arduino lcd display circuit made in china

@Railroader Thanks for your advice, although I felt that it was a little patronising. But I guess that since the Arduino is primarily targeted at schoolchildren and for educational purposes, that"s a fair enough assumption of my age and career.
I am aware that there are better alternatives for screens that can be found for under £15. I was curious what was in a £15 quid projector and bought it for that reason. Disassembling it was fun and has already netted me lenses, heatsinks, and LEDs etc. for other projects which is worth more than its cost. The reason I asked was because a) I am loathe to bin the LCD and hence contribute to our electronic waste problems, and b) I am specifically looking for LEDs (most of the displays on eBay and Amazon are OLEDs) as I want to make an ESP32-controlled projector as a project. Non-OLEDs are difficult to find on eBay/Amazon nowadays. Hence I was asking on the off-chance that this screen might be similar to something else in Occidental part of the world that I could use.
From what you say it feels its very unlikely for there to be a shortcut and I"ll have decode the signals manually. Designing and manufacturing (or finding a 30 pin adapter) is not a problem but I can"t justify to myself spending the better part of my weekends in a month to decode the signals just to use it when I can spend £10 buying an SPI LCD from eBay which does the exact same thing. I"ll probably bite the bullet and do that.
Shame about having to bin the screen though. I have found the schematics for the GM8284DD chip and probably with a magnifying glass would be able to make out the LCD connections (RGB input etc.) on the circuit board but again, I"m not sure if its that cost-efficient spending that many weekends working on it...

I suspected the pinout. Got another LCD and used a loupe to see if I could find anything and well, there were numbering of pinout printed, and to my strange they were different from what on all documentation I found (and on link of Sparkfun on this LCD):
Next I supposed that the right pinout is what is printed on the board and connected the circuit based on Chinese pinout. The strange thing is that, connecting +6.5 to BL, changes nothing, both when putting the circuit working or having non of pins other than (vcc and gnd of) BL connected.
Now when I connect PIN1 to vcc 3.3v and PIN2 which must be RESET, to GND, the LCD turns on in pale blue. If at this time I connect the BL to anything from 3.3 to 6.5 nothing changes! Also nothing other than pale blue comes up at all.
Now if, say, Chinese printed wrong and pinout is the same, or say, they both printed pinout differently, and set up wiring differently as it is a copy LCD, then PIN 1 and 2 which I considered VCC and RESET are actually BL + and -, but well, connecting them to 6.5v, burns out the LCD! At the same time, connecting power to pin 9 and 10 if we suppose they are real BL + and - won"t change anything!

I have issue with my Arduino uno board the L named led is not glowing and RX and TX leds are glowing and code is also not uploading and the centre IC is getting hot too plzzz help me out
Great explanation on how to fix the clone Arduino UNO. What about the clone Arduino pro mini from China? I can upload the sketch, but they just seem not to work properly or don"t work at all. Can you do the same with pro mini since the microcontroller is the same as UNO? Thank you and I appreciate your work?
I like to do a Burn Bootloader to my chineesboard. Bud I am consernd that it wil harm my original arduino? Is dat a risk? What purpes dos the capacitor serve?
I have purchased several clone arduinos UNO and never have I had a problem.One thing you do not realize is that all high speed manufacturing is done in China and the units produced all pass the same test as any others. Now if you were to design a product yes you could do a test run in your own home country but when you need 5 million than you will need a high speed high throughput producer and that"s where the Chinese companies shine so please stop using the word CLONE and stop being PREJUDICE as we all live in this world and when we are born we do not push a button to chose race,creed or color or birth location.Now check that you are using a data cable and not a CHARGING cable and if you truly get a bad device that send it back and a new one will be sent to you.0
I have a clone arduino uno with ch340g. It works well. But it dosnot recognize sd card module. The 11~13 pins works as output. Please help me. Thanks0
If you guys are having problem with arduino uploading sketch. You tried all solution but it never worked. So last option you have is to upload the sketch through using other arduino.

In this Arduino touch screen tutorial we will learn how to use TFT LCD Touch Screen with Arduino. You can watch the following video or read the written tutorial below.
As an example I am using a 3.2” TFT Touch Screen in a combination with a TFT LCD Arduino Mega Shield. We need a shield because the TFT Touch screen works at 3.3V and the Arduino Mega outputs are 5 V. For the first example I have the HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor, then for the second example an RGB LED with three resistors and a push button for the game example. Also I had to make a custom made pin header like this, by soldering pin headers and bend on of them so I could insert them in between the Arduino Board and the TFT Shield.
Here’s the circuit schematic. We will use the GND pin, the digital pins from 8 to 13, as well as the pin number 14. As the 5V pins are already used by the TFT Screen I will use the pin number 13 as VCC, by setting it right away high in the setup section of code.
So now I will explain how we can make the home screen of the program. With the setBackColor() function we need to set the background color of the text, black one in our case. Then we need to set the color to white, set the big font and using the print() function, we will print the string “Arduino TFT Tutorial” at the center of the screen and 10 pixels down the Y – Axis of the screen. Next we will set the color to red and draw the red line below the text. After that we need to set the color back to white, and print the two other strings, “by HowToMechatronics.com” using the small font and “Select Example” using the big font.
In order the code to work and compile you will have to include an addition “.c” file in the same directory with the Arduino sketch. This file is for the third game example and it’s a bitmap of the bird. For more details how this part of the code work you can check my particular tutorial. Here you can download that file:

The ST7789 TFT module contains a display controller with the same name: ST7789. It’s a color display that uses SPI interface protocol and requires 3, 4 or 5 control pins, it’s low cost and easy to use. This display is an IPS display, it comes in different sizes (1.3″, 1.54″ …) but all of them should have the same resolution of 240×240 pixel, this means it has 57600 pixels. This module works with 3.3V only and it doesn’t support 5V (not 5V tolerant).
The ST7789 display module shown in project circuit diagram has 7 pins: (from right to left): GND (ground), VCC, SCL (serial clock), SDA (serial data), RES (reset), DC (or D/C: data/command) and BLK (back light).
As mentioned above, the ST7789 TFT display controller works with 3.3V only (power supply and control lines). The display module is supplied with 3.3V (between VCC and GND) which comes from the Arduino board.
To connect the Arduino to the display module, I used voltage divider for each line which means there are 4 voltage dividers. Each voltage divider consists of 2.2k and 3.3k resistors, this drops the 5V into 3V which is sufficient.
The first library is a driver for the ST7789 TFT display which can be installed from Arduino IDE library manager (Sketch —> Include Library —> Manage Libraries …, in the search box write “st7789” and install the one from Adafruit).

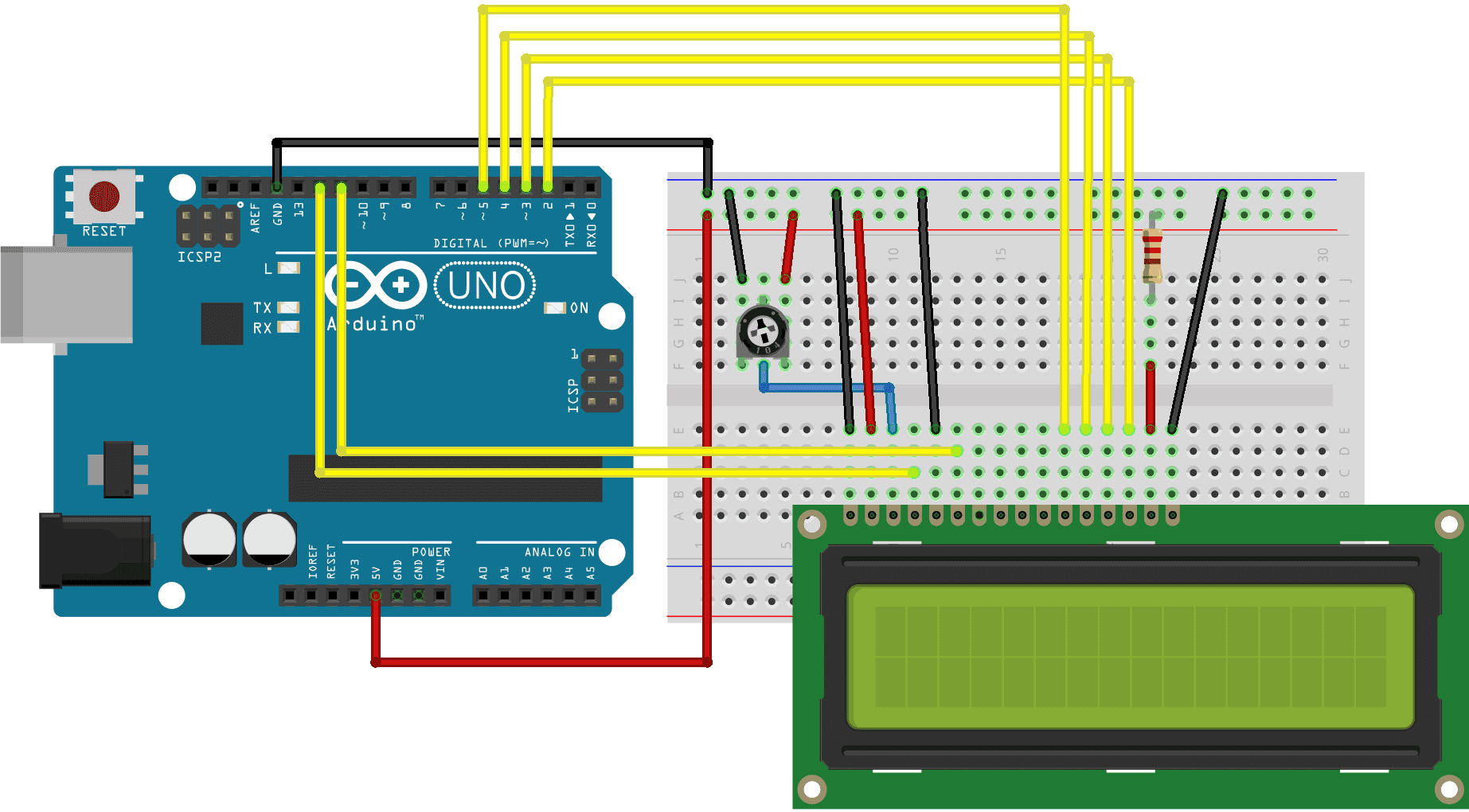
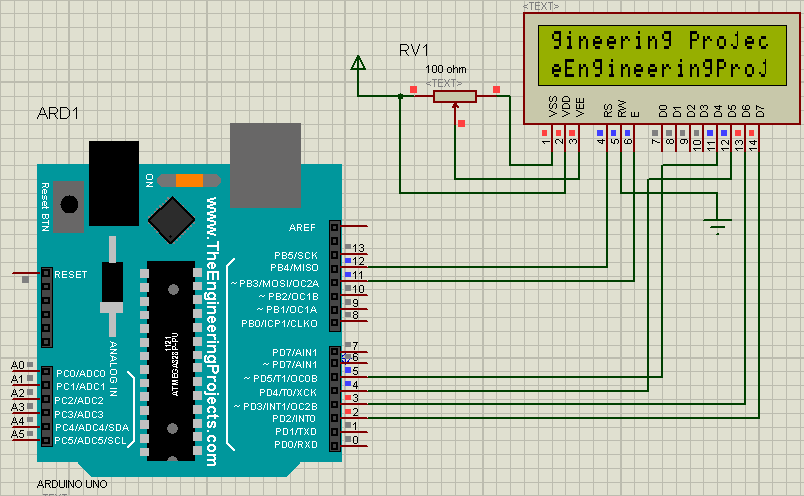
In this tutorial, I’ll explain how to set up an LCD on an Arduino and show you all the different ways you can program it. I’ll show you how to print text, scroll text, make custom characters, blink text, and position text. They’re great for any project that outputs data, and they can make your project a lot more interesting and interactive.
The display I’m using is a 16×2 LCD display that I bought for about $5. You may be wondering why it’s called a 16×2 LCD. The part 16×2 means that the LCD has 2 lines, and can display 16 characters per line. Therefore, a 16×2 LCD screen can display up to 32 characters at once. It is possible to display more than 32 characters with scrolling though.
The code in this article is written for LCD’s that use the standard Hitachi HD44780 driver. If your LCD has 16 pins, then it probably has the Hitachi HD44780 driver. These displays can be wired in either 4 bit mode or 8 bit mode. Wiring the LCD in 4 bit mode is usually preferred since it uses four less wires than 8 bit mode. In practice, there isn’t a noticeable difference in performance between the two modes. In this tutorial, I’ll connect the LCD in 4 bit mode.
Here’s a diagram of the pins on the LCD I’m using. The connections from each pin to the Arduino will be the same, but your pins might be arranged differently on the LCD. Be sure to check the datasheet or look for labels on your particular LCD:
Also, you might need to solder a 16 pin header to your LCD before connecting it to a breadboard. Follow the diagram below to wire the LCD to your Arduino:
All of the code below uses the LiquidCrystal library that comes pre-installed with the Arduino IDE. A library is a set of functions that can be easily added to a program in an abbreviated format.
In order to use a library, it needs be included in the program. Line 1 in the code below does this with the command #include
Now we’re ready to get into the programming! I’ll go over more interesting things you can do in a moment, but for now lets just run a simple test program. This program will print “hello, world!” to the screen. Enter this code into the Arduino IDE and upload it to the board:
There are 19 different functions in the LiquidCrystal library available for us to use. These functions do things like change the position of the text, move text across the screen, or make the display turn on or off. What follows is a short description of each function, and how to use it in a program.
TheLiquidCrystal() function sets the pins the Arduino uses to connect to the LCD. You can use any of the Arduino’s digital pins to control the LCD. Just put the Arduino pin numbers inside the parentheses in this order:
This function sets the dimensions of the LCD. It needs to be placed before any other LiquidCrystal function in the void setup() section of the program. The number of rows and columns are specified as lcd.begin(columns, rows). For a 16×2 LCD, you would use lcd.begin(16, 2), and for a 20×4 LCD you would use lcd.begin(20, 4).
This function clears any text or data already displayed on the LCD. If you use lcd.clear() with lcd.print() and the delay() function in the void loop() section, you can make a simple blinking text program:
Similar, but more useful than lcd.home() is lcd.setCursor(). This function places the cursor (and any printed text) at any position on the screen. It can be used in the void setup() or void loop() section of your program.
The cursor position is defined with lcd.setCursor(column, row). The column and row coordinates start from zero (0-15 and 0-1 respectively). For example, using lcd.setCursor(2, 1) in the void setup() section of the “hello, world!” program above prints “hello, world!” to the lower line and shifts it to the right two spaces:
You can use this function to write different types of data to the LCD, for example the reading from a temperature sensor, or the coordinates from a GPS module. You can also use it to print custom characters that you create yourself (more on this below). Use lcd.write() in the void setup() or void loop() section of your program.
The function lcd.noCursor() turns the cursor off. lcd.cursor() and lcd.noCursor() can be used together in the void loop() section to make a blinking cursor similar to what you see in many text input fields:
Cursors can be placed anywhere on the screen with the lcd.setCursor() function. This code places a blinking cursor directly below the exclamation point in “hello, world!”:
This function creates a block style cursor that blinks on and off at approximately 500 milliseconds per cycle. Use it in the void loop() section. The function lcd.noBlink() disables the blinking block cursor.
This function turns on any text or cursors that have been printed to the LCD screen. The function lcd.noDisplay() turns off any text or cursors printed to the LCD, without clearing it from the LCD’s memory.
This function takes anything printed to the LCD and moves it to the left. It should be used in the void loop() section with a delay command following it. The function will move the text 40 spaces to the left before it loops back to the first character. This code moves the “hello, world!” text to the left, at a rate of one second per character:
Like the lcd.scrollDisplay() functions, the text can be up to 40 characters in length before repeating. At first glance, this function seems less useful than the lcd.scrollDisplay() functions, but it can be very useful for creating animations with custom characters.
lcd.noAutoscroll() turns the lcd.autoscroll() function off. Use this function before or after lcd.autoscroll() in the void loop() section to create sequences of scrolling text or animations.
This function sets the direction that text is printed to the screen. The default mode is from left to right using the command lcd.leftToRight(), but you may find some cases where it’s useful to output text in the reverse direction:
This code prints the “hello, world!” text as “!dlrow ,olleh”. Unless you specify the placement of the cursor with lcd.setCursor(), the text will print from the (0, 1) position and only the first character of the string will be visible.
This command allows you to create your own custom characters. Each character of a 16×2 LCD has a 5 pixel width and an 8 pixel height. Up to 8 different custom characters can be defined in a single program. To design your own characters, you’ll need to make a binary matrix of your custom character from an LCD character generator or map it yourself. This code creates a degree symbol (°):
In this article, you will learn how to use TFT LCDs by Arduino boards. From basic commands to professional designs and technics are all explained here.
In electronic’s projects, creating an interface between user and system is very important. This interface could be created by displaying useful data, a menu, and ease of access. A beautiful design is also very important.
There are several components to achieve this. LEDs, 7-segments, Character and Graphic displays, and full-color TFT LCDs. The right component for your projects depends on the amount of data to be displayed, type of user interaction, and processor capacity.
TFT LCD is a variant of a liquid-crystal display (LCD) that uses thin-film-transistor (TFT) technology to improve image qualities such as addressability and contrast. A TFT LCD is an active matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven LCDs with a few segments.
In Arduino-based projects, the processor frequency is low. So it is not possible to display complex, high definition images and high-speed motions. Therefore, full-color TFT LCDs can only be used to display simple data and commands.
In this article, we have used libraries and advanced technics to display data, charts, menu, etc. with a professional design. This can move your project presentation to a higher level.
In electronic’s projects, creating an interface between user and system is very important. This interface could be created by displaying useful data, a menu, and ease of access. A beautiful design is also very important.
There are several components to achieve this. LEDs, 7-segments, Character and Graphic displays, and full-color TFT LCDs. The right component for your projects depends on the amount of data to be displayed, type of user interaction, and processor capacity.
TFT LCD is a variant of a liquid-crystal display (LCD) that uses thin-film-transistor (TFT) technology to improve image qualities such as addressability and contrast. A TFT LCD is an active matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven LCDs with a few segments.
In Arduino-based projects, the processor frequency is low. So it is not possible to display complex, high definition images and high-speed motions. Therefore, full-color TFT LCDs can only be used to display simple data and commands.
In this article, we have used libraries and advanced technics to display data, charts, menu, etc. with a professional design. This can move your project presentation to a higher level.
Size of displays affects your project parameters. Bigger Display is not always better. if you want to display high-resolution images and signs, you should choose a big size display with higher resolution. But it decreases the speed of your processing, needs more space and also needs more current to run.
After choosing the right display, It’s time to choose the right controller. If you want to display characters, tests, numbers and static images and the speed of display is not important, the Atmega328 Arduino boards (such as Arduino UNO) are a proper choice. If the size of your code is big, The UNO board may not be enough. You can use Arduino Mega2560 instead. And if you want to show high resolution images and motions with high speed, you should use the ARM core Arduino boards such as Arduino DUE.
In electronics/computer hardware a display driver is usually a semiconductor integrated circuit (but may alternatively comprise a state machine made of discrete logic and other components) which provides an interface function between a microprocessor, microcontroller, ASIC or general-purpose peripheral interface and a particular type of display device, e.g. LCD, LED, OLED, ePaper, CRT, Vacuum fluorescent or Nixie.
The display driver will typically accept commands and data using an industry-standard general-purpose serial or parallel interface, such as TTL, CMOS, RS232, SPI, I2C, etc. and generate signals with suitable voltage, current, timing and demultiplexing to make the display show the desired text or image.
The LCDs manufacturers use different drivers in their products. Some of them are more popular and some of them are very unknown. To run your display easily, you should use Arduino LCDs libraries and add them to your code. Otherwise running the display may be very difficult. There are many free libraries you can find on the internet but the important point about the libraries is their compatibility with the LCD’s driver. The driver of your LCD must be known by your library. In this article, we use the Adafruit GFX library and MCUFRIEND KBV library and example codes. You can download them from the following links.
You must add the library and then upload the code. If it is the first time you run an Arduino board, don’t worry. Just follow these steps:Go to www.arduino.cc/en/Main/Software and download the software of your OS. Install the IDE software as instructed.
By these two functions, You can find out the resolution of the display. Just add them to the code and put the outputs in a uint16_t variable. Then read it from the Serial port by Serial.println(); . First add Serial.begin(9600); in setup().
First you should convert your image to hex code. Download the software from the following link. if you don’t want to change the settings of the software, you must invert the color of the image and make the image horizontally mirrored and rotate it 90 degrees counterclockwise. Now add it to the software and convert it. Open the exported file and copy the hex code to Arduino IDE. x and y are locations of the image. sx and sy are sizes of image. you can change the color of the image in the last input.
Upload your image and download the converted file that the UTFT libraries can process. Now copy the hex code to Arduino IDE. x and y are locations of the image. sx and sy are size of the image.
In this template, We converted a .jpg image to .c file and added to the code, wrote a string and used the fade code to display. Then we used scroll code to move the screen left. Download the .h file and add it to the folder of the Arduino sketch.
In this template, We used sin(); and cos(); functions to draw Arcs with our desired thickness and displayed number by text printing function. Then we converted an image to hex code and added them to the code and displayed the image by bitmap function. Then we used draw lines function to change the style of the image. Download the .h file and add it to the folder of the Arduino sketch.
In this template, We created a function which accepts numbers as input and displays them as a pie chart. We just use draw arc and filled circle functions.
In this template, We added a converted image to code and then used two black and white arcs to create the pointer of volumes. Download the .h file and add it to the folder of the Arduino sketch.
In this template, We added a converted image and use the arc and print function to create this gauge. Download the .h file and add it to folder of the Arduino sketch.
In this template, We display simple images one after each other very fast by bitmap function. So you can make your animation by this trick. Download the .h file and add it to folder of the Arduino sketch.
In this template, We just display some images by RGBbitmap and bitmap functions. Just make a code for touchscreen and use this template. Download the .h file and add it to folder of the Arduino sketch.

I2C_LCD is an easy-to-use display module, It can make display easier. Using it can reduce the difficulty of make, so that makers can focus on the core of the work.
We developed the Arduino library for I2C_LCD, user just need a few lines of the code can achieve complex graphics and text display features. It can replace the serial monitor of Arduino in some place, you can get running informations without a computer.
More than that, we also develop the dedicated picture data convert software (bitmap converter)now is available to support PC platform of windows, Linux, Mac OS. Through the bitmap convert software you can get your favorite picture displayed on I2C_LCD, without the need for complex programming.
Select the board: Click Tools > Board > "Arduino Duemilanove or Diecimila"(Seeeduino V3.0 Or early version), "Arduino Uno"(Seeeduino Lotus or Seeeduino V4.0).

The Arduino board has a wide variety of compatible displays that you can use in your electronic projects. In most projects, it’s very useful to give the user some sort of feedback from the Arduino.
With the TFT display you can display colorful images or graphics. This module has a resolution of 480 x 320. This module includes the SD card socket and SPI FLASH circuit.
This is a tiny display with just 1 x 0.96 Inch. This display has a black background, and displays characters in white. There are other similar displays that can show the characters in other colors.
Development board is a printed circuit board with circuitry and hardware on-board to facilitate experimentation with certain microcontrollers. These boards can save you from a lot of repetitive tasks. Arduino is a Development Board.
Crystal Oscillator : The crystal oscillator helps Arduino in dealing with time issues. Arduino calculates time by using the crystal oscillator. The number printed on top of the Arduino crystal is 16.000H9H. It tells us that the frequency is 16,000,000 Hertz or 16 MHz.
The Arduino UNO board has6 analog input pins A0 through A5. These pins can read the signal from an analog sensor like the humidity sensor or temperature sensor and convert it into a digital value that can be read by the microprocessor.
Each Arduino board has its own microcontroller (11). You can assume it as the brain of your board. The main IC (integrated circuit) on the Arduino is slightly different from board to board. Arduino consists of ATMega328P.
9. TX and RX Pins: On the board, there are find two labels: TX (transmit) and RX (receive).They appear in two places on the Arduino UNO board.First, at the digital pins 0 and 1, to indicate the pins responsible for serial communication.
10. Digital I/O Pins:The Arduino UNO board has 14 digital I/O pins(of which 6 provide PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) output. These pins can be configured to work as input digital pins to read logic values (0 or 1) or as digital output pins to drive different modules like LEDs, relays, etc. The pins labeled “~” can be used to generate PWM.
lcd.begin(rows,cols): Initializes the interface to the LCD screen, and specifies the dimensions (width and height) of the display. It needs to be called before any other LCD library commands. We have 16 rows and 2 columns.

Cheap LCD Modules, Buy Quality Electronic Components & Supplies Directly from China Suppliers:3.5 inch TFT Touch Screen LCD Module Display 320*480 intelligent LCD Adapter for ar…




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey