jdi lcd panel factory

Japan Display Inc.(株式会社ジャパンディスプレイ, Kabushiki-gaisha Japan Disupurei), commonly called by its abbreviated name, JDI, is the Japanese display technology joint venture formed by the merger of the small and medium-sized liquid crystal display businesses of Sony, Toshiba, and Hitachi.
On August 31, 2011, Sony, Toshiba, and Hitachi agreed to a merger of their respective small-to-medium-sized LCD businesses, supported by an investment of two hundred billion yen from INCJ. Soon after, INCJ and Panasonic also began talks on the acquisition of one of Panasonic"s factories.
JDI had accumulated consecutive losses since its IPO, a restructuring plan was announced in 2017, including closing down a production line in Japan and layoffs of approximately a third of its workforce.
A newly-created entity INCJ, Ltd. had become the largest shareholder of JDI with 25,29 % of total shares since September 21, 2018 as a result of a corporate split of the old INCJ.
On June 12, 2019, JDI disclosed that major changes are to be implemented due to sluggish sales in the Mobile Business Division. It announced one plant would be closed and another has suspended operation. A major reduction of the workforce was also planned.Apple, boosting the stock price of JDI by 32 percent at the time.
Due to the financial trouble caused by its late decision to manufacture OLED displays and the loan from Apple, the company"s OLED affiliate, JOLED, has not yet been able to compete with other manufacturers, whilst more than half of JDI"s revenue still came from the shrinking IPS LCD panel sales to Apple.
In February 2020, Ichigo Asset management, a multinational private investment fund, gained control of JDI in exchange for US$715 million of investment. In turn, the memorandum signed with Suwa a year before was terminated.
In April 2020, in accordance with the talks held in December, JDI began to sell LCD production equipment valued at US$200 million to Apple, with plans to sell the real estate of the Hakusan plant to Sharp. This will allow JDI to focus on its remaining product demand and factories. The sales have been completed by October.
In July 2020, the CEO of JDI revealed the company"s plan to start mass production of OLED display panels for smartphones "as early as 2022" with a novel manufacturing technology, adding that it would require new funding.
JDI has produced active-matrix displays driven by TFTs based on a In-Plane-Switching technology developed by Hitachi also has been used. The company has developed an improvement for darker black pixels (true-black appearance), called "IPS-NEO", which reduces the light shining through from the backlighting.
Its "Pixel Eyes" technology incorporates the touch function into the LCD panel itself; combined with the company"s transparent display technology, a transparent fingerprint reader that could be featured in smartphones was announced in 2018.
For reflective LCDs without backlighting, JDI has developed an addressing technique using a thin-film memory device SRAM in addition to the conventional TFT for each pixel, so that a still image can be stored consuming a low amount of energy.

TOKYO -- Japan Display will sell its China-based subsidiary Suzhou JDI Electronics to a local buyer, the money-losing Japanese panel maker said Friday, as it continues to shed assets in a sweeping overhaul.
Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing Co. will buy all of Suzhou JDI Electronics for 20.5 billion yen ($140 million) in a transaction to be completed between January and March 2023.

Japan Display Inc. is a Japanese company that manufactures and supplies LCD panels for smartphones, tablets, automotive applications and laptops. The company was founded in 2010 and is headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. As of March 2016, the company had a market capitalization of US$2.4 billion.
Japan Display Inc."s products are used in a variety of electronic devices including smartphones, tablets, automotive applications and laptops. The company"s panels are used by major electronics manufacturers such as Apple Inc., Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., LG Electronics Inc., HTC Corporation and Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Japan Display Inc. (JDI) is a leading display panel manufacturer based in Tokyo, Japan. The company was formed in 2011 as a joint venture between Sony, Hitachi and Toshiba. JDI supplies LCD panels to some of the world’s largest electronics manufacturers, including Apple, LG and Samsung.
JDI’s cutting-edge technology has made it one of the leaders in the global display market. The company’s products are used in a wide range of devices, from smartphones and tablets to TVs and laptops. JDI has a strong R&D team that is constantly developing new display technologies. The company is publicly listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange and had a revenue of US$5.6 billion in 2018.
Japan Display Inc. is a leading display panel manufacturer that designs, develops, and manufactures cutting-edge display panels and systems for smartphones, tablets, notebooks, automotive applications, digital cameras, camcorders and digital signage. The company has over 8,000 employees and operates 13 factories in 9 countries around the world.
Japan Display Inc. offers a wide range of products and services that are designed to meet the needs of its customers. The company’s product portfolio includes: LCD panels, OLED panels, touch panels, flexible displays and integrated modules. Japan Display Inc. also provides a variety of value-added services such as: design support, engineering support, production support and after-sales service. The company’s products are used in a variety of market segments including consumer electronics, automotive, industrial and medical. Japan Display Inc.
Japan Display Inc. (JDI) is a leading display manufacturer that designs, develops, and manufactures LCDs for smartphones, tablets, automotive applications, and other consumer electronics. The company went public in 2010 and is listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange. JDI reported a net loss of ¥23.4 billion ($205 million) in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016, compared to a net profit of ¥10.3 billion in the previous fiscal year. This was primarily due to lower sales of LCD panels for smartphones and increased competition from Chinese manufacturers.
Looking at Japan Display"s financial performance over the past few years, it"s clear that the company has been struggling to maintain profitability. In the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016, JDI reported a net loss of ¥23.4 billion ($205 million), compared to a net profit of ¥10.
One of the biggest challenges that Japan Display Inc. (JDI) is facing is the competition from South Korean and Chinese display manufacturers. JDI has been losing market share to these companies in recent years, and it is becoming increasingly difficult for JDI to compete on price. Additionally, JDI is also facing challenges from new technologies such as OLED and quantum dot displays. While JDI has developed its own OLED technology, it has yet to commercialize it on a large scale. And while quantum dot displays are not yet widely used in smartphones, they are expected to gain popularity in the coming years.
Another challenge for JDI is its reliance on Apple Inc. for a significant portion of its revenue. In 2017, Apple accounted for approximately 60% of JDI’s revenue.

Japan Display (JDI) will sell a Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) factory and the land it sits on to Sharp for US$390 million, the company announced on Friday.
The company also said it will sell the equipment at the Hakusan LCD plant to an “overseas customer” for US$285 million, JDI said. The customer in question is likely Apple.
Sharp, which is owned by Foxconn, is reportedly buying the factory from Apple’s request. Sharp supplies sensors, camera modules and LCD panels to Cupertino.
The company will produce LCD panels for Apple at Hakusan, while burrowing the equipment for the iPhone maker. It will also reportedly install new equipment and develop next-generation display panels there.
Sharp has been producing LCD panels for Cupertino at its Kameyama factory previously but this will be shifted for those used in automobiles and medical devices.
Meanwhile, JDI was initially planning to wrap up the sales of Hakusan plant in March but this was delayed due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The plant has been operating since late 2016 and can produce 7 million small- to mid-sized LCD panels per month.
Production output dropped beginning in July of last year, however, as Apple shifted the panels on its iPhones from LCD to organic light emitting diode (OLED).

Japan Display Inc. (JDI) is a leading global manufacturer of small- and medium-sized display panels. It develops, designs and manufactures displays that provide high resolution, low power consumption and an ultra-thin structure. The company‘s major customers include leading consumer electronics manufacturers and other well-known global companies. In Europe the focus is set on the automotive industry. JDI was formed through the consolidation of the display panel businesses of Sony, Hitachi and Toshiba and commenced operations on April 1, 2012.

Japan Display Inc. (JDI) decided at its Board of Directors meeting to approve the signing of a term sheet between Wise Cap Limited Company, a wholly owned subsidiary of Wistron Corporation, an EMS to whom JDI outsources module manufacturing, JDI Taiwan, Inc. (JDIT), a wholly owned subsidiary of JDI, and Kaohsiung Opto-Electronics Inc. (KOE), a wholly owned subsidiary of JDIT.
The term sheet specifies that JDIT, Wise Cap, and KOE will hold discussions to finalize the sale of all KOE shares to Wise Cap. Wise Cap, JDIT, and KOE all signed the term sheet. The sale price is JPY 8 billion ($72.3 million).
JDI is working to strengthen its competitiveness and drive growth by optimizing its asset profile, increasing its cost-competitiveness, and diversifying its supply chain. As part of these strategic initiatives, JDI has decided to sell the shares of KOE, which designs and manufactures LCD modules for JDI, to Wistron Group.
Wistron Group has been a significant and trusted partner of JDI to whom JDI outsources smartphone display module manufacturing for many years. By joining Wistron Group, KOE is expected to benefit from the scale and resources of Wistron Group, an EMS with advanced technological capabilities and strong purchasing power, thereby improving JDI’s cost-competitiveness.
JDI has agreed with Wistron Corporation to enter into a new EMS contract with KOE at the time of the share sale and continue outsourcing the manufacturing of display modules for automotive and industrial devices to KOE in order to strengthen the competitiveness of JDI’s core automotive and industrial businesses.
By shedding assets and converting fixed costs to variable costs, JDI believes that the share sale will increase JDI’s operating flexibility, ability to respond quickly to changes in market environment, core earnings power, and capital efficiency. Furthermore, JDI will use this share sale as an opportunity to further strengthen its ties with Wistron Group.

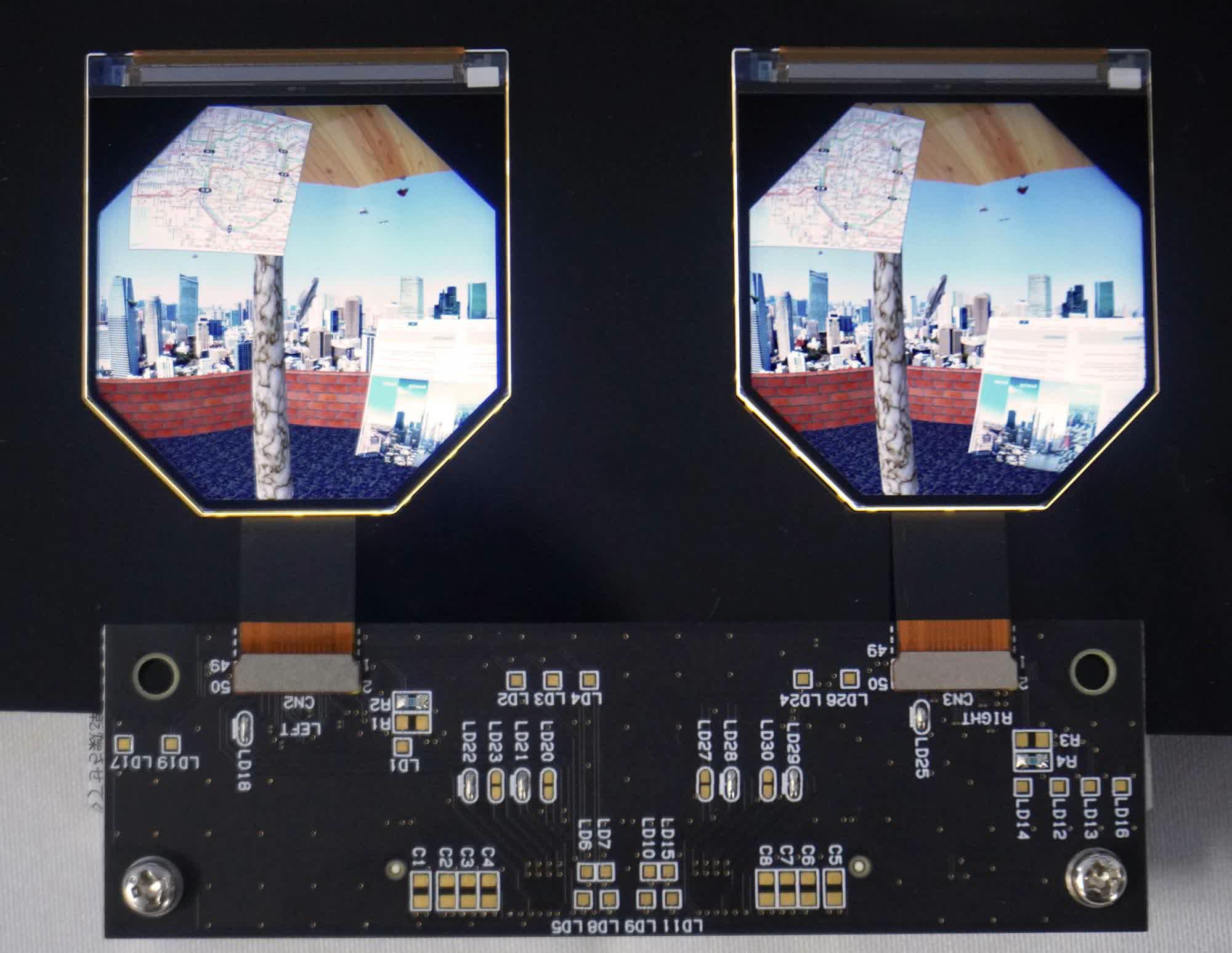
The Tokyo-based LCD specialist expects its favored display technology to become the standard for VR because it can achieve higher resolution than OLED while keeping costs reasonable. That advantage is imperceptible in mobile devices but becomes critical in the more demanding VR scenario.
Many of the first wave of headsets released five years ago used OLED screens -- or organic light-emitting diodes, the same as used across most flagship phones today -- for their responsiveness to fast-moving action, a common feature of gaming experiences. But major players such as HTC Corp. and Facebook have moved to LCDs for their latest products, betting on the more economical standard to improve the user experience and immersion. Industry researchers at Omdia saw LCD adoption rise in 2020 and forecast the technology will dominate the category over the next five years.
“It’s hard to find a VR headset maker who doesn’t have a relationship with us," JDI’s VR chief Takeshi Harayama said in an interview. At the company’s last earnings call in May, Chief Executive Officer Scott Callon said he expects revenue from gaming-oriented VR headsets to pick up from the second half of next fiscal year.
One important holdout remains: Sony Group Corp. plans to use Samsung Display Co. OLED panels in its next-generation PlayStation VR goggles, according to people with knowledge of the matter. The Japanese console giant sold more than 5 million units of the original PS VR, launched in 2016, and is aiming to release the successor in the holiday period next year, the people said, asking not to be named discussing internal plans.
To grab a bigger share of the market, JDI is working to convince VR companies it can solve two of their biggest hurdles: display quality and cost. Because VR goggles place the screen so much closer to the human eye, they require higher resolution and clarity than mobile screens, achieved by packing pixels closer together. JDI is capable of producing displays with 1,200 pixels per inch, more than double the typical density of top-tier phone panels, according to its chief VR headset engineer, Yoshihiro Watanabe.
The threshold for a high-quality VR experience is to have a display with at least 1,000 pixels per inch, Watanabe said, adding that JDI is one of the few display makers -- if not the only -- that can mass-produce such panels at a reasonable production yield.
JDI was created in 2012 by the combination of the display-making units of Sony, Hitachi Ltd. and Toshiba Corp., with much of its revenue since then coming from mobile handsets, especially iPhones. More than half of its total sales used to come from the Apple business, but the iPhone maker’s adoption of OLED technology left the company reeling.
Unable to develop its own OLED panels to a competitive level with leader Samsung Display, JDI has seen its revenue from phones drop from 838 billion yen ($7.7 billion) in the year ended March 2016 to an expected 81 billion yen this fiscal year. The firm sold the factory it had used mainly to produce panels for Apple to Sharp Corp. last year.
Major smartphone makers universally adopted OLED for their premium models in part because of the broader set of design options it offered. Flexible OLED panels could be curved, as with the banana-like LG G Flex, rolled or folded, as with the Samsung Galaxy Fold and Huawei Mate X.
“When it comes to VR, the quality of picture the panel produces will be the most important because the headset doesn’t really need other features such as flexibility and energy efficiency," said Omdia research manager Hiroshi Hayase.
It’s difficult to say that LCD is in all cases superior to OLED for VR, Hayase said, because OLED offers better contrast in addition to faster response times. The key for JDI will be to establish a solid footing in the industry by addressing customer needs that other suppliers would turn down owing to the small market size, he added. JDI has experience of doing that from its business supplying display panels for digital cameras.
While JDI doesn’t disclose particular customers, the company expects revenue from non-mobile businesses, which includes VR headsets, to grow 25% to 70 billion yen in the current fiscal year.
“I wouldn’t say the market will be rosy in two to three years, but the growth rate is good enough for us to call it a big business for us," JDI’s Watanabe said. “Other makers may try to come in when the market is finally big enough, but by that time we expect to have built strong ties with customers and accumulated the technological know-how to hold our position."

In May, the media reported that Samsung to sell L7-2 and L8-2-1 two LCD panel factory part of the equipment; June, the media reported that Panasonic decided to withdraw from the LCD panel business in 2021, its Himeji 8.5 generation plant production equipment will be auctioned for bidding.
For example, huaxing photoelectric investment of 35 billion yuan in guangzhou 8.6 generation line T9 project just completed “bidding “. This will be the world’s one-time planning of the largest single production capacity of one of the 8.6 generation LCD panel project. — In fact, the domestic mainstream large-size display panel manufacturers, BOE, Huaxing photoelectric and Huike are expanding “LCD” production capacity.
In accordance with the original industry chain planning, 2020 South Korea LG and Samsung have been prepared to completely withdraw and shut down all LCD panel manufacturing projects.
Even so, in 2021, with the launch of vaccination, the new crown epidemic into the “post-era”. Display panel demand growth tends to stagnate, the high price trend is eager to usher in a turnaround at the end of the year. LG and Samsung choose to finally implement the “LCD panel shutdown” decision, not surprisingly.
And Japan’s LCD panel industry chain has been in the “lowest level of operation N years”. Sharp sold out to Taiwan-invested enterprises, specializing in small and medium-sized LCD panels JDI has said to enter the OLED field, Panasonic can hold on to the possibility of “from the industry chain cluster perspective has been zero. Japanese display industry in the LCD panel continues to do subtraction, which is the expected thing.
In the last 5 years, China’s Taiwan region also did not “new planning” brand new large LCD panel project – Taiwan enterprises Honghai commitment to invest in the United States LCD panel project also “repeatedly shrink “, whether there will be the following and not fixed; Taiwan’s regional enterprises capacity changes are the most important in 2016 to put into operation an 8.6 generation line, and cooperation with Japan Sharp in Guangzhou construction of 10.5 generation line.
Therefore, it can be said that the global LCD panel new investment is almost all concentrated in China’s mainland region. Especially in 2021 is the trend of “others retreat, we advance” the reverse movement. What is the secret behind this? The answer is actually very obvious.
For example, huaxing photoelectric guangzhou T9 project is 8.6 generation line panel;is on the amount of juice Changsha project is also 8.6 generation line – before huike Chongqing and Chuzhou project, is also 8.6 generation line, as the world’s last rise of large-size LCD panel enterprises, huike to create the world’s largest 8.6 generation line cluster capacity; at the same time 2021 BOE and Huaxing photoelectric is also vigorously expanding 10.5 / 11 generation line capacity.
The shutdown is 8.5 generation and the following generation panel line, the expansion is 10.5 / 11 generation and 8.6 generation panel line – of which, 10.5 / 11 generation line is more in line with the color TV, commercial display and other needs of the development trend of large size, which does not need to be said: 10.5 / 11 generation line, is still the industry shortage of capacity. 8.6 Generation line, although with 8.5 generation line most of the product capacity overlap is high, in 50 and 58 inches, it can cut 8 and 6 blocks; compared with 8.5 generation line 48 inches and 55 inches of 8 and 6 blocks, basically “cost unchanged”, the market competitiveness is enhanced. With an 8.6 generation line pressure 8.5 generation line head, these Taiwan panel companies invented the method, by mainland enterprises to play fire!
In fact, from IT panels to TV panels, 8.6 generation lines can be similar cost, in the cut display area pressure 8.5 generation line head. This pattern, if the “industry into a relative surplus cycle”, the competitiveness of the 8.5 generation line is obviously a little worse.
2020-2021 LCD panel out of the “most fierce ever strong cycle”, thereafter will certainly be in the “consumer overdraft” effect under the “production line efficiency” battle. At this time, the mainland enterprises by virtue of the total scale advantage, industry chain supporting advantages, and generation line leading advantage, competitiveness will be more prominent. In this context, Korean and Japanese enterprises take advantage of the second-hand equipment prices are okay, selling the corresponding equipment, is the best choice.
According to media reports, the Samsung panel line trend is a strategic decision. Samsung Electronics Vice President Lee Jae-yong personally involved in the decision to withdraw the LCD project. Lee also personally announced a plan to invest 13 trillion won in next-generation display technology development by 2025. Among them, the QD-OLED screen is an important direction.
Aiming at the next generation, a new round of competition for display panels has already begun. For example, BOE Chongqing 6 generation OLED line is moving in equipment; Huaxing photoelectric in Guangzhou planning a T8 printed OLED 8.5 generation line project; Huike is also preparing to validate OLED technology on the Changsha project. …… South Korea LG is currently upgrading Guangzhou 8.5 generation OLED production capacity, and accelerate the construction of South Korea 10.5 generation OLED project. It is reported that Samsung sold LCD panel project, the vacated plant, and equipment which will also be imported to the 6 generation OLED and future high generation QD-OLED production capacity.
A certain perspective, Japanese companies out of the LCD panel camp, is indeed a “retreat”; and Korean companies are making space for OLED LCD – is to “change the road to overtake the car “, its planning is to rival “new technology downgrade strike”.
This background, the domestic LCD industry, still expanding the LCD production capacity is “worth” and “wise” becomes a problem: in fact, OLED or MICRO-LED, QLED and so on, are facing two problems.
First, with the LCD shared glass substrate TFT capacity, that is, the LCD panel line more than half of the investment in the future display panel is universal.
There are color TV and commercial display products, the development of large size “demand fierce”. The latter needs “in line with the trend of large size” of new production capacity construction. Almost all of the domestic 5 years of LCD panel new line construction, and the current capacity enhancement project, are around this trend. Is also precisely the domestic mainland enterprises to take the lead in this step, to establish the “competitive advantage” of the LCD panel manufacturing industry in Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan, and other regions.
The immediate, short, and medium-term demand for large-size LCD is still growing rapidly, which is not contradictory to the long-term view that must be the world of next-generation technology.
The sooner the next-generation technology can not achieve the standardization of technical routes, the longer the life of the LCD large size market.” That is, the risk of the domestic LCD panel industry does not lie in the “next generation” itself, but in the next generation of technology process route selection and “capacity expansion direction of the switch” timing issues.
At present, the domestic display panel two leaders, BOE and Huaxing photoelectric have built a vapor deposition technology process of the 6th generation OLED line and carried out vapor deposition and printing process of large-size OLED technology verification experiments. Domestic display industry in the next generation of technology investment is not significantly behind – due to the domestic panel sector in the large size of the LCD lead, the actual result, the domestic display panel companies to actively introduce large-size OLED urgency is not strong, this aspect of the domestic enterprises can go more relaxed some.
In addition, in the direction of small and medium-sized OLED, flexible OLED, and silicon-based OLED three characteristic differentiation, the domestic display panel industry investment, in global China, Japan, Taiwan, and South Korea in the four camps, basically, maintain the lead.
Therefore, in the display panel industry chain and the future-oriented supply battle, the domestic display industry has advantages and disadvantages, the overall advantage is greater than the disadvantages, the recent advantages are particularly obvious. Korean and Japanese companies selling LCD panel equipment, which does not constitute a reason to deny the legitimacy of investment in the domestic LCD industry chain. However, the domestic LCD industry should also pay great attention to new technologies, next-generation display direction and the degree of development, and timely “to the new track”.
In both LCD and OLED displays, producing these cells – which are highly complex – is by far the most difficult element of the production process. Indeed, the complexity of these cells, combined with the levels of investment needed to achieve expertise in their production, explains why there are less than 30 companies in the whole world that can produce them. China, for instance, has invested more than 300 billion yuan (approximately $45 billion USD) in just one of these companies – BOE – over the past 14 years.
Panox Display has been involved in the display industry for many years and has built strong and long-term partner relationships with many of the biggest OLED and LCD panel manufacturers. As a result, we are able to offer our clients guaranteed access to display products from the biggest manufacturers.
LG Display was, until 2021, the No. 1 display panel manufacturer in the world. Owned by LG Group and headquartered in Seoul, South Korea, it has R&D, production, and trade institutions in China, Japan, South Korea, the United States, and Europe.
Founded in 2001, AUO – or AU Optronics – is the world’s leading TFT-LCD panel manufacturer (with a 16% market share) that designs, develops, and manufactures the world’s top three liquid crystal displays. With panels ranging from as small as 1.5 inches to 46 inches, it boasts one of the world"s few large-, medium -and small-sized product lines.
AUO offers advanced display integration solutions with innovative technologies, including 4K2K ultra-high resolution, 3D, ultra-thin, narrow bezel, transparent display, LTPS, OLED, and touch solutions. AOU has the most complete generation production line, ranging from 3.5G to 8.5G, offering panel products for a variety of LCD applications in a range of sizes, from as small as 1.2 inches to 71 inches.
Now Sharp is still top 10 TV brands all over the world. Just like BOE, Sharp produce LCDs in all kinds of size. Including small LCD (3.5 inch~9.1 inch), medium LCD (10.1 ~27 inch), large LCD (31.5~110 inch). Sharp LCD has been used on Iphone series for a long time.
Beside those current LCDs, the industrial LCD of Sharp is also excellent and widely used in public facilities, factories, and vehicles. The Sharp industrial LCD, just means solid, high brightness, super long working time, highest stability.
Since its establishment, Truly Semiconductors has focused on researching, developing, and manufacturing liquid crystal flat panel displays. Now, after twenty years of development, it is the biggest small- and medium-sized flat panel display manufacturer in China.
Truly’s factory in Shanwei City is enormous, covering an area of 1 million square meters, with a net housing area of more than 100,000 square meters. It includes five LCD production lines, one OLED production line, three touch screen production lines, and several COG, LCM, MDS, CCM, TAB, and SMT production lines.
Its world-class production lines produce LCD displays, liquid crystal display modules (LCMs), OLED displays, resistive and capacitive touch screens (touch panels), micro camera modules (CCMs), and GPS receiving modules, with such products widely used in the smartphone, automobile, and medical industries. The LCD products it offers include TFT, TN, Color TN with Black Mark (TN type LCD display for onboard machines), STN, FSTN, 65K color, and 262K color or above CSTN, COG, COF, and TAB modules.
In its early days, Innolux attached great importance to researching and developing new products. Mobile phones, portable and mounted DVD players, digital cameras, games consoles, PDA LCDs, and other star products were put into mass production and quickly captured the market, winning the company considerable market share.
Looking forward to the future, the group of photoelectric will continue to deep LCD display field, is committed to the development of plane display core technology, make good use of global operations mechanism and depth of division of labor, promise customers high-quality products and services, become the world"s top display system suppliers, in 2006 in the global mobile phone color display market leader, become "Foxconn technology" future sustained rapid growth of the engine.
Founded in June 1998, Hannstar specializes in producing thin-film transistor liquid crystal display panels, mainly for use in monitors, notebook displays and televisions. It was the first company in Taiwan to adopt the world’s top ultra-wide perspective technology (AS-IPS).
The company has three LCD factories and one LCM factory. It has acquired state-of-the-art TFT-LCD manufacturing technology, which enables it to achieve the highest efficiency in the mass production of thin-film transistor liquid crystal display production technology. Its customers include many of the biggest and most well-known electronics companies and computer manufacturers in Taiwan and overseas.
TCL CSOT – short for TCL China Star Optoelectronics Technology (TCL CSOT) – was founded in 2009 and is an innovative technology enterprise that focuses on the production of semiconductor displays. As one of the global leaders in semiconductor display market, it has bases in Shenzhen, Wuhan, Huizhou, Suzhou, Guangzhou, and India, with nine panel production lines and five large modules bases.
TCL CSOT actively produces Mini LED, Micro LED, flexible OLED, printing OLED, and other new display technologies. Its product range is vast – including large, medium, and small panels and touch modules, electronic whiteboards, splicing walls, automotive displays, gaming monitors, and other high-end display application fields – which has enabled it to become a leading player in the global panel industry.
In the first quarter of 2022, TCL CSOT’s TV panels ranked second in the market, 55 inches, 65 " and 75 inches second, 8K, 120Hz first, the first, interactive whiteboard and digital sign plate; LTPS flat panel, the second, LTPS and flexible OLED fourth.
EDO (also known as EverDisplay Optonics) was founded in October 2012 and focuses on the production of small- and medium-sized high-resolution AMOLED semiconductor display panels.
Tianma Microelectronics was founded in 1983 and listed on the Shenzhen Stock Exchange in 1995. It is a high-tech enterprise specializing in the production of liquid crystal displays (LCD) and liquid crystal display modules (LCM).
After more than 30 years of development, it has grown into a large publicly listed company integrating LCD research and development, design, production, sales, and servicing. Over the years, it has expanded by investing in the construction of STN-LCD, CSTN-LCD, TFT-LCD and CF production lines and module factories across China (with locations in Shenzhen, Shanghai, Chengdu, Wuhan and Xiamen), as well R&D centers and offices in Europe, Japan, South Korea and the United States.
JDI (Japan Display Inc.) was established on November 15, 2011, as a joint venture between the Industrial Innovation Corporation, Sony, Hitachi, and Toshiba. It is dedicated to the production and development of small-sized displays. It mainly produces small- and medium-sized LCD display panels for use in the automotive, medical, and industrial fields, as well as personal devices including smartphones, tablets, and wearables.
Although Sony’s TVs use display panels from TCL CSOT (VA panel), Samsung. Sony still produces the world’s best micro-OLED display panels. Sony has many micro OLED model such as 0.23 inch, 0.39 inch, 0.5 inch, 0.64 inch, 0.68 inch, 0.71 inch. Panox Display used to test and sell many of them, compare to other micro OLED manufacuturers, Sony`s micro OLEDs are with the best image quality and highest brightness (3000 nits max).

In China. The biggest LCD panel manufacturer in the world now. BOE has G4 (Chengdu), G5 (Beijing), G5.5 (Ordos), G6 (Hefei, Chengdu, Mianyang, Dalian), G8 (Beijing, Hefei, Chongqing), Fuqing, Dalian, Chongqing) and 10.5 (Hefei) production lines.
In Taiwan. One of the daughter company of Foxconn/Hon Hai. In 2010, it bought the then famous LCD manufacturer, ChiMei, then changed its name to Innolux. It has G7.5 production lines.
In Korea and China. It is used to be the 2nd biggest TFT LCD manufacturers. LG also planned to stop the production but delayed the plan after the price increased. LG has G7.5 and G8.5 (Guangzhou) production lines.
In Korea. It used to be the biggest TFT LCD manufacturers before it was dethroned by BOE in 2019. Because of tough competition, Samsung planned to stop the production in 2021 but delayed because the price increase during the pandemic. Samsung has G7 and G8.5 production lines.
In Japan and China. The pioneer and queen of LCD industry. Because of high cost and tough competitor, Sharp was acquired by Foxconn/Hon Hai in 2016. Sharp has G8, G8.5(Suzhou), G10, G10.5 (Guangzhou) production lines.

JDI will exhibit the new 20.8-Inch Rælclear at CES 2023 in Las Vegas from January 5th to the 8th, 2023. Visitors will be able to envision a new future of design combining artificial intelligence and the technology of Rælclear.
Japan Display Inc. (JDI) has developed the world’s first flexible tactile sensor that enables high-precision measurement over a wide area using a matrix of LTPS TFTs (lowtemperature polysilicon thin-film transistors).
Highly accurate tactile measurement is required for the development of a number of new technologies and products, as well as for advanced sports and medical research. JDI’s flexible tactile sensor is suitable for a wide range of applications, such as measuring the grip strength of a robot grasping an object or the pressure distribution on the sole...
In response to strong customer demand, Japan Display Inc. (JDI) has further developed its breakthrough transparent Rælclear display technology and expects to begin mass production of a new 20.8-inch Rælclear display with 2X brightness in the fall of 2023.
Samsung Display has sold its LCD factory in China to Chinese display maker CSOT, a company under TCL group, to further cut down its LCD capacity, which goes in line with Samsung’s plan to quit LCD business. By ending its LCD panel production, Samsung aims to expand its development in QD displays and OLED displays. The Korean giant has also reportedly t...
Japan Display (JDI) is going to sell its LCD plant in Hakusan, Japan, to Sharp and Apple, so that the Japanese display maker can pay off its debt to Apple. The total transfer price is estimated to be JPY 71 billion (US$ 672 million).
The plant will be transferred to Sharp, who is also a display supplier of Apple, by the end of September. With the transaction, Sharp will take over most of the debt of JDI which JDI borrowed from Apple when building the plant. The plant was originally built for supplying LCD panels for iPhone. But S...
Sharp, one of the panel providers of Apple, is reportedly developing small size Micro LED displays and will mass produce the products by 2023 for eye-wear smart devices, reported Nikkan Kogyo Shimbun.
According to the report, Sharp Fukuyama Semiconductor, a subsidiary of Sharp, has developed Micro LED prototypes including a 0.38-inch full color panel featuring 1053 PPI and a 0.13-inch blue display with 3000 PPI. The company deploys its proprietary color conversion technology to achieve full color display and aims to mass produce the products in 2023 to 2024 for A...
The investigation showed that JDI recorded fictitious inventory of JPY 10 billion (US$92.86 million) in total since the fourth quarter of fiscal 2013. The investigation also...
Japan Display (JDI) announced the development of a Micro LED display. The prototype Micro LED display will be presented at “FINTECH JAPAN 2019,” which is taking place in Makuhari Messe from December 4 to 6, 2019. The 1.6-inch Micro LED display of JDI is based on LTPS backplane developed by the company and Micro LED chips from glō, a Micro LED technology provider. The display achieves a resolution of 265 ppi with a pixel number of 300*300. (Image: JDI) JDI also noted that the Micro LED display has a wide viewin...
Mini LED backlight solution seems to be a “must have” technology for all the panel exhibitors at this year’s Display Week. Despite that adopting Mini LED backlight to consumer electronic products is rather difficult due to high production cost; panel makers still proactively demonstrated related products. Therefore, Mini LED backlight might not be a flash in the pan. LEDinside noticed that almost every display maker participated in Display Week disclosed the focus on automotive display incorporating LCD panel and Mini LED backlight. The solut...
Japan Display Inc. (JDI) has been negotiating with Chinese companies and investors to receive financial supports of JPY 50 billion (US$ 440.65 million), reported NHK. The potential investors include mobile component producer Ofilm, automotive component manufacturer Minth Group and the Silk Road Fund.
With the support, the Chinese investors will hold 33 percent or more of the share of JDI, suppressing the current major shareholder INCJ, who owns 25.29 percent of the share. In addition to the investment, the Chinese investors were also reportedly offering a ...
LEDinside forecasts that the development of Mini LED will accelerate in 2019 and 2020 and its market value will reach US$ 1699 million by 2022. Several industry players including San’an, HC Semitek, Epistar, NationStar, Harvatek, and Macroblock have reported their progress of Mini LED development. Meanwhile, panel producers such as AUO, BOE, Innolux and JDI have also unveiled applications adopting Mini LED technology.
During Display Week 2018, many big giants have been simultaneously releasing Mini LED backlight products. LEDinside found those Mini LED panels majorly adopt direct-type local dimming and support HDR mode, making the vivid contract ratio, which can compete with OLED panel.
Japan Display Inc. (JDI) announced that it has developed a transparent glass-based capacitive fingerprint sensor by applying the company"s capacitive multi-touch technology used in its other liquid crystal displays (LCDs). JDI plans to start commercial shipments within its 2018 fiscal year, which ends March of 2019.
Appearing to be strapped for cash, smartphone screen manufacturer Japan Display (JDI) is currently in talks with Chinese panel makers, including BOE, Tianma, and CSOT, over an investment more than USD 1.8 billion. The Japanese company hopes to seal the deal by the end of March 2018, reported Kyodo News.
The Japanese digital panel giant Japan Display Inc. (JDI) had a struggle revamping its liquid crystal display (LCD) panel business. To make the recovery happen, JDI planned to accept fundings from outside investors. Not only that, JDI will restructure LCD panel production sites, and lay off employees at a large scale, slashing about 4,000 jobs, according to Nikkei"s report on August 8.
It has been spreading like crazy that in 2H17 three iPhone models- the high-end iPhone 8 featuring an OLED display, iPhone 7s and iPhone 7s Plus that continue to use LCD displays- will hit the shelves. Latest sources leaked Apple might increase OLED display use in its products and all the three new iPhones to roll out in 2018 are likely to sport OLED displays. That possibly implies orders Apple places with LCD display providers Sharp and Japan Display Inc. (JDI) would plummet. It will be much of a shock to JDI which earns over 50% of its revenue from Apple’s phone screen demand.
Sumitomo Chemical, the Japan-based chemical giant, is reported to have successfully developed new technologies to facilitate more cost efficient OLED display manufacture. According to Nikkei, the new materials and equipment the company introduced could possibly bring down the current production cost of OLED panels by 50%, which is able to further reduce the selling prices of OLED TVs and expand the penetration of OLED products.
Japan Display Inc. (JDI) announced the commencement of mass production at its newly-constructed low temperature poly-silicon (LTPS) LCD line in its Hakusan Plant, located in Hakusan City, Ishikawa Prefecture, Japan. JDI had been preparing for mass production since Dec. 1, and commenced mass production on Dec. 23.
Small to mid-sized display manufacturer Japan Display Inc. (JDI) third quarter financial results were in the red, due to lower demands than expected from Chinese clients and its largest client Apple, reported Chinese-language media Money DJ.
LCD display manufacturer Japan Display Inc. (JDI) developed an ultra-thin bezel LCD that is merely millimeters thick, which could greatly increase smartphone makers design flexibility, reported Nikkei.
Sharp President Tai Jeng-wu told The Nikkei and other reporters that it intended to collaborate with Japan Display Inc. (JDI) in the development of OLED displays to catch up with Korean competitors Samsung.
Japan Display Inc. (JDI), a manufactuerr of small to mid-sized LCD displays issued a statement on Saturday refuting claims made by Nikkeiand other media that it was seeking financial support from INCJ.
Innovation Network Corporation of Japan (“INCJ”), Japan Display Inc. (“JDI”), Sony Corporation (“Sony”), and Panasonic Corporation (“Panasonic”) announced hat they have executed a definitive agreement to establish a new company, JOLED Inc. (“JOLED”), to integrate Sony and Panasonic’s R&D functions for organic light-emitting diode (“OLED”) display panels. Through this collaboration, the companies aim to accelerate the development and early commercialization of OLED display panels. JOLED is scheduled to be launched in January 2015, subject to receipt of any necessary approvals.

The Japan Display factory in question is based in the Ishikawa Prefecture and has reportedly been shut since July this year due to poor sales. The company has also been restructuring itself ever since Apple, one of its main customers, switched focus from LCD panels manufactured in the plant to mostly OLED panels for its new iPhones.
Right now, Nikkei’s sources are saying that JDI is negotiating the sale with Apple for around 80 billion to 90 billion yen. Sharp, which also supplies LCD panels to Apple, is in talks to buy the factory from JDI as well, and both Sharp and Apple are reportedly contemplating how to share stakes in the facility.
Japan Display, on the other hand, released a statement that it is not currently in talks with any third parties regarding sale of the factory, and that it’s “considering all of the options regarding handling of the Hakusan Plant nothing has been decided.” JDI also added that “in order to consider all of the options, JDI is currently running a comprehensive check on the production equipment and infrastructure facilities at the Hakusan Plant.”




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey