arduino ili9341 tft lcd library brands
![]()
To download. click the DOWNLOADS button in the top right corner, rename the uncompressed folder Adafruit_ILI9341. Check that the Adafruit_ILI9341 folder contains Adafruit_ILI9341.cpp and Adafruit_ILI9341.
Place the Adafruit_ILI9341 library folder your arduinosketchfolder/libraries/ folder. You may need to create the libraries subfolder if its your first library. Restart the IDE
I got a requirement to display QRCode. Luckily I found ILI9341 in my garage but I didn"t find any related tutorial in our World Wide Web. So I decide write this article because now a days QRCode is a part of our life especially in the countries like INDIA. There are various application like UPI payments, encode Wi-Fi password, URL redirection, location info, ticket info and so on. So, let"s dive into the details.

In this article, you will learn how to use TFT LCDs by Arduino boards. From basic commands to professional designs and technics are all explained here.
There are several components to achieve this. LEDs, 7-segments, Character and Graphic displays, and full-color TFT LCDs. The right component for your projects depends on the amount of data to be displayed, type of user interaction, and processor capacity.
TFT LCD is a variant of a liquid-crystal display (LCD) that uses thin-film-transistor (TFT) technology to improve image qualities such as addressability and contrast. A TFT LCD is an active matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven LCDs with a few segments.
In Arduino-based projects, the processor frequency is low. So it is not possible to display complex, high definition images and high-speed motions. Therefore, full-color TFT LCDs can only be used to display simple data and commands.
There are several components to achieve this. LEDs, 7-segments, Character and Graphic displays, and full-color TFT LCDs. The right component for your projects depends on the amount of data to be displayed, type of user interaction, and processor capacity.
TFT LCD is a variant of a liquid-crystal display (LCD) that uses thin-film-transistor (TFT) technology to improve image qualities such as addressability and contrast. A TFT LCD is an active matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven LCDs with a few segments.
In Arduino-based projects, the processor frequency is low. So it is not possible to display complex, high definition images and high-speed motions. Therefore, full-color TFT LCDs can only be used to display simple data and commands.
After choosing the right display, It’s time to choose the right controller. If you want to display characters, tests, numbers and static images and the speed of display is not important, the Atmega328 Arduino boards (such as Arduino UNO) are a proper choice. If the size of your code is big, The UNO board may not be enough. You can use Arduino Mega2560 instead. And if you want to show high resolution images and motions with high speed, you should use the ARM core Arduino boards such as Arduino DUE.
In electronics/computer hardware a display driver is usually a semiconductor integrated circuit (but may alternatively comprise a state machine made of discrete logic and other components) which provides an interface function between a microprocessor, microcontroller, ASIC or general-purpose peripheral interface and a particular type of display device, e.g. LCD, LED, OLED, ePaper, CRT, Vacuum fluorescent or Nixie.
The LCDs manufacturers use different drivers in their products. Some of them are more popular and some of them are very unknown. To run your display easily, you should use Arduino LCDs libraries and add them to your code. Otherwise running the display may be very difficult. There are many free libraries you can find on the internet but the important point about the libraries is their compatibility with the LCD’s driver. The driver of your LCD must be known by your library. In this article, we use the Adafruit GFX library and MCUFRIEND KBV library and example codes. You can download them from the following links.
You must add the library and then upload the code. If it is the first time you run an Arduino board, don’t worry. Just follow these steps:Go to www.arduino.cc/en/Main/Software and download the software of your OS. Install the IDE software as instructed.
First you should convert your image to hex code. Download the software from the following link. if you don’t want to change the settings of the software, you must invert the color of the image and make the image horizontally mirrored and rotate it 90 degrees counterclockwise. Now add it to the software and convert it. Open the exported file and copy the hex code to Arduino IDE. x and y are locations of the image. sx and sy are sizes of image. you can change the color of the image in the last input.
Upload your image and download the converted file that the UTFT libraries can process. Now copy the hex code to Arduino IDE. x and y are locations of the image. sx and sy are size of the image.
In this template, We converted a .jpg image to .c file and added to the code, wrote a string and used the fade code to display. Then we used scroll code to move the screen left. Download the .h file and add it to the folder of the Arduino sketch.
In this template, We used sin(); and cos(); functions to draw Arcs with our desired thickness and displayed number by text printing function. Then we converted an image to hex code and added them to the code and displayed the image by bitmap function. Then we used draw lines function to change the style of the image. Download the .h file and add it to the folder of the Arduino sketch.
In this template, We added a converted image to code and then used two black and white arcs to create the pointer of volumes. Download the .h file and add it to the folder of the Arduino sketch.
In this template, We added a converted image and use the arc and print function to create this gauge. Download the .h file and add it to folder of the Arduino sketch.
while (a < b) { Serial.println(a); j = 80 * (sin(PI * a / 2000)); i = 80 * (cos(PI * a / 2000)); j2 = 50 * (sin(PI * a / 2000)); i2 = 50 * (cos(PI * a / 2000)); tft.drawLine(i2 + 235, j2 + 169, i + 235, j + 169, tft.color565(0, 255, 255)); tft.fillRect(200, 153, 75, 33, 0x0000); tft.setTextSize(3); tft.setTextColor(0xffff); if ((a/20)>99)
while (b < a) { j = 80 * (sin(PI * a / 2000)); i = 80 * (cos(PI * a / 2000)); j2 = 50 * (sin(PI * a / 2000)); i2 = 50 * (cos(PI * a / 2000)); tft.drawLine(i2 + 235, j2 + 169, i + 235, j + 169, tft.color565(0, 0, 0)); tft.fillRect(200, 153, 75, 33, 0x0000); tft.setTextSize(3); tft.setTextColor(0xffff); if ((a/20)>99)
In this template, We display simple images one after each other very fast by bitmap function. So you can make your animation by this trick. Download the .h file and add it to folder of the Arduino sketch.
In this template, We just display some images by RGBbitmap and bitmap functions. Just make a code for touchscreen and use this template. Download the .h file and add it to folder of the Arduino sketch.

I read in forums and could see that there were some adafruit libraries in the ESP8266 Arduino but now that it is not available and only some TFT_Touch_Shield_V2 are present.

My project is to build a data logger. I"m using an ESP32 and a 2,8" SPI TFT-LCD with an ILI9341 controller and integrated SD-card slot along with some other sensors. I us the Arduino IDE because of the libraries and documentation. As seen in the code below, before starting the SD card everything works fine. However, after the SD card gets started (or any other function that originated from an included library gets called) any commands for the TFT simply get ignored. What is the reason for this?

I just purchased a 2.8" TFT Touch Shield (PID 1651) and a metro board (PID 50) as well as an Arduino mega. The shield will not work with either of the arduinos. I have checked and set (and unset!) the #define in Adafruit_tftlcd.h and nothing changes. When I run the graphics test I get the following on the monitor :
I also have the FTDI driver installed (or it would not upload). This is on a new MacBook Pro with a fresh copy of the Arduino studio and the port/board are set correctly
Started off on the ardu-phone page, followed it to the TFT tutorial page and loaded the libraries from there. Should I delete the TFT library and only use the ILI9341 ?
8-Bit Library InstallWe have example code ready to go for use with these TFTs. It"s written for Arduino, which should be portable to any microcontroller by adapting the C++ source.
Put the screen(3.2 inch screen schematic) into shield (TFT01-3.2 shield schematic) first, then connect the shield to Arduino, it is quite straight forward.
3)Download and install UTFT ,URTouch ,SdFat,UTFT_Buttons and UTFT_SdRaw library file from following link and copy them into Arduino library folder. ( i.e. D:\arduino ide\Arduino 1.6.9\libraries )
You will see the code in each sketch: UTFT myGLCD(CTE32_R2, 38, 39, 40, 41).The first value of code refer to the mode of LCD screen. Please write CTE32_R2 or ILI9341_16 if you LCD screen is ILI9341; Please write CTE32 if you LCD screen is SSD1289;
When you use the others LCD screen from the others seller, you could check the PDF instruction in documentation file or open the UTFT.h file to find the correct code.The controller mode could be identifitied by the back mark as the following pictures.
Note: In the project of testing the SD card,please insert the SD card into the slot in back of the 3.2’’ LCD screen. The format of files in SD card must be the FAT32, you need to put the test files(i.e. ICONS.RAW,WAIT4GPS.RAW,SK45) into the SD card root directory.

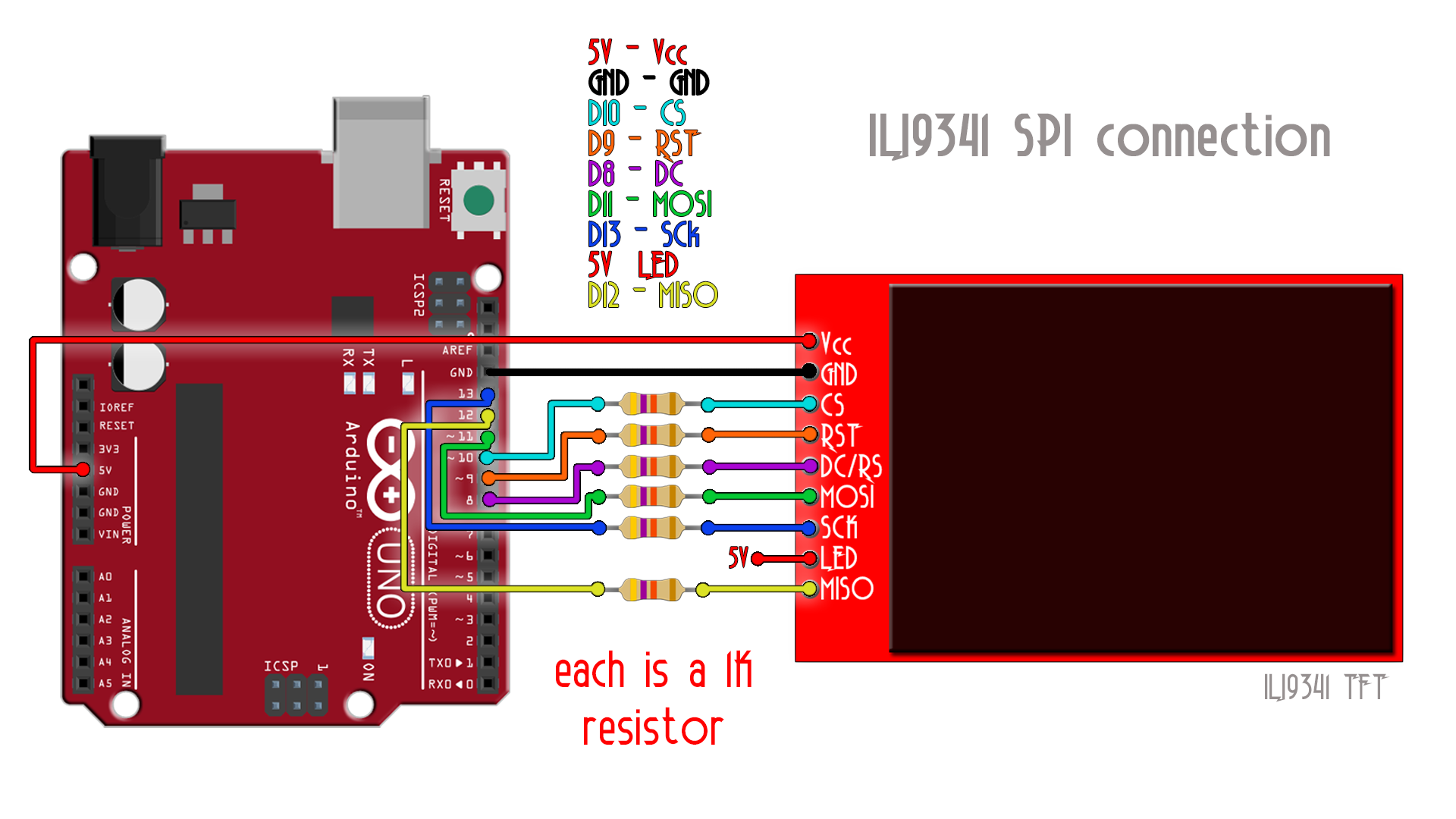
The ILI9341 TFT module contains a display controller with the same name: ILI9341. It’s a color display that uses SPI interface protocol and requires 4 or 5 control pins, it’s low cost and easy to use. The resolution of this TFT display is 240 x 320 which means it has 76800 pixels. This module works with 3.3V only and it doesn’t support 5V (not 5V tolerant).
The ILI9341 TFT display board which is shown in the circuit diagram above has 14 pins, the first 9 pins are for the display and the other 5 pins are for the touch module.
As mentioned above, the ILI9341 TFT display controller works with 3.3V only (power supply and control lines). The display module is supplied with 5V that comes from the Arduino board. This module has a built-in 3.3V regulator which supplies the display controller with 3.3V from the 5V source.
To connect the Arduino to the display module, I used voltage divider for each line which means there are 5 voltage dividers. Each voltage divider consists of 2.2k and 3.3k resistors, this drops the 5V into 3V which is sufficient.
The first library is a driver for the ILI9341 TFT display which can be installed from Arduino IDE library manager (Sketch —> Include Library —> Manage Libraries …, in the search box write “ili9341” and choose the one from Adafruit).
The ILI9341 TFT display is connected to Arduino hardware SPI module pins (clock and data), the other pins which are: CS (chip select), RST (reset) and DC (data/command) are defined as shown below:
The following Arduino code is from Adafruit ILI9341 library (graphicstest.ino) with some modifications in order to work with the above circuit diagram.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey