esp8266 tft lcd display quotation

In the previous article (“WiFi OLED Mini Weather Station with ESP8266“) I have used the OLED kit from https://blog.squix.org. And as promised, this time it is about the “ESP8266 WiFi Color Display Kit”:
I had ordered both because I thought that the Color Display kit is needs the other kit as a base. Well, it turned out that both kits work independently. My bad. Actually this is good, as I have now two independent ESP8266 weather stations :-). An addition to that, they can exchange data (e.g. temperature/humidity) with a server, so that makes them a perfect dual weather station.
This time assembling the kit needs basic soldering skills. With the excellent tutorial by Daniel Eichhorn (https://blog.squix.org/wifi-color-display-kit) this should be a piece of cake. The only consideration is what kind of headers to use. I opted for the ‘larger but flexible’ approach. That way I can separate the boards if needed.
Example code is available on GitHub (https://github.com/squix78/esp8266-weather-station-color). The code is very well documented I had no issues to make all the needed configuration (WiFi SSID and connection settings). After a few hours I had the ESP8266 weather station up and running in the first prototype of the enclosure:
After a few hours, I have now my second ESP8266 WiFi weather station with touch LCD. It is not looking good and I very much enjoy it. The design is available on Thingiverse (https://www.thingiverse.com/thing:2527282).

// https://www.aliexpress.com/store/product/3-2-TFT-LCD-Display-module-Touch-Screen-Shield-board-onboard-temperature-sensor-w-Touch-Pen/1199788_32755473754.html?spm=2114.12010615.0.0.bXDdc3

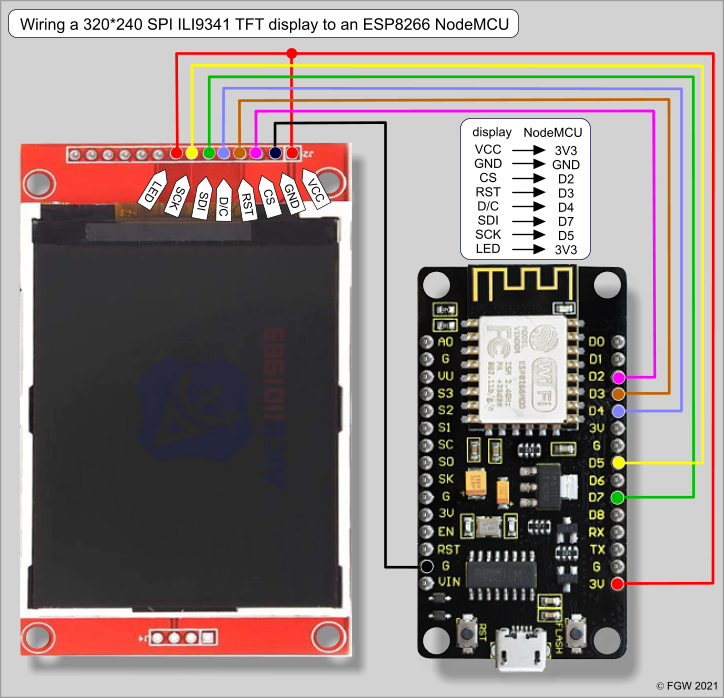
The ILI9341 TFT module contains a display controller with the same name: ILI9341. It’s a color display that uses SPI interface protocol and requires 4 or 5 control pins, it’s low cost and easy to use.
The resolution of this TFT display is 240 x 320 which means it has 76800 pixels. This module works with 3.3V only and it doesn’t support 5V (not 5V tolerant).
The ILI9341 TFT display board which is shown in project circuit diagram has 14 pins, the first 9 pins are for the display and the other 5 pins are for the touch module.
So, the display part pins are numbered from 1 to 9 (from left to right): VCC (5V), GND (ground), CS (chip select), RST (reset), DC (or D/C: data/command), MOSI (or SDI), SCK (clock), BL (back light LED) and MISO (or SDO).
Pins D5 (GPIO14) and D7 (GPIO13) are hardware SPI module pins of the ESP8266EX microcontroller respectively for SCK (serial clock) and MOSI (master-out slave-in).
The first library is a driver for the ILI9341 TFT display which can be installed from Arduino IDE library manager (Sketch —> Include Library —> Manage Libraries …, in the search box write “ili9341” and choose the one from Adafruit).
The ILI9341 TFT display is connected to NodeMCU hardware SPI module pins (clock and data), the other pins which are: CS (chip select), RST (reset) and DC (data/command) are defined as shown below:

The ST7789 TFT module contains a display controller with the same name: ST7789. It’s a color display that uses SPI interface protocol and requires 3, 4 or 5 control pins, it’s low cost and easy to use.
This display is an IPS display, it comes in different sizes (1.3″, 1.54″ …) but all of them should have the same resolution of 240×240 pixel, this means it has 57600 pixels. This module works with 3.3V only and it doesn’t support 5V.
The ST7789 display module shown in project circuit diagram has 7 pins: (from right to left): GND (ground), VCC, SCL (serial clock), SDA (serial data), RES (reset), DC (or D/C: data/command) and BLK (back light).
Pins D5 (GPIO14) and D7 (GPIO13) are hardware SPI module pins of the ESP8266EX microcontroller respectively for SCK (serial clock) and MOSI (master-out slave-in).
The first library is a driver for the ST7789 TFT display which can be installed from Arduino IDE library manager (Sketch —> Include Library —> Manage Libraries …, in the search box write “st7789” and install the one from Adafruit).

In this Arduino touch screen tutorial we will learn how to use TFT LCD Touch Screen with Arduino. You can watch the following video or read the written tutorial below.
As an example I am using a 3.2” TFT Touch Screen in a combination with a TFT LCD Arduino Mega Shield. We need a shield because the TFT Touch screen works at 3.3V and the Arduino Mega outputs are 5 V. For the first example I have the HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor, then for the second example an RGB LED with three resistors and a push button for the game example. Also I had to make a custom made pin header like this, by soldering pin headers and bend on of them so I could insert them in between the Arduino Board and the TFT Shield.
Here’s the circuit schematic. We will use the GND pin, the digital pins from 8 to 13, as well as the pin number 14. As the 5V pins are already used by the TFT Screen I will use the pin number 13 as VCC, by setting it right away high in the setup section of code.
I will use the UTFT and URTouch libraries made by Henning Karlsen. Here I would like to say thanks to him for the incredible work he has done. The libraries enable really easy use of the TFT Screens, and they work with many different TFT screens sizes, shields and controllers. You can download these libraries from his website, RinkyDinkElectronics.com and also find a lot of demo examples and detailed documentation of how to use them.
After we include the libraries we need to create UTFT and URTouch objects. The parameters of these objects depends on the model of the TFT Screen and Shield and these details can be also found in the documentation of the libraries.
So now I will explain how we can make the home screen of the program. With the setBackColor() function we need to set the background color of the text, black one in our case. Then we need to set the color to white, set the big font and using the print() function, we will print the string “Arduino TFT Tutorial” at the center of the screen and 10 pixels down the Y – Axis of the screen. Next we will set the color to red and draw the red line below the text. After that we need to set the color back to white, and print the two other strings, “by HowToMechatronics.com” using the small font and “Select Example” using the big font.

I read in forums and could see that there were some adafruit libraries in the ESP8266 Arduino but now that it is not available and only some TFT_Touch_Shield_V2 are present.
Hi guys, over the past few tutorials, we have been discussing TFT displays, how to connect and use them in Arduino projects, especially the 1.8″ Colored TFT display. In a similar way, we will look at how to use the 1.44″ TFT Display (ILI9163C) with the Arduino.
The ILI9163C based 1.44″ colored TFT Display, is a SPI protocol based display with a resolution of 128 x 128 pixels. It’s capable of displaying up to 262,000 different colors. The module can be said to be a sibling to the 1.8″ TFT display, except for the fact that it is much faster and has a better, overall cost to performance ratio when compared with the 1.8″ TFT display. Some of the features of the display are listed below;
TheTFT Display, as earlier stated, communicates with the microcontroller over SPI, thus to use it, we need to connect it to the SPI pins of the Arduino as shown in the schematics below.
Please note that the version of the display used for this tutorial is not available on fritzing which is the software used for the schematics, so follow the pin connection list below to further understand how each pin of the TFT display should be connected to the Arduino.
When connecting the display, ensure that has a voltage regulator (shown in the image below) before connecting it directly to the 5v logic level of the Arduino. This is because the display could be destroyed if the version of the display you have does not have the regulator.
In order to allow the Arduino to work with the display, we need two Arduino libraries; the sumotoy TFT ILI9163C Arduino library which can be downloaded from this link and the popular Adafruit GFX Arduino library which we have used extensively in several tutorials. Download these libraries and install them in the Arduino IDE.
For today’s tutorial, we will be using the bigtest example which is one of the example codes that comes with the sumotoy ILI9163C Arduino library to show how to use the TFT display.
The example can be opened by going to File–>Examples–>TFT_ILI9163c–>bigtest as shown in the image below. It should be noted that this will only be available after the sumotoy library has been installed.
Next, an object of the ILI9163c library named “display” was created with CS and DC parameter as inputs but due to the kind of display being used, we need to include the pin of the Arduino to which the A0 pin of the TFT display is connected which is D8.
With this done, we move to the void setup() function. Under this function, we issue the commands that initialize the display then create a time variable updated by millis, after which we issue a command to clear the screen and display some random text on it.
Some of the functions which perform actions ranging from displaying fastlines, drawing rectangles etc are then called with a delay after each function so the text or graphics stays long enough on the screen to be visible.
Up next is the void loop function. The void loop function also calls some of the same functions called under the void setup() function to display circles, rectangles etc including the testline function which is essentially used to test the screen.
With the libraries installed, open an instance of the Arduino IDE, open the examples as described initially, don’t forget to make the A0 pin (D8) correction to the code then upload to the Arduino board. You should see different kind of text and graphics being displayed on the screen. I captured the screen in action and its shown in the image below.
That’s it for this tutorial guys, what interesting thing are you going to build with this display? Let’s get the conversation started. Feel free to reach me via the comment section if you have any questions about the tutorial.

ILI9341 is a 262,144-color single-chip SOC driver for a-TFT liquid crystal display with resolution of 240RGBx320 dots, comprising a 720-channel source driver, a 320-channel gate driver, 172,800 bytes GRAM for graphic display data of 240RGBx320 dots, and power supply circuit. ILI9341 supports parallel 8-/9-/16-/18-bit data bus MCU interface, 6-/16-/18-bit data bus RGB interface and 3-/4-line serial peripheral interface (SPI). The moving picture area can be specified in internal GRAM by window address function. The specified window area can be updated selectively, so that moving picture can be displayed simultaneously independent of still picture area.
You can find ILI9341-based TFT displays in various sizes on eBay and Aliexpress. The one I chose for this tutorial is 2.2″ length along the diagonal, 240×320 pixels resolution, supports SPI interface, and can be purchased for less than $10.
Note that we will be using the hardware SPI module of the ESP8266 to drive the TFT LCD. The SPI communication pins are multiplexed with I/O pins D5 (SCK), D6 (MISO), and D7 (MOSI). The chip select (CS) and Data/Command (DC) signal lines are configurable through software.
For ILI9341-based TFT displays, there are some options for choosing the library for your application. The most common one is using Bodmer. We will use this library in this tutorial. So go ahead and download the
The library contains proportional fonts, different sizes can be enabled/disabled at compile time to optimise the use of FLASH memory. The library has been tested with the NodeMCU (ESP8266 based).
The library is based on the Adafruit GFX and Adafruit ILI9341 libraries and the aim is to retain compatibility. Significant additions have been made to the library to boost the speed for ESP8266 processors (it is typically 3 to 10 times faster) and to add new features. The new graphics functions include different size proportional fonts and formatting features. There are a significant number of example sketches to demonstrate the different features.
Configuration of the library font selections, pins used to interface with the TFT and other features is made by editting the User_Setup.h file in the library folder. Fonts and features can easily be disabled by commenting out lines.
Now you are all set to try out tons of really cool built-in examples that come with the library. The following output corresponds to the TFT_Pie_Chart example.
My favorite example is TFT terminal, which implements a simple “Arduino IDE Serial Monitor” like serial receive terminal for monitoring debugging messages from another Arduino or ESP8266 board.

Along 3 years I have been trying several leg mechanism, at first I decided to do a simple desing with tibial motor where placed on femur joint.This design had several problems, like it wasn"t very robust and the most importat is that having the motor (with big mass) that far from the rotating axis, caused that in some movements it generate unwanted dynamics to the robot body, making controlability worse.New version have both motors of femur/tibial limb at coxa frame, this ends with a very simple setup and at the same time, the heaviest masses of the mechanism are centered to the rotating axis of coxa limb, so even though the leg do fast movements, inertias won"t be strong enough to affect the hole robot mass, achieving more agility.Inverse Kinematics of the mechanismAfter building it I notice that this mechanism was very special for another reason, at the domain the leg normally moves, it acts as a diferential mecanism, this means that torque is almost all the time shared between both motor of the longer limbs. That was an improvent since with the old mechanism tibial motor had to hold most of the weight and it was more forced than the one for femur.To visualize this, for the same movement, we can see how tibial motor must travel more arc of angel that the one on the new version.In order to solve this mechanism, just some trigonometry is needed. Combining both cosine and sine laws, we can obtain desired angle (the one between femur and tibia) with respect to the angle the motor must achieve.Observing these equations, with can notice that this angle (the one between femur and tibia) depends on both servos angles, which means both motors are contributing to the movement of the tibia.Calibration of servosAnother useful thing to do if we want to control servo precisely is to print a calibration tool for our set up. As shown in the image below, in order to know where real angles are located, angle protactor is placer just in the origin of the rotating joint, and choosing 2 know angles we can match PWM signal to the real angles we want to manipulate simply doing a lineal relation between angles and PWM pulse length.Then a simple program in the serial console can be wrtten to let the user move the motor to the desired angle. This way the calibration process is only about placing motor at certain position and everything is done and we won"t need to manually introduce random values that can be a very tedious task.With this I have achieved very good calibrations on motors, which cause the robot to be very simetrial making the hole system more predictable. Also the calibration procedure now is very easy to do, as all calculations are done automatically. Check Section 1 for the example code for calibration.More about this can be seen in the video below, where all the building process is shown as well as the new leg in action.SECTION 1:In the example code below, you can see how calibration protocol works, it is just a function called calibrationSecuence() which do all the work until calibration is finished. So you only need to call it one time to enter calibration loop, for example by sending a "c" character thought the serial console.Also some useful function are used, like moving motor directly with analogWrite functions which all the calculations involved, this is a good point since no interrupts are used.This code also have the feature to calibrate the potentiometer coming from each motor.#define MAX_PULSE 2500 #define MIN_PULSE 560 /*---------------SERVO PIN DEFINITION------------------------*/ int m1 = 6;//FR int m2 = 5; int m3 = 4; int m4 = 28;//FL int m5 = 29; int m6 = 36; int m7 = 3;//BR int m8 = 2; int m9 = 1; int m10 = 7;//BL int m11 = 24; int m12 = 25; int m13 = 0;//BODY /*----------------- CALIBRATION PARAMETERS OF EACH SERVO -----------------*/ double lowLim[13] = {50, 30, 30, 50, 30, 30, 50, 30, 30, 50, 30, 30, 70}; double highLim[13] = {130, 150, 150, 130, 150, 150, 130, 150, 150, 130, 150, 150, 110}; double a[13] = { -1.08333, -1.06667, -1.07778, //FR -1.03333, 0.97778, 1.01111, //FL 1.03333, 1.05556, 1.07778, //BR 1.07500, -1.07778, -1.00000, //BL 1.06250 }; double b[13] = {179.0, 192.0, 194.5, //FR 193.0, 5.5, -7.5, //FL 7.0, -17.0, -16.0, //BR -13.5, 191.5, 157.0, //BL -0.875 }; double ae[13] = {0.20292, 0.20317, 0.19904 , 0.21256, -0.22492, -0.21321, -0.21047, -0.20355, -0.20095, -0.20265, 0.19904, 0.20337, -0.20226 }; double be[13] = { -18.59717, -5.70512, -2.51697, -5.75856, 197.29411, 202.72169, 185.96931, 204.11902, 199.38663, 197.89534, -5.33768, -32.23424, 187.48058 }; /*--------Corresponding angles you want to meassure at in your system-----------*/ double x1[13] = {120, 135, 90, 60, 135 , 90, 120, 135, 90, 60, 135, 90, 110}; //this will be the first angle you will meassure double x2[13] = {60, 90, 135, 120, 90, 135, 60, 90, 135, 120, 90, 135, 70};//this will be the second angle you will meassure for calibration /*--------You can define a motor tag for each servo--------*/ String motorTag[13] = {"FR coxa", "FR femur", "FR tibia", "FL coxa", "FL femur", "FL tibia", "BR coxa", "BR femur", "BR tibia", "BL coxa", "BL femur", "BL tibia", "Body angle" }; double ang1[13] = {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}; double ang2[13] = {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}; float xi[500]; float yi[500]; float fineAngle; float fineL; float fineH; int motorPin; int motor = 0; float calibrationAngle; float res = 1.0; float ares = 0.5; float bres = 1.0; float cres = 4.0; float rawAngle; float orawAngle; char cm; char answer; bool interp = false; bool question = true; bool swing = false; int i; double eang; int freq = 100; // PWM frecuency can be choosen here. void connectServos() { analogWriteFrequency(m1, freq); //FR coxa digitalWrite(m1, LOW); pinMode(m1, OUTPUT); analogWriteFrequency(m2, freq); //femur digitalWrite(m2, LOW); pinMode(m2, OUTPUT); analogWriteFrequency(m3, freq); //tibia digitalWrite(m3, LOW); pinMode(m3, OUTPUT); analogWriteFrequency(m4, freq); //FL coxa digitalWrite(m4, LOW); pinMode(m4, OUTPUT); analogWriteFrequency(m5, freq); //femur digitalWrite(m5, LOW); pinMode(m5, OUTPUT); analogWriteFrequency(m6, freq); //tibia digitalWrite(m6, LOW); pinMode(m6, OUTPUT); analogWriteFrequency(m7, freq); //FR coxa digitalWrite(m7, LOW); pinMode(m7, OUTPUT); analogWriteFrequency(m8, freq); //femur digitalWrite(m8, LOW); pinMode(m8, OUTPUT); analogWriteFrequency(m9, freq); //tibia digitalWrite(m9, LOW); pinMode(m9, OUTPUT); analogWriteFrequency(m10, freq); //FR coxa digitalWrite(m10, LOW); pinMode(m10, OUTPUT); analogWriteFrequency(m11, freq); //femur digitalWrite(m11, LOW); pinMode(m11, OUTPUT); analogWriteFrequency(m12, freq); //tibia digitalWrite(m12, LOW); pinMode(m12, OUTPUT); analogWriteFrequency(m13, freq); //body digitalWrite(m13, LOW); pinMode(m13, OUTPUT); } void servoWrite(int pin , double angle) { float T = 1000000.0f / freq; float usec = float(MAX_PULSE - MIN_PULSE) * (angle / 180.0) + (float)MIN_PULSE; uint32_t duty = int(usec / T * 4096.0f); analogWrite(pin , duty); } double checkLimits(double angle , double lowLim , double highLim) { if ( angle >= highLim ) { angle = highLim; } if ( angle <= lowLim ) { angle = lowLim; } return angle; } int motorInfo(int i) { enc1 , enc2 , enc3 , enc4 , enc5 , enc6 , enc7 , enc8 , enc9 , enc10 , enc11 , enc12 , enc13 = readEncoders(); if (i == 0) { rawAngle = enc1; motorPin = m1; } else if (i == 1) { rawAngle = enc2; motorPin = m2; } else if (i == 2) { rawAngle = enc3; motorPin = m3; } else if (i == 3) { rawAngle = enc4; motorPin = m4; } else if (i == 4) { rawAngle = enc5; motorPin = m5; } else if (i == 5) { rawAngle = enc6; motorPin = m6; } else if (i == 6) { rawAngle = enc7; motorPin = m7; } else if (i == 7) { rawAngle = enc8; motorPin = m8; } else if (i == 8) { rawAngle = enc9; motorPin = m9; } else if (i == 9) { rawAngle = enc10; motorPin = m10; } else if (i == 10) { rawAngle = enc11; motorPin = m11; } else if (i == 11) { rawAngle = enc12; motorPin = m12; } else if (i == 12) { rawAngle = enc13; motorPin = m13; } return rawAngle , motorPin; } void moveServos(double angleBody , struct vector anglesServoFR , struct vector anglesServoFL , struct vector anglesServoBR , struct vector anglesServoBL) { //FR anglesServoFR.tetta = checkLimits(anglesServoFR.tetta , lowLim[0] , highLim[0]); fineAngle = a[0] * anglesServoFR.tetta + b[0]; servoWrite(m1 , fineAngle); anglesServoFR.alpha = checkLimits(anglesServoFR.alpha , lowLim[1] , highLim[1]); fineAngle = a[1] * anglesServoFR.alpha + b[1]; servoWrite(m2 , fineAngle); anglesServoFR.gamma = checkLimits(anglesServoFR.gamma , lowLim[2] , highLim[2]); fineAngle = a[2] * anglesServoFR.gamma + b[2]; servoWrite(m3 , fineAngle); //FL anglesServoFL.tetta = checkLimits(anglesServoFL.tetta , lowLim[3] , highLim[3]); fineAngle = a[3] * anglesServoFL.tetta + b[3]; servoWrite(m4 , fineAngle); anglesServoFL.alpha = checkLimits(anglesServoFL.alpha , lowLim[4] , highLim[4]); fineAngle = a[4] * anglesServoFL.alpha + b[4]; servoWrite(m5 , fineAngle); anglesServoFL.gamma = checkLimits(anglesServoFL.gamma , lowLim[5] , highLim[5]); fineAngle = a[5] * anglesServoFL.gamma + b[5]; servoWrite(m6 , fineAngle); //BR anglesServoBR.tetta = checkLimits(anglesServoBR.tetta , lowLim[6] , highLim[6]); fineAngle = a[6] * anglesServoBR.tetta + b[6]; servoWrite(m7 , fineAngle); anglesServoBR.alpha = checkLimits(anglesServoBR.alpha , lowLim[7] , highLim[7]); fineAngle = a[7] * anglesServoBR.alpha + b[7]; servoWrite(m8 , fineAngle); anglesServoBR.gamma = checkLimits(anglesServoBR.gamma , lowLim[8] , highLim[8]); fineAngle = a[8] * anglesServoBR.gamma + b[8]; servoWrite(m9 , fineAngle); //BL anglesServoBL.tetta = checkLimits(anglesServoBL.tetta , lowLim[9] , highLim[9]); fineAngle = a[9] * anglesServoBL.tetta + b[9]; servoWrite(m10 , fineAngle); anglesServoBL.alpha = checkLimits(anglesServoBL.alpha , lowLim[10] , highLim[10]); fineAngle = a[10] * anglesServoBL.alpha + b[10]; servoWrite(m11 , fineAngle); anglesServoBL.gamma = checkLimits(anglesServoBL.gamma , lowLim[11] , highLim[11]); fineAngle = a[11] * anglesServoBL.gamma + b[11]; servoWrite(m12 , fineAngle); //BODY angleBody = checkLimits(angleBody , lowLim[12] , highLim[12]); fineAngle = a[12] * angleBody + b[12]; servoWrite(m13 , fineAngle); } double readEncoderAngles() { enc1 , enc2 , enc3 , enc4 , enc5 , enc6 , enc7 , enc8 , enc9 , enc10 , enc11 , enc12 , enc13 = readEncoders(); eang1 = ae[0] * enc1 + be[0]; eang2 = ae[1] * enc2 + be[1]; eang3 = ae[2] * enc3 + be[2]; eang4 = ae[3] * enc4 + be[3]; eang5 = ae[4] * enc5 + be[4]; eang6 = ae[5] * enc6 + be[5]; eang7 = ae[6] * enc7 + be[6]; eang8 = ae[7] * enc8 + be[7]; eang9 = ae[8] * enc9 + be[8]; eang10 = ae[9] * enc10 + be[9]; eang11 = ae[10] * enc11 + be[10]; eang12 = ae[11] * enc12 + be[11]; eang13 = ae[12] * enc13 + be[12]; return eang1 , eang2 , eang3 , eang4 , eang5 , eang6 , eang7 , eang8 , eang9 , eang10 , eang11 , eang12 , eang13; } void calibrationSecuence( ) { //set servos at their middle position at firstt for (int i = 0; i <= 12; i++) { rawAngle , motorPin = motorInfo(i); servoWrite(motorPin , 90); } // sensorOffset0 = calibrateContacts(); Serial.println(" "); Serial.println("_________________________________SERVO CALIBRATION ROUTINE_________________________________"); Serial.println("___________________________________________________________________________________________"); Serial.println("(*) Don"t send several caracter at the same time."); delay(500); Serial.println(" "); Serial.println("Keyboard: "x"-> EXIT CALIBRATION. "c"-> ENTER CALIBRATION."); Serial.println(" "i"-> PRINT INFORMATION. "); Serial.println(" "); Serial.println(" "n"-> CHANGE MOTOR (+). "b" -> CHANGE MOTOR (-)."); Serial.println(" "m"-> START CALIBRATION."); Serial.println(" "q"-> STOP CALIBRATION."); Serial.println(" "); Serial.println(" "r"-> CHANGE RESOLUTION."); Serial.println(" "p"-> ADD ANGLE. "o"-> SUBTRACT ANGLE. "); Serial.println(" "s"-> SAVE ANGLE."); delay(500); Serial.println(" "); Serial.println("---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------"); Serial.print("SELECTED MOTOR: "); Serial.print(motorTag[motor]); Serial.print(". SELECTED RESOLUTION: "); Serial.println(res); while (CAL == true) { if (Serial.available() > 0) { cm = Serial.read(); if (cm == "x") { Serial.println("Closing CALIBRATION program..."); CAL = false; secuence = false; startDisplay(PAGE); angleBody = 90; anglesIKFR.tetta = 0.0; anglesIKFR.alpha = -45.0; anglesIKFR.gamma = 90.0; anglesIKFL.tetta = 0.0; anglesIKFL.alpha = -45.0; anglesIKFL.gamma = 90.0; anglesIKBR.tetta = 0.0; anglesIKBR.alpha = 45.0; anglesIKBR.gamma = -90.0; anglesIKBL.tetta = 0.0; anglesIKBL.alpha = 45.0; anglesIKBL.gamma = -90.0; } else if (cm == "i") { // + Serial.println(" "); Serial.println("---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------"); Serial.println("---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------"); Serial.println("(*) Don"t send several caracter at the same time."); delay(500); Serial.println(" "); Serial.println("Keyboard: "x"-> EXIT CALIBRATION. "c"-> ENTER CALIBRATION."); Serial.println(" "i"-> PRINT INFORMATION. "); Serial.println(" "); Serial.println(" "n"-> CHANGE MOTOR (+). "b" -> CHANGE MOTOR (-)."); Serial.println(" "m"-> START CALIBRATION."); Serial.println(" "q"-> STOP CALIBRATION."); Serial.println(" "); Serial.println(" "r"-> CHANGE RESOLUTION."); Serial.println(" "p"-> ADD ANGLE. "o"-> SUBTRACT ANGLE. "s"-> SAVE ANGLE."); Serial.println(" "); delay(500); Serial.println(" "); Serial.println("---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------"); Serial.println(" "); Serial.print("SELECTED MOTOR: "); Serial.print(motorTag[motor]); Serial.print(". SELECTED RESOLUTION: "); Serial.println(res); Serial.println("Actual parameters of the motor: "); Serial.print("High limit: "); Serial.print(highLim[motor]); Serial.print(" Low limit: "); Serial.print(lowLim[motor]); Serial.print(" Angle 1: "); Serial.print(ang1[motor]); Serial.print(" Angle 2: "); Serial.println(ang2[motor]); Serial.println("---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------"); } else if (cm == "m") { // + secuence = true; } else if (cm == "s") { // + } else if (cm == "n") { // + motor++; if (motor >= 13) { motor = 0; } Serial.print("SELECTED MOTOR: "); Serial.println(motorTag[motor]); } else if (cm == "b") { // + motor--; if (motor < 0) { motor = 13 - 1; } Serial.print("SELECTED MOTOR: "); Serial.println(motorTag[motor]); } else if (cm == "r") { // + if (res == ares) { res = bres; } else if (res == bres) { res = cres; } else if (res == cres) { res = ares; } Serial.print("SELECTED RESOLUTION: "); Serial.println(res); } } if (secuence == true) { Serial.print("Starting secuence for motor: "); Serial.println(motorTag[motor]); for (int i = 0; i <= 30; i++) { delay(20); Serial.print("."); } Serial.println("."); while (question == true) { unsigned long currentMicros = micros(); if (currentMicros - previousMicros >= 100000) { previousMicros = currentMicros; if (Serial.available() > 0) { answer = Serial.read(); if (answer == "y") { question = false; interp = true; secuence = true; } else if (answer == "n") { question = false; interp = false; secuence = true; } else { Serial.println("Please, select Yes(y) or No(n)."); } } } } answer = "t"; question = true; if (interp == false) { Serial.println("___"); Serial.println(" | Place motor at 1ts position and save angle"); Serial.println(" | This position can be the higher one"); rawAngle , motorPin = motorInfo(motor); calibrationAngle = 90; //start calibration at aproximate middle position of the servo. while (secuence == true) { /* find first calibration angle */ if (Serial.available() > 0) { cm = Serial.read(); if (cm == "p") { // + Serial.print(" | +"); Serial.print(res); Serial.print(" : "); calibrationAngle = calibrationAngle + res; servoWrite(motorPin , calibrationAngle); Serial.println(calibrationAngle); } else if (cm == "o") { // - Serial.print(" | -"); Serial.print(res); Serial.print(" : "); calibrationAngle = calibrationAngle - res; servoWrite(motorPin , calibrationAngle); Serial.println(calibrationAngle); } else if (cm == "r") { // + if (res == ares) { res = bres; } else if (res == bres) { res = cres; } else if (res == cres) { res = ares; } Serial.print("SELECTED RESOLUTION: "); Serial.println(res); } else if (cm == "q") { // quit secuence secuence = false; Serial.println(" | Calibration interrupted!!"); } else if (cm == "s") { // save angle ang1[motor] = calibrationAngle; secuence = false; Serial.print(" | Angle saved at "); Serial.println(calibrationAngle); } } } if (cm == "q") { Serial.println(" |"); } else { secuence = true; Serial.println("___"); Serial.println(" | Place motor at 2nd position and save angle"); Serial.println(" | This position can be the lower one"); } while (secuence == true) { /* find second calibration angle */ if (Serial.available() > 0) { cm = Serial.read(); if (cm == "p") { // + Serial.print(" | +"); Serial.print(res); Serial.print(" : "); calibrationAngle = calibrationAngle + res; servoWrite(motorPin , calibrationAngle); Serial.println(calibrationAngle); } else if (cm == "o") { // - Serial.print(" | -"); Serial.print(res); Serial.print(" : "); calibrationAngle = calibrationAngle - res; servoWrite(motorPin , calibrationAngle); Serial.println(calibrationAngle); } else if (cm == "r") { // + if (res == ares) { res = bres; } else if (res == bres) { res = cres; } else if (res == cres) { res = ares; } Serial.print("SELECTED RESOLUTION: "); Serial.println(res); } else if (cm == "q") { // quit secuence secuence = false; Serial.println(" | Calibration interrupted!!"); } else if (cm == "s") { // save angle ang2[motor] = calibrationAngle; secuence = false; Serial.print(" | Angle saved at "); Serial.println(calibrationAngle); } } } /*--------------------start calibration calculations------------------*/ if (cm == "q") { Serial.println("___|"); Serial.println("Calibration finished unespected."); Serial.println(" Select another motor."); Serial.print("SELECTED MOTOR: "); Serial.print(motorTag[motor]); Serial.print(". SELECTED RESOLUTION: "); Serial.println(res); } else { Serial.println("___"); Serial.println(" |___"); Serial.print( " | | Interpolating for motor: "); Serial.println(motorTag[motor]); secuence = true; //real angle is calculated interpolating both angles to a linear relation. a[motor] = (ang2[motor] - ang1[motor]) / (x2[motor] - x1[motor]); b[motor] = ang1[motor] - x1[motor] * (ang2[motor] - ang1[motor]) / (x2[motor] - x1[motor]); Serial.println(" | |"); } interp = true; } /*---------------------------make swing movement to interpolate motor encoder-----*/ if (interp == true and secuence == true) { delay(200); double x; int k = 0; int stp = 180; swing = true; i = 0; orawAngle , motorPin = motorInfo(motor); previousMicros = 0; while (swing == true) { // FIRST unsigned long currentMicros = micros(); if (currentMicros - previousMicros >= 10000) { // save the last time you blinked the LED previousMicros = currentMicros; x = x2[motor]; calibrationAngle = a[motor] * x + b[motor]; servoWrite(motorPin , calibrationAngle); rawAngle , motorPin = motorInfo(motor); if ((i % 3) == 0) { yi[k+1] = x; xi[k] = rawAngle; Serial.print(" | | Real ang: "); Serial.print(x); Serial.print(" -> Servo ang: "); Serial.print(calibrationAngle); Serial.print(" Enc: "); Serial.println(rawAngle); k++; } if (i >= stp) { swing = false; } i++; } } swing = true; i = 0; while (swing == true) { // moving unsigned long currentMicros = micros(); if (currentMicros - previousMicros >= 10000) { // save the last time you blinked the LED previousMicros = currentMicros; x = x2[motor] + float(i) * (x1[motor] - x2[motor]) / stp; calibrationAngle = a[motor] * x + b[motor]; servoWrite(motorPin , calibrationAngle); rawAngle , motorPin = motorInfo(motor); if ((i % 6) == 0) { yi[k+1] = x; xi[k] = rawAngle; Serial.print(" | | Real ang: "); Serial.print(x); Serial.print(" -> Servo ang: "); Serial.print(calibrationAngle); Serial.print(" Enc: "); Serial.println(rawAngle); k++; } if (i >= stp) { swing = false; } i++; } } swing = true; i = 0; while (swing == true) { // SECOND unsigned long currentMicros = micros(); if (currentMicros - previousMicros >= 10000) { // save the last time you blinked the LED previousMicros = currentMicros; x = x1[motor]; calibrationAngle = a[motor] * x + b[motor]; servoWrite(motorPin , calibrationAngle); rawAngle , motorPin = motorInfo(motor); if ((i % 3) == 0) { yi[k+1] = x; xi[k] = rawAngle; Serial.print(" | | Real ang: "); Serial.print(x); Serial.print(" -> Servo ang: "); Serial.print(calibrationAngle); Serial.print(" Enc: "); Serial.println(rawAngle); k++; } if (i >= stp) { swing = false; } i++; } } swing = true; i = 0; while (swing == true) { // moving unsigned long currentMicros = micros(); if (currentMicros - previousMicros >= 10000) { // save the last time you blinked the LED previousMicros = currentMicros; x = x1[motor] + float(i) * (x2[motor] - x1[motor]) / stp; calibrationAngle = a[motor] * x + b[motor]; servoWrite(motorPin , calibrationAngle); rawAngle , motorPin = motorInfo(motor); if ((i % 6) == 0) { yi[k+1] = x; xi[k] = rawAngle; Serial.print(" | | Real ang: "); Serial.print(x); Serial.print(" -> Servo ang: "); Serial.print(calibrationAngle); Serial.print(" Enc: "); Serial.println(rawAngle); k++; } if (i >= stp) { swing = false; } i++; } } swing = true; i = 0; while (swing == true) { // FIRST unsigned long currentMicros = micros(); if (currentMicros - previousMicros >= 10000) { // save the last time you blinked the LED previousMicros = currentMicros; x = x2[motor]; calibrationAngle = a[motor] * x + b[motor]; servoWrite(motorPin , calibrationAngle); rawAngle , motorPin = motorInfo(motor); if ((i % 3) == 0) { yi[k+1] = x; xi[k] = rawAngle; Serial.print(" | | Real ang: "); Serial.print(x); Serial.print(" -> Servo ang: "); Serial.print(calibrationAngle); Serial.print(" Enc: "); Serial.println(rawAngle); k++; } if (i >= stp) { swing = false; } i++; } } swing = true; i = 0; while (swing == true) { // moving unsigned long currentMicros = micros(); if (currentMicros - previousMicros >= 10000) { // save the last time you blinked the LED previousMicros = currentMicros; x = x2[motor] + float(i) * (x1[motor] - x2[motor]) / stp; calibrationAngle = a[motor] * x + b[motor]; servoWrite(motorPin , calibrationAngle); rawAngle , motorPin = motorInfo(motor); if ((i % 6) == 0) { yi[k+1] = x; xi[k] = rawAngle; Serial.print(" | | Real ang: "); Serial.print(x); Serial.print(" -> Servo ang: "); Serial.print(calibrationAngle); Serial.print(" Enc: "); Serial.println(rawAngle); k++; } if (i >= stp) { swing = false; } i++; } } swing = true; i = 0; while (swing == true) { // SECOND unsigned long currentMicros = micros(); if (currentMicros - previousMicros >= 10000) { // save the last time you blinked the LED previousMicros = currentMicros; x = x1[motor]; calibrationAngle = a[motor] * x + b[motor]; servoWrite(motorPin , calibrationAngle); rawAngle , motorPin = motorInfo(motor); if ((i % 3) == 0) { yi[k+1] = x; xi[k] = rawAngle; Serial.print(" | | Real ang: "); Serial.print(x); Serial.print(" -> Servo ang: "); Serial.print(calibrationAngle); Serial.print(" Enc: "); Serial.println(rawAngle); k++; } if (i >= stp) { swing = false; } i++; } } Serial.println(" | | Interpolation finished!"); /*-------Calculate linear interpolation of the encoder from 60 meassures done in swing------*/ double sx = 0; double sy = 0; double sx2 = 0; double sy2 = 0; double sxy = 0; double xmean = 0; double ymean = 0; int n = 300; for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) { sx += xi[i+10]; sy += yi[i+10]; sx2 += xi[i+10] * xi[i+10]; sy2 += yi[i+10] * yi[i+10]; sxy += xi[i+10] * yi[i+10]; } ae[motor] = (n * sxy - sx * sy) / (n * sx2 - sx * sx); //sxy / sx2; // be[motor] = (sy - ae[motor] * sx) / n; //ymean - ae[motor] * xmean; Serial.println(" | | Moving back to ZERO position."); // turn the motor back to middle position swing = true; i = 0; while (swing == true) { unsigned long currentMicros = micros(); if (currentMicros - previousMicros >= 10000) { // save the last time you blinked the LED previousMicros = currentMicros; x = x1[motor] + float(i) * (90 - x1[motor]) / 60; calibrationAngle = a[motor] * x + b[motor]; servoWrite(motorPin , calibrationAngle); rawAngle , motorPin = motorInfo(motor); eang = ae[motor] * rawAngle + be[motor]; if ((i % 4) == 0) { Serial.print(" | | Servo ang: "); Serial.print(calibrationAngle); Serial.print(" -> Real ang: "); Serial.print(x); Serial.print(" -> Encoder ang: "); Serial.println(eang); } if (i >= 60) { swing = false; } i++; } } Serial.println("___|___|"); Serial.println(" | "); Serial.println("___"); Serial.println(" | Calibration finished satisfactory. Results data:"); Serial.print(" | HIGH lim: "); Serial.print(highLim[motor]); Serial.print(" LOW lim: "); Serial.println(lowLim[motor]); Serial.print(" | angle 1: "); Serial.print(ang1[motor]); Serial.print(" angle 2 "); Serial.println(ang2[motor]); Serial.print(" | Regression Motor a: "); Serial.print(a[motor], 5); Serial.print(" b: "); Serial.println(b[motor], 5); Serial.print(" | Regression Encoder a: "); Serial.print(ae[motor], 5); Serial.print(" b: "); Serial.println(be[motor], 5); Serial.println(" |"); Serial.println(" | ______________________________________________________________"); Serial.println(" | | |"); Serial.println(" | | This code won"t be able to save the updated parameters |"); Serial.println(" | | once the robot is shutted down. |"); Serial.println(" | | |"); Serial.println(" | | Please, write down the results |"); Serial.println(" | | and save them in the definition of each variable. |"); Serial.println(" | |_____________________________________________________________|"); Serial.println(" |"); Serial.println("___|"); Serial.println(" Select another motor."); Serial.print("SELECTED MOTOR: "); Serial.print(motorTag[motor]); Serial.print(". SELECTED RESOLUTION: "); Serial.println(res); } interp = false; secuence = false; } } SAFE = false; Serial.println("Calibration killed"); } // END OF CALIBRATION

The beauty of an ESP8266 is not just that the used microcontroller is faster or cheaper. On top of that: it has more memory than most Arduino models (Flash memory of 4Mb, and typically more SRAM – however, EEPROM is more limited though).
These pin are often referred to as GPIO (General Purpose Input/Output pins), and the ESP8266 has at least 11 of these pins (depending on the model). This can be a few less than your good old Arduino, but newer ESP8266 models have more (Arduino Uno: 14, my Makerfocus ESP8266 has 16).
Compared to most Arduino’s, there could be one downside and that is that most ESP8266’s have only 1 or 2 analog pins (mine has only one it seems). The other pins are all digital.
Note: There are quite a few manufacturers that use the ESP8266 chip for their little boards, and the ESP8266 comes in a few different versions as well. Keep in mind that the implementation and specifications can be different depending on the board manufacturer and the used chip (the original, v2 and v3 and there is the ESP32. The latter has even way more pins to play with).
In short: the ESP8266 houses a microcontroller (like your Arduino, just more powerful) and everything you need to get wirelessly connected, and that at a ridiculously low price of about $5 or even less.
For beginners the now following picture may not make much sense – and my Makerfocus ESP8266 has a very clear text on the back indicating what pin is what. Nevertheless, this picture may be good info for those not having an ESP8266 yet, or as reference for future projects.
Note: the ESP8266 can be powered by most simple adapters (5 – 12 Volt), from what I have read it will use 450 mA at peak moments, but power usage can drop even below 1 mA. So I think it is safe to say that your old adapter of one of your old cell phones will be more than adequate.
While, on paper, the ESP8266 has plenty of GPIO pins, in reality, 6 of these are blocked off from use. GPIO6, GPIO7, GPIO8, GPIO9, GPIO10, and GPIO11 and are all unavailable to you. In addition, if you are using Serial input/output at all, attempting to use GPIO1 for leds may cause the device to reset.
You may, like myself, already have some Arduino experience, and moving to an ESP8266 may look a little daunting at first especially when using it like a regular Arduino. Fear not, it is surprisingly easy to get started, below I’ll share my own experiences in hopes that it will be helpful for you as well.
Note: I’m focussing here on the ESP8266 that I own, a Makerfocus ESP8266, which set me back $10 for 2 modules. You can get them from Amazon in the USA and in Germany (both do deliver to a select number of other countries as well).
Not knowing what I’m doing, I just selected the “Generic ESP8266 module”, which worked. However after selecting this option, suddenly a ton of configurable details became visible, which made me think that there could be a more optimized board I could choose.
Obviously, as an ESP8266 beginner, I didn’t quite know what I was looking at. Of course, quite a few of these parameters I did understand, but I didn’t know how they correlated with my ESP8266 board.
So I went to my Amazon order to lookup what the heck I had purchased and found the following text “ESP8266 NodeMCU LUA CP2102 ESP-12E” which gave me a few hints. For one, I should probably give one of the NodeMCU boards a try. There were 2 listed: the v0.9 (ESP-12 module) and the v1.0 (ESP-12E module). So for me a dead give away that selecting the second option, the “NodeMCU v1.0 (ESP-12E module)” was my best option.
My Arduino Uno uses a USB-A to USB-B cable, but the connector on my ESP8266 was a USB micro-B connector. This is one of the most commonly used small USB connectors, as they are being used for cell phones, tablets, cameras etc.
The function “handleButtonDisplay()” is something I’ll discus in the HTML part – its task is to push out the correct HTML for the buttons, depending on the LED state (on or off).
Initially, the serial monitor will show some garbage characters. This is actually not garbage, but debug info send from the ESP8266 at a baudrate of 74880. This weird baudrate is said to be a non-standard baudrate so we know information is debug info (versus application specific info). Source: ESP8266.com.
When clicking on the buttons we should have the browser load a new page, for this we have 2 “pages” on our ESP8266 webserver to switch a LED on (LEDOn) and off (LEDOff). So:
First we need to define a global variable to hold our ESP8266WebServer object (don’t overthink it!), which we will call “server” and which listens to port 80 (the default port).
I won’t go too much into detail, but in essence we can give the ESP8266WebServer object event conditions when a certain page (link) is being asked for. I intentionally wrote this in a consistent way, but it can be written shorter.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey