tft lcd ips vs gorilla glass price

If you want to buy a new monitor, you might wonder what kind of display technologies I should choose. In today’s market, there are two main types of computer monitors: TFT LCD monitors & IPS monitors.
The word TFT means Thin Film Transistor. It is the technology that is used in LCD displays. We have additional resources if you would like to learn more about what is a TFT Display. This type of LCDs is also categorically referred to as an active-matrix LCD.
These LCDs can hold back some pixels while using other pixels so the LCD screen will be using a very minimum amount of energy to function (to modify the liquid crystal molecules between two electrodes). TFT LCDs have capacitors and transistors. These two elements play a key part in ensuring that the TFT display monitor functions by using a very small amount of energy while still generating vibrant, consistent images.
Industry nomenclature: TFT LCD panels or TFT screens can also be referred to as TN (Twisted Nematic) Type TFT displays or TN panels, or TN screen technology.
IPS (in-plane-switching) technology is like an improvement on the traditional TFT LCD display module in the sense that it has the same basic structure, but has more enhanced features and more widespread usability.
These LCD screens offer vibrant color, high contrast, and clear images at wide viewing angles. At a premium price. This technology is often used in high definition screens such as in gaming or entertainment.
Both TFT display and IPS display are active-matrix displays, neither can’t emit light on their own like OLED displays and have to be used with a back-light of white bright light to generate the picture. Newer panels utilize LED backlight (light-emitting diodes) to generate their light hence utilizing less power and requiring less depth by design. Neither TFT display nor IPS display can produce color, there is a layer of RGB (red, green, blue) color filter in each LCD pixels to produce the color consumers see. If you use a magnifier to inspect your monitor, you will see RGB color in each pixel. With an on/off switch and different level of brightness RGB, we can get many colors.
Winner. IPS TFT screens have around 0.3 milliseconds response time while TN TFT screens responds around 10 milliseconds which makes the latter unsuitable for gaming
Winner. the images that IPS displays create are much more pristine and original than that of the TFT screen. IPS displays do this by making the pixels function in a parallel way. Because of such placing, the pixels can reflect light in a better way, and because of that, you get a better image within the display.
As the display screen made with IPS technology is mostly wide-set, it ensures that the aspect ratio of the screen would be wider. This ensures better visibility and a more realistic viewing experience with a stable effect.
Winner. While the TFT LCD has around 15% more power consumption vs IPS LCD, IPS has a lower transmittance which forces IPS displays to consume more power via backlights. TFT LCD helps battery life.
Normally, high-end products, such as Apple Mac computer monitors and Samsung mobile phones, generally use IPS panels. Some high-end TV and mobile phones even use AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diodes) displays. This cutting edge technology provides even better color reproduction, clear image quality, better color gamut, less power consumption when compared to LCD technology.
This kind of touch technology was first introduced by Steve Jobs in the first-generation iPhone. Of course, a TFT LCD display can always meet the basic needs at the most efficient price. An IPS display can make your monitor standing out.

Before you get a new monition for your organization, comparing the TFT display vs IPS display is something that you should do. You would want to buy the monitor which is the most advanced in technology. Therefore, understanding which technology is good for your organization is a must. click to view the 7 Best Types Of Display Screens Technology.
Technology is changing and becoming advanced day by day. Therefore, when you are looking to get a new monitor for your organization, LCD advantages, and disadvantage, you have to be aware of the pros and cons of that monitor. Moreover, you need to understand the type of monitor you are looking to buy.
That is why it is important to break it down and discuss point by point so that you can understand it in a layman’s language devoid of any technical jargon. Therefore, in this very article, let’s discuss what exactly TFT LCDs and IPS LCDs are, and what are their differences? You will also find out about their pros and cons for your organization.
The word TFT means Thin-Film-Translator. It is the technology that is used in LCD or Liquid Crystal Display. Here you should know that this type of LCD is also categorically referred to as active-matrix LCDs. It tells that these LCDs can hold back some pixels while using other pixels. So, the LCD will be using a very minimum amount of energy to function. TFT LCDs have capacitors and transistors. These are the two elements that play a key part in ensuring that the display monitor functions by using a very small amount of energy without running out of operation.
Now, it is time to take a look at its features that are tailored to improve the experience of the monitor users significantly. Here are some of the features of the TFT monitor;
No radiation, no scintillation, no harm to the user’s health. In particular, the emergence of TFT LCD electronic books and periodicals will bring humans into the era of a paperless office and paperless printing, triggering a revolution in the civilized way of human learning, dissemination, and recording.
It can be normally used in the temperature range from -20℃ to +50℃, and the temperature-hardened TFT LCD can operate at low temperatures up to -80 ℃. It can not only be used as a mobile terminal display, or desktop terminal display but also can be used as a large screen projection TV, which is a full-size video display terminal with excellent performance.
The manufacturing technology has a high degree of automation and good characteristics of large-scale industrial production. TFT LCD industry technology is mature, a mass production rate of more than 90%.
TFT LCD screen from the beginning of the use of flat glass plate, its display effect is flat right angles, let a person have a refreshing feeling. And LCDs are easier to achieve high resolution on small screens.
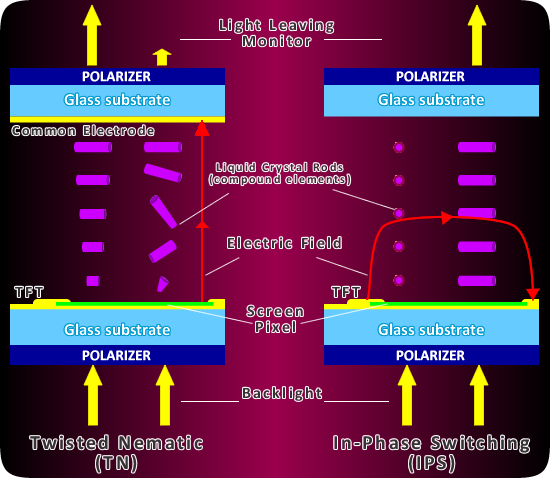
The word IPS refers to In-Plane-Switching which is a technology used to improve the viewing experience of the usual TFT displays. You can say that the IPS display is a more advanced version of the traditional TFT LCD module. However, the features of IPS displays are much more advanced and their applications are very much widespread. You should also know that the basic structure of the IPS LCD is the same as TFT LCD if you compare TFT LCD vs IPS.
As you already know, TFT displays do have a very quick response time which is a plus point for it. But, that does not mean IPS displays a lack of response time. In fact, the response time of an IPS LCD is much more consistent, stable, and quick than the TFT display that everyone used to use in the past. However, you will not be able to gauge the difference apparently by watching TFT and IPS displays separately. But, once you watch the screen side-by-side, the difference will become quite clear to you.
The main drawback of the TFT displays as figured above is the narrow-angle viewing experience. The monitor you buy for your organization should give you an experience of wide-angle viewing. It is very much true if you have to use the screen by staying in motion.
So, as IPS displays are an improved version of TFT displays the viewing angle of IPS LCDs is very much wide. It is a plus point in favor of IPS LCDs when you compare TFT vs IPS. With a TFT screen, you cannot watch an image from various angles without encountering halo effects, blurriness, or grayscale that will cause problems for your viewing.
It is one of the major and remarkable differences between IPS and TFT displays. So, if you don’t want to comprise on the viewing angles and want to have the best experience of viewing the screen from wide angles, the IPS display is what you want. The main reason for such a versatile and wonderful viewing angle of IPS display is the screen configuration which is widely set.
Now, when you want to achieve wide-angle viewing with your display screen, you need to make sure it has a faster level of frequency transmittance. It is where IPS displays overtake TFT displays easily in the comparison because the IPS displays have a much faster and speedier transmittance of frequencies than the TFT displays.
Now the transmittance difference between TFT displays and IPS displays would be around 1ms vs. 25ms. Now, you might think that the difference in milliseconds should not create much of a difference as far as the viewing experience is concerned. Yes, this difference cannot be gauged with a naked eye and you will find it difficult to decipher the difference.
However, when you view and an IPS display from a side-by-side angle and a TFT display from a similar angle, the difference will be quite evident in front of you. That is why those who want to avoid lagging in the screen during information sharing at a high speed; generally go for IPS displays. So, if you are someone who is looking to perform advanced applications on the monitor and want to have a wider viewing angle, then an IPS display is the perfect choice for you.
As you know, the basic structure of the IPS display and TFT displays are the same. So, it is quite obvious that an IPS display would use the same basic colors to create various shades with the pixels. However, there is a big difference with the way a TFT display would produce the colors and shade to an IPS display.
The major difference is in the way pixels get placed and the way they operate with electrodes. If you take the perspective of the TFT display, its pixels function perpendicularly once the pixels get activated with the help of the electrodes. It does help in creating sharp images.
But the images that IPS displays create are much more pristine and original than that of the TFT screen. IPS displays do this by making the pixels function in a parallel way. Because of such placing, the pixels can reflect light in a better way, and because of that, you get a better image within the display.
As the display screen made with IPS technology is mostly wide-set, it ensures that the aspect ratio of the screen would be wider. This ensures better visibility and a more realistic viewing experience with a stable effect.
As you already know the features of both TFT and IPS displays, it would be easier for you to understand the difference between the two screen-types. Now, let’s divide the matters into three sections and try to understand the basic differences so that you understand the two technologies in a compressive way. So, here are the difference between an IPS display and a TFT display;
Now, before starting the comparison, it is quite fair to say that both IPS and TFT displays have a wonderful and clear color display. You just cannot say that any of these two displays lag significantly when it comes to color clarity.
However, when it comes to choosing the better display on the parameter of clarity of color, then it has to be the IPS display. The reason why IPS displays tend to have better clarity of color than TFT displays is a better crystal oriental arrangement which is an important part.
That is why when you compare the IPS LCD with TFT LCD for the clarity of color, IPS LCD will get the nod because of the better and advanced technology and structure.
IPS displays have a wider aspect ratio because of the wide-set configuration. That is why it will give you a better wide-angle view when it comes to comparison between IPS and TFT displays. After a certain angle, with a TFT display, the colors will start to get a bit distorted.
But, this distortion of color is very much limited in an IPS display and you may see it very seldom after a much wider angle than the TFT displays. That is why for wide-angle viewing, TFT displays will be more preferable.
When you are comparing TFT LCD vs. IPS, energy consumption also becomes an important part of that comparison. Now, IPS technology is a much advanced technology than TFT technology. So, it is quite obvious that IPS takes a bit more energy to function than TFT.
Also, when you are using an IPS monitor, the screen will be much larger. So, as there is a need for much more energy for the IPS display to function, the battery of the device will drain faster. Furthermore, IPS panels cost way more than TFT display panels.
1. The best thing about TFT technology is it uses much less energy to function when it is used from a bigger screen. It ensures that the cost of electricity is reduced which is a wonderful plus point.
2. When it comes to visibility, the TFT technology enhances your experience wonderfully. It creates sharp images that will have no problems for older and tired eyes.
1. One of the major problems of TFT technology is that it fails to create a wider angle of view. As a result, after a certain angle, the images in a TFT screen will distort marring the overall experience of the user.
Although IPS screen technology is very good, it is still a technology based on TFT, the essence of the TFT screen. Whatever the strength of the IPS, it is a TFT-based derivative.
Finally, as you now have a proper understanding of the TFT displays vs IPS displays, it is now easier for you when it comes to choose one for your organization. Technology is advancing at a rapid pace. You should not be surprised if you see more advanced display screens in the near future. However, so far, TFT vs IPS are the two technologies that are marching ahead when it comes to making display screens.
STONE provides a full range of 3.5 inches to 15.1 inches of small and medium-size standard quasi TFT LCD module, LCD display, TFT display module, display industry, industrial LCD screen, under the sunlight visually highlight TFT LCD display, industrial custom TFT screen, TFT LCD screen-wide temperature, industrial TFT LCD screen, touch screen industry. The LCD module is very suitable for industrial control equipment, medical instruments, POS system, electronic consumer products, vehicles, and other products.

IPS (In-Plane Switching) lcd is still a type of TFT LCD, IPS TFT is also called SFT LCD (supper fine tft ),different to regular tft in TN (Twisted Nematic) mode, theIPS LCD liquid crystal elements inside the tft lcd cell, they are arrayed in plane inside the lcd cell when power off, so the light can not transmit it via theIPS lcdwhen power off, When power on, the liquid crystal elements inside the IPS tft would switch in a small angle, then the light would go through the IPS lcd display, then the display on since light go through the IPS display, the switching angle is related to the input power, the switch angle is related to the input power value of IPS LCD, the more switch angle, the more light would transmit the IPS LCD, we call it negative display mode.
The regular tft lcd, it is a-si TN (Twisted Nematic) tft lcd, its liquid crystal elements are arrayed in vertical type, the light could transmit the regularTFT LCDwhen power off. When power on, the liquid crystal twist in some angle, then it block the light transmit the tft lcd, then make the display elements display on by this way, the liquid crystal twist angle is also related to the input power, the more twist angle, the more light would be blocked by the tft lcd, it is tft lcd working mode.
A TFT lcd display is vivid and colorful than a common monochrome lcd display. TFT refreshes more quickly response than a monochrome LCD display and shows motion more smoothly. TFT displays use more electricity in driving than monochrome LCD screens, so they not only cost more in the first place, but they are also more expensive to drive tft lcd screen.The two most common types of TFT LCDs are IPS and TN displays.

IPS-LCDs are costlier than normal TFT LCD and hence are found only on higher end smartphones. A higher resolution (640 x 960 pixels) version of IPS LCD is used in Apple iPhone 4 and is called Retina Display because of its brilliant picture quality.
It is a special alkali-aluminosilicate glass shield with exceptional damage resistance that helps protect mobile displays from scratches, drops, and bumps of everyday use. Many companies like Motorola, Samsung and Nokia are now using Gorilla Glass to make their mobile displays more durable and reliable. It is always better to go for a smartphone with Gorilla Glass for that added protection and peace of mind.
LCDs use a simple grid to supply the charge to a particular pixel on the display. Creating the grid is quite a process! It starts with two glass layers called substrates.

Welcome at Riverdi University. In this lecture we’ll talk about different kinds of glass in TFT LCD displays and surfaces that we use to protect displays, or we can use to protect with the glass the entire devices
We will talk about different types of glass in TFT LCD displays, then the surface treatments, what we do to achieve different parameters of glass surfaces, about the hardness – important when we want to protect something, then about painting the glass, how we do it and what we can achieve, IK rate, how much mechanical impact we can place on the glass, and will it withstand this still and at the end about laminated glass, why we laminate glass and what we can achieve by doing that.
The most important thing with the glass in TFT LCD displays is to protect the display, but not only. As you can see on the pictures above, glass is an element of the design of the devices. It makes devices look better and can be designed in a way that protects not only the display, but the entire surface of a device, like for example for the coffee machine on the picture above, where we have a display with some additional graphic that covers the whole front of the device. Glass is one of the best materials that we use in electronics to protect screens, because it is very hard and it is hard to scratch. It is mechanically strong, cheap, and exceptionally good in optics. For glass, the transparency rate is typically more than 90% or even 95% percent. It is widely available, we know a lot of techniques how to manufacture it and how to prepare it for some special advanced designs as we can change the shape of glass quite easily nowadays.
Now we will talk about types of glass that we use to protect screens and devices. Mainly we use two types of glass in TFT LCD displays, one is chemically strengthened glass, that we call CS type glass, the other is thermally tempered glass, hardened glass where we use hot temperature to make it stronger. For our standard products we typically use on the touch screens chemically strengthened glass. Our standard thickness is 1.1-millimeter thickness. This kind of glass is pretty strong, comparing to the regular glass. Chemical strengthening means that we treat the surface with ions, usually silver ions. We increase the strength of the surface of the glass because glass usually breaks when the surface breaks. We do not change the glass internally with chemical strengthening, we just change the surface hardness, and it is enough to make the glass much stronger.
As you can see in the table above, with chemical strengthening we can make glass even 6 or 8 times mechanically stronger than the regular one. This is a very long process; it can take several hours, and we need hot temperature, 400 or more degrees. Thermally tempered glass is a separate way of strengthening glass. We use hot temperature and very fast cooling to make the glass stronger. We need a higher temperature, 700 degrees in this process, but it is much faster, it takes just several minutes, and we achieve strong glass, 4 to 5 times stronger than regular float glass. Thermally tempered glass is not as strong as chemically strengthened glass. It is cheaper, but we cannot use it for thin glass. The thinnest glass that we can thermally temper is 3-4 millimeter. If the glass is thinner, with hot temperature it starts floating and the surface will not be flat again. So, if we have a thick glass, it would be cheaper to use the thermally tempered solution. That is why it is more popular. For thinner glass we use chemical strengthening, because we cannot use the thermally tempered solution.
Now we will talk about the other difference between these two methods of strengthening glass. On the left side of the picture above, you can see chemically strengthened glass broken, and on the right side there is thermally tempered glass broken. Chemically strengthened glass breaks like regular glass because we do not change the internal part of the glass. We only make the surface stronger, but inside the glass is the same as regular float glass, and it breaks just like it. Thermally tempered glass changes the internal structure of the glass and it breaks into very small pieces. In many cases it is better because it is safer for humans, that is why we normally use thermally tempered glass in cars or in places where broken glass may injure people.
Another property or type of glass that we will talk about is Optiwhite and Float. Float is the most common glass that we use in architecture designs, but also in many touchscreens. The float glass is the most common, most popular and the cheapest, but sometimes we have specific requirements. We sometimes need to have very good color reproduction, especially light colors, white color. Then we use glass called Optiwhite. To achieve that we need to remove the iron from the glass. Float glass has a little bit of iron which makes it green or greenish. If we look straight through the glass, we may not see that but if we look like from an angle, we can see the green color. If we put a white background, we will also see this greenish color a little bit. So, if there are specific requirements, we use Optiwhite, it is especially worth considering if you have a white background. Usually, the Optiwhite is a little bit more expensive, so it is worth checking with the manufacturer of the display what we can use in our case.
Now we know how glass is made, how it is being strengthened, how it breaks and what types of glass, Float and Optiwhite, we have. To continue, we will talk about surface treatments other than strengthening. The other treatments that we use are anti-glare, anti-fingerprint, anti-reflective and anti-bacterial. About anti-reflective treatment we have talked in another video about
On the picture above there are examples of glass. One of them is a little bit blurry, it is anti-glare and the other one is clear – it is anti-reflective. In the past, anti-glare glass was more popular and used in some commercial devices, but later manufacturers have found that devices with anti-glare are being sold less frequently than the glare ones. It is because as humans we think that there is something wrong with a little bit blurry image even if the reflections are lower. When we are in a shop and looking at phones, we do not see the image clearly and we think that there is something wrong and we do not want this device. That is why we do not see any more anti-glare glass in consumer products. Everything is glare in consumer products, it could be anti-reflective or could be only regular without any surface treatment. But in the professional market that we are working on, like medical devices, military devices, we have many projects where we use anti-glare and anti-reflective treatments, both solutions to reduce reflections and increase contrast.
Now let us talk about hardness of glass in TFT LCD displays. Of course, to talk about hardness we need to measure it. For that we have the Mohs scale where we have 11 different levels of hardness. Like you see on the picture above, the 10th is diamond and the 1st is talk. What we normally use is glass with hardness between 5 and 7. In some cases we also use Gorilla glass with hardness 9. It is used on our phones or tablets. As you can see, we can achieve hardness 7 with chemically strengthened glass and usually 6 with thermally strengthened glass. Gorilla glass is also chemically strengthened glass, patented by the Corning company and it is the strongest that we can achieve in the cover glass to protect the screen.
This scale is about surface hardness – how hard is it to scratch the surface. As you know, even glass with hardness 9 can be scratched, everybody has some scratches on their phone because this hard layer is very thin – 10 micrometers only. If we put enough force and break this barrier, then we have soft glass with hardness 6 or even lower, that is why we have the scratches.
A couple more words about Gorilla glass. Now there is the sixth generation of Gorilla Glass on the market. The goal for Corning company and Gorilla Glass is to make the glass as strong and as light as possible, because most of the cases are handheld devices, where we want the glass to be light, that is why we want to make it very thin. We have also other companies that are making equivalents of Gorilla Glass, like Dragontrail from AGC or Xensation from Shott. They are not so popular but in many mobile phones or tablets on the market you can find these types of glass.
Now let us talk about the painting. We know the types of glass that we use in TFT LCD displays, we know how to make the glass stronger, we know the surface treatments, how to make the glass less reflective or anti-fingerprint or antibacterial, but it is not enough because glass will only be transparent. If we want to cover it, we need to paint it. Typically, we paint glass with the technique called Screen Printing. It is the most popular, cheapest and fastest technique.
When we do the Screen Printing, we need a screen for each color, so to minimize cost, we try to reduce the number of colors to 2–4, like the background and the colored logo. Each color is a different process, we need to wait until the previous painting dries and then we need to put another screen and print another color. More colors mean a longer process and of course a higher cost. Of course, we can change the shape of the glass, we can make rounded corners or custom design of the glass, but it is expensive because first it is just the rectangular piece, then you need to go to the CNC machine to make the proper shape of the glass.
Now we will talk about mechanical impact protection. It is different than the surface hardness we talked about before. On the picture above, we have the test and scale to measure the mechanical strength of glass, that means how much energy we can put on the glass before it breaks. It is measured in IK rate. IK rate is a scale where we have different levels and different energy that will boost. For example, if we want to test IK 9, we need to take 5-kilogram mass from 200-millimeter height. The mass is kept above the tested glass using an electromagnet, then we just drop it, and we see if it breaks or not. If not, of course the test is passed.
If the glass has not passed the test, we can try to change the glass type from thermally tempered to chemically strengthened or go to a thicker glass.
The last point in this article is laminated glass. We laminate glass because of a few reasons. First, what is laminated glass. Laminated glass is like putting the film inside two glass sheets. This process is expensive, we need pressure, we need temperature, we need time, and we need an exceptionally clean environment, because when we laminate together two sheets of glass, we need to be sure that no particles get inside. This kind of process needs to be done in a Clean Room, so it is expensive, but as you see on the picture above, even if the glass is broken, it still holds up because of the laminated film inside.
We laminate glass mainly because of two reasons. One is mechanical strength and impact. We use it even in our homes. Many windows used nowadays are anti-vandal and that means they are laminated glass, and they are extraordinarily strong. The other reason to laminate glass is to put a film inside with some properties, usually to block the UV or IR light. IR means infrared so heat and UV means ultraviolet, short wavelength, extremely dangerous for electronics. When we have an outdoor application, some customers want to protect the displays, touchscreens or the e-paper displays also against UV. Then we use laminated glass and as you can see on the chart above the IR cut film and UV cut film are both transparent for visible light. We can see everything through them, but what is higher and what is lower is cut by UV and IR films. Most often we use only UV cut film because UV is more dangerous, for example it makes the film sensors for capacitive touchscreens turn yellow or it can decrease the contrast of the TFT (Thin Film Transistor) display by damaging the polarizer or color filters. The IR film is used in some applications to protect the display from heat. If we add it, we can decrease the temperature of the display surface. In another video we were talking about High-TN, so liquid crystals that can work in very high temperatures. For this kind of liquid crystals, we usually do not need to decrease the temperature of the surface because they can go up to 100 or 110 degrees, but regular displays can work up to 50- or 70-degrees maximum temperature. Using the IR cut film can solve the problem with blackening and increasing the display temperature too much.
With the newest addition to the displays like LCD and LED, we have some significant modifications to them. These displays are most often used in smartphones. A smartphone usually has a Touch screen interface and thus people are more into the display quality. Manufacturers are trying to provide customers with displays that could be better, brighter, and vivid. There are three most popular displays that we often see with most of the phones. These are IPS LCD, AMOLED and Super AMOLED which are the modification to the traditional LCD and LED.
The IPS LCD(In-Plane Switching Liquid Crystal Display) is a modified version of the old LCD and was developed to overcome the limitations of it. If you remember using a phone with a plain old LCD, we didn’t get much of a viewing angle. Colors used to fade away while looking at it from another direction and the image quality was blurry due to poor color reproduction.
When these crystals are subjected to an electric field by two sets of electrodes they tend to obtain a 90 degree twisted structure. The IPS works on the same strategy but the alignment of the electrodes is a little different. In the IPS display, they are located on the same plane. Electrodes in the IPS LCD generate an electric field that is parallel to the lower glass plate. It then uses a polarised light that passes through these liquid crystal molecules with additional horizontal and vertical filters on either side.
The AMOLED(Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode) has an active matrix of Organic LEDs. These consist of the electroluminescent layer which is made up of organic compounds. Whenever electricity is passed through the Thin Film Transistor (TFT) which houses the organic compound, it generates light. The transistor also acts as a series of switches that control the illumination by controlling the current flow.
The IPS needs a good backlight to produce a proper polarised light. Which in turn gives us a brighter white and good visibility in sunlight. It also gives good screen clarity too. The power consumption of the IPS LCD is almost 15% greater than the AMOLED.
On the other hand, the IPS LCD has great color reproduction. The whites are far better than that of the AMOLED, which look a little yellowish. It also adds natural color to the other segments. The electric field changes the nature of the liquid crystal’s behavior to produce good viewing angles. Thus most of the time photographers usually prefer to use an IPS LCD display in a camera.
The cost related to the development of the AMOLED is very high. The fabricating substances needed to build up the display are very costly. Another factor is the complexity to assemble them together makes it much more expensive than building an LCD. Thus we mostly see AMOLED displays in high-end devices like Samsung.
The IPS LCD also has a higher cost in development than that of the TFT LCD, but it is not as expensive as that of AMOLED. IPS LCDs are also used by some of the renowned phone manufacturers like Apple (in their earlier iPhone 8, 7, and so on), and HTC.
Since the AMOLED uses organic compounds for electroluminescent. Like all, these organic compounds tend to fade after a long-span use. The Red and Green pixel have a longer life span than that of the blue. These Red, Blue, Green are the base pixel that gives us the multi viewable color. Thus fading of one of the fundamentals pixels can lead to a significant color change. There is another term known as Burn-in, where the pixels permanently lose their ability to return to the relaxed state. Well, this phenomenon also happens in IPS LCD but it’s not permanent.
This works the same as the Super AMOLED, reducing the gap between the touch-sensitive screen and the physical display. This specific display is used by HTC in its flagship phones. The resulting combination has a similar effect to super AMOLED like increased visibility in sunlight and low power consumption. There are also Super LCD 2 and 3 which differ in terms of brightness. Super LCD 3 is much brighter than its predecessors.
People often confuse Gorilla glass with the categories of displays. You cannot differentiate Gorilla Glass and AMOLED or IPS LCD. The Gorilla glass is a chemically strengthened glass that is used over your display like AMOLED or IPS LCD to prevent them from scratches. The Gorilla Glass is developed by Corning and now in its sixth generation.

AMOLED and TFT are two types of display technology used in smartphones. AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode) displays are made up of tiny organic light-emitting diodes, while TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) displays use inorganic thin-film transistors.
AMOLEDs are made from organic materials that emit light when an electric current is passed through them, while TFTs use a matrix of tiny transistors to control the flow of electricity to the display.
Refresh Rate: Another key difference between AMOLED and TFT displays is the refresh rate. The refresh rate is how often the image on the screen is updated. AMOLED screens have a higher refresh rate than TFT screens, which means that they can display images more quickly and smoothly.
Response Time: The response time is how long it takes for the pixels to change from one colour to another. AMOLED screens have a shorter response time than TFT screens..
Colour Accuracy/Display Quality: AMOLED screens are more accurate when it comes to displaying colours. This is because each pixel on an AMOLED screen emits its own light, which means that the colours are more pure and true to life. TFT screens, on the other hand, use a backlight to illuminate the pixels, which can cause the colours to appear washed out or less vibrant.
Viewing Angle: The viewing angle is the angle at which you can see the screen. AMOLED screens have a wider viewing angle than TFT screens, which means that you can see the screen from more angles without the colours looking distorted.
Power Consumption: One of the main advantages of AMOLED displays is that they consume less power than TFT displays. This is because the pixels on an AMOLED screen only light up when they need to, while the pixels on a TFT screen are always illuminated by the backlight.
Production Cost: AMOLED screens are more expensive to produce than TFT screens. This is because the manufacturing process for AMOLED screens is more complex, and the materials used are more expensive.
Availability: TFT screens are more widely available than AMOLED screens and have been around for longer. They are typically used in a variety of devices, ranging from phones to TVs.
Usage: AMOLED screens are typically used in devices where power consumption is a concern, such as phones and wearable devices. TFT screens are more commonly used in devices where image quality is a higher priority, such as TVs and monitors.
AMOLED and TFT are two different types of display technology. AMOLED displays are typically brighter and more vibrant, but they are more expensive to produce. TFT displays are cheaper to produce, but they are not as bright or power efficient as AMOLED displays.
The display technology that is best for you will depend on your needs and preferences. If you need a screen that is bright and vibrant, then an AMOLED display is a good choice. If you need a screen that is cheaper to produce, then a TFT display is a good choice. However, if you’re worried about image retention, then TFT may be a better option.

Before we dive in, it"s helpful to understand the layout of a smartphone screen. The oversimplified version is that displays are composed of several layers of material, starting backing material and including a lighting element (like the backlight for LCD screens), which is then topped with a TFT (thin-film transistor) layer, which uses voltage-sipping transistors to keep the display"s pixels shining until you refresh or change the image.
There"s also the touch-sensitive panel; various films and filters that might reduce glare, for instance; and the cover glass, which is often bonded to the touch layer like Gorilla Glass. And there are also sensitive digitizer screens found on Samsung Note family..... ..... enough
The LCD screens are the most common technology used on mobile phones and they range from the budget smartphones like the HTC desire C to high-end tablets, like the Google Nexus 7. Two types of LCDs are primarily found in mobile phones: TFT and IPS technology.
TFT-LCD stands for thin-film transistor - liquid crystal display and use the thin-film transistor technology to improve image quality. They are often just referred to as LCD, since TFT-based LCD screens are the only type used in practice. Each pixel on a TFT-LCD has its own transistor on the glass itself, which offers more control over the images and colors that it renders.
While TFT-LCDs can deliver sharp images, they also tend to offer relatively poor viewing angles. TFT are found on more low-end smartphones or feature phones, and on basic cell phones.
IPS stands for in-plane switching. It involves arranging and switching the molecules of the liquid crystal (LC) layer between the glass substrates. This is done in a plane parallel to these glass plates. It features two transistors for each pixel, where TFT use just one. Requires a more powerful back-light (up to 15% comparing to TFT screens) but resolves the TFT"s weaknesses related to relatively high response time (lower is better), strong viewing angle dependence and low-quality color reproduction.
IPS are more expensive in production and typically are found on high-end mobile phones and portable devices. Apple"s iPhone, iPad, HTC One X and Nokia 920 are a good example of high quality IPS-LCDs screens.
The liquid crystals do no emit light themselves, so LCDs require a backlight. That means that LCD requires more power, and could potentially be more taxing on your phone’s battery.
The LCDs however produce some of the most realistic colors you can find on a screen, but might not offer as wide of a contrast ratio (darker darks and brighter brights) as AMOLED or OLED.
Due to this simple construction, AMOLED offers many advantages over LCD displays as it is thinner, brighter, more power efficient and provides wider viewing angles. They also provide much better contrast and response times.
Mostly those advantages are down to the fact that AMOLED technology doesn"t require a back-light. The black colour stays truly black without producing an energy (unlike on many LCDs where the black is rather grey and its being artificially made), which also leads to expanding battery life as long as the background of your phone is close to black.
However AMOLED screens have proved costly and difficult to produce in the same numbers as LCD, a fact that forced HTC company to replace AMOLED screen in their HTC Desire for Super-LCD halfway through its manufacturing life. A decision that led HTC to stick with LCD screens onward. Often those screens were also criticized to have lower visibility in the direct light than their LCDs counterparts and having over-saturated colours, until Samsung introduced the next generation of Super AMOLED technology, which solved the above issues.
LCD screens start with an always-on backlight; this technology requires light to create black, white, and colors. High-end LCDs produce the most accurate colors, though their manufacturers sometimes intentionally calibrate LCDs to produce weaker red, blue, and purple shades in order to reduce the device"s power consumption.
AMOLEDs also age more rapidly than LCD"s. Using an organic polymers, means that the red and blue colors deteriorate faster than green. Samsung used Super AMOLED plus screens in their Galaxy S II phones, but reverted back to Super AMOLED screens for the Galaxy S III citing screen life as the reason for the switch.
Both display technologies offer advantages and disadvantages. AMOLED screens have higher contrasts and deeper, true blacks, but LCD’s tend to offer more accurate colors. While AMOLED displays are brighter when viewed off-center, LCD panels can be viewed more easily under direct sunlight.
AMOLED displays tend to be more power efficient overall however, LCD panels are more power efficient when it comes to displaying web pages. AMOLED screens have better viewing angles, but LCD panels tend to be sharper on lower resolution panels thanks to the use of the RGB structure instead of PenTile/RGBG.
One of the problems with existing LCD displays used on smartphones is that they can’t keep up. While the internal hardware and operating system are fast enough to deliver a full 60 frames-per-second (FPS), the screens themselves lag behind, leading to pixelated video and ghost images appearing as your screen moves.
PureMotion HD+ uses an IPS type LCD display that is also given a higher voltage difference when changing states to produce a clean transition from frame to frame, even when operating at top speeds. This allows the display to deliver a steady 60FPS without any blurring. Nokia claims it lights up twice as fast on 920 than on any competing LCDs smartphones.
Ever take your phone outside and squint to read the screen? Phones with high reflectance can be a real setback, but some manufacturers are good at getting on top of it. ClearBlack is Nokia"s name for an anti-glare filters applied to the screen above the touch layer (but below the glass) on its high-end phones. It works on both AMOLED and LCD screens.
The color saturation is beyond the reach of any LCD out there, which make even the dullest image appear remarkably vibrant. Still, if you are not a fan of the oversaturated look of AMOLEDs, Samsung gives you the option to tune down the saturation to more natural levels and enjoy the best of both worlds. There"s a dedicated Adobe RGB setting that gets this done.
Triluminos is a technology that enables LCD TFT displays to show a wider range of colors, therefore the images are richer and more vivid. It’s all down to intelligent backlight technology, a Triluminos display reproduces more tones and textures than standard LED backlighting. Sony says that it boasts a color gamut that is 50 percent larger than that of a conventional LCD panel.
Conventional LCD displays use a white backlight that passes through red, blue, and green filters to form the color that the user perceives. The problem with this approach is that filters are not very selective – in other words, it’s hard to form very specific colors, and the end result might be a washed out colors (LCD needs very careful calibration to work perfectly). With Triluminos, the white backlight is replaced by a blue LED, which emits a blue light that causes a film of quantum dots to produce pure green and pure red. The different wavelength light is combined to form the color on the screen. This way the display can show more pure, unadulterated colors.
Sony has been using the X-Reality and X-Reality Pro image processors on its high-end TVs for a while now, though it’s not clear if X-Reality for mobile is the same thing.
According to Sony,Triluminos and X-Realityshould allow the Sony screens to compete with the Super AMOLED displays on Samsung flagships, which are recognized for their rich colors. But that’s the theory. In practice Xperia"s Z1 screen is a huge improvement in image quality since the Xperia Z and the images are truly coming to live (also the viewing angles has been greatly improved) but still cannot compete fully not only with super AMOLED screens, but also with the top IPS LCD panels.
Saying that this technology is superior to conventional LCD"s, and most likely will become dominant in the next couple of years. The very first example of implementing it into LCD IPS screen is a new Amazon Kindle Fire HDX 8.9, that surpasses every panel on the market related to intensity and accuracy of the colours produced. Here are some of the key findings from DisplayMate"s regarding Nexus 7 vs Fire HDX vs new iPad Mini display shootout
When Apple rolled out the iPhone 5, they announced that it had a full sRGB gamut, and would be a substantial improvement over the 4 and 4S displays. They also had done away with layers of technology below the screen to bring the display as close to the glass as possible, something they said would bring increased brightness and sharpness to the user"s eye. In practice however, compering the quality and brightness, Iphone 4S has still upper hand.
Retina Display - Apple"s proprietary name for its LCD screen, which serves up a 1,136x640 pixel resolution in mobile phones.1080p - The highest common high-definition screen resolution, measuring 1,920 pixels by 1,080 pixels. Also called "full HD."
720p -The lower high-definition designation, 1,280 by 720 pixels.Super LCD - Manufactured by Samsung, but used mostly by HTC, Super LCD is a display technology which removes the air gap between the outer glass and the display elements. This reduces the glare, and also consumes less power and has better outdoor visibility than regular LCD screens.
IPS - A type of LCD screen technology known for producing clearer image quality and wider viewing angles, among other traits. It"s used in many smartphones.

On some lower quality LCD screens, you can see bright spots in the middle or on the perimeters of screens. This is caused by uneven light distribution. The downside to using backlights, is that black is never true black, because no matter what, light has to be coming through, so it will never have as dark of a screen as an AMOLED screen. Its comparable to being able to slow a car down to 2 mph versus coming to a complete stop.

AMOLED Display and Gorilla Glass Has Been Popular Out of Marketing by the Companies. What Are AMOLED Display and Gorilla Glass of Smartphones? In very short – AMOLED Display is a display technology like OLED, TFT-LCD are display technologies. Basic is any type of LED display is one multi color RGB LED controlled by a programmable micro-controller, multiple RGB LED controlled via multiplexing. Up to RGB LED display is what we can do with Arduino to built DIY color display unit. After that, the individual units become too small SMD components. As they many a times AMOLED Display and Gorilla Glass co-exist in advertisements for the display units of modern Android smartphones, we thought to discuss them together in one article divided in two sub-headers.
Corning Inc is an 167 years old company who manufactures patented glass related things like yellow colored headlamp lenses of automobile. Today after 100 years, that yellow colored headlight seems ordinary. Corning is a glass expert company themselves with huge resources :
Gorilla Glass is a branded toughened or tempered glass. Tempered glass glasses upon fracture stress does not splinter into jagged shards plate glasses but cause the glass to crumble into small granular chunks. These glasses are most susceptible to breakage due if extra stress applied to the edge of the glass. But shattering can also occur in the event of a hard impact in the middle of the glass.
Gorilla Glass is simply a branded scratch resistant touchscreen glass. Corning is manufacturing similar tempered glass since 1960s, which are used for both industrial and commercial fields. In 2005, 2008 they introduced newer type of tempered glass. Gorilla Glass is an alkali-aluminosilicate thin glass designed to function as protective cover glass for smartphone display (in our current context). That Gorilla is made by a proprietary process named Corning’s fusion draw. Gorilla Glass does not interfere with Capacitive Touch Screen. Gorilla Glass has versions and Gorilla Glass 5 is towards latest version. Corning has full lists unless smartphone manufacturer not allowed to publish :
2.5D glass is kind of generic version of toughened glass for smartphones which can have edges like Gorilla Glass. There are 3D Curved Surface Tempered Glass for J7 Max with videos on YouTube. That will give you an idea of “curved edges”.
Samsung, LG are working on plastic screens which can be folded and are lighter than Corning’s products. Gorilla Glass is exactly like Corning’s yellow colored headlamp lenses of automobile. It is important now, sells well; may be outdated in future.

Anti-Glare coatings and glass etching processes use a material’s diffusive properties to disperse reflected light across the screen surface, making it appear fuzzy or blurred, eliminating any sharp reflections or hot spots. Learn more.
Backlight. The source of light for the LCD panel in a display, today a grid of light-emitting diodes, or LEDs. Edge-lit LEDs form a line around the rim of the screen with a diffusion panel to spread the light evenly. In a direct full LED array the LEDs are arranged behind the screen at equally spaced intervals. In a mini or micro LED backlight, a larger number of smaller LEDs (less than .2 mm) provide the illumination, improving contrast by showing little or no light behind black pixels. Learn more.
Bezel. The frame, or edge, around the LCD panel in a display. Zero bezel panels, with no frame around the front edges, are favored in monitor-based video walls because there is little or no gap between the displays forming an image. They are also preferred for many medical devices, as they offer fewer places for pathogens to collect.
Brightness. Typically measured in candelas per square meter (cd/m2) or nits. Displays in laptops and mobile devices usually produce between 200 and 500 nits, with many televisions higher and outdoor TVs often at 1,000 nits or higher.
Cover glassis a protective layer of glass installed over an LCD panel to protect it from damage and to hold display enhancements, such as a touch sensor, in place. The glass used may be plain or tempered soda lime glass or a chemically-hardened glass such as Gorilla Glass or Dragontrail Glass. Learn more.
Display Interfaces internally connect the liquid crystal display module which consists of a TFT Cell, Driver IC/Source PCB and a backlight unit. Common interfaces used today are Low Voltage Differential Signaling or LVDS, Embedded Display Port or eDP, Mobile Industry Processor Interface - Display Serial Interface (MIPI-DSI), RGB, V-by-One, I2C, Serial Peripheral Interface or SPI and MCU. Learn more.
EMI, or Electromagnetic Interference, is a disturbance generated by a nearby electromagnetic source that can affect the electrical circuits within an LCD display. RFI, or Radio Frequency Interference, is closely related. Either or both can be generated by electrical devices including motors, microwave ovens, transformers, CRT monitors, and power supplies, and wireless devices including phones and network transmitters.
Optical Bonding. The process of bonding a touch screen and/or cover glass to an LCD panel, while at the same time filling the gap between them with an optically transparent material that eliminates internal reflections, thus improving durability, brightness and contrast. OCR, or wet bonding, uses optically clear resin to fill in the gap between the elements, creating the strongest bond and the most readable image, because it does the best job of eliminating internal reflections. OCA, or dry bonding, uses optically clear adhesive to create good durability and readability. Air Gap is the least expensive and least effective, using double-sided tape to bond the elements.Learn more.
Pixel. The “picture element” or dot formed by a single liquid diode, or LCD. The overall image seen on an LCD display is formed by millions of pixels, blended together by the human eye into a single picture.
Polarizer. A layer of crystalline material placed between the backlight and the LCD element within a display to direct the alignment of the light waves passing through the LCDs.
In an LCD module, a rear polarizer, placed between the backlight and the LCD panel, forces all of the light passing through the LCD element to be aligned in one direction. Since the ambient light outside the panel will be aligned in different random directions, a front polarizer, placed on the outside of the panel, eliminates virtually all of the transmission of light into the panel. Thus the two polarizers work together to keep ambient light from washing out the image created by the display.
Refresh Rate.A measure of how often a display updates its picture each second. Most LCD displays refresh at 60 cycles per second, or 60 Hz, but some special purpose displays, notably those used for gaming, resulting in smoother on-screen motion.
TFT LCD.Thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display, the technology used in most displays today. There are three types commonly used. The oldest, twisted nematic (TN) displays offer extremely fast response times but originally had limited color reproduction and viewing angles. Over time, however, TN has been improved to display 8-bits per channel RGB (16.7 million colors) and relatively wide viewing angles. In-plane switching (IPS) offers deeper color depth and wider viewing but somewhat lower response times. Newer technologies, including VA (vertical alignment) panels offer various tradeoffs between color, response, viewing angles and cost.
Touch Interface.A technology to translate touches to the display to the computer or processor. Three are most commonly used: PCAP or Projected Capacitive Touch, which uses a conductive grid to recognizes changes in an electromagnetic field caused by the touch of a finger or stylus; Surface Capacitive Touch, which uses a glass overlay with a conductive layer to recognize the touch; Resistive Touch, in which the touch presses two electrically resistive layers together; and IR, which uses an array of invisible infrared LED light sources and detectors around the edges of the screen to recognize the touch of the finger or stylus. Learn more.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey