2.0 spi tft lcd arduino free sample
![]()
This module is a 2-inch TFT LCD module with “220×176” resolution and 65K color display. It is suitable for Arduino Uno and Mega2560 development boards, and also supports SD card expansion function. The driver IC is ILI9225.
The 2-inch display is a ready-made shield for Arduino Uno, which can also be placed on the Arduino Mega. The pins of this shield are designed to be easily installed on the Arduino.
my_lcd.Fill_Triangle(x_spec+i*side_len-1,y_spec+(i+1)*h_len-1,x_spec+side_len/2+i*side_len-1,y_spec+i*h_len-1,x_spec+(i+1)*side_len-1,y_spec+(i+1)*h_len-1);
my_lcd.Fill_Triangle(x_spec+i*side_len-1,y_spec+(5-i)*h_len-1,x_spec+side_len/2+i*side_len-1,y_spec+(4-i)*h_len-1,x_spec+(i+1)*side_len-1,y_spec+(5-i)*h_len-1);
my_lcd.Draw_Line(2+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Width()-4),12+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Height()-24),2+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Width()-4),12+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Height()-24));
my_lcd.Draw_Rectangle(2+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Width()-4),12+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Height()-24),2+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Width()-4),12+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Height()-24));
my_lcd.Draw_Round_Rectangle(2+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Width()-4),13+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Height()-26),2+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Width()-4),13+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Height()-26),5);
my_lcd.Draw_Triangle(2+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Width()-4),12+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Height()-24),2+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Width()-4),12+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Height()-24),2+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Width()-4),12+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Height()-24));
my_lcd.Fill_Round_Rectangle(my_lcd.Get_Display_Width()/2-1-72+1, my_lcd.Get_Display_Height()/2-1-45+1, my_lcd.Get_Display_Width()/2-1+72-1, my_lcd.Get_Display_Height()/2-1+45-1,5);

The ST7789 TFT module contains a display controller with the same name: ST7789. It’s a color display that uses SPI interface protocol and requires 3, 4 or 5 control pins, it’s low cost and easy to use. This display is an IPS display, it comes in different sizes (1.3″, 1.54″ …) but all of them should have the same resolution of 240×240 pixel, this means it has 57600 pixels. This module works with 3.3V only and it doesn’t support 5V (not 5V tolerant).
As mentioned above, the ST7789 TFT display controller works with 3.3V only (power supply and control lines). The display module is supplied with 3.3V (between VCC and GND) which comes from the Arduino board.
To connect the Arduino to the display module, I used voltage divider for each line which means there are 4 voltage dividers. Each voltage divider consists of 2.2k and 3.3k resistors, this drops the 5V into 3V which is sufficient.
The first library is a driver for the ST7789 TFT display which can be installed from Arduino IDE library manager (Sketch —> Include Library —> Manage Libraries …, in the search box write “st7789” and install the one from Adafruit).

In this Arduino touch screen tutorial we will learn how to use TFT LCD Touch Screen with Arduino. You can watch the following video or read the written tutorial below.
As an example I am using a 3.2” TFT Touch Screen in a combination with a TFT LCD Arduino Mega Shield. We need a shield because the TFT Touch screen works at 3.3V and the Arduino Mega outputs are 5 V. For the first example I have the HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor, then for the second example an RGB LED with three resistors and a push button for the game example. Also I had to make a custom made pin header like this, by soldering pin headers and bend on of them so I could insert them in between the Arduino Board and the TFT Shield.
Here’s the circuit schematic. We will use the GND pin, the digital pins from 8 to 13, as well as the pin number 14. As the 5V pins are already used by the TFT Screen I will use the pin number 13 as VCC, by setting it right away high in the setup section of code.
I will use the UTFT and URTouch libraries made by Henning Karlsen. Here I would like to say thanks to him for the incredible work he has done. The libraries enable really easy use of the TFT Screens, and they work with many different TFT screens sizes, shields and controllers. You can download these libraries from his website, RinkyDinkElectronics.com and also find a lot of demo examples and detailed documentation of how to use them.
After we include the libraries we need to create UTFT and URTouch objects. The parameters of these objects depends on the model of the TFT Screen and Shield and these details can be also found in the documentation of the libraries.
So now I will explain how we can make the home screen of the program. With the setBackColor() function we need to set the background color of the text, black one in our case. Then we need to set the color to white, set the big font and using the print() function, we will print the string “Arduino TFT Tutorial” at the center of the screen and 10 pixels down the Y – Axis of the screen. Next we will set the color to red and draw the red line below the text. After that we need to set the color back to white, and print the two other strings, “by HowToMechatronics.com” using the small font and “Select Example” using the big font.
In order the code to work and compile you will have to include an addition “.c” file in the same directory with the Arduino sketch. This file is for the third game example and it’s a bitmap of the bird. For more details how this part of the code work you can check my particular tutorial. Here you can download that file:

An excellent new compatible library is available which can render TrueType fonts on a TFT screen (or into a sprite). This has been developed by takkaO and is available here. I have been reluctant to support yet another font format but this is an amazing library which is very easy to use. It provides access to compact font files, with fully scaleable anti-aliased glyphs. Left, middle and right justified text can also be printed to the screen. I have added TFT_eSPI specific examples to the OpenFontRender library and tested on RP2040 and ESP32 processors, however the ESP8266 does not have sufficient RAM. Here is a demo screen where a single 12kbyte font file binary was used to render fully anti-aliased glyphs of gradually increasing size on a 320x480 TFT screen:
For ESP32 ONLY, the TFT configuration (user setup) can now be included inside an Arduino IDE sketch providing the instructions in the example Generic->Sketch_with_tft_setup are followed. See ReadMe tab in that sketch for the instructions. If the setup is not in the sketch then the library settings will be used. This means that "per project" configurations are possible without modifying the library setup files. Please note that ALL the other examples in the library will use the library settings unless they are adapted and the "tft_setup.h" header file included. Note: there are issues with this approach, #2007 proposes an alternative method.
Support for the ESP32-S2, ESP32-S3 and ESP32-C3 has been added (DMA not supported at the moment). Tested with v2.0.3 RC1 of the ESP32 board package. Example setups:
Smooth fonts can now be rendered direct to the TFT with very little flicker for quickly changing values. This is achieved by a line-by-line and block-by-block update of the glyph area without drawing pixels twice. This is a "breaking" change for some sketches because a new true/false parameter is needed to render the background. The default is false if the parameter is missing, Examples:
Frank Boesing has created an extension library for TFT_eSPI that allows a large range of ready-built fonts to be used. Frank"s library (adapted to permit rendering in sprites as well as TFT) can be downloaded here. More than 3300 additional Fonts are available here. The TFT_eSPI_ext library contains examples that demonstrate the use of the fonts.
Users of PowerPoint experienced with running macros may be interested in the pptm sketch generator here, this converts graphics and tables drawn in PowerPoint slides into an Arduino sketch that renders the graphics on a 480x320 TFT. This is based on VB macros created by Kris Kasprzak here.
The RP2040 8 bit parallel interface uses the PIO. The PIO now manages the "setWindow" and "block fill" actions, releasing the processor for other tasks when areas of the screen are being filled with a colour. The PIO can optionally be used for SPI interface displays if #define RP2040_PIO_SPI is put in the setup file. Touch screens and pixel read operations are not supported when the PIO interface is used.
The use of PIO for SPI allows the RP2040 to be over-clocked (up to 250MHz works on my boards) in Earle"s board package whilst still maintaining high SPI clock rates.
DMA can now be used with the Raspberry Pi Pico (RP2040) when used with both 8 bit parallel and 16 bit colour SPI displays. See "Bouncy_Circles" sketch.
The library now supports the Raspberry Pi Pico with both the official Arduino board package and the one provided by Earle Philhower. The setup file "Setup60_RP2040_ILI9341.h" has been used for tests with an ILI9341 display. At the moment only SPI interface displays have been tested. SPI port 0 is the default but SPI port 1 can be specifed in the setup file if those SPI pins are used.
The library now provides a "viewport" capability. See "Viewport_Demo" and "Viewport_graphicstest" examples. When a viewport is defined graphics will only appear within that window. The coordinate datum by default moves to the top left corner of the viewport, but can optionally remain at top left corner of TFT. The GUIslice library will make use of this feature to speed up the rendering of GUI objects (see #769).
An Arduino IDE compatible graphics and fonts library for 32 bit processors. The library is targeted at 32 bit processors, it has been performance optimised for RP2040, STM32, ESP8266 and ESP32 types, other processors may be used but will use the slower generic Arduino interface calls. The library can be loaded using the Arduino IDE"s Library Manager. Direct Memory Access (DMA) can be used with the ESP32, RP2040 and STM32 processors with SPI interface displays to improve rendering performance. DMA with a parallel interface (8 and 16 bit parallel) is only supported with the RP2040.
For other processors only SPI interface displays are supported and the slower Arduino SPI library functions are used by the library. Higher clock speed processors such as used for the Teensy 3.x and 4.x boards will still provide a very good performance with the generic Arduino SPI functions.
"Four wire" SPI and 8 bit parallel interfaces are supported. Due to lack of GPIO pins the 8 bit parallel interface is NOT supported on the ESP8266. 8 bit parallel interface TFTs (e.g. UNO format mcufriend shields) can used with the STM32 Nucleo 64/144 range or the UNO format ESP32 (see below for ESP32).
The library supports some TFT displays designed for the Raspberry Pi (RPi) that are based on a ILI9486 or ST7796 driver chip with a 480 x 320 pixel screen. The ILI9486 RPi display must be of the Waveshare design and use a 16 bit serial interface based on the 74HC04, 74HC4040 and 2 x 74HC4094 logic chips. Note that due to design variations between these displays not all RPi displays will work with this library, so purchasing a RPi display of these types solely for use with this library is NOT recommended.
Some displays permit the internal TFT screen RAM to be read, a few of the examples use this feature. The TFT_Screen_Capture example allows full screens to be captured and sent to a PC, this is handy to create program documentation.
The library includes a "Sprite" class, this enables flicker free updates of complex graphics. Direct writes to the TFT with graphics functions are still available, so existing sketches do not need to be changed.
A Sprite is notionally an invisible graphics screen that is kept in the processors RAM. Graphics can be drawn into the Sprite just as they can be drawn directly to the screen. Once the Sprite is completed it can be plotted onto the screen in any position. If there is sufficient RAM then the Sprite can be the same size as the screen and used as a frame buffer. Sprites by default use 16 bit colours, the bit depth can be set to 8 bits (256 colours) , or 1 bit (any 2 colours) to reduce the RAM needed. On an ESP8266 the largest 16 bit colour Sprite that can be created is about 160x128 pixels, this consumes 40Kbytes of RAM. On an ESP32 the workspace RAM is more limited than the datasheet implies so a 16 bit colour Sprite is limited to about 200x200 pixels (~80Kbytes), an 8 bit sprite to 320x240 pixels (~76kbytes). A 1 bit per pixel Sprite requires only 9600 bytes for a full 320 x 240 screen buffer, this is ideal for supporting use with 2 colour bitmap fonts.
If an ESP32 board has SPIRAM (i.e. PSRAM) fitted then Sprites will use the PSRAM memory and large full screen buffer Sprites can be created. Full screen Sprites take longer to render (~45ms for a 320 x 240 16 bit Sprite), so bear that in mind.
The "Animated_dial" example shows how dials can be created using a rotated Sprite for the needle. To run this example the TFT interface must support reading from the screen RAM (not all do). The dial rim and scale is a jpeg image, created using a paint program.
The XPT2046 touch screen controller is supported for SPI based displays only. The SPI bus for the touch controller is shared with the TFT and only an additional chip select line is needed. This support will eventually be deprecated when a suitable touch screen library is available.
The library supports SPI overlap on the ESP8266 so the TFT screen can share MOSI, MISO and SCLK pins with the program FLASH, this frees up GPIO pins for other uses. Only one SPI device can be connected to the FLASH pins and the chips select for the TFT must be on pin D3 (GPIO0).
The library contains proportional fonts, different sizes can be enabled/disabled at compile time to optimise the use of FLASH memory. Anti-aliased (smooth) font files in vlw format stored in SPIFFS are supported. Any 16 bit Unicode character can be included and rendered, this means many language specific characters can be rendered to the screen.
Configuration of the library font selections, pins used to interface with the TFT and other features is made by editing the User_Setup.h file in the library folder, or by selecting your own configuration in the "User_Setup_Selet,h" file. Fonts and features can easily be enabled/disabled by commenting out lines.
The .vlw files must be uploaded to the processors FLASH filing system (SPIFFS, LittleFS or SD card) for use. Alternatively the .vlw files can be converted to C arrays (see "Smooth Font -> FLASH_Array" examples) and stored directly in FLASH as part of the compile process. The array based approach is convenient, provides performance improvements and is suitable where: either use of a filing system is undesirable, or the processor type (e.g. STM32) does not support a FLASH based filing system.
It would be possible to compress the vlw font files but the rendering performance to a TFT is still good when storing the font file(s) in SPIFFS, LittleFS or FLASH arrays.
Anti-aliased fonts can also be drawn over a gradient background with a callback to fetch the background colour of each pixel. This pixel colour can be set by the gradient algorithm or by reading back the TFT screen memory (if reading the display is supported).
Unfortunately the typical UNO/mcufriend TFT display board maps LCD_RD, LCD_CS and LCD_RST signals to the ESP32 analogue pins 35, 34 and 36 which are input only. To solve this I linked in the 3 spare pins IO15, IO33 and IO32 by adding wires to the bottom of the board as follows:
If you load a new copy of TFT_eSPI then it will overwrite your setups if they are kept within the TFT_eSPI folder. One way around this is to create a new folder in your Arduino library folder called "TFT_eSPI_Setups". You then place your custom setup.h files in there. After an upgrade simply edit the User_Setup_Select.h file to point to your custom setup file e.g.:
The library was intended to support only TFT displays but using a Sprite as a 1 bit per pixel screen buffer permits support for the Waveshare 2 and 3 colour SPI ePaper displays. This addition to the library is experimental and only one example is provided. Further examples will be added.
Minimal bit-bang send serial 115200 or 38400 baud for 1 MHz or 230400 baud for 8/16 MHz ATtiny clock.Perfect for debugging purposes.Code size is only 76 bytes@38400 baud or 196 bytes@115200 baud (including first call)
This library enables you to use Hardware-based PWM channels on Arduino AVR ATtiny-based boards (ATtiny3217, etc.), using megaTinyCore, to create and output PWM to pins.
This library enables you to use ISR-based PWM channels on Arduino AVR ATtiny-based boards (ATtiny3217, etc.), using megaTinyCore, to create and output PWM any GPIO pin.
Small low-level classes and functions for Arduino: incrementMod(), decToBcd(). strcmp_PP(), PrintStr, PrintStrN, printPad{N}To(), printIntAsFloat(), TimingStats, formUrlEncode(), FCString, KString, hashDjb2(), binarySearch(), linearSearch(), isSorted(), reverse(), and so on.
Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) algorithms (crc8, crc16ccitt, crc32) programmatically converted from C99 code generated by pycrc (https://pycrc.org) to Arduino C++ using namespaces and PROGMEM flash memory.
Various sorting algorithms for Arduino, including Bubble Sort, Insertion Sort, Selection Sort, Shell Sort (3 versions), Comb Sort (4 versions), Quick Sort (3 versions).
Date, time, timezone classes for Arduino supporting the full IANA TZ Database to convert epoch seconds to date and time components in different time zones.
Clock classes for Arduino that provides an auto-incrementing count of seconds since a known epoch which can be synchronized from external sources such as an NTP server, a DS3231 RTC chip, or an STM32 RTC chip.
Useful Arduino utilities which are too small as separate libraries, but complex enough to be shared among multiple projects, and often have external dependencies to other libraries.
Fast and compact software I2C implementations (SimpleWireInterface, SimpleWireFastInterface) on Arduino platforms. Also provides adapter classes to allow the use of third party I2C libraries using the same API.
Enables Bluetooth® Low Energy connectivity on the Arduino MKR WiFi 1010, Arduino UNO WiFi Rev.2, Arduino Nano 33 IoT, Arduino Nano 33 BLE and Nicla Sense ME.
Fully Asynchronous UDP Library for RASPBERRY_PI_PICO_W using CYW43439 WiFi with arduino-pico core. The library is easy to use and includes support for Unicast, Broadcast and Multicast environments.
The last hope for the desperate AVR programmer. A small (344 bytes) Arduino library to have real program traces and to find the place where your program hangs.
Enable inclusion of both ESP32 Blynk BT/BLE and WiFi libraries. Then select one at reboot or run both. Eliminate hardcoding your Wifi and Blynk credentials and configuration data saved in either LittleFS, SPIFFS or EEPROM.
Simple Ethernet Manager for MultiBlynk for Teensy, SAM DUE, SAMD21, SAMD51, nRF52, ESP32, ESP8266, RP2040-based (Nano_RP2040_Connect, RASPBERRY_PI_PICO) boards, etc. with or without SSL, configuration data saved in ESP8266/ESP32 LittleFS, SPIFFS, nRF52/RP2040 LittleFS/InternalFS, EEPROM, DueFlashStorage or SAMD FlashStorage.
Simple GSM shield Credentials Manager for Blynk and ESP32 / ESP8266 boards, with or without SSL, configuration data saved in LittleFS / SPIFFS / EEPROM.
Simple WiFiManager for Blynk and ESP32 with or without SSL, configuration data saved in either SPIFFS or EEPROM. Enable inclusion of both ESP32 Blynk BT/BLE and WiFi libraries. Then select one at reboot or run both. Eliminate hardcoding your Wifi and Blynk credentials and configuration data saved in either LittleFS, SPIFFS or EEPROM. Using AsyncWebServer instead of WebServer, with WiFi networks scanning for selection in Configuration Portal.
Simple GSM shield Credentials Manager for Blynk and ESP32 / ESP8266 boards, with or without SSL, configuration data saved in LittleFS / SPIFFS / EEPROM.
Simple Async WiFiManager for Blynk and ESP32 (including ESP32-S2, ESP32-C3), ESP8266 with or without SSL, configuration data saved in either LittleFS, SPIFFS or EEPROM. Now working with new ESP8266 core v3.0.1 and ESP32 core v1.0.6
Simple WiFiManager for Blynk and ESP32 (including ESP32-S2, ESP32-C3), ESP8266 with or without SSL, configuration data saved in either LittleFS, SPIFFS or EEPROM. Now working with new ESP8266 core v3.0.0 and ESP32 core v1.0.6
An Arduino library that takes input in degrees and output a string or integer for the 4, 8, 16, or 32 compass headings (like North, South, East, and West).
Library to detect a double reset, using EEPROM, DueFlashStorage, FlashStorage_SAMD, FlashStorage_RTL8720, FlashStorage_STM32 or LittleFS/InternalFS. For AVR, Teensy, SAM DUE, SAMD, STM32F/L/H/G/WB/MP1, nRF52, RP2040-based Nano_RP2040_Connect, RASPBERRY_PI_PICO, RTL8720DN, MBED nRF52840-based Nano_33_BLE, Portenta_H7, etc. boards. Now using efficient FlashStorage_STM32 library and supporting new RP2040-based Nano_RP2040_Connect, Portenta_H7, RASPBERRY_PI_PICO and STM32 core v2.0.0
Directly interface Arduino, esp8266, and esp32 to DSC PowerSeries and Classic security systems for integration with home automation, remote control apps, notifications on alarm events, and emulating DSC panels to connect DSC keypads.
This library enables you to use Hardware-based PWM channels on Arduino AVRDx-based boards (AVR128Dx, AVR64Dx, AVR32Dx, etc.), using DxCore, to create and output PWM.
This library enables you to use ISR-based PWM channels on Arduino AVRDx-based boards (AVR128Dx, AVR64Dx, AVR32Dx, etc.), using DxCore, to create and output PWM any GPIO pin.
Small and easy to use Arduino library for using push buttons at INT0/pin2 and / or any PinChangeInterrupt pin.Functions for long and double press detection are included.Just connect buttons between ground and any pin of your Arduino - that"s itNo call of begin() or polling function like update() required. No blocking debouncing delay.
Arduino library for controlling standard LEDs in an easy way. EasyLed provides simple logical methods like led.on(), led.toggle(), led.flash(), led.isOff() and more.
OpenTherm Library to control Central Heating (CH), HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, Air Conditioning) or Solar systems by creating a thermostat using Arduino IDE and ESP32 / ESP8266 hardware.
An ESP8266/ESP32-AT library for Arduino providing an easy-to-use way to control ESP8266-AT/ESP32-AT WiFi shields using AT-commands. For AVR, Teensy, SAM DUE, SAMD21, SAMD51, STM32, nRF52, SIPEED_MAIX_DUINO and RP2040-based (Nano_RP2040_Connect, RASPBERRY_PI_PICO, etc.) boards using ESP8266/ESP32 AT-command shields.
Library to detect a multi reset within a predetermined time, using RTC Memory, EEPROM, LittleFS or SPIFFS for ESP8266 and ESP32, ESP32_C3, ESP32_S2, ESP32_S3
Simple Ethernet WebServer, HTTP Client and WebSocket Client library for AVR, AVR Dx, Portenta_H7, Teensy, SAM DUE, SAMD21, SAMD51, STM32F/L/H/G/WB/MP1, nRF52 and RASPBERRY_PI_PICO boards using Ethernet shields W5100, W5200, W5500, ENC28J60 or Teensy 4.1 NativeEthernet/QNEthernet
Simple TLS/SSL Ethernet WebServer, HTTP Client and WebSocket Client library for for AVR, Portenta_H7, Teensy, SAM DUE, SAMD21, SAMD51, STM32F/L/H/G/WB/MP1, nRF52 and RASPBERRY_PI_PICO boards using Ethernet shields W5100, W5200, W5500, ENC28J60 or Teensy 4.1 NativeEthernet/QNEthernet. It now supports Ethernet TLS/SSL Client.
Simple Ethernet library for AVR, AVR Dx, Portenta_H7, Teensy, SAM DUE, SAMD21, SAMD51, STM32F/L/H/G/WB/MP1, nRF52 and RASPBERRY_PI_PICO boards using Ethernet shields W5100, W5200, W5500, W5100S
Simple Ethernet Manager for Teensy, SAM DUE, SAMD, nRF52, ESP32 (including ESP32-S2/C3), ESP8266, RP2040-based Nano_RP2040_Connect, RASPBERRY_PI_PICO, etc. boards. Config data saved in ESP LittleFS, SPIFFS or EEPROM, nRF52 LittleFS, EEPROM, DueFlashStorage or SAMD FlashStorage.
ezTime - pronounced "Easy Time" - is a very easy to use Arduino time and date library that provides NTP network time lookups, extensive timezone support, formatted time and date strings, user events, millisecond precision and more.
A library for implementing fixed-point in-place Fast Fourier Transform on Arduino. It sacrifices precision and instead it is way faster than floating-point implementations.
The FlashStorage_STM32 library aims to provide a convenient way to store and retrieve user data using the non-volatile flash memory of STM32F/L/H/G/WB/MP1. It is using the buffered read and write to minimize the access to Flash. It now supports writing and reading the whole object, not just byte-and-byte. New STM32 core v2.0.0+ is also supported now.
The FlashStorage_STM32F1 library aims to provide a convenient way to store and retrieve user"s data using the non-volatile flash memory of STM32F1/F3. It"s using the buffered read and write to minimize the access to Flash. It now supports writing and reading the whole object, not just byte-and-byte. New STM32 core v2.0.0+ is supported now.
The GCodeParser library is a lightweight G-Code parser for the Arduino using only a single character buffer to first collect a line of code (also called a "block") from a serial or file input and then parse that line into a code block and comments.
Arduino library for the Flysky/Turnigy RC iBUS protocol - servo (receive) and sensors/telemetry (send) using hardware UART (AVR, ESP32 and STM32 architectures)
An Arduino library to control the Iowa Scaled Engineering I2C-IRSENSE ( https://www.iascaled.com/store/I2C-IRSENSE ) reflective infrared proximity sensor.
Treat PCF8574, MCP23017 and Shift registers like pins, matrix keypad, touch screen handler, button press and rotary encoder management (switches) on any supported IO (including DfRobot & Joysticks) with event handling, interchangable AVR/I2C(AT24) EEPROMs.
Convinient way to map a push-button to a keyboard key. This library utilize the ability of 32u4-based Arduino-compatible boards to emulate USB-keyboard.
This library allows you to easily create light animations from an Arduino board or an ATtiny microcontroller (traffic lights, chaser, shopkeeper sign, etc.)
LiquidCrystal fork for displays based on HD44780. Uses the IOAbstraction library to work with i2c, PCF8574, MCP23017, Shift registers, Arduino pins and ports interchangably.
This library enables you to use ISR-based PWM channels on RP2040-based boards, such as Nano_RP2040_Connect, RASPBERRY_PI_PICO, with Arduino-mbed (mbed_nano or mbed_rp2040) core to create and output PWM any GPIO pin.
Arduino library for MCP4728 quad channel, 12-bit voltage output Digital-to-Analog Convertor with non-volatile memory and I2C compatible Serial Interface
This library enables you to use ISR-based PWM channels on an Arduino megaAVR board, such as UNO WiFi Rev2, AVR_Nano_Every, etc., to create and output PWM any GPIO pin.
Replace Arduino methods with mocked versions and let you develop code without the hardware. Run parallel hardware and system development for greater efficiency.
A library package for ARDUINO acting as ModBus slave communicating through UART-to-RS485 converter. Originally written by Geabong github user. Improved by Łukasz Ślusarczyk.
Library to detect a multi reset, using EEPROM, DueFlashStorage, FlashStorage_SAMD, FlashStorage_RTL8720, FlashStorage_STM32 or LittleFS/InternalFS. For AVR, Teensy, SAM DUE, SAMD, STM32F/L/H/G/WB/MP1, nRF52, RP2040-based Nano_RP2040_Connect, RASPBERRY_PI_PICO, RTL8720DN, MBED nRF52840-based Nano_33_BLE, Portenta_H7, etc. boards. Now using efficient FlashStorage_STM32 library and supporting new RP2040-based Nano_RP2040_Connect, RASPBERRY_PI_PICO and STM32 core v2.0.0
This library enables you to use ISR-based PWM channels on an nRF52-based board using Arduino-mbed mbed_nano core such as Nano-33-BLE to create and output PWM any GPIO pin.
This library enables you to use ISR-based PWM channels on an nRF52-based board using Adafruit_nRF52_Arduino core such as Itsy-Bitsy nRF52840 to create and output PWM any GPIO pin.
An Arduino library for the Nano 33 BLE Sense that leverages Mbed OS to automatically place sensor measurements in a ring buffer that can be integrated into programs in a simple manner.
his library enables you to use Hardware-based PWM channels on RP2040-based boards, such as Nano_RP2040_Connect, RASPBERRY_PI_PICO, with either Arduino-mbed (mbed_nano or mbed_rp2040) or arduino-pico core to create and output PWM to any GPIO pin.
This library enables you to use SPI SD cards with RP2040-based boards such as Nano_RP2040_Connect, RASPBERRY_PI_PICO using either RP2040 Arduino-mbed or arduino-pico core.
This library enables you to use ISR-based PWM channels on RP2040-based boards, such as ADAFRUIT_FEATHER_RP2040, RASPBERRY_PI_PICO, etc., with arduino-pico core to create and output PWM any GPIO pin.
The most powerful and popular available library for using 7/14/16 segment display, supporting daisy chaining so you can control mass amounts from your Arduino!
Enables smooth servo movement. Linear as well as other (Cubic, Circular, Bounce, etc.) ease movements for servos are provided. The Arduino Servo library or PCA9685 servo expanders are supported.
Use the low-power high-resolution ICM 20948 9 DoF IMU from Invensense with I2C or SPI. Version 1.2 of the library includes support for the InvenSense Digital Motion Processor (DMP™).
Enables reading and writing on SD card using SD card slot connected to the SDIO/SDMMC-hardware of the STM32 MCU. For slots connected to SPI-hardware use the standard Arduino SD library.
Menu library for Arduino with IoT capabilities that supports many input and display devices with a designer UI, code generator, CLI, and strong remote control capability.
Adds tcUnicode UTF-8 support to Adafruit_GFX, U8G2, tcMenu, and TFT_eSPI graphics libraries with a graphical font creation utility available. Works with existing libraries
A library for creating Tickers which can call repeating functions. Replaces delay() with non-blocking functions. Recommanded for ESP and Arduino boards with mbed behind.
This library enables you to use Interrupt from Hardware Timers on an Arduino, Adafruit or Sparkfun AVR board, such as Nano, UNO, Mega, Leonardo, YUN, Teensy, Feather_32u4, Feather_328P, Pro Micro, etc.
This library enables you to use Interrupt from Hardware Timers on supported Arduino boards such as AVR, Mega-AVR, ESP8266, ESP32, SAMD, SAM DUE, nRF52, STM32F/L/H/G/WB/MP1, Teensy, Nano-33-BLE, RP2040-based boards, etc.
Really tiny library to basic RTC functionality on Arduino. DS1307, DS3231 and DS3232 RTCs are supported. See https://github.com/Naguissa/uEEPROMLib for EEPROM support. Temperature, Alarms, SQWG, Power lost and RAM support.
Monochrome LCD, OLED and eInk Library. Display controller: SSD1305, SSD1306, SSD1309, SSD1312, SSD1316, SSD1318, SSD1320, SSD1322, SSD1325, SSD1327, SSD1329, SSD1606, SSD1607, SH1106, SH1107, SH1108, SH1122, T6963, RA8835, LC7981, PCD8544, PCF8812, HX1230, UC1601, UC1604, UC1608, UC1610, UC1611, UC1617, UC1638, UC1701, ST7511, ST7528, ST7565, ST7567, ST7571, ST7586, ST7588, ST75160, ST75256, ST75320, NT7534, ST7920, IST3020, IST3088, IST7920, LD7032, KS0108, KS0713, HD44102, T7932, SED1520, SBN1661, IL3820, MAX7219, GP1287, GP1247, GU800. Interfaces: I2C, SPI, Parallel.
True color TFT and OLED library, Up to 18 Bit color depth. Supported display controller: ST7735, ILI9163, ILI9325, ILI9341, ILI9486,LD50T6160, PCF8833, SEPS225, SSD1331, SSD1351, HX8352C.
RFC6455-based WebSockets Server and Client for Arduino boards, such as nRF52, Portenta_H7, SAMD21, SAMD51, STM32F/L/H/G/WB/MP1, Teensy, SAM DUE, RP2040-based boards, besides ESP8266/ESP32 (ESP32, ESP32_S2, ESP32_S3 and ESP32_C3) and WT32_ETH01. Ethernet shields W5100, W5200, W5500, ENC28J60, Teensy 4.1 NativeEthernet/QNEthernet or Portenta_H7 WiFi/Ethernet. Supporting websocket only mode for Socket.IO. Ethernet_Generic library is used as default for W5x00. Now supporting RP2040W
Enables network connection (local and Internet) and WiFiStorage for SAM DUE, SAMD21, SAMD51, Teensy, AVR (328P, 32u4, 16u4, etc.), Mega, STM32F/L/H/G/WB/MP1, nRF52, NINA_B302_ublox, NINA_B112_ublox, RP2040-based boards, etc. in addition to Arduino MKR WiFi 1010, Arduino MKR VIDOR 4000, Arduino UNO WiFi Rev.2, Nano 33 IoT, Nano RP2040 Connect. Now with fix of severe limitation to permit sending much larger data than total 4K and using new WiFi101_Generic library
Universal Timer with 1 millisecond resolution, based on system uptime (i.e. Arduino: millis() function or STM32: HAL_GetTick() function), supporting OOP principles.
Hi guys, over the past few tutorials, we have been discussing TFT displays, how to connect and use them in Arduino projects, especially the 1.8″ Colored TFT display. In a similar way, we will look at how to use the 1.44″ TFT Display (ILI9163C) with the Arduino.
The ILI9163C based 1.44″ colored TFT Display, is a SPI protocol based display with a resolution of 128 x 128 pixels. It’s capable of displaying up to 262,000 different colors. The module can be said to be a sibling to the 1.8″ TFT display, except for the fact that it is much faster and has a better, overall cost to performance ratio when compared with the 1.8″ TFT display. Some of the features of the display are listed below;
TheTFT Display, as earlier stated, communicates with the microcontroller over SPI, thus to use it, we need to connect it to the SPI pins of the Arduino as shown in the schematics below.
Please note that the version of the display used for this tutorial is not available on fritzing which is the software used for the schematics, so follow the pin connection list below to further understand how each pin of the TFT display should be connected to the Arduino.
When connecting the display, ensure that has a voltage regulator (shown in the image below) before connecting it directly to the 5v logic level of the Arduino. This is because the display could be destroyed if the version of the display you have does not have the regulator.
In order to allow the Arduino to work with the display, we need two Arduino libraries; the sumotoy TFT ILI9163C Arduino library which can be downloaded from this link and the popular Adafruit GFX Arduino library which we have used extensively in several tutorials. Download these libraries and install them in the Arduino IDE.
For today’s tutorial, we will be using the bigtest example which is one of the example codes that comes with the sumotoy ILI9163C Arduino library to show how to use the TFT display.
The example can be opened by going to File–>Examples–>TFT_ILI9163c–>bigtest as shown in the image below. It should be noted that this will only be available after the sumotoy library has been installed.
Next, an object of the ILI9163c library named “display” was created with CS and DC parameter as inputs but due to the kind of display being used, we need to include the pin of the Arduino to which the A0 pin of the TFT display is connected which is D8.
With the libraries installed, open an instance of the Arduino IDE, open the examples as described initially, don’t forget to make the A0 pin (D8) correction to the code then upload to the Arduino board. You should see different kind of text and graphics being displayed on the screen. I captured the screen in action and its shown in the image below.

TFT displays bring life to the project. Why shy with the LCD character display? OLED displays look good and stand out too but small size and limited colors limit the application to basic graphics but are still colorless. No color? No life!
Having the option of TFT display in your next Arduino project can add so many vibrant menu options, can display images, and hence can be a very rich user experience thing.
In this article, you will get a working Arduino project which has a simulated TFT display. The display will exactly work in the same way how it would work in the real world and with the real hardware. You can try any TFT project you have!
Let us get started. You will complete the code, connection diagram as well as live working Arduino simulation link so that you can start playing with the code instantly! For more information on the Simulated TFT display,click here.

This is a simple guide about SPI communication protocol with the ESP32 using Arduino IDE. We’ll take a look at the ESP32 SPI pins, how to connect SPI devices, define custom SPI pins, how to use multiple SPI devices, and much more.
This tutorial focus on programming the ESP32 using the Arduino core, so before proceeding, you should have the ESP32 add-on installed in your Arduino IDE. Follow the next tutorial to install the ESP32 on the Arduino IDE, if you haven’t already.
SPI stands for Serial Peripheral Interface, and it is a synchronous serial data protocol used by microcontrollers to communicate with one or more peripherals. For example, your ESP32 board communicating with a sensor that supports SPI or with another microcontroller.
In an SPI communication, there is always a controller(also called master) that controls the peripheraldevices (also called slaves). Data can be sent and received simultaneously. This means that the master can send data to a slave, and a slave can send data to the master at the same time.
Warning: depending on the board you’re using, the default SPI pins might be different. So, make sure you check the pinout for the board you’re using. Additionally, some boards don’t have pre-assigned SPI pins, so you need to set them on code.
When using libraries to interface with your SPI peripherals, it’s usually simple to use custom SPI pins because you can pass them as arguments to the library constructor.
If you’re not using a library, or the library you’re using doesn’t accept the pins in the library constructor, you may need to initialize the SPI bus yourself. In that case, you would need to call the SPI.begin() method on the setup() and pass the SPI pins as arguments:
You can see an example of this scenario in this tutorial, in which we initialize an SPI LoRa transceiver that is connected to custom SPI pins. Or this example showing how to use custom SPI pins with a microSD card module.
As we’ve seen previously, you can use two different SPI buses on the ESP32 and each bus can connect up to three different peripherals. This means that we can connect up to six SPI devices to the ESP32. If you need to use more, you can use an SPI multiplexer.
To communicate with multiple SPI peripherals simultaneously, you can use the ESP32 two SPI buses (HSPI and VSPI). You can use the default HSPI and VSPI pins or use custom pins.
This article was a quick and simple guide showing you how to use SPI communication with the ESP32 using the Arduino core—with the ESP32 acting as a controller (master).
In summary, the ESP32 has four SPI buses, but only two can be used to control peripherals, the HSPI and VSPI. Most ESP32 have pre-assigned HSPI and VSPI GPIOs, but you can always change the pin assignment in the code.
You can use the HSPI and VSPI buses simultaneously to drive multiple SPI peripherals, or you can use multiple peripherals on the same bus as long as their CS pin is connected to a different GPIO.
We didn’t dive deeply into examples, because each sensor, library, and case scenario is different. But, now you should have a better idea of how to interface one or multiple SPI devices with the ESP32.

Spice up your Arduino project with a beautiful large touchscreen display shield with built in microSD card connection. This TFT display is big (3.5" diagonal) bright (6 white-LED backlight) and colorful (18-bit 262,000 different shades)! 320x480 pixels with individual pixel control. As a bonus, this display has a optional resistive touch panel with controller XPT2046 attached by default and a optional capacitive touch panel with controller FT6236 attached by default, so you can detect finger presses anywhere on the screen and doesn"t require pressing down on the screen with a stylus and has nice glossy glass cover.
The pin32 (SDO) of 3.5 display module is also used by touch panel or SD card SPI interface, so we must cut off this pin to avoid conflict with the touch panel or SD card.
The shield is fully assembled, tested and ready to go. No wiring, no soldering! Simply plug it in and load up our library - you"ll have it running in under 10 minutes! Works best with any classic Arduino (Due/Mega 2560).
Of course, we wouldn"t just leave you with a datasheet and a "good luck!" - we"ve written a full open source graphics library at the bottom of this page that can draw pixels, lines, rectangles, circles and text. We also have a touch screen library that detects x,y and z (pressure) and example code to demonstrate all of it. The code is written for Arduino but can be easily ported to your favorite microcontroller!
If you"ve had a lot of Arduino DUEs go through your hands (or if you are just unlucky), chances are you’ve come across at least one that does not start-up properly.The symptom is simple: you power up the Arduino but it doesn’t appear to “boot”. Your code simply doesn"t start running.You might have noticed that resetting the board (by pressing the reset button) causes the board to start-up normally.The fix is simple,here is the solution.

I just purchased Seeed"s TFT Touch Shield 2.0 for Arduino, but I cannot seem to figure out how to access the SD card while maintaining the ability to draw to the screen. The tutorials and documentation are quite insubstantial (for me), and most questions on the product site seem to be directed to the same wiki page, which doesn"t explain anything about the SD interface, other than what example file draws bitmaps from the card.
What I assume is happening is that pins 11 through 13 are set to input for some SPI-related reason, the TFT chip select "enabled" mode is set to HIGH, and then the screen is subsequently enabled. Serial moniter is started, followed by SPI, and then the TFT. After those things happen, it does something unknown to me, starts the card, and then uses the standard card initialization method. It finishes up by preparing to draw the bitmaps and sends this "command 0x2c", which is used frequently in the underlying libraries to "start to write to display ram".
The problem is that I have tried initializing the TFT and SD card using this code, and then attempted to draw graphics as shown in my second example, but this did not work. I need to be able to read bytes from the SD card, and then be able to draw simple graphics on-screen, and repeat.
So my question is: Is anyone who has used this shield before or has experience with this able to explain how one should go about writing the code to allow usage of both the SD card and screen or how the initialization and SPI processes work to make this possible?
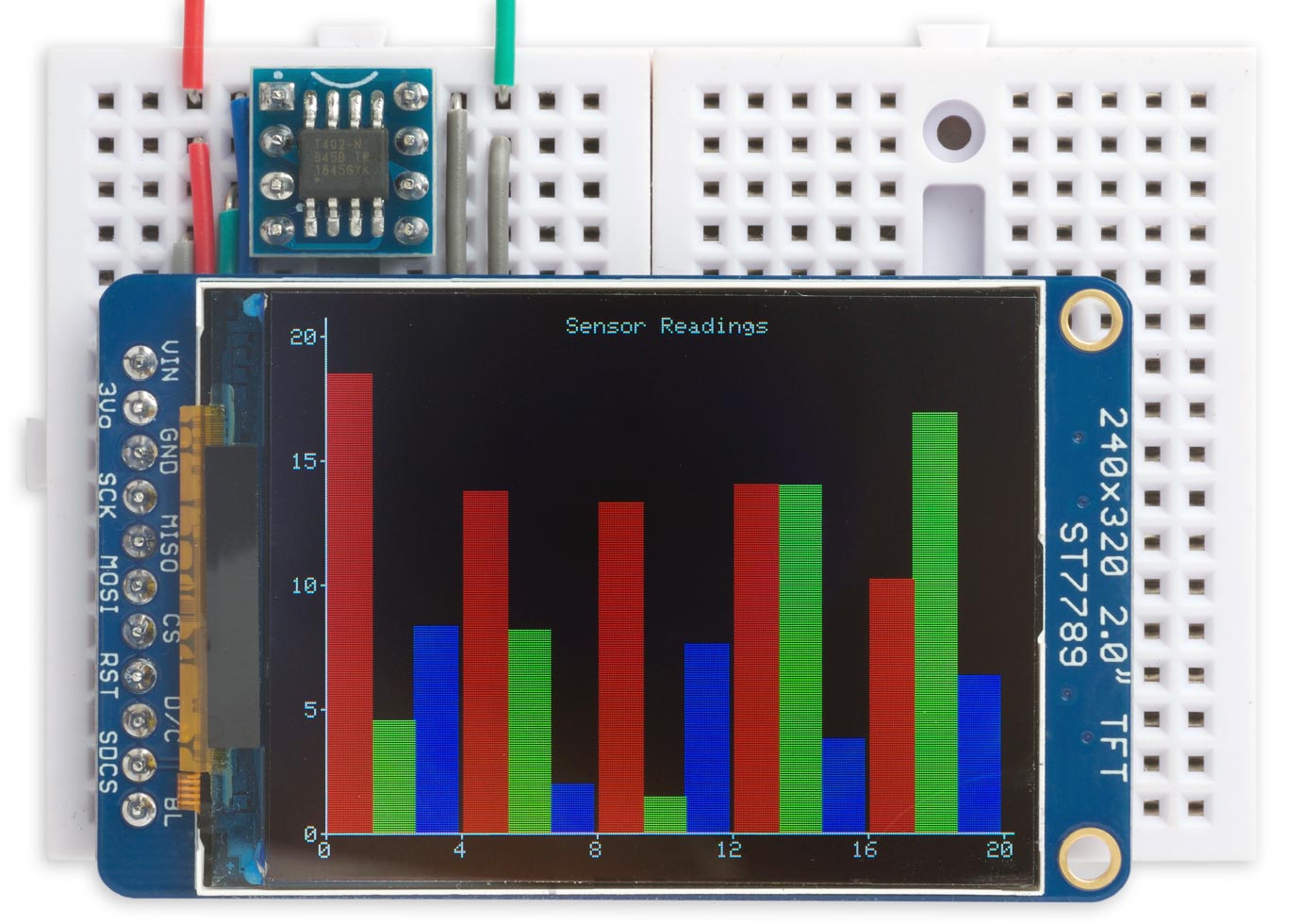
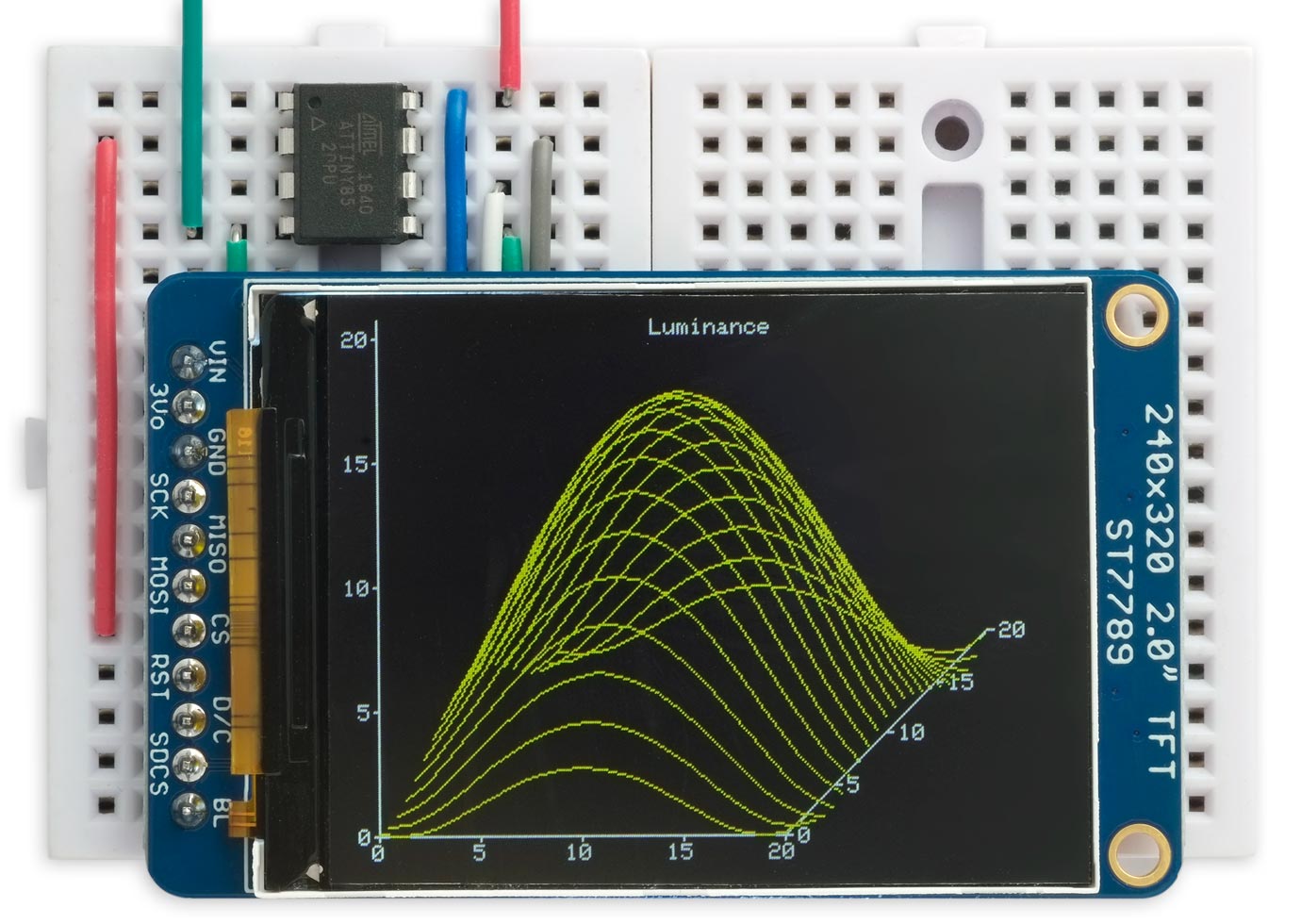
This is a small graphics library, specifically aimed at ATtiny microcontrollers, for the variety of small colour TFT displays available at low cost from suppliers like Adafruit, AliExpress, or Banggood:
It"s an updated version of my Tiny TFT Graphics Library. This latest version of the library supports both the classic ATtiny processors, such as the ATtiny85, and the new 0-series, 1-series, and 2-series ATtiny processors, such as the ATtiny402. Like the original library it allows you to plot points, draw lines, draw filled rectangles, and plot characters and text with an optional scale factor, in 16-bit colour.
This library supports TFT displays that use an SPI interface and require four pins to drive the display. This leaves one pin free on an 8-pin chip such as the ATtiny85 or ATtiny402. If you need more pins choose a larger chip, such as the ATtiny84 or ATtiny404.
Unlike my Compact TFT Graphics Library which uses standard Arduino SPI calls, this library uses direct I/O pin manipulations. This means that you can use any assignment of pins to the four I/O lines needed by the display, and makes it about twice as fast as one using SPI calls. I"ve also added support for some additional displays, so it now supports 16 different TFT displays.
This library will work with displays based on the ST7735 which supports a maximum display size of 162x132, or the ST7789 and ILI9340/1 which support a maximum display size of 320x240. It includes parameters for the following colour TFT displays:
* These Adafruit displays conveniently all have the same edge-connector layout, so you can make a prototyping board or PCB that will take any of them, such as my Universal TFT Display Backpack.
The library will probably support other TFT displays that use the same ST7735, ST7789, ILI9340/1 driver chips, but you may need to experiment with the parameters to get the image scaled and centered correctly.
The display needs to be connected to the microcontroller via four I/O lines: MOSI, SCK, CS, and DC. You can use any pins for these, but they should all be in the same port. You need to specify the port pin numbers of the pins you are using at the start of the Tiny TFT Graphics Library listing.
The library will probably support other TFT displays that use the same driver chips, but you may need to experiment with the parameters to get the image scaled and centered correctly.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey