tft lcd difference quotation
IPS (In-Plane Switching) lcd is still a type of TFT LCD, IPS TFT is also called SFT LCD (supper fine tft ),different to regular tft in TN (Twisted Nematic) mode, theIPS LCD liquid crystal elements inside the tft lcd cell, they are arrayed in plane inside the lcd cell when power off, so the light can not transmit it via theIPS lcdwhen power off, When power on, the liquid crystal elements inside the IPS tft would switch in a small angle, then the light would go through the IPS lcd display, then the display on since light go through the IPS display, the switching angle is related to the input power, the switch angle is related to the input power value of IPS LCD, the more switch angle, the more light would transmit the IPS LCD, we call it negative display mode.
The regular tft lcd, it is a-si TN (Twisted Nematic) tft lcd, its liquid crystal elements are arrayed in vertical type, the light could transmit the regularTFT LCDwhen power off. When power on, the liquid crystal twist in some angle, then it block the light transmit the tft lcd, then make the display elements display on by this way, the liquid crystal twist angle is also related to the input power, the more twist angle, the more light would be blocked by the tft lcd, it is tft lcd working mode.
A TFT lcd display is vivid and colorful than a common monochrome lcd display. TFT refreshes more quickly response than a monochrome LCD display and shows motion more smoothly. TFT displays use more electricity in driving than monochrome LCD screens, so they not only cost more in the first place, but they are also more expensive to drive tft lcd screen.The two most common types of TFT LCDs are IPS and TN displays.

Key Difference: LCDs are a type of television screen that uses liquid crystals sandwiched between two sheets of polarizing material. TFT (Thin-film transistor) is a field-effect transistor that is used to build the LCD screen and is embedded in every pixel, making it faster and giving a better image quality.
An LCD is type of television screen that uses liquid crystals sandwiched between two sheets of polarizing material. LCDs are used in TVs, computer monitors, clocks, calculators, cell phones, etc. LCDs provide significant benefits compared to CRTs and plasmas, such as they consume less power than both. Both CRTs and Plasmas are susceptible to burn-ins while LCDs are not. However, LCDs require a backlight as it does not emit light by itself.

Have you ever wonder where TFT derive from? Why is TFT referred to as LCD? The phenomenon started in early days, when bulky CRT displays were thing of the past and LCD was its replacement, but as time progresses, there were still room for improvement, which leads to the birth of TFT’s.
TFT is a variant of an LCD which uses thin film transistor technology to improve an image quality, while an LCD is class of displays that uses modulating properties of liquid crystals to form what we call an LCD (liquid crystals display) which in fact does not emits light directly.
Even though LCDs were very energy efficient, light weight and thin in nature, LCD were falling behind to the CRT display, which then leads to a change in LCD manufacturing, where performance became a big problem.
For example, having a 2001 Mustang vs a 2014 Mustang, the dimensions and engine of the 2014 has been redesign for performance reasons, not mentioning user friendly, so does the LCD to TFT.
As the birth of TFT, the elements are deposited directly on the glass substrate which in fact the main reason for the switch was because TFTs are easier to produce, better performance in terms of adjusting the pixels within the display to get better quality.
LCDs became ineffective over a period of time, almost all aspect of watching a TV, playing video games or using a handheld device to surf the net became daunting, this phenomenon is known as high response time with low motion rate.
Another problem with LCD was crosstalking, in terms of pixelating, this happens when signals of adjacent pixels affects operations or gives an undesired effect to the other pixel.
As TFT’s become very popular throughout the century due to its elaborate low charge associate and outstanding response time, LCDs became a thing of the past, and TFT became the predominant technology with their wider viewing angles and better quality this technology will be around for a long time.

A thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display (TFT LCD) is a variant of a liquid-crystal display that uses thin-film-transistor technologyactive matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven (i.e. with segments directly connected to electronics outside the LCD) LCDs with a few segments.
In February 1957, John Wallmark of RCA filed a patent for a thin film MOSFET. Paul K. Weimer, also of RCA implemented Wallmark"s ideas and developed the thin-film transistor (TFT) in 1962, a type of MOSFET distinct from the standard bulk MOSFET. It was made with thin films of cadmium selenide and cadmium sulfide. The idea of a TFT-based liquid-crystal display (LCD) was conceived by Bernard Lechner of RCA Laboratories in 1968. In 1971, Lechner, F. J. Marlowe, E. O. Nester and J. Tults demonstrated a 2-by-18 matrix display driven by a hybrid circuit using the dynamic scattering mode of LCDs.T. Peter Brody, J. A. Asars and G. D. Dixon at Westinghouse Research Laboratories developed a CdSe (cadmium selenide) TFT, which they used to demonstrate the first CdSe thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display (TFT LCD).active-matrix liquid-crystal display (AM LCD) using CdSe TFTs in 1974, and then Brody coined the term "active matrix" in 1975.high-resolution and high-quality electronic visual display devices use TFT-based active matrix displays.
The circuit layout process of a TFT-LCD is very similar to that of semiconductor products. However, rather than fabricating the transistors from silicon, that is formed into a crystalline silicon wafer, they are made from a thin film of amorphous silicon that is deposited on a glass panel. The silicon layer for TFT-LCDs is typically deposited using the PECVD process.
Polycrystalline silicon is sometimes used in displays requiring higher TFT performance. Examples include small high-resolution displays such as those found in projectors or viewfinders. Amorphous silicon-based TFTs are by far the most common, due to their lower production cost, whereas polycrystalline silicon TFTs are more costly and much more difficult to produce.
The twisted nematic display is one of the oldest and frequently cheapest kind of LCD display technologies available. TN displays benefit from fast pixel response times and less smearing than other LCD display technology, but suffer from poor color reproduction and limited viewing angles, especially in the vertical direction. Colors will shift, potentially to the point of completely inverting, when viewed at an angle that is not perpendicular to the display. Modern, high end consumer products have developed methods to overcome the technology"s shortcomings, such as RTC (Response Time Compensation / Overdrive) technologies. Modern TN displays can look significantly better than older TN displays from decades earlier, but overall TN has inferior viewing angles and poor color in comparison to other technology.
Most TN panels can represent colors using only six bits per RGB channel, or 18 bit in total, and are unable to display the 16.7 million color shades (24-bit truecolor) that are available using 24-bit color. Instead, these panels display interpolated 24-bit color using a dithering method that combines adjacent pixels to simulate the desired shade. They can also use a form of temporal dithering called Frame Rate Control (FRC), which cycles between different shades with each new frame to simulate an intermediate shade. Such 18 bit panels with dithering are sometimes advertised as having "16.2 million colors". These color simulation methods are noticeable to many people and highly bothersome to some.gamut (often referred to as a percentage of the NTSC 1953 color gamut) are also due to backlighting technology. It is not uncommon for older displays to range from 10% to 26% of the NTSC color gamut, whereas other kind of displays, utilizing more complicated CCFL or LED phosphor formulations or RGB LED backlights, may extend past 100% of the NTSC color gamut, a difference quite perceivable by the human eye.
The transmittance of a pixel of an LCD panel typically does not change linearly with the applied voltage,sRGB standard for computer monitors requires a specific nonlinear dependence of the amount of emitted light as a function of the RGB value.
Less expensive PVA panels often use dithering and FRC, whereas super-PVA (S-PVA) panels all use at least 8 bits per color component and do not use color simulation methods.BRAVIA LCD TVs offer 10-bit and xvYCC color support, for example, the Bravia X4500 series. S-PVA also offers fast response times using modern RTC technologies.
TFT dual-transistor pixel or cell technology is a reflective-display technology for use in very-low-power-consumption applications such as electronic shelf labels (ESL), digital watches, or metering. DTP involves adding a secondary transistor gate in the single TFT cell to maintain the display of a pixel during a period of 1s without loss of image or without degrading the TFT transistors over time. By slowing the refresh rate of the standard frequency from 60 Hz to 1 Hz, DTP claims to increase the power efficiency by multiple orders of magnitude.
Due to the very high cost of building TFT factories, there are few major OEM panel vendors for large display panels. The glass panel suppliers are as follows:
External consumer display devices like a TFT LCD feature one or more analog VGA, DVI, HDMI, or DisplayPort interface, with many featuring a selection of these interfaces. Inside external display devices there is a controller board that will convert the video signal using color mapping and image scaling usually employing the discrete cosine transform (DCT) in order to convert any video source like CVBS, VGA, DVI, HDMI, etc. into digital RGB at the native resolution of the display panel. In a laptop the graphics chip will directly produce a signal suitable for connection to the built-in TFT display. A control mechanism for the backlight is usually included on the same controller board.
The low level interface of STN, DSTN, or TFT display panels use either single ended TTL 5 V signal for older displays or TTL 3.3 V for slightly newer displays that transmits the pixel clock, horizontal sync, vertical sync, digital red, digital green, digital blue in parallel. Some models (for example the AT070TN92) also feature input/display enable, horizontal scan direction and vertical scan direction signals.
New and large (>15") TFT displays often use LVDS signaling that transmits the same contents as the parallel interface (Hsync, Vsync, RGB) but will put control and RGB bits into a number of serial transmission lines synchronized to a clock whose rate is equal to the pixel rate. LVDS transmits seven bits per clock per data line, with six bits being data and one bit used to signal if the other six bits need to be inverted in order to maintain DC balance. Low-cost TFT displays often have three data lines and therefore only directly support 18 bits per pixel. Upscale displays have four or five data lines to support 24 bits per pixel (truecolor) or 30 bits per pixel respectively. Panel manufacturers are slowly replacing LVDS with Internal DisplayPort and Embedded DisplayPort, which allow sixfold reduction of the number of differential pairs.
Kawamoto, H. (2012). "The Inventors of TFT Active-Matrix LCD Receive the 2011 IEEE Nishizawa Medal". Journal of Display Technology. 8 (1): 3–4. Bibcode:2012JDisT...8....3K. doi:10.1109/JDT.2011.2177740. ISSN 1551-319X.
K. H. Lee; H. Y. Kim; K. H. Park; S. J. Jang; I. C. Park & J. Y. Lee (June 2006). "A Novel Outdoor Readability of Portable TFT-LCD with AFFS Technology". SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers. AIP. 37 (1): 1079–82. doi:10.1889/1.2433159. S2CID 129569963.
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) is a synchronous serial communication interface best-suited for short distances. It was developed by Motorola for components to share data such as flash memory, sensors, Real-Time Clocks, analog-to-digital converters, and more. Because there is no protocol overhead, the transmission runs at relatively high speeds. SPI runs on one master (the side that generates the clock) with one or more slaves, usually the devices outside the central processor. One drawback of SPI is the number of pins required between devices. Each slave added to the master/slave system needs an additional chip select I/O pin on the master. SPI is a great option for small, low-resolution displays including PMOLEDs and smaller LCDs.
Philips Semiconductors invented I2C (Inter-integrated Circuit) or I-squared-C in 1982. It utilizes a multi-master, multi-slave, single-ended, serial computer bus system. Engineers developed I2C for simple peripherals on PCs, like keyboards and mice to then later apply it to displays. Like SPI, it only works for short distances within a device and uses an asynchronous serial port. What sets I2C apart from SPI is that it can support up to 1008 slaves and only requires two wires, serial clock (SCL), and serial data (SDA). Like SPI, I2C also works well with PMOLEDs and smaller LCDs. Many display systems transfer the touch sensor data through I2C.
Low-Voltage Differential Signaling (LVDS) was developed in 1994 and is a popular choice for large LCDs and peripherals in need of high bandwidth, like high-definition graphics and fast frame rates. It is a great solution because of its high speed of data transmission while using low voltage. Two wires carry the signal, with one wire carrying the exact inverse of its companion. The electric field generated by one wire is neatly concealed by the other, creating much less interference to nearby wireless systems. At the receiver end, a circuit reads the difference (hence the "differential" in the name) in voltage between the wires. As a result, this scheme doesn’t generate noise or gets its signals scrambled by external noise. The interface consists of four, six, or eight pairs of wires, plus a pair carrying the clock and some ground wires. 24-bit color information at the transmitter end is converted to serial information, transmitted quickly over these pairs of cables, then converted back to 24-bit parallel in the receiver, resulting in an interface that is very fast to handle large displays and is very immune to interference.

The liquid crystal display (LCD) technology has been used in several electronic products over the years. There are more reasons for LCDs to be more endearing than CRTs.
There are different components of a TFT displays that can be modified to create a custom color LCD. Some of the modifications are not too expensive, while others can be cost prohibitive. We will cover some of the main options available and their estimated cost when customizing a TFT display module.
Note: If you need a color LCD module, but do not need video or dot matrix (Graphical) capabilities, I would suggest using a lower cost alternative such as FSC*(Field Sequential Color display) aka known as a TN color display. A second option for a lower cost and much lower power requirement would be a custom segmented display module with color overlays.
This is by far the most expensive component of the TFT module to customize. There are industry standard glass sizes for TFT’s. The list includes, but is not limited to, 2.8 inch, 3.5 inch, 5.7 inch, 7 inch, 10.2 inch and larger. If you can design your product to make use of these standard sizes, then do it. If you need a unique size, say a something between a 2.8 inch and 3.5 inch, you may be forced to invest in a custom glass size. We have seen quotes for custom glass sizes for TFT run between $100,000 dollars to $150,000 dollars. Not a minor investment for most companies.
A TFT LCD display with a modified PCB, is still considered a custom color TFT. Modification costs to customize the PCB is an estimated $400 to $1,200 one-time tooling fee. The unit cost of the TFT display, with a modified PCB will be slightly higher than the cost of the TFT with a standard PCB.
Many products that incorporate a custom color LCD display will contain a touch screen or touch panel. These can be modified to meet a customer’s particular size for an estimated tooling cost of $3,000 to $4,000.

We have over two dozen TFT LCD display modules to choose from. All of them are full-color graphic displays. Unlike standard monochrome character displays, you can create complex images for imaginative user experiences. Thin and light, these are ideal for handheld devices, communications equipment, information displays, and test and measurement equipment.
Listed by the diagonal size of the active area (the usable area for lit pixels), our TFT display sizes range from 1.3 inches to 10.1 inches. Choose from six different interfaces, many of our TFT modules have more than one interface available. Arduino users should select modules with SPI for fast and easy communications to add color graphics to their projects.
Contrast ratio is the difference between a pixel that is lit or dark. Standard STN LCD displays typically have a 10:1 contrast ratio while TFT displays are 300:1 and up, so details stand out and text looks extra sharp. For standard STN displays, you must choose a display limited to a specific viewing angle (12, 3, 6 or 9 o"clock) while TFTs can have a viewing cone greater than 160 degrees.

Looking for a specific TFT resolution? We offer LCD TFTs varying in resolution from 128x160 pixels to 800x480 pixels. Many of our TFT LCDs also have carrier boards to make integrating them into your product as simple as possible. All of our TFT LCDs offer full color RGB. If you"re not finding the correct TFT LCD for your product or project, please contact our support team to see if they can help you find an appropriate TFT display module for you.

TFT displays are full color LCDs providing bright, vivid colors with the ability to show quick animations, complex graphics, and custom fonts with different touchscreen options. Available in industry standard sizes and resolutions. These displays come as standard, premium MVA, sunlight readable, or IPS display types with a variety of interface options including HDMI, SPI and LVDS. Our line of TFT modules include a custom PCB that support HDMI interface, audio support or HMI solutions with on-board FTDI Embedded Video Engine (EVE2).

Our standard TFT displays are available in a variety of sizes from 1.8" to 7.0". These displays are TN (Twisted Nematic) and offer basic characteristics such as wide operating temperatures ranging from -20°C to +70°C, 12:00 or 6:00 viewing angles, and support full-motion graphics. TN TFTs are an affordable option for various applications requiring full-color graphics.

LCD stands for “Liquid Crystal Display” and TFT stands for “Thin Film Transistor”. These two terms are used commonly in the industry but refer to the same technology and are really interchangeable when talking about certain technology screens. The TFT terminology is often used more when describing desktop displays, whereas LCD is more commonly used when describing TV sets. Don’t be confused by the different names as ultimately they are one and the same. You may also see reference to “LED displays” but the term is used incorrectly in many cases. The LED name refers only to the backlight technology used, which ultimately still sits behind an liquid crystal panel (LCD/TFT).
As TFT screens are measured differently to older CRT monitors, the quoted screen size is actually the full viewable size of the screen. This is measured diagonally from corner to corner. TFT displays are available in a wide range of sizes and aspect ratios now. More information about the common sizes of TFT screens available can be seen in our section about resolution.
The aspect ratio of a TFT describes the ratio of the image in terms of its size. The aspect ratio can be determined by considering the ratio between horizontal and vertical resolution.
The resolution of a TFT is an important thing to consider. All TFT’s have a certain number of pixels making up their liquid crystal matrix, and so each TFT has a “native resolution” which matches this number. It is always advisable to run the TFT at its native resolution as this is what it is designed to run at and the image does not need to be stretched or interpolated across the pixels. This helps keep the image at its most clear and at optimum sharpness. Some screens are better than others at running below the native resolution and interpolating the image which can sometimes be useful in games.
You generally cannot run a TFT at a resolution of above its native resolution although some screens have started to offer “Virtual” resolutions, for example “virtual 4k” where the screen will accept a 3840 x 2160 input from your graphics card but scale it back to match the native resolution of the panel which is often 2560 x 1440 in these examples. This whole process is rather pointless though as you lose a massive amount of image quality in doing so.
Unlike on CRT’s where the dot pitch is related to the sharpness of the image, the pixel pitch of a TFT is related to the distance between pixels. This value is fixed and is determined by the size of the screen and the native resolution (number of pixels) offered by the panel. Pixel pitch is normally listed in the manufacturers specification. Generally you need to consider that the ‘tighter’ the pixel pitch, the smaller the text will be, and potentially the sharper the image will be. To be honest, monitors are normally produced with a sensible resolution for their size and so even the largest pixel pitches return a sharp images and a reasonable text size. Some people do still prefer the larger-resolution-crammed-into-smaller-screen option though, giving a smaller pixel pitch and smaller text. It’s down to choice and ultimately eye-sight.
While this aspect is not always discussed by display manufacturers it is a very important area to consider when selecting a TFT monitor. The LCD panels producing the image are manufactured by many different panel vendors and most importantly, the technology of those panels varies. Different panel technologies will offer different performance characteristics which you need to be aware of. Their implementation is dependent on the panel size mostly as they vary in production costs and in target markets. The four main types of panel technology used in the desktop monitor market are:
Nowadays IPS panels are produced and developed by several leading panel manufacturers. LG.Display technically own the IPS name and continue to invest in this popular technology. Samsung began production of their very similar PLS (Plane to Line Switching) technology, as did AU Optronics with their AHVA (Advanced Hyper Viewing Angle). These are all so similar in performance and features that they can be simply referred to now as “IPS-type”. Indeed monitor manufacturers will normally stick to the common IPS name but the underlying panel may be produced by any number of different manufacturers investing in this type of panel tech. AU Optronics have done a good job with finally increasing the refresh rate of their IPS panels, and making them a more viable option for gamers. Native 144Hz IPS-type panels are now available and response times continue to be reduced as well. Modern IPS panels are characterized by decent response times, if not quite as fast as TN Film they are certainly more fluid than older panels. Contrast ratios are typically around 1000:1 and viewing angles continue to be the widest and most stable of any panel technology. You will find varying colour depths including 6-bit+FRC and 8-bit commonly being used, although this makes little difference in practice. One of the remaining limitations with IPS-type technologies are the so-called “IPS glow”, where darker content introduces a pale glow when viewed from an angle. It’s a characteristic of the panel technology and pretty hard to avoid without additional filters being added to the panels. On larger and wider screens some people find this glow distracting and problematic.
This technology was developed by Sharp for use in some of their TFT displays. It consists of several improvements that Sharp claim to have made, mainly to counter the drawbacks of the popular TN Film technology. They have introduced an Anti-Glare / Anti-Reflection (AGAR) screen coating which forms a quarter-wavelength filter. Incident light is reflected back from front and rear surfaces 180° out of phase, thus canceling reflection rather diffusing it as others do. As well as reducing glare and reflection from the screen, this is marketed as being able to offer deeper black levels. Sharp also claim to offer better contrast ratios than any competing technology (VA and IPS); but with more emphasis on improving these other technologies, this is probably not the case with more modern panels. There are very few ASV monitors around really, with the majority of the market being dominated by TN, VA and IPS panels.
This technology was developed by BOE Hydis, and is not really very widely used in the desktop TFT market, more in the mobile and tablet sectors. It is worth mentioning however in case you come across displays using this technology. It was developed by BOE Hydis to offer improved brightness and viewing angles to their display panels and claims to be able to offer a full 180/180 viewing angle field as well as improved colours. This is basically just an advancements from IPS and is still based on In Plane technology. They claim to “modify pixels” to improve response times and viewing angles thanks to improved alignment. They have also optimised the use of the electrode surface (fringe field effect), removed shadowed areas between pixels, horizontally aligned electric fields and replaced metal electrodes with transparent ones. More information about AFFS can be found here.
This panel technology was developed by NEC LCD, and is reported to offer wide viewing angles, fast response times, high luminance, wide colour gamut and high definition resolutions. Of course, there is a lot of marketing speak in there, and the technology is not widely employed in the mainstream monitor market. Wide viewing angles are possible thanks to the horizontal alignment of liquid crystals when electrically charged. This alignment also helps keep response times low, particularly in grey to grey transitions. Their SFT range also offers high definition resolutions and are commonly used in medical displays where extra fine detail is required.
NEC’s SFT technology was first developed to be labelled as Advanced-SFT (A-SFT) which offered enhanced luminance figures. This then developed further to Super Advanced-SFT (SA-SFT) where colour gamut reached 72% of the NTSC colour space, and then to Ultra Advanced-SFT (UA-SFT) where the gamut was still at 72% or higher, but with a further enhancement of the luminance as compared with SA-SFT. These changes were all made possible thanks to the improved transmissivity of the SFT technology. More information is available from NEC LCD
The traditional response time standard (ISO response time) is measured as the rise time (tR) and fall time (tF) of a pixel as it changes black > white > black. The total ‘response time’ is quoted as the total of the tR + tF. On older screens users needed to be wary of the figures manufacturers quote, as sometimes the ‘response time’ can be quoted as just the rise time, and not the total response time. This measurement of the black > white > black transition was defined as the ISO standard for response time measurements before the days of ‘overdrive’ being used (discussed in a moment). The reason this particular transition was selected as the response time figure was that it was always the fastest change possible, and manufacturers therefore quoted their best measurement. The reason this was the fastest was because at the time the highest voltage was applied to the pixels to make that change (since it was the most drastic difference from black to white).
One thing to note regarding pixel response time is that the overall performance of the TFT will also depend on the technology of the panel used. TN film panels offer response time graphs similar to that above, but screens based on traditional VA / IPSvariant panels can show response time graphs more like this (we are assuming for now non-overdriven panels):
Some reviews sites including TFTCentral have access to advanced photosensor (photodiodе + low-noise operational amplifier) and oscilloscope measurement equipment which allows them to measure response time as detailed above. See our article about response times for more information on that method. Graphs showing response time according to their equipment are produced. Other sites rely on observed responsiveness to compare how well a panel can perform in practice and what a user might see in normal use. We think it is important to study both methods if possible to give a fuller picture of a panels performance. For visual tests TFTCentral uses a program called PixPerAn (developed by Prad.de) which is good for comparing monitor responsiveness with its series of tests. The favourite seems to be the moving car test as shown here:
In addition to pixel response time measurements and visual tests described above, it is also possible to capture the levels of blurring and smearing the human eye will experience on a display. This is achieved using a pursuit camera setup. They are simply cameras which follow the on-screen motion and are extremely accurate at measuring motion blur, ghosting and overdrive artefacts of moving images. Since they simulate the eye tracking motion of moving eyes, they can be useful in giving an idea of how a moving image appears to the end user. It is the blurring caused by eye tracking on continuously-displayed refreshes (sample-and-hold) that we are keen to analyse with this new approach. This is not pixel persistence caused by response times; but a different cause of display motion blur which cannot be captured using static camera tests. Low response times do have a positive impact on motion blur, and higher refresh rates also help reduce blurring to a degree. It does not matter how low response times are, or how high refresh rates are, you will still see motion blur from LCD displays under normal operation to some extent and that is what this section is designed to measure. Further technologies specifically designed to reduce perceived motion blur are required to eliminate the blur seen on these type of sample-and-hold displays which we will also look at.
These tests capture the kind of blurring you would see with the naked eye when tracking moving objects across the screen (example from the Asus ROG Swift PG279Q). As you increase the refresh rate the perceived blurring is reduced, as refresh rate has a direct impact on motion blur. It is not eliminated entirely due to the nature of the sample-and-hold LCD display and the tracking of your eyes. No matter how fast the refresh rate and pixel response times are, you cannot eliminate the perceived motion blur without other methods.Tests like the above would give you an idea of the kind of perceived motion blur range when using the particular screen without any bur reduction mode active.
The Contrast Ratio of a TFT is the difference between the darkest black and the brightest white it is able to display. This is really defined by the pixel structure and how effectively it can let light through and block light out from the backlight unit. As a rule of thumb, the higher the contrast ratio, the better. The depth of blacks and the brightness of the whites are better with a higher contrast ratio. This is also referred to as the static contrast ratio.
When considering a TFT monitor, a contrast ratio of 1000:1 is pretty standard nowadays for TN Film and IPS-type panels. VA-type panels can offer static contrast ratios of 3000:1 and above which are significantly higher than other competing panel technologies.
Some technologies boast the ability to dynamically control contrast (Dynamic Contrast Ratio – DCR) and offer much higher contrast ratios which are incredibly high (millions:1 for instance!). Be wary of these specs as they are dynamic only, and the technology is not always very useful in practice. Traditionally, TFT monitors were said to offer poor black depth, but with the extended use of VA panels, the improvements from IPS and TN Film technology, and new Dynamic Contrast Control technologies, we are seeing good improvements in this area. Black point is also tied in to contrast ratio. The lower the black point, the better, as this will ensure detail is not lost in dark image when trying to distinguish between different shades.
Brightness as a specification is a measure of the brightest white the TFT can display, and is more accurately referred to as its luminance. Typically TFT’s are far too bright for comfortable use, and the On Screen Display (OSD) is used to turn the brightness setting down. Brightness is measure in cd/m2 (candella per metre squared). Note that the recommended brightness setting for a TFT screen in normal lighting conditions is 120 cd/m2. Default brightness of screens out of the box is regularly much higher so you need to consider whether the monitor controls afford you a decent adjustment range and the ability to reduce the luminance to a comfortable level based on your ambient lighting conditions. Different uses may require different brightness settings as well so it is handy when reviews record the luminance range possible from the screen as you adjust the brightness control from 100 to 0%.
The colour depth of a TFT panel is related to how many colours it can produce and should not be confused with colour space (gamut). The more colours available, the better the colour range can potentially be. Colour reproduction is also different however as this related to how reliably produced the colours are compared with those desired.
Colour gamut in TFT monitors refers to the range of colours the screen is capable of displaying, and how much of a given reference colour space it might be able to display. It is ultimately linked to backlight technology and not to the panel itself.
Laser Displays are capable of producing the biggest colour gamut for a system with three basic colours, but even a laser display cannot reproduce all the colours the human eye can see, although it is quite close to doing that. However, in today’s monitors, both CRT and LCD (except for some models I’ll discuss below), the spectrum of each of the basic colours is far from monochromatic. In the terms of the CIE diagram it means that the vertexes of the triangle are shifted from the border of the diagram towards its centre.
Traditionally, LCD monitors were capable of giving approximate coverage of the sRGB reference colour space as shown in the diagram above. This is defined by the backlighting used in these displays – Cold-cathode fluorescent lamps (CCFL) that are employed which emit radiation in the ultraviolet range which is transformed into white colour with the phosphors on the lamp’s walls. These backlight lamps shine through the LCD panel, and through the RGB sub-pixels which act as filters for each of the colours. Each filter cuts a portion of spectrum, corresponding to its pass-band, out of the lamp’s light. This portion must be as narrow as possible to achieve the largest colour gamut.
To help develop and improve on the colour space a screen is capable of displaying a new generation CCFL backlighting was introduced. These so-called “wide gamut” backlights allow a gamut coverage of typically 92 – 102% of the NTSC colour space. There is a difference in practice which all users should be able to detect. The colour space available is extended mainly in green shades as you can see from the image above. Red coverage is also extended in some cases. This extended colour space sounds appealing on face value since the screens featuring WCG-CCFL backlighting can offer a broader range of colours. Manufacturers will often promote the colour space coverage of their screens with these high figures. In practice you need to consider what impact this would have on your use.
Viewing angles are quoted in horizontal and vertical fields and often look like this in listed specifications: 170/160 (170° in horizontal viewing field, 160° in vertical). The angles are related to how the image looks as you move away from the central point of view, as it can become darker or lighter, and colours can become distorted as you move away from your central field of view. Because of the pixel orientation, the screen may not be viewable as clearly when looking at the screen from an angle, but viewing angles of TFT’s vary depending on the panel technology used.
TFT screens do not refresh in the same way as a CRT screen does, where the image is redrawn at a certain rate. As a TFT is a static image, and each pixel refreshes independently, setting the TFT at a common 60Hz native refresh rate does not cause the same problems as it would on a CRT. There is no cathode ray gun redrawing the image as a whole on a TFT. You will not get flicker, which is the main reason for having a high refresh rate on a CRT in the first place. Standard TFT monitors operate with a 60Hz recommended refresh rate, but can sometimes support up to 75Hz maximum (within the spec) or sometimes even further using ‘overclocking’ methods. The reason that 60Hz is recommended by all the manufacturers is that it is related to the vertical frequency that TFT panels run at. Some more detailed data sheets for the panels themselves clearly show that the operating vertical frequency is between about 56 and 64Hz, and that the panels ‘typically’ run at 60Hz (see the LG.Philips LM230W02 datasheet for instance – page 11). If you decide to run your refresh rate from your graphics card above the recommended 60Hz it will work fine, but the interface chip on the monitor will be in charge of scaling the frequency down to 60Hz anyway. Some screens will allow you to run at the maximum 75Hz as well for an additional boost in frame rates and some minor improvements in motion clarity. The support of this will really depend on the screen, your graphics card and the video connection being used. You may find the screen operates fine at the higher refresh rate setting but in reality the screen will often drop frames to meet the 60Hz recommended setting (or spec of the panel) anyway. Generally we would suggest sticking to 60Hz on standard TFT monitors.
You will see more mention of higher refresh rates from both LCD televisions and now desktop monitors. It’s important to understand the different technologies being used though and what constitutes a ‘real’ 120Hz and what is ‘interpolated’:
Interpolated 120Hz+– These technologies are the ones commonly used in LCD TV’s where TV signal input is limited to 50 / 60 Hz anyway (depending on PAL vs NTSC). To help overcome the issues relating to motion blur on such sets, manufacturers began to introduce a technology to artificially boost the frame rate of the screen. This is done by an internal processing within the hardware which adds an intermediate and interpolated (guessed / calculated) frame between each real frame, boosting from 50 / 60fps to 100 / 120 fps. This technology can offer a noticeable improvement in practice when it is controlled very well. Some sets even have 240 and 480Hz technologies which operate in the same way, but with further interpolation and inserted frames. See here for further information.
Manufacturer specifications will usually list power consumption levels for the monitor which tell you the typical power usage you can expect from their model. This can help give you an idea of running costs, carbon footprint and electricity demands which are particularly important when you’re talking about multiple monitors or a large office environment. Power consumption of an LCD monitor is typically impacted by 3 areas:
This relates to the connection type from the TFT to your PC or other external device. Older screens nearly all came with an analogue connection, commonly referred to as D-sub or VGA. This allows a connection from the VGA port on your graphics card, where the signal being produced from the graphics card is converted from a pure digital to an analogue signal. There are a number of algorithms implemented in TFT’s which have varying effectiveness in improving the image quality over a VGA connection. Some TFT’s with then offer a DVI input as well to allow you to make use of the DVI output from your graphics card which you might have. This will allow a pure digital connection which can sometimes offer an improved image quality. It is possible to get DVI – VGA converters. These will not offer any improvements over a standard analogue connection, as you are still going through a conversion from digital to analogue somewhere along the line. Dual-Link DVI is also sometimes used which is a single DVI connection but with more pins, allowing for higher resolution/refresh rate support than a single-link DVI.

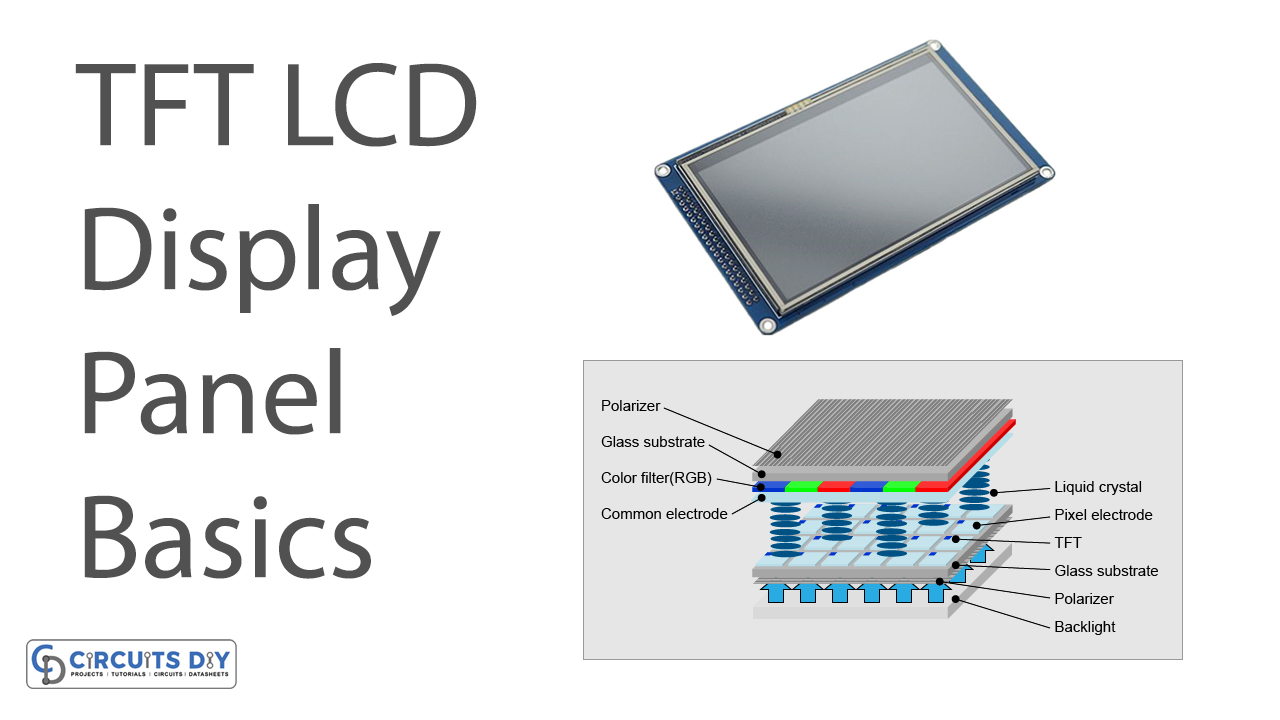
Dr Pan: Hello, Greg. TFT LCD module is one of the best LCD technology. We can simply consider it as TFT+LCD+LED backlight, and monochrome LCD module consists of LCD+LED backlight. An image on an LCD we can see is composed of pixels. TFT is the abbreviation for thin film transistor and it controls the R, G, B colors of each pixel respectively on the surface of LCD.
TFT LCD is a high standard product and it is not well customized as monochrome LCD. But still, it has a variety of options to meet the customers’ requirements.The sizes range from 1.44 inch to 130.0 inch;

Technology can be confusing because it evolves quickly, and there are complex acronyms for almost everything. If you are thinking ofbuildinga monitor or want to learn about the technology, you will encounter the term TFT Monitor at some point.
A lot goes on behind the glass surface, and we will look at this in comparison to other technologies to paint a clear picture of what TFT is and how it evolved.
TFT is an acronym for Thin Film Transistor, and it is a technology used in Liquid Crystal Display screens. It came about as an improvement to passive-matrix LCDs because it introduced a tiny, separate transistor for each pixel. The result? Such displays could keep up with quick-moving images, which passive-matrix LCDs could not do.
Also, because the transistors are tiny, they have a low power consumption and require a small charge to control each one. Therefore, it is easy to maintain a high refresh rate, resulting in quick image repainting, making a TFT screen the ideal gaming monitor.
The technology improved on the TN (Twisted Nematic) LCD monitor because the shifting pattern of the parallel, horizontal liquid crystals gives wide viewing angles. Therefore, IPS delivers color accuracy and consistency when viewed at different angles.
Both TFT and IPS monitors are active-matrix displays and utilize liquid crystals to paint the images. Technically, the two are intertwined because IPS is a type of TFT LCD. IPS is an improvement of the old TFT model (Twisted Nematic) and was a product of Hitachi displays, which introduced the technology in 1990.
The monitors can create several colors using the different brightness levels and on/off switches. But unlike OLED, both TFT and IPS do not emit light, so most have bright fluorescent lamps or LED backlights to illuminate the picture. Also, neither of them can produce color, so they have an RGB color filter layer.
Easy to Integrate and Update: By combining large-scale semiconductor IC and light source technology, TFTs have the potential for easy integration and updating/development.
Wide Application Range: TFTs are suitable for mobile, desktop screens, and large-screen TVs. Additionally, the technology can operate at a temperature range of -20°C to +50°C, while the temperature-hardened design can remain functional at temperatures not exceeding -80°C.
Impressive Display Effect: TFT displays use flat glass plates that create an effect of flat right angles. Combine this with the ability of LCDs to achieve high resolutions on small screen types, and you get a refreshing display quality.
Good Environmental Protection: The raw materials used to make TFT displays produce zero radiation and scintillation. Thus, the technology does not harm the user or the environment.
Mature Manufacturing Technology: TFT technology came into existence in the 60s. Over time, its manufacturing technology has matured to have a high degree of automation, leading to cheaper, large-scale industrial production.
Wide View Angle: One of the main advantages of IPS screens is their wide viewing angle due to the horizontal liquid crystals. They do not create halo effects, grayscale, or blurriness, but these are common flaws with TFTs.
Better Color Reproduction and Representation: The pixels in TFTs function perpendicularly after activation with the help of electrodes. However, IPS technology makes the pixels function while parallel horizontally. Thus, they reflect light better and create a more original and pristine image color.
Faster Frequency Transmittance: Compared to TFT, IPS screens transmit frequencies at about 25ms, which is 25x faster. This high speed is necessary to achieve wide viewing angles.
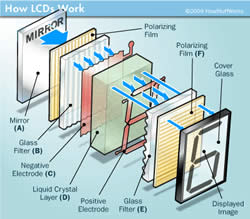
Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) is a front panel display that utilizes liquid crystals held between two layers of polarized glass to adjust the amount of blocked light. The technology does not produce light on its own, so it needs fluorescent lamps or white LEDs.
As explained earlier, TFT improved on the passive-matrix LCD design because it introduces a thin film transistor for each pixel. The technology reducescrosstalkbetween the pixels because each one is independent and does not affect the adjacent pixels.
LED screens are like the new kids on the block in the display market, and they operate very differently from LCDs. Instead of blocking light, LEDs emit light and are thinner, provide a faster response rate, and are more energy-efficient.
Since IPS is a type of TFT, when comparing the two, we are essentially looking at the old Thin-Film Transistor technology (Twisted Nematic) vs. the new (IPS). Even though TN is relatively old, this digital display type has its advantages, a vital one being the fast refresh rate. This feature makes such screens the preferred option by competitive gamers. If you have any inquiries about the technology,contact usfor more information.

1. Passive Matrix LCD: It uses a grid of vertical and horizontal conductors comprised of Indium Tin Oxide to create an image. Each pixel is controlled by an intersection of two conductors. It represents the off state of LCD i.e the pixel is OFF.
2. Active Matrix LCD: It uses thin-film transistors that are arranged in a matrix on a glass surface. To control the voltage tiny switching transistors and capacitors are used at each pixel location. The active pixel is called so because it has the ability to control the individual pixels and switch them quickly. thin-filmwhich
Difference between Active Matrix LCD and Passive Matrix LCD:Active Matrix LCDPassive Matrix LCDIt uses thin film transistors that are arranged in a matrix on a glass surface. To control the voltage tiny switching transistors and capacitors are used at each pixel location.It uses grid of vertical and horizontal conductors such that the intersection of two of those conductors allows for controlling a single pixel.
Active matrix LCDs are used in full-color LCD TVs monitors, cell phones etc.They are used in calculators display or a digital wrist watches where the display contains a limited number of segment and does not require full color. They are often created for custom applications.
On an elaborative note, passive and active displays also have several types which run down their very own category. For example, passive LCDs may be of the following types:Monochrome TN (Twisted Nematic) – here the liquid crystal cells do not require any current to flow past them and automatically work with lower voltages provided by the batteries.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey