transparent character lcd module free sample

Previous examples connect the white LED backlight to power. The following example is specifically for those using an LCD with a RGB LED backlight. The only difference between the connection is the LED"s backlight on pins 15-18.

There are three types of transparent lcd modules, and lcd displays. On the other hand, the transparent lcd display is based on the type of display that would be suitable for many applications. Clearly transparent lcd display, on the other hand, can have only 12 pixels per second and is the suitable size for all displays.
One transparent lcd display is the most common type. Clear looking for cheap transparent lcdds in bulk, you can find from suppliers on Alibaba.com who offer a wide range of transparent lcdds for bulk suppliers.
transparent lcdds have high dynamic range, and has a low- consumptionaint rate as well as high-pernaming requirements. Among all lcdds, highly compatible lcdds have high dynamic capabilities, and quad-acid batteries. On top of that, it is highly resistant to pressure, even if it is unchected, and has a low- consumption.

We come across Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) displays everywhere around us. Computers, calculators, television sets, mobile phones, and digital watches use some kind of display to display the time.
An LCD screen is an electronic display module that uses liquid crystal to produce a visible image. The 16×2 LCD display is a very basic module commonly used in DIYs and circuits. The 16×2 translates a display of 16 characters per line in 2 such lines. In this LCD, each character is displayed in a 5×7 pixel matrix.
Contrast adjustment; the best way is to use a variable resistor such as a potentiometer. The output of the potentiometer is connected to this pin. Rotate the potentiometer knob forward and backward to adjust the LCD contrast.
A 16X2 LCD has two registers, namely, command and data. The register select is used to switch from one register to other. RS=0 for the command register, whereas RS=1 for the data register.
Command Register: The command register stores the command instructions given to the LCD. A command is an instruction given to an LCD to do a predefined task. Examples like:
Data Register: The data register stores the data to be displayed on the LCD. The data is the ASCII value of the character to be displayed on the LCD. When we send data to LCD, it goes to the data register and is processed there. When RS=1, the data register is selected.
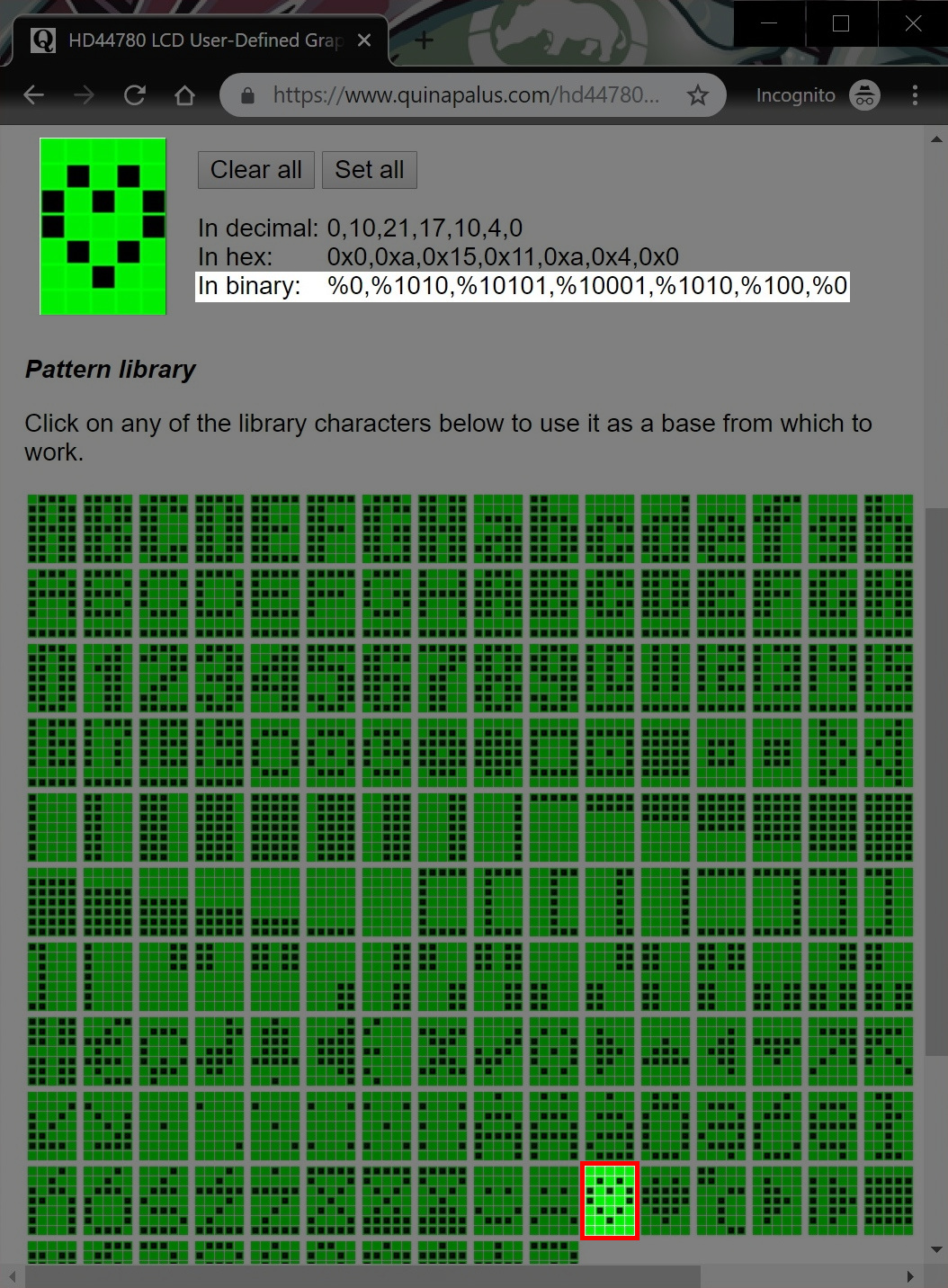
Generating custom characters on LCD is not very hard. It requires knowledge about the custom-generated random access memory (CG-RAM) of the LCD and the LCD chip controller. Most LCDs contain a Hitachi HD4478 controller.
CG-RAM is the main component in making custom characters. It stores the custom characters once declared in the code. CG-RAM size is 64 bytes providing the option of creating eight characters at a time. Each character is eight bytes in size.
CG-RAM address starts from 0x40 (Hexadecimal) or 64 in decimal. We can generate custom characters at these addresses. Once we generate our characters at these addresses, we can print them by just sending commands to the LCD. Character addresses and printing commands are below.
LCD modules are very important in many Arduino-based embedded system designs to improve the user interface of the system. Interfacing with Arduino gives the programmer more freedom to customize the code easily. Any cost-effective Arduino board, a 16X2 character LCD display, jumper wires, and a breadboard are sufficient enough to build the circuit. The interfacing of Arduino to LCD display is below.
The combination of an LCD and Arduino yields several projects, the most simple one being LCD to display the LED brightness. All we need for this circuit is an LCD, Arduino, breadboard, a resistor, potentiometer, LED, and some jumper cables. The circuit connections are below.

Customized lcd display used in all kinds of meters ,like: water meter ,energy meter ,temperature controllor , thermostat , medical deviece...what kind of customized lcd display you want to applicated ? Just send to me and we can customize for you .
Initializes the display for use with the standard C function printf(). This is not available in the Arduino environment. See the avr-libc manual for more information on how to use printf() with an AVR, and please note that using printf() will consume a significant amount of your Orangutan’s program and data memory. This function is intended to work with the LCD that came with your Orangutan; if you are using a different LCD, you can use lcd_init_printf_with_dimensions() to initialize printf() for the width and height of your LCD. This function only needs to be called once in your program, prior to any printf() calls.
Initializes the display for use with the standard C function printf() and lets you specify the width and height of your LCD using the lcd_width and lcd_height arguments. This is not available in the Arduino environment. See the avr-libc manual for more information on how to use printf() with an AVR, and please note that using printf() will consume a significant amount of your Orangutan’s program and data memory. If you are using the LCD that came with your Orangutan, you can use the argument-free lcd_init_printf(), which automatically initializes printf() for the width and height of your Orangutan’s (or 3pi’s) LCD. This version of the function is useful if you are using a different LCD or for some reason only want to use a portion of your LCD. This function only needs to be called oncce in your program, prior to any printf() calls.
Prints a zero-terminated string of ASCII characters to the display starting at the current cursor position. The string will not wrap or otherwise span lines.
Moves the cursor to the specified (x, y) location on the LCD. The top line is y = 0 and the leftmost character column is x = 0, so you can return to the upper-left home position by calling lcd.gotoXY(0, 0), and you can go to the start of the second LCD line by calling lcd.gotoXY(0, 1);
Moves the cursor left or right by distance spaces. This library defines literals LCD_LEFT and LCD_RIGHT for use as a direction argument to this method.
Shifts the display left or right by distance spaces, delaying for delay_time milliseconds between each shift. This library defines literals LCD_LEFT and LCD_RIGHT for use as a direction argument to this method. Execution does not return from this method until the shift is complete.
Loads a custom character drawing into the memory of the LCD. The parameter ‘number’ is a character value between 0 and 7, which represents the character that will be customized. That is, lcd.print((char)number) or print_character(number) will display this drawing in the future.
The pointer picture_ptr must be a pointer to an 8 byte array in program space containing the picture data. Bit 0 of byte 0 is the upper-right pixel of the 5×8 character, and bit 4 of byte 7 is the lower-left pixel. The example below demonstrates how to construct this kind of array.
In this Arduino tutorial we will learn how to connect and use an LCD (Liquid Crystal Display)with Arduino. LCD displays like these are very popular and broadly used in many electronics projects because they are great for displaying simple information, like sensors data, while being very affordable.
You can watch the following video or read the written tutorial below. It includes everything you need to know about using an LCD character display with Arduino, such as, LCD pinout, wiring diagram and several example codes.
An LCD character display is a unique type of display that can only output individual ASCII characters with fixed size. Using these individual characters then we can form a text.
If we take a closer look at the display we can notice that there are small rectangular areas composed of 5×8 pixels grid. Each pixel can light up individually, and so we can generate characters within each grid.
The number of the rectangular areas define the size of the LCD. The most popular LCD is the 16×2 LCD, which has two rows with 16 rectangular areas or characters. Of course, there are other sizes like 16×1, 16×4, 20×4 and so on, but they all work on the same principle. Also, these LCDs can have different background and text color.
Next, The RSpin or register select pin is used for selecting whether we will send commands or data to the LCD. For example if the RS pin is set on low state or zero volts, then we are sending commands to the LCD like: set the cursor to a specific location, clear the display, turn off the display and so on. And when RS pin is set on High state or 5 volts we are sending data or characters to the LCD.
Next comes the R/W pin which selects the mode whether we will read or write to the LCD. Here the write mode is obvious and it is used for writing or sending commands and data to the LCD. The read mode is used by the LCD itself when executing the program which we don’t have a need to discuss about it in this tutorial.
After all we don’t have to worry much about how the LCD works, as the Liquid Crystal Library takes care for almost everything. From the Arduino’s official website you can find and see the functions of the library which enable easy use of the LCD. We can use the Library in 4 or 8 bit mode. In this tutorial we will use it in 4 bit mode, or we will just use 4 of the 8 data pins.
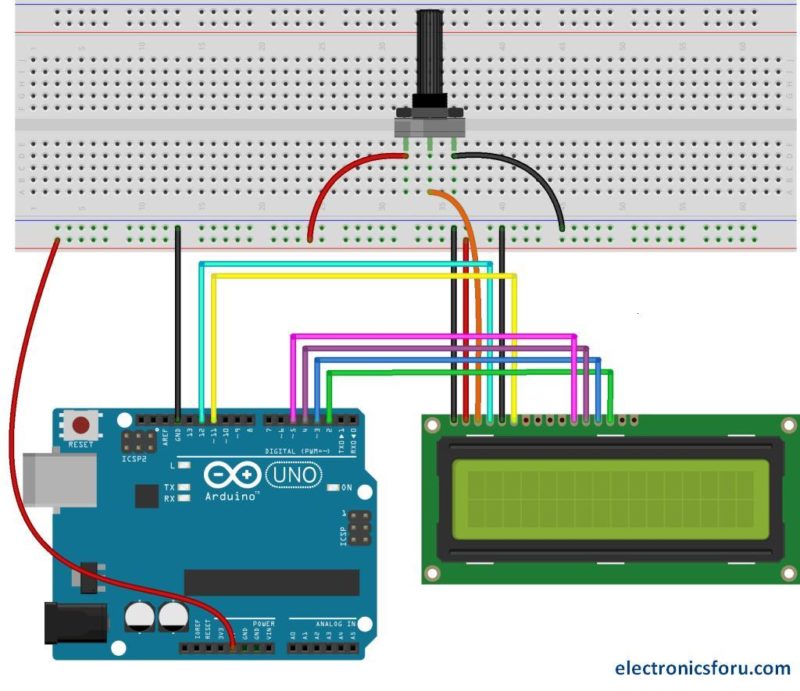
We will use just 6 digital input pins from the Arduino Board. The LCD’s registers from D4 to D7 will be connected to Arduino’s digital pins from 4 to 7. The Enable pin will be connected to pin number 2 and the RS pin will be connected to pin number 1. The R/W pin will be connected to Ground and theVo pin will be connected to the potentiometer middle pin.
We can adjust the contrast of the LCD by adjusting the voltage input at the Vo pin. We are using a potentiometer because in that way we can easily fine tune the contrast, by adjusting input voltage from 0 to 5V.
Yes, in case we don’t have a potentiometer, we can still adjust the LCD contrast by using a voltage divider made out of two resistors. Using the voltage divider we need to set the voltage value between 0 and 5V in order to get a good contrast on the display. I found that voltage of around 1V worked worked great for my LCD. I used 1K and 220 ohm resistor to get a good contrast.
There’s also another way of adjusting the LCD contrast, and that’s by supplying a PWM signal from the Arduino to the Vo pin of the LCD. We can connect the Vo pin to any Arduino PWM capable pin, and in the setup section, we can use the following line of code:
It will generate PWM signal at pin D11, with value of 100 out of 255, which translated into voltage from 0 to 5V, it will be around 2V input at the Vo LCD pin.
First thing we need to do is it insert the Liquid Crystal Library. We can do that like this: Sketch > Include Library > Liquid Crystal. Then we have to create an LC object. The parameters of this object should be the numbers of the Digital Input pins of the Arduino Board respectively to the LCD’s pins as follow: (RS, Enable, D4, D5, D6, D7). In the setup we have to initialize the interface to the LCD and specify the dimensions of the display using the begin()function.
The cursor() function is used for displaying underscore cursor and the noCursor() function for turning off. Using the clear() function we can clear the LCD screen.
In case we have a text with length greater than 16 characters, we can scroll the text using the scrollDisplayLeft() orscrollDisplayRight() function from the LiquidCrystal library.
The first parameter in this function is a number between 0 and 7, or we have to reserve one of the 8 supported custom characters. The second parameter is the name of the array of bytes.
So, we have covered pretty much everything we need to know about using an LCD with Arduino. These LCD Character displays are really handy for displaying information for many electronics project. In the examples above I used 16×2 LCD, but the same working principle applies for any other size of these character displays.
There is an LCD I2C master library included in the Arduino IDE. But there"s a slight problem with the code in it. All the examples in this library assumes the default address of the I2C as 0x27. So first we have to find out what the address of our I2C is. We can do this by using the I2C scanner code. Once we have the I2C address we can replace this value in the example code and start using it.

The mikroC PRO for PIC provides a library for communication with Lcds (with HD44780 compliant controllers) through the 4-bit interface. An example of Lcd connections is given on the schematic at the bottom of this page.





 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey