. We investigated the screen time on weekdays (Monday to Friday) and weekends (Saturday and Sunday). The evaluator calculated and recorded the average daily screen time of the children using the following formula: average daily screen time (h) = [screen time per day on weekdays (h) × 5 + screen time per day on weekends (h) × 2]/7.
The symptom evaluation scales included the ABC and the CARS. The ABC is a 57-item screening checklist for autism containing 5 subscales (i.e., body behavior, sensory, self-care, language and social interaction). The ABC is designed for parent interviews. The CARS was developed by Schopler and Reichler et al. and used as a diagnostic scale. The CARS consists of 15 scales, and each scale is scored on a continuum from normal to severely abnormal. The CARS requires observation of the performance of ASD children in a consulting room. The reliability and validity of the ABC and CARS are sufficiently good in China (29), reflecting the scales" usefulness for clinical diagnosis and evaluation of ASD symptoms.
In addition, we divided the ASD group into an older group and a younger group according to the average age (39 months) to determine whether the screen time was correlated with the ASD symptoms and DQs in these two subgroups. The older subgroup was defined as an age ≥ 39 m, and the younger subgroup was defined as an age <39 m. The older subgroup included 48 ASD children, and the average age was 56.46 ± 16.45 m. The younger subgroup included 53 ASD children, and the average age was 29.00 ± 6.07 m. The results showed that in the younger subgroup, screen time was positively correlated with the CARS score (r = 0.314, P = 0.021) and negatively correlated with the adaptive behavior (r = −0.301, P = 0.040), gross motor (r = −0.307, P = 0.036), fine motor (r = −0.335, P = 0.021) and language (r = −0.386, P = 0.007) DQs of the GDS (see details in Table 4). However, we did not find any correlation between the screen time and the ASD-related scale scores or DQs in the older subgroup.
The main findings of this study are as follows: 1. the screen time of children with ASD was longer than that of TD children, and 2. The screen time was related to the autistic symptoms and DQs of the children with ASD.
A study conducted by Chonchaiya et al. in Thailand in 2011 showed that children with autism watched TV earlier and more frequently than TD children (30). The average age when children start watching TV was 6.44 months, and the average screen time was 4.60 h/d. Mazurek et al. studied the screen time of children with ASD aged 8–18 years and compared with that of their TD siblings and found that the average screen time of the ASD children was 4.5 h/d, which was significantly longer than that of their siblings (15). Other studies have reached similar conclusions. As previously mentioned, the problem of excessive screen time among ASD children is very serious.
Adverse environmental factors constitute an important factor affecting the clinical symptoms of children with ASD. Excessive screen time has adverse effects on children"s social participation and behavior regulation (32, 33). Yousef"s study found that a screen time > 2 h/d among school-age children was positively correlated with children"s autism-like symptoms (34). Our results showed that the screen time was positively correlated with the CARS score. The CARS is a standardized diagnostic scale that, to some extent, reflects the severity of autism-like symptoms. Our results demonstrate that the longer the screen time, the more obvious the autistic symptoms. We did not observe a correlation between the screen time and the ABC scale score, which may be due to the bias of the ABC as a parent-reported scale. All patients included in our study were newly diagnosed. Parents usually visit a doctor due to their child"s language impairment and are often unwilling to admit social and autism-related issues. In addition, many families have elderly family members and nannies as the main caregivers of children. Sometimes, parents" knowledge of their children"s performance is limited, resulting in bias in the ABC scale. As a result, the ABC scale score might be low and not completely and accurately reflect autism symptoms. The CARS scale is completed by professionals based on observations and can avoid this problem.
In addition, we conducted correlation study on the screen time of children with ASD and the 15 items of the CARS scale, in order to further observe which aspect of the symptoms of children with ASD is affected by the screen exposure. The results showed that there is a positive correlation between the screen time of children with ASD and the score of “taste, smell and touch” item. Till now, no research has been done on this subject. It is speculated that the reasons may be as follows: First, this phenomenon is related to abnormal sensory development in children with autism, and children with obvious sensory abnormalities are more likely to be fond of the visual stimulation brought by screen exposure. Second, it may be due to the long exposure time of the screen, which caused the abnormal development of its sensory pathways and neurodevelopment. However, this is a cross-sectional study, and causality cannot be inferred. In the future, we look forward to a related cohort study to clarify it.
The subgroup analysis showed that the correlation between the screen time and the CARS score was statistically significant in the subgroups with a longer screen time and subgroups with a younger age, while no statistical correlation was observed in the subgroups with a shorter screen time and an older age. This result is consistent with our expectations. ASD is closely related to brain development. Studies have shown that during the early postnatal period or even before birth, the brain of ASD children has multiple neurological defects. The brain undergoes rapid development early after birth and is influenced by the developmental environment (35–37). Therefore, we speculate that the longer children with autism are exposed to unfavorable environmental factors, the lower their brain maturity, and the more obvious their developmental delay and autistic symptoms. Obviously, a longer screen time is a type of unfavorable environment factor. Thus, we speculate that a longer screen time resulted in shorter play time, shorter companionship time with caregivers and shorter interaction time, resulting in worse social behavior and more obvious autism symptoms. However, this interaction requires further exploration.
The screen time was related to the development of language in the children with ASD in this study. The younger the age and the longer the screen exposure time, the more serious the impact on language development. Hermawati reported that early exposure to electronic media in early life (an age < 2 years) had a negative impact on language (38). Chonchaiya et al. found that children who started watching TV as early as 12 months and watched TV for more than 2 h a day were six times more likely to have language delays. This finding is consistent with our research results. Our Spearman rank correlation results showed that the screen time was negatively correlated with the language DQ in the children with ASD; the longer the screen time, the lower the language DQ. This result was also observed in the ASD subgroup with a longer screen time and the subgroup with a younger age, indicating that the screen time was strongly related to the language DQ.
The screen time of children with ASD is longer than that of neurotypical children. The screen time is related to autistic symptoms and the DQs of children with ASD. The correlation between the screen time and DQs may be more pronounced in children with ASD who have a longer screen time and younger children with ASD. Whether reducing the screen time has positive effects on autism-like symptoms and DQs in children with ASD requires further investigation.
38. Hermawati D, Rahmadi FA, Sumekar TA, Winarni TI. Early electronic screen exposure and autistic-like symptoms. Intract Rare Dis Res. (2018) 7:69–71. doi: 10.5582/irdr.2018.01007
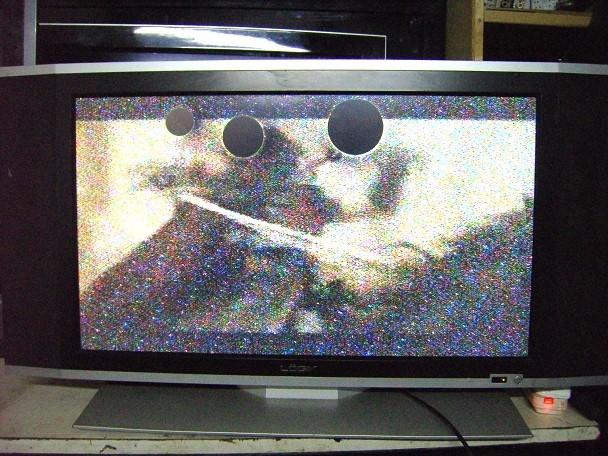
I own a Philips 32" PFL 3403 LCD TV. The panel is an MVA from AOU. The TV was purchased during November, 2008. It was all the while connected through a Belkins Surge Protector to the mains. Despite the antiquated panel, I was fond of its picture quality. However, one fine evening in October, 2011, while the TV was on, the colours of the TV suddenly became pale and white, and there was ghosting / clouding of the image. The Philips Service Centre guy said it was a panel problem which cannot be repaired, and asked me to buy a new TV. To have a second opinion, I approached a reputed, independent LCD TV repair centre, to be told the same thing. When I checked online (Consumer Court), I found innumerable cases like mine, where the LCD TV has developed panel problems within three years. Most such complaints in India were related to Samsung LCD / LED TVs, may be due to purely statistical reasons such as the number of TVs sold of the brand. Some were related to Sony LCD TVs. Other brands like LG, Philips (in my case), Toshiba and Panasonic do also figure.
Not to abandon hope, I contacted "Repair & Return" of Bangalore (Repair & Return Technology India Private limited), which claims to have a state-of-art LCD panel repair facility. In turn, I was told that they are a B2B company and not B2C.
1. Why do LCD/LED panels go bad all of a sudden without any apparent reason (even when they are protected through surge suppressors and voltage stabilizers), and without any warning?
3. Repair & Return says they are a B2B firm. Since they are thriving successfully, it means there would be certainly B2C panel repair guys linked up with them. Where to find them?

The Hisense U8H matches the excellent brightness and color performance of much pricier LCD TVs, and its Google TV smart platform is a welcome addition. But it’s available in only three screen sizes.
The Hisense U8H is the best LCD/LED TV for most people because it delivers the performance of a much pricier TV yet starts at under $1,000, for the smallest (55-inch) screen size. This TV utilizes quantum dots, a full-array backlight with mini-LEDs, and a 120 Hz refresh rate to deliver a great-looking 4K HDR image. It’s compatible with every major HDR format. And it’s equipped with two full-bandwidth HDMI 2.1 inputs to support 4K 120 Hz gaming from the newest Xbox and PlayStation consoles. Add in the intuitive, fully featured Google TV smart-TV platform, and the U8H’s price-to-performance ratio is of inarguable value.
Chief among the U8H’s many strengths is its impressive peak brightness. When sending it HDR test patterns, I measured an average brightness of 1,500 nits, with peaks just north of 1,800 nits (a measurement of luminance; see TV features, defined for more info). To put that into perspective, consider that the 65-inch version of our budget 4K TV pick (the TCL 5-Series) typically costs around half as much as the 65-inch U8H but achieves only around 30% to 40% of its brightness. On the other side of the coin, the 65-inch version of our upgrade pick (the Samsung QN90B) costs almost twice as much as the 65-inch U8H, but it achieves only nominally higher brightness. Adequate light output creates convincing highlights and image contrast and (when necessary) combats ambient light from lamps or windows. It is a necessity for any TV worth buying—especially if you hope to watch HDR movies or play HDR games—and the U8H simply outpaces most TVs in its price range (and some in the next price bracket up, too).
Key to this functionality is the U8H’s employment of mini-LED backlighting with local dimming, which allows this TV to produce very bright light while still maintaining satisfyingly deep black levels that are typically free of blooming (or light bleed that’s visible around bright objects against a dark backdrop). This not only ensures impressive image contrast, it also makes the U8H a viable choice for most rooms, whether they’re brighter than average or dimmed down like a movie theater.
That’s not to say the U8H has pixel-precise light control—it’s not an OLED TV, after all—but it does a terrific job most of the time. In fact, in our tests, the U8H bested last year’s upgrade pick, the Samsung QN90A, in certain scenarios: The intro to Guillermo del Toro’s Cabinet of Curiosities on Netflix features the filmmaker against a pitch-black backdrop. Though last year’s QN90A failed to maintain perfect control over dimming elements during this scene (the black backdrop brightened distractingly once a sufficient amount of brighter content appeared on screen), the U8H did not. (For the record, the newer QN90B also passed this test.) The U8H’s mini-LEDs also help the screen look uniformly bright: Although the U8H is still not as good as an OLED TV in this respect, it shows very little indication of being a backlight-driven display, even during tricky scenes with large swaths of dim lighting.
The U8H’s brightness, black-level integrity, and local-dimming abilities make this an excellent TV for watching HDR content. The U8H is capable of playing HDR content in all of the major formats (HDR10, HDR10+, Dolby Vision, and HLG), but when it comes to impressive HDR, what’s under the hood is much more important than format compatibility. The most crucial thing for good HDR is high brightness and deep color saturation, and the U8H’s quantum dots achieve the latter. It’s not as simple as just having quantum dots, however: While many TVs (even the budget options) have quantum dots nowadays, what is often not taken into account is that brightness directly affects color saturation. For example, both the 2022 TCL 6-Series and the Hisense U8H are equipped with quantum dots, mini-LED backlights, and local dimming. But because the U8H is notably brighter than the 6-Series, it also achieves a higher total color volume. During our color-volume testing, the U8H exhibited color ranges at more than 100% of the DCI-P3 color space (the range of color needed to properly display HDR content), and it is capable of roughly 10% more total color volume compared with the 6-Series.
What does this mean in real-world terms? It means that the Hisense U8H truly excels as a modern 4K HDR TV, whether you’re watching the latest episode of Rings of Power or playing Overwatch 2. While watching HDR content side by side on the U8H and on our upgrade pick, the Samsung QN90B, I was truly surprised by how similar they looked at times, given that our upgrade pick is much more expensive. That said, though the U8H achieves impressive results where light output and color volume are concerned, it also exhibited some occasional video processing and upscaling issues (see Flaws but not dealbreakers), which videophiles and AV enthusiasts may take umbrage with. But in general, the picture quality punches well above its weight, metaphorically speaking.
And thanks to Hisense’s inclusion of Filmmaker Mode, it’s easy to rein in the U8H’s brightness abilities for a more-subdued and filmic experience in a darker room. Our measurements revealed that this mode has a very accurate white balance, mostly accurate colors (green is a bit oversaturated, but not egregiously so), and a perfect “dark room” gamma (which controls how quickly the video signal transitions from dark to light). Additionally, the TV’s 120 Hz refresh rate means it can play Blu-ray discs at 24 fps without the judder that’s usually present on TVs with 60 Hz refresh rates.
The TV’s higher refresh rate also reduces motion blur in faster-moving sports and allows for smoother, more stable motion in games. Two of the four HDMI inputs support 4K gaming at 120 Hz. The U8H measured low input lag while playing in 4K resolution, and Hisense’s helpful GameZone setting in the picture menu allowed me to confirm the presence of 120 Hz playback and variable refresh rate during games.
The onboard Google TV smart platform is another feather in this TV’s cap. As usual, however, it will be much more satisfying to use if you have a Google account and already take advantage of Google’s connected services, like Photos. The experience of navigating the TV’s smart features—scanning QR codes to sign into apps, using the onscreen keyboard, and browsing your Google Photos to set a photo as a screensaver—was very satisfying in terms of responsiveness and speed. Powering on the TV and booting into an app took just seconds. The included Bluetooth remote is also equipped with a handy “Hey Google” button, allowing you to pull up Google’s assistant and use voice commands to search for content or set a reminder. If you have multiple users with their own Google accounts, you can designate separate profiles (attached to a Gmail account) so that each user can customize the experience to their liking, as well as access their own Google Drive or Photos. While some reviewers have reported instances of momentary freezing while using the U8H’s platform, I didn’t personally experience any instances of slowdown that were egregiously worse than with any other smart-TV platform.
In terms of design, the Hisense U8H is not as svelte as our upgrade pick, but it’s plenty sturdy and doesn’t look or feel cheap. Two narrow, metal feet jut out from beneath the panel and steadily hold the TV. They can be attached in two separate spots, either closer in toward the middle of the panel or out toward the edges, to account for different-size TV stands. The feet are also equipped with cable organization clasps—a nice touch for keeping your TV stand free of cable clutter. Though the TV is primarily plastic, its bezels are lined with metal strips, providing a bit more durability in the long run. I moved it around my home, and it was no worse for wear, but we’ll know more after doing some long-term testing.
The Hisense U8H has some difficulties with banding, or areas of uneven gradation, where transitions that should appear smooth instead look like “bands” of color (sometimes also called posterization). Like many current 4K HDR TVs, the U8H uses an 8-bit panel rather than a 10-bit panel, which affects the color decoding and color presentation process. This is usually relevant only with HDR video and games. When playing games on the PlayStation 5 and Xbox Series X, I saw a few instances where the content wasn’t rendered correctly and displayed ugly splotches of color on the screen. However, this almost always occurred during static screens (such as a pause menu or loading screen); I rarely spotted it during actual gameplay. Hisense has stated that it would address the problem in a future firmware update, but at the time of writing it was still present. This is a flaw that may give dedicated gamers pause, but we don’t consider it to be a dealbreaker for most people.
I also saw occasional instances of banding with TV shows and movies, though they were few and far between. The U8H isn’t the best at upscaling sub-4K content, so videos with a 1080p or lower resolution looked a little soft. You can get better overall video processing and upscaling by springing for our upgrade pick (this is one reason it’s more expensive, after all).
Although the UH8 TV has four HDMI inputs, only two of them are fully HDMI 2.1–compatible. And one of those is designated as the eARC input (intended as an audio connection for a soundbar or AV receiver connection). So if you’re pairing an external audio system with the U8H, you may have only one input remaining that can support HDMI 2.1 features like 4K 120 Hz playback, variable refresh rate, and auto game mode; this could be a dealbreaker if you own more than one current-gen gaming console. If you’re in that boat, you may want to splash out some extra dough for our upgrade pick. Additionally, folks using pre-HDMI source devices—like the five-cable composite connector with green, red, blue, and red/white audio inputs—should be aware that this TV requires an adapter to allow those devices to connect, and an adapter is not included in the box.
Finally, like most TVs that use vertical alignment (VA) LCD panels, the U8H has a limited horizontal viewing angle, which may be a bit annoying if you’re hoping to entertain a large crowd. Our upgrade pick uses a special wide-angle technology to address this.
For gaming, use the game picture mode (the TV should switch into this mode automatically when paired with the newer game consoles), and then go into the Gaming submenu to make sure the right settings (VRR) are enabled. We recommend leaving the HDMI setting in “auto,” unless you notice that your game console is incorrectly identified.

It is essential to verify if the problem is inherent with the monitor, video card (GPU) or video settings on your computer. A straightforward way to identify this is to connect the computer to a known-good external monitor or TV and ensure that the display cable (S-video, VGA, DVI, HDMI, DisplayPort, USB-C, or Thunderbolt 3) is firmly connected to the video port on the computer and the monitor.
Performance issues may occur if there is any type of damage that is caused to the display cables or the LCD screen. LCD screen may show that symptoms like LCD screen stops working, work intermittently, color mismatch, flickering, display horizontal or vertical lines if there is damage to the display cables or the LCD screen.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey