16 by 9 aspect ratio lcd module factory
4:3 aspect ratio televisions were the standard for many years. However, 16:9 aspect ratio is now the dominant widescreen monitor format. Consequently, TRU-Vu offers an extensive selection of 1080p monitors and touch screens with a variety of aspect ratios. Similarly, we also offer our industrial-grade monitors and touch screens with 16:10 aspect ratio. Browse our 16:9 wide-screen displays to find the perfect solution for your needs. You can even search exclusively for only 16:9 monitors with our search tool.
Our 16×9 monitors are an ideal match for 1920×1080 aspect ratio cameras and 16:9 resolutions from other devices. Widescreen monitors range from 800 x 480 to 1920×1080 aspect ratios, as well as 4K resolution. We are pleased to offer our 16:9 and 16:10 resolution widescreen monitors in a wide range of sizes and configurations. This includes convenient panel-mount LCD monitors and Sunlight Readable monitors and waterproof outdoor monitor options. These are built for tough conditions.
We are often asked “What is my aspect ratio?” Or sometimes “Do you have a 1080p monitor?” “Can you tell me the aspect ratio of 1920×1080?” A widescreen aspect ratio refers to a 16:9 aspect ratio screen. This is the rectangular shape similar to any modern television. Older TV’s and monitors had a 4:3 aspect ratio, which looked more like a square monitor. Check out our 4:3 vs 16:9 Aspect Ratio article in order to help you understand the differences between the two monitor formats. You can also use this handy aspect ratio calculator. Likewise, you can speak with one of our application specialists about all of the technical specifications on our displays. Feel free to request a recommendation. They will help determine the ideal 16:9 aspect ratio or 16:10 aspect ratio monitors for your environment. If you are interested to learn more about aspect ratios, please also check our terminology guide.
We would be happy to modify any of our monitors for you. For instance, TRU-Vu can customize nearly aspect of your display, from the inputs and electronics, to screen treatments and enclosures.Modified options are often available at low or no additional cost. Additionally, we also offer custom monitors to meet your exact requirements. Lastly, Private label options are also available for your brand promotion.

Availability of a comprehensive range of industrial specification, wide aspect ratio 7.0-inch TFT display modules is announced by Review Display Systems.
These modules feature a 16:9 widescreen aspect ratio and are available in variety of resolutions including 800 x 480 pixels (WVGA), 1024 x 600 pixels (WSVGA), and 1280 x 800 pixels (WXGA).
In-plane switching (IPS) is available on some of the modules which enables exceptional optical performance, highly consistent colour reproduction and wide viewing angles. Long-lifetime LED backlights with brightness specifications from 300cd/m² up to high luminance 1500cd/m² versions are supported.
Justin Coleman, display business manager, RDS said, “Over recent years, the widescreen 7.0-inch TFT display module has become an informal industry standard. At RDS we are able to supply, support and design-in a wide range of cost effective 7.0-inch TFT display modules with different options and value-added features. This concept provides engineers with the ability to enhance, upgrade and add new features to their products without the need to redesign their mechanical fixtures and fittings, or change the electronics driving the display.”
A choice of data interfaces includes 24-bit RGB, 6-bit and 8-bit LVDS and MIPI (Mobile Industry Processor Interface) enable support for a colour palette of up to 16.7 million colours. Interconnect options include FFC (flat flexible cable) and ZIF (zero insertion force) connectors.

Resingstar 16:9 17 inch lcd display module ,the brightness 350-1500nits can be optional,Original AUO module with LED side-entry backlight for uniform brightness,can clearly readable at any time.
17inch high bright lcd module work normally in direct sunlight. Combined with a high Tni 80℃-110 ℃,industrial grade OC, the 17inch lcd display can working 24 hours.

Once seen as exotic,televisions and computer monitors, and is also the international standard image format for UHD, HDTV, Full HD, and SD digital television. It has replaced the "fullscreen" 4:3 aspect ratio.
16:9 (1.77:1) (spoken as "sixteen by nine" or "sixteen to nine") is the international standard format of Ultra HD, non-HD digital widescreen television and analog widescreen television systems PALplusWide-aspect Clear-vision.Hi-Vision originally started with a 5:3 (1.66:1) ratio but converted when the international standards group introduced a wider ratio of 16 to 9. Many digital video cameras have the capability to record in 16:9, and 16:9 is the only widescreen aspect ratio natively supported by the DVD standard. It is also the native aspect ratio of Blu-ray discs, but Blu-ray and DVD producers can also choose to show even wider ratios such as 1.85:1, 2.00:1, and 2.40:1 within the 16:9 DVD and Blu-ray frame by hard matting or adding black bars within the image itself.
Derivation of the 16:9 aspect ratioThe main figure shows 4:3, 1.85:1, and 2.35:1 rectangles with the same area A, and 16:9 rectangles that covers (black) or is common to (grey) them. The calculation considers the extreme rectangles, where m and n are multipliers to maintain their respective aspect ratios and areas.
Dr. Kerns H. Powers, a member of the SMPTE Working Group on High-Definition Electronic Production, first proposed the 16:9 (1.77:1) aspect ratio in 1984,6:1 ratio), 1.85:1 (the American "flat" ratio) and 2.35:1 (the CinemaScope/Panavision) ratio for anamorphic widescreen.
Powers cut out rectangles with equal areas, shaped to match each of the popular aspect ratios. When overlapped with their center points aligned, he found that all of those aspect ratio rectangles fit within an outer rectangle with an aspect ratio of 1.77:1 and all of them also covered a smaller common inner rectangle with the same aspect ratio 1.77:1.geometric mean of the extreme aspect ratios, 4:3 and 2.35:1, 47
While 16:9 (1.77:1) was initially selected as a compromise format, the subsequent popularity of HDTV broadcast has solidified 16:9 as perhaps the most common video aspect ratio in use.3:1) and 2.40:1 video is now recorded using a "shoot and protect" technique7:1) inner rectangle to facilitate HD broadcastopen matte.
In 1993, the European Union instituted the 16:9 Action Plan,PALplus (compatible with regular PAL broadcasts) and also in HD-MAC (an early HD format). The Community fund for the 16:9 Action Plan amounted to €228,000,000.
Over a long period in the late 2000s and early 2010s, the computer industry switched from 4:3 to 16:9 as the most common aspect ratio for monitors and laptops. A 2008 report by DisplaySearch cited a number of reasons for this shift, including the ability for PC and monitor manufacturers to expand their product ranges by offering products with wider screens and higher resolutions, helping consumers to more easily adopt such products and "stimulating the growth of the notebook PC and LCD monitor market".
In 2011, Bennie Budler, product manager of IT products at Samsung South Africa, confirmed that monitors capable of 1920 × 1200 resolutions are not being manufactured anymore. "It is all about reducing manufacturing costs. The new 16:9 aspect ratio panels are more cost-effective to manufacture locally than the previous 16:10 panels".
In March 2011, the 16:9 resolution 1920 × 1080 became the most common used resolution among Steam"s users. The previous most common resolution was 1680 × 1050 (16:10).
16:9 is the only widescreen aspect ratio natively supported by the DVD format. An anamorphic PAL region DVD video frame has a maximum resolution of 720 × 576p, but a video player software will stretch this to 1024 × 576p.
Producers can also choose to show even wider ratios such as 1.85:1 and 2.4:1 within the 16:9 DVD frame by hard matting or adding black bars within the image itself. Some films which were made in a 1.85:1 aspect ratio, such as the U.S.-Italian co-production Kenneth Branagh"s 7:1 HDTV screen and have been issued as an enhanced version on DVD without the black bars. Many digital video cameras have the capability to record in 16:9.
In Europe, 16:9 is the standard broadcast format for most digital SD TV channels and all HD broadcasts. Some countries adopted the format for analogue television, first by using the PALplus standard (now obsolete) and then by simply using WSS on normal PAL broadcasts.
Japan pioneered its analogue HDTV system (MUSE) in 16:9 format, which started in the 1980s. There were also analog NTSC-compatible widescreen broadcasts using the Clear-Vision system. Currently all main channels have digital terrestrial television channels in 16:9. Many satellite broadcast channels are being broadcast in 16:9 as well.
All channels, however 16:9 contents look squashed on older 4:3 sets. Also, all 4:3 contents including news clips are stretched as stretching is common.
channels that are originally broadcasting in 4:3 on analog terrestrial, but upscaled or stretched to 16:9 for digital terrestrial television, cable and satellite

LCD display doesn’t operate the same way as CRT displays , which fires electrons at a glass screen, a LCD display has individual pixels arranged in a rectangular grid. Each pixel has RGB(Red, Green, Blue) sub-pixel that can be turned on or off. When all of a pixel’s sub-pixels are turned off, it appears black. When all the sub-pixels are turned on 100%, it appears white. By adjusting the individual levels of red, green, and blue light, millions of color combinations are possible
The pixels of the LCD screen were made by circuitry and electrodes of the backplane. Each sub-pixel contains a TFT (Thin Film Transistor) element. These structures are formed by depositing various materials (metals and silicon) on to the glass substrate that will become one part of the complete display “stack,” and then making them through photolithography. For more information about TFT LCDs, please refer to “
The etched pixels by photolith process are the Native Resolution. Actually, all the flat panel displays, LCD, OLED, Plasma etc.) have native resolution which are different from CRT monitors
HD TV has 1280×720 = 921,600 pixels; Full HD has 1920x 1080=2,073,600 pixels; 8K TV has 7,680×4,320=33,177,600 pixels. he “K” in 8K stands for Kilo (1000), meaning a TV that has achieved a horizonal resolution of about 8,000 pixels.
Although we can define a LCD display with resolution, a Full HD resolution on screen size of a 15” monitor or a 27” monitor will show different. The screen “fineness” is very important for some application, like medical, or even our cell phone. If the display “fineness” is not enough, the display will look “pixelized” which is unable to show details.
DPI stands for dots per inch and refers to the resolution of a printer. It describes the density of ink dots placed on a sheet of paper (or another photographic medium) by a printer to create a physical print.
PPI stands for number of pixels per inch. It is kind of pixel density. PPI describes the resolution of a digital image, not a print. PPI is used to resize images in preparation for printing
But you see other lower resolution available, that is because video cards are doing the trick. A video card can display a lower LCD screen resolution than the LCD’s built-in native resolution. The video cards can combine the pixels and turn a higher resolution into lower resolution, or just use part of the full screen. But video cards can’t do the magic to exceed the native resolution.
Aspect Ratio: You might hear 4:3 which is full screen, 16:9 is for widescreen; 21:9 is for ultrawide computer monitors and televisions, as well as cinematic widescreen projectors. Some ultrawide monitors are trying to replace dual monitor.
Special names by individual companies: Apple Macbook Pro Retina 6K display, Acer Nitro, ASUS Pro Art , ViewSonic Elite, ASUS TUF ,Samsung edge Infinity-O Display etc.

Knowledge of different aspect ratios is proving quite essential when deploying various digital signage solutions. As technology advances, digital signage continues to outpace its static counterpart. Nowadays, businesses are embracing interactive digital signage to boost user experience.
Interactive mediums involve customer participation, and the content could range from text, animation, video, audio, and even games. Here a 3:2 or 4:3 ratio would do just fine. For motion signage, businesses would always go for the highest resolution possible (4k), supported by the 16:9 aspect ratio.
On the other hand, static digital signage includes audio, video, and images that do not change or adapt to the adjacent environment. The choice of aspect ratio will depend on the resolution needed, the type of content, and what the business wants to accomplish.
The 4:5 or the 1.91:1 is a vertical or portrait format (1080 x 1350px) commonly used for Instagram main feed. When you multiply this by 2, you get 8:10. This is the aspect ratio used with the popular 8″ x 10″ photos and can work well for digital advertising on relatively smaller screens.
The 16:9 is a widescreen aspect ratio widely used in video players. It’s one of the most common aspect ratios you’ll find in the latest TV designs. This 4k aspect ratio supports up to 4096 by 2160 pixels (px) and works well with high-definition marketing videos.
The 16:10 became popular between 2005 and 2008, where it was common with laptop displays. If you are using a native wide XGA projector, this would be the best option to choose. An XGA projector receives 1920 x 1080 px but outputs 1024 x 768. Some computer monitors still use this aspect ratio.
Aspect ratio and resolution are two terms that describe the format and the quality of an image you see on a screen. Understanding these terms will guide you when designing content for your digital signage. By now, you must be familiar with aspect ratio. Let’s see what resolution is and how it relates to the image or video aspect ratios.
Resolution is the number of pixels/dots making up the picture/video on your screen. The more the number of dots/pixels in a picture, the higher the resolution, which means high-quality images and videos to create a captivating display. To get the resolution, you multiply the width (W) times the height (H) while dividing the two for the aspect ratio.
A higher resolution video contains more details than a lower-resolution video and would need a larger screen to display everything. When displaying smaller file sizes, you’ll need to encode your high-quality video into a lower-resolution copy. Once you know what your audience wants to see, it’s easy to choose the right aspect and resolution. You’ll then proceed to develop content for your digital signage that will meet your audience’s expectations.
How to find the aspect ratio of video/image? Locate the pixel dimensions of the image or video you have (e.g., 4096 by 2160 pixels). Divide the long side (higher number) by the short side (lower number). Then take note of the resulting number (here, the answer would be 16:9).
How to check the aspect ratio of the monitor? Find the ratio of width to height by dividing the height by the width. Some monitors allow you to change the display’s proportions via settings.
If the content source has fixed formatting and can’t modify the monitor’s aspect ratio to suit your viewing needs, you’ll need to use encoding software to change the proportions of the content. In summary, aspect ratio challenges can be solved by investing in the right digital signage hardware and the software.

I"ve been lucky enough in the last couple of months to have three of the latest IPS monitors sitting on my desk for weeks at a time. They range from several 23in 1,920 x 1,080 models to a 27in screen of the same resolution - all 16:9 aspect ratios of course. However, key to the point of this article is the middle man - a 24in monitor with a resolution of 1,920 x 1,200 - an aspect ratio of 16:10.
If you"re familiar with aspect ratios, you"ll probably know about the fact that in the last four or so years, monitors have switched from being predominately 16:10 (typically 1,680 x 1,050 or 1,920 x 1,200) to 16:9 (usually 1,600 x 900 or 1,920 x 1,080). This is to cut production costs by tying them in with flatscreen TV manufacturing which also sports a 16:9 aspect ratio. As you can see from the above resolutions, you lose a considerable amount of vertical screen real-estate with 16:9 compared to 16:10.
This has real knock-on effects when it comes to viewing photos or webpages, the latter requiring a lot more scrolling for example, while you end up with a narrower field of vision in games too. These are disadvantages that enthusiasts have been crowing about for some time, but having used a larger 27in 16:9 monitor, compared to the seemingly much smaller 24in 16:10 for a few weeks and just having switched back, do you know what I realised?
I have to admit I’ve been on the fence in this argument till now. After all, 16:10 monitors are usually far more expensive too. However, having seen that even a 27in 16:9 monitor can’t usurp a 24in 16:10 example sporting all those extra vertical pixels, it really did make me by surprise and I’d have no qualms now recommending a 24in 16:10 monitor over a larger one that can only offer 1080p.
As 27in monitors become cheaper (the model I looked at costs a similar price to the 24in 16:10 model I’d also been using), the question is a popular one in enthusiast forums - 27in 16:9 or 24in 16:10? While I believe the sweet spot for large monitors is in the 27inch range (I find they’re not too big as to make you constantly move your head around as you would with a 30in monitor on your desk, but offer substantial gains over 24in models) this would have to be with one sporting a 16:10 aspect ratio. As for the above question, my mind is certainly made up – I’d recommend the 24in 16:10 option every time.

In order to avoid video images which are stretched, chopped, squeezed, shrunk or distorted, be sure to choose a LCD monitor with a aspect ratio (4:3 or 16:9) that matches your camera or other incoming video signal.
There’s no doubt that today’s HD televisions look fantastic. However, are 16:9 aspect ratio monitors really the best choice for your industrial/commercial project?
Aspect ratio is the relationship of the width of a video image compared to its height. The two most common aspect ratios are 4:3, also known as 1.33:1 or fullscreen, and 16:9, also known as 1.78:1 or widescreen. (Larger aspect ratio formats are used in the motion picture industry.)
All the older TV’s and computer monitors you grew up with had the squarish 4:3 shape-- 33 percent wider than it was high. 4:3 LCD monitors can display analog video signals that conform to NTSC and PAL standards. They are not capable of displaying HD (high-definition) video.
The 4:3 aspect ratio dates back to 1917, when the Society of Motion Picture Engineers adopted it as the standard format for film. In the 1930’s, the television industry adopted the same 4:3 standard. But in the mid-1950’s, the motion picture industry began developing several widescreen formats to improve their decreasing audience numbers. Television broadcasting stayed with the 4:3 standard, until the recent move to HDTV and 16:9 widescreens.
16:9 is the native aspect ratio of most high-definition LCD monitors and TV’s (15:9 and 16:10 are very similar). It is 78 percent wider than it is tall, and fully one-third wider than a 4:3 screen. 16:9 widescreen monitors are ideally suited to display HD video signals. Some models can also display SD (standard definition) video signals, but this will require some compromises, as you will read below.
Nearly all experts agree that in order to display optimal video images, it is critical to match the aspect ratio of the monitor to the aspect ratio of the camera (or other incoming video source). Below is a example of a 16:9 image on a 16:9 monitor:
However, the majority of cameras in the industrial, commercial, security, and law enforcement industries still utilize 4:3 CCD or CMOS imagers. Therefore, to display clear, undistorted video images, it is important to utilize monitors with the same 4:3 aspect ratio to match the cameras. Failure to do so will result in distorted images, as shown below.
Unfortunately, despite the continued widespread use of 4:3 cameras, LCD monitors with a 4:3 aspect ratio are getting harder and harder to find, as many manufacturers have transitioned to the newer 16:9 widescreens. TRU-Vu Monitors still offers a complete line of industrial-grade 4:3 aspect ratio LCD monitors. These range in size from 3.5” to 20” screens, in standard, touch screen, rack mount, sunlight readable, medical-grade, optically bonded and open frame LCD monitor configurations. See www.TRU-VuMonitors.com for more details.
16:9 widescreen LCD monitors are the ideal complement to 16:9 format HD cameras, increasingly used in video conferencing, broadcast and medical applications. They display superb, distortion-free, high-definition images. TRU-Vu Monitors offers these in 21.5” to 46” LCD screen sizes, in standard, touch screen, sunlight readable, medical-grade, optically bonded and open frame configurations.
In conclusion, in order to avoid video images which are stretched, chopped, squeezed, shrunk or distorted, be sure to choose a LCD monitor with a aspect ratio (4:3 or 16:9) that matches your camera or other incoming video signal.

What is aspect ratio, you ask? Aspect ratio is the ratio of the width of the screen to the height of the screen. Essentially, it describes the shape of the rectangle. Today the most popular aspect ratio for consumer video display is 16:9, which is the standard HDTV format. The numbers mean that the picture is 16 units wide for every 9 units in height.
Sometimes you will see the 16:9 aspect ratio referred to as 1.78:1, or simply 1.78. Why? Because 16 divided by 9 = 1.78. But it means the same thing. A 1.78 screen is 1.78 units in width for every unit of height.
If you are going to use a flatscreen HDTV for your home theater, you are stuck with the 16:9 format for better or for worse. Though they come in a wide variety of sizes, they are all 16:9 aspect ratio. But if you are planning to use a projector and screen, you have another option, which is 2.4:1, commonly known as the Cinemascope format. This is a wider format than standard 16:9. Many people prefer it because it matches the aspect ratio of a lot of movies being produced today.
Here is a simple fact of life: Videos and movies are made in a variety of different aspect ratios. There is no standard. So no matter what aspect ratio your screen is, you will always end up with black bars at the top and bottom of some material, and black pillars at the sides of other material. The only time you don"t get black bars is if you are viewing video or film shot in the format of the screen you are using--either a film done in 1.78 displayed on a 16:9 screen, or a movie shot in 2.4 on a 2.4 Cinemascope screen. In both of those cases, the screen frame will match the picture precisely, and no black bars will exist.
(By the way, we"re assuming you want to see the material you watch in its correct original aspect ratio, as the director created it. If you don"t, there are several ways to stretch, manipulate, or crop video images to get them to fill a 16:9 screen and eliminate the black bars.)
So in choosing between a screen aspect ratio of 1.78 vs. 2.4, you are really deciding how the various film and video formats will appear on your screen. For example, if you select a 16:9 screen, all of your 2.4 format movies will have black bars top and bottom. If you select a 2.4 screen, all of your 16:9 material will be "pillar-boxed" in the center of the screen with black columns on each side.
Well, not so fast. Many people assume that all modern films are being done in the super widescreen 2.4 format. They aren"t. A few, including some new and popular titles, are done in plain ol" 16:9 (1.78). As examples, here are some movies that are either done in 1.78, or have been modified to 1.78 for Blu-ray...Avatar
Another format that is very close in aspect ratio to 1.78 is 1.85. This format has been popular for a long time, so there is a huge library of 1.85 films on the market. Examples of movies done in 1.85 include....Saving Private Ryan
Obviously, most films today are done in the wider format 2.4 Cinemascope. Part Two of this article will focus on the display of 2.4 movies, and the selection of the 2.4 format screen as an alternative to conventional 16:9.
Dear Evan, Soon I will purchase a JVC DLA HD-250. My question is if I purchase 2.35 screen, I have already purchased a 16x9 portable, and watch 2.35 without having to purchase an anamorphic screen? My setup requires portable as much as I would like fixed.
ALL THING ARE RIGHT BUT ORIGINAL WATCH "CINEMA" MOVIES WATCH IN 2:40.1 SCREEN IT"S ORIGINAL THEATER SCREEN, AND 16:9 IS ONLY TV "aspect ratio" NOT A HOME THEATER SCREEN...............
There is in fact another view, which is more quantitative and "scientific". On a 16:9 screen to watch the movie in the same size, whide-format movies are down-scalled, or rather the source is down-scalled and black bars are inserted. Meaning the optimal sitting distance changes when you change movie-format. You have to move closer when watching a down-scaled movie ( when watching Cinemascope material ).
If you consider a 50" 21:9, it is often argued why not get a 60" 16:9 instead - well, apart form the problem of space, there is the old problem of optimal viewing distance - on the 60" 16:9 content will be blown up to a huge format, giving less picture quality and you have to move further back to get an optimal viewing distance each time you change format.
On a 21:9 TV set, there is no up- or down-scalling of either 21:9 or 19:9 contents, the viewing distance is the same on both formats. Then you of cause instead have the black bars at the sides - but on the positive side you can streach the 16:9 content if you like - you have the option.
I"m sorry your revision omits the "old" 4:3 format for TV screens, which we have at home and everything looks fine on it (with Verizon FiOS cable). On vacation recently we were in a flat with 16:9 TV, and all, ALL!, the images were disturbingly fattened sideways. All, ALL!, the people looked very stout or fat - tolerable for football and baseball players, maybe, but not for ordinary people on screen. The TV did not allow the format to be changed, either, so we were stuck. Long live 4:3 screens!
Good article, Evan. Seems to me a straightforward approach is simply to match screen aspect ration to the native resolution of the projector. That way, you"ll be seeing the best the projector can do with any given content. An HD projector will fully fill a 16:9 (1.78:1) HD screen with HD content (sat or cable HDTV, Bluray). Sure, standard-def (DVD) content will display in a more narrow image, with black pillars on the sides. But that"s to be expected, as are the minor top and bottom bars that result from showing ultra-wide-screen movie content with an HD projector. As you point out, trying to make black bars go away forever involves either significant picture compromises, or expensive projector lenses/automation. Or post-display tweaking (e.g. screens with variable masking).
"What screen aspect ratio do you want: 16:9 or 2.4?" Thank you for a very well written article on the subject matter. There is a lot of useful information here. I built my dedicated home theater 13 years ago. It is now undergoing the upgrade number 3. Affordable HD projectors made all the difference when it came to enjoyable watching of the movies. One thing that I have not been able to avoid are those "black bars" on the 16:9 screen. Everybody calls them black bars when in fact I can only see dark grey at the best of times. Since I watch only movies in my theater, I would love to have a projector with the native 21:9 aspect ratio. I can"t get one! Changing the screen is an easy problem to solve. But projector... Your article gives pros and cons of various aspect ratios of the screen. It appears that the amount of the real estate of the screen surface was an important issue. For some people it may be so. The widest possible 16:9 screen in a room may produce the largest screen area and a wow factor. However, I fail to see how a huge 16:9 screen is going to improve the quality of the image with the current crop of projectors. I am talking about the loss of vertical resolution here of course. By the way I dislike the usage of an anamorphic lens. My argument is: The vast percentage of the movies are released on DVD/BD in original theatrical aspect ratios, so why no projectors to cater for this format. 16:9 screens do nothing for the quality of the image.(good for TV sports etc.) I would like to see 21:9 projectors available, or somehow force movie studios to release all Blu-Ray discs in 16:9 aspect ratio. I"ll keep on dreaming. Regards, Ben
I recently bought a Sony blu ray player and feel that some of the videos I purchased were a rip off as the screen size aspect is not highly visible. I wish they would print Wide Screen in large bold letters and the exact aspect ratio in small print at the bottom of the packaging
16:9 is a really awkward aspect ratio for devices, and switching to 16:10 would make a huge difference. Most of us would be a lot more productive with a 16:10 laptop then with a 16:9 one.
I say have all the program material be transferred in the proper aspect ratio, let the view make the choice as to what they want on their screen. Black bars or no black bars. Just so long as you don"t make the choice for me.
Now they"re doing the same thing with the 16X9 HD stuff. They"re cropping the 2.35 films to fit l.78 screen. WHY DO THEY DO THAT? Gee"s, it just drives me up the wall.

Popular desktop sized LCDs for monitor applications have for a while been available from 19" (WSXGA+) to 27" (WUXGA). A higher resolution 30" LCD (2560x1600) is also available. All these monitors and displays have been in a 16:10 aspect ratio.
As a consequence of this, major players in the market are shifting towards 16:9, also for monitors. This has already happened for smaller sized products, if you are buying a 20" LCD for your office today, the most competitive product will be a 16:9 monitor.
This market-transition is happening fast! We know that it is still possible to get 16:10 monitors in 19" to 27" segment for still some time, but we believe that sometime soon they will all be announced End Of Life - (if not already...)
For this reason, we recommend our customers to take this shift into consideration as soon as possible. Re-design to new mechanical and software aspect ratio is not done overnight, and must be planned. Maritime business is in the bigger context representing a very small portion of the total production volumes of displays and monitors.

If you’re reading this article, you probably have suffered from false aspect ratio issues, the same as the users asking the questions above. You spent hours downloading some MP4 videos and were ready to watch them on your devices. But when you put them on the devices, the image looked overly stretched because of the incorrect aspect ratio.
So what to do next? To deal with the screen size defect of video enjoyment, it’s good for you to change the aspect ratio of a video to make the display effect better fit. This article is mainly to expand your knowledge on how to change video aspect ratio easily with a powerful video aspect ratio converter.

Well, if you haven’t, today, through this article, let us help you explore everything about this ratio (and other popular ratios) along with its history, resolution, and application in detail.
The comparable relation between the width and height of a screen or video display is known as the aspect ratio. The ratio is usually used in camera sensors, television displays, as well as in printed and digital media.
The list also includes 3:2 aspect ratios suitable for sensors in devices like phones and cameras for shooting different media. Additionally, Cinemascope is a 2.35:1 extra wide aspect ratio used for making films for cinemas.
Aspect ratios are important because there are many standards. The 19:9 ratio in phones is different from the 16:9 horizontal ratio in the modern laptop screens. Also, old computers have a 4:3 aspect ratio while mainstream media is displayed mostly in a 16:9 ratio.
However, in the early days, almost all televisions and monitors had a 4:3 aspect ratio. It was square in shape, which was 33% wider than its height, and was generally known as a square monitor. However, they were not ideal for high-definition video displays.
The 16:9 aspect ratio is widely used in HDTV, non-HD TV, Full HD, and analog television screens. The ratio is obtained when you divide vertical pixels by horizontal pixels (in numbers), containing 1920 vertical lines and 1080 horizontal lines of resolution.
For reference, a 16:9 aspect ratio on television simply means that the horizontal viewing area is wider (16) than the vertical viewing area (9). Practically all the television broadcasts were using this format by the end of 2005.
Moreover, the 16:9 format is natively supported in DVD format and is further used on Vimeo, YouTube, and other popular video websites attracting a very high view rate.
Also, the aspect ratio is clearly specified in the video production by mentioning the widths relative to height, such as 16:9. Today, this ratio has become the common video player size and is the default aspect ratio for most devices, both professional and consumer-grade electronics.
When it comes to displaying a presentation or video on an electronic device, resolutions and aspect ratios are quite significant. The sharpness and clarity of your screen"s image are also determined by its resolution.
Moreover, even the sharpness of a picture on a display is determined by the monitor"s resolution and size. Also, as the same number of pixels are spread out across a greater number of inches, the very same pixel resolution will be crisper on a smaller panel, and gradually lose sharpness on bigger monitors.
Now talking about the computer display system, its greatest resolution is determined by its physical ability to concentrate light (in which case the physical dot size - the dot pitch - corresponds to the pixel size), and it normally has lower resolutions.
However, a display system with a maximum resolution of 1280 by 1023 pixels, for example, could additionally support resolutions of 1024x768, 800x600, and 640x480 pixels. Also, the highest resolution on a given display size may provide a crisper image, but it will be distributed across a space that is too tiny to read comfortably.
Now coming to the aspect ratio of a picture, it is the proportion of its width to its height, represented as two integers separated by a colon, for instance, 4:3. There are several aspect ratios in use in many mainstream press applications; nevertheless, in the television business, the 4:3 and 16:9 aspect ratios are the most frequent.
Moreover, the 4:3 widescreen format, which is utilized for both standard and high definition video, has replaced the old standard definition format that is no longer used by broadcasters.
Although there are other resolutions to pick from, here is a list of the most commonly utilized resolutions (and their corresponding aspect ratios) today:
The 4:3 aspect ratio, which was created by William Dickson in 1892, was established as the standard format for the film in 1917 by the Society of Motion Picture Engineers, and by the television industry in the 1930s. However, in the mid-1950s, the motion picture industry began to develop a variety of widescreen formats to boost their dwindling audience numbers.
Despite the universal usage of 4:3 cameras, LCDs with a 4:3 aspect ratio were becoming increasingly difficult to come by. Many manufacturers moved on to the newer 16:9 widescreens.
This makes it 1.33:1, which serves as the aspect ratio of a 4:3 TV or projector screen. However, this aspect ratio only remained as long as the shape of the television remained square.
This quickly changed when the 16:9 ratio came into the picture. It was much easier on the eyes, and the wide shape of the image closely reflected the natural way of seeing. This accounted for most high-definition widescreen LCDs and TVs with a 16:9 aspect ratio as their default standard (16:9 and 16:10 are very similar). Nonetheless, it"s 78% broader than tall, and one-third bigger than a 4:3 screen.
Now, the 16:9 aspect ratio becomes 16 units wide and 9 units high - much wider in comparison to the 4:3 aspect ratio. Also, when the width is divided by the height it is:
Today, widescreen LCDs with a 16:9 aspect ratio act as the best complement to 16:9 format HD cameras. On top of that, this aspect ratio provides high-definition pictures that are clear and distortion-free, making video conferencing, and broadcasting more and more popular now.
Before I discuss the most common ratios in films, you must first understand that a fixed aspect ratio is used while making a film or television program. This is determined by the camera that is used to film the show, as well as the interface where it will be shown. As a result, TV series’ will almost certainly have a distinct native aspect ratio as compared to big-budget films.
With a few exceptions, most films released after 1953 were in either 1.85:1 or 2.35:1 aspect ratios. However, most modern films are shot in 1.85:1, 2.35:1, or 2.39:1 widescreen aspect ratios. A few silent films, such as Grandeur and " Vision, were shot in other unusual aspect ratios.
Although there have been various aspect ratios used in the last few years, there are 4 popular formats that you will encounter frequently. This includes the following:1.33:1 Ratio
This is the most common aspect ratio of SD (standard-definition) pictures and TVs, sometimes known as 4:3. However, as new TV displays migrate to widescreen, this is becoming less prevalent.
Although there are still many older TV shows that are only accessible in this aspect ratio. As a result, you can watch any of the 4:3 television shows on your old 4:3 television without compromising much on quality. Surprising, it?
However, on the widescreen TV (16:9), there will be bars on both sides due to the image not being large enough for the TV. In technical terms, this is referred to as vertical letterboxing or pillar boxing.
The aspect ratio for almost all the widescreen TVs is 1.78:1, as previously stated. 16 x 9 or 16:9 are other names for it. Additionally, is also a term used to describe this same aspect ratio.
Frequently, 16:9 is the optimum aspect ratio used for presenting content on HDTV as it is the standard for high-definition television screens. Also, in case a show has a 16:9 aspect ratio, you can be assured that it will easily match the aspect ratio of the screen and that the contents of the show will fill the entire screen.
For numerous films, 1.85:1 is a typical widescreen aspect ratio. It is widely used as a widescreen format in the United States, and it is somewhat wider than the normal 16:9 format. But, as the aspect ratio is nearly the same, a video with this aspect ratio may fit perfectly on a normal 16:9 HD TV.
Letterboxing occurs when a 1.85:1 show is displayed on a 16:9 screen, although the bars at the bottom and top may be minimal since this form is already a good fit.
When it comes to 2.39:1, it is a famous aspect ratio used in big movie releases, sometimes known as Panavision or CinemaScope. The aspect ratio used to be 2.35:1, but in the 1970s it was changed to 2.39:1. Apart from this, 2.40:1 is another popular rounding.
If you are wondering where to find this information about aspect ratios, then let me tell you, the aspect ratio of the show or movie on the disc, as well as other information, may be found on the rear of your Blu-ray or DVD packaging.
The 16:9 aspect ratio has a long history dating back to 1984 when Dr. Kerns H. Powers first proposed this aspect ratio to the electronic industry. This was the time when hardly anyone was creating videos in an aspect ratio other than 4:3. Moreover, this aspect ratio (16:9) was then used to solve the difficulty of cinematographic projectors fitting inside booths that were too tall for their width.
Today"s widescreen displays and HDTVs, with their wide 16:9 aspect ratio, have completely transformed the way we view the world. They provide more working space and allow you to see larger pictures without compromising visibility.
On top of that, the 16:9 aspect ratio has been increasingly popular in recent years due to the growing usage of computer displays and LCD televisions. Nonetheless, high-definition (HD) television has used the 16:9 aspect ratio since 2009, which 16:9 appeared in a wide range of media, including movies, television, video games, and even sports.
In motion pictures, video images, and still photos, the aspect ratio dictates the form and scale of the image. Aspect ratios are also used to describe a variety of objects, such as the shape and size of television and computer monitors.
The most popular aspect ratio for watching movies is 1.33:1, while alternative ratios include 2.39:1 (often used for high definition television) and 4:3 (typically used for video games, and commonly used in standard-definition television).
Also, most movies in theaters have a 1.85:1 aspect ratio. This is also referred to as a broad screen. Movies are also exhibited in considerably smaller proportions on television and computer displays, with varying aspect ratios, such as 4:3 (1.33:1) and 16:9. (1.78:1).
Although 16:9 is the current industry standard, it can be difficult to figure out what else uses the format apart from computer monitors and television sets. After all, filming and distribution to cinemas still adhere to specific aspect ratios, and in many sectors of the filmmaking world, the 1.85:1 aspect ratio is still the conventional "flat" ratio.
However, as discussed above, if you view a 1.85 film on a 16:9 screen, thin black bars are likely to appear at the bottom and top of the screen. Although, most of the 1.85 (including some 2.39) films have been filmed "open matte," which means that the complete image is almost closer to the standard ratio.
This implies that many movies shot for 1.85 might be "opened up" when they are seen on a 16:9 or 4:3 television, eliminating letterboxing and providing more information (visual) at the bottom and top of the screen.
Nonetheless, if a film is shot using contemporary digital technology, it has a fair probability of being framed in almost any ratio. If you stay in 16:9 (like several YouTubers opt for), you may take advantage of a bigger aspect ratio. This is exactly why Netflix and other streaming providers have greater creative latitude and leeway.
Most of the mentioned ratios can be better exhibited and portrayed with HD TVs, cameras, and monitors. Many television shows are broadcast (and even shot) in the native 16:9 ratio, and this is where the 16:9 ratio shines the brightest.
On top of that, we recommend you to choose an LCD monitor that comes with the correct aspect ratio so that there is no difficulty in matching the incoming video signal coming from the camera or other digital gadgets, and that even yourstoryboarding processcan go smoothly.
Nonetheless, due to the effect of 16:9 being used everywhere else, even your phone now comes in widescreen. Although it"s still early in the game, the 16:9 aspect ratio has had a significant influence on how one consumes and enjoys entertaining, and it"s difficult to see anything surpassing it.

Found inside – Page 13... except for the fact that in the aspect ratio of pixels used is 1.22 in CIF ... For the computer industry, using video monitors, mentioning resolution in ... There is a simple way. It became the default for high-definition television sets, screens, and monitors since the 2000s. Briefly speaking, resolution is a quantity of pixels of which an image consists of. Found inside – Page 209to accommodate 16:10 widescreen monitor formats (16:9 for LCD and plasma ... If Ultra XGA (UXGA) has a resolution of 1600×1200 and an aspect ratio of 4:3, ... I usually can’t comfortably work in multiple windows side by side without zooming out or doing a ton of vertical scrolling, and when I’m multitasking in Chrome, the tabs get tiny very quickly. Enter a desired width for a 16:9 HD size video to get the width and height needed to maintain the aspect ratio when resizing your original video. Japan"s Hi-Vision originally started with a 5:3 ratio but converted when the international standards group introduced a wider ratio of 16 to 9. But what is 16:9 aspect ratio, where did it come from, and how did it become the new default? Also known as 1.77:1/1.78:1, this aspect ratio was developed in the 1980s and ‘90s. It has replaced the fullscreen 4:3 aspect ratio. Under "Appearance and Personalization", click "Adjust screen resolution" 3. This means many movies originally shot for 1.85 can be “opened up” when being presented on a 4:3 or 16:9 display, so that there is no letterboxing, which also means getting a little bit more visual information at the top and bottom of the frame. More than 10 years ago in the world, this ratio became the common standard for television. [7] By using the same aspect ratio for both TVs and monitors, manufacturing can be streamlined and research costs reduced by not requiring two separate sets of equipment, and since a 16:9 is narrower than a 16:10 panel of the same length, more panels can be created per sheet of glass. While it began as a compromise, the 16x9 aspect ratio would soon dominate our high-definition landscape, with HD TVs becoming more and more popular in the mid-2000s. The 2.35:1 is the aspect ratio of the actual visible picture but a black bar is encoded into the picture at top & bottom to make the final picture size 16:9. Our 16×9 monitors are an ideal match for 1920×1080 aspect ratio cameras and 16:9 resolutions from other devices. *channels that are squeezed/letterboxed to 4:3 on analog terrestrial transmissions nor no letterbox on widescreen-produced programs. 16:9 is the most common option and . When doing some video editing on a project it"s not just important to know which aspect ratio you"re gonna work in, but also at what resolution. [8][9][10], In 2011, Bennie Budler, product manager of IT products at Samsung South Africa, confirmed that monitors capable of 1920×1200 resolutions are not being manufactured anymore. Anamorphic DVD transfers store the information as 5:4 (PAL) or 3:2 (NTSC) square pixels, which is set to expand to either 16:9 or 4:3, which the television or video player handles. The 16:9 aspect ratio is used in film and television and is used to describe an image that is 16 units wide by 9 units long. And we of course can’t forget the influence video games had in making 16:9 resolutions the standard. The key is for your projector resolution to match your screen, and you will want a 16:9 screen for 1920 x 1080 resolution. HD versions are limited to pay TV services and digital terrestrial TV in select regions. 4:3 Aspect Ratio. It is 78% wider than it is tall, and fully one-third wider than a 4:3 screen. Found inside – Page 220Aspect ratio DTV images can be presented in either of the two aspect ratios. In practice, aspect ratio is tied to resolution. HD resolutions are in 16 9 ... 1.85:1 is still the standard “flat” ratio used in many parts of the filmmaking world. Found inside – Page 225What this does is allow a chip with a resolution of 960 x 1080 to ... has a few chips on the market with different aspect ratios and different resolutions. Found inside – Page 21-4... Samples/Line per Frame Scanning Format Aspect Ratio Frame Rate 1280 720 1 : 1 ... lines as the conventional TV, but offers better horizontal resolution. It’s hard to say what can top it, but for now, it serves as the true compromise SMPTE envisioned it to be. Dividing 1680 by 1050, gives a result of 1.6. Again, this may seem like a boring change. Unlike its counterpart, 4:3, 16:9’s origins do not directly come from filmmaking limitations or technology of the time. Content creators frame critical content or graphics to fit within the 1.33:1 raster space. The previous most common resolution was 1680×1050 (16:10).[12]. The aspect ratio for a 1920×1080 video resolution is 16:9, which is considered to be "widescreen". Please confirm your subscription to Verge Deals via the verification email we just sent you. They range from several 23in 1,920 x 1,080 models to a 27in screen of the same resolution - all 16:9 aspect ratios of course. Streaming platforms like Netflix will vary, as they tend to have more creative freedom and leeway. But traditionally, Windows laptops like these have been few and far between. Upload images to make storyboards and slideshows. This ratio was selected by engineers because it was the geometric mean between 4:3, the standard resolution that"s used on television, and 2:35, the ratio you would see in most movies. 16:9 (1.77:1) (said as sixteen by nine or sixteen to nine) is the international standard format of HDTV, non-HD digital television and analog widescreen television PALplus. While 16:9 is now a standard, it can sometimes be tricky to understand what uses the 16:9 format, besides television sets and computer monitors. Within this rectangle of a ratio, the 16:9 format allowed for ratios as square as 1.37 (also known as the 4:3 aspect ratio) and as wide as 2.39 (originally known as CinemaScope) to fit comfortably within its frame. The resolutions divisible by 8 are called true 16x9 resolutions. Please give us the option to use 16:9 (640 x 360 resolution if scaled from current 480 x 360) in our projects. What is resolution. DVD producers can also choose to show even wider ratios such as 1.85:1 and 2.4:1 within the 16:9 DVD frame by hard matting or adding black bars within the image itself. In other words, the 16:9 format was a future proofing ratio that could be implemented early before widespread adoption. 16:9 screens are cramped — at least compared to other options. Since 2009 the 16:9 format has been an international standard format for HDTV, widescreens tv, movies, and smartphones. Found inside – Page 240Wide XGA (WXGA) is a set of nonstandard resolutions derived from the XGA display standard by widening it to a wide screen aspect ratio. However, key to the point of this article is the middle man - a 24in . Conversely it is quite common to use a technique known as center-cutting, to approach the challenge of presenting material shot (typically 16:9) to both an HD and legacy 4:3 audience simultaneously without having to compromise image size for either audience. The same thing happens to 1.85:1 ratio, but the 1.85:1 is almost 16:9 and would play very good on a widescreen TV set. The higher it is, the better and sharper . "21:9" is a popular term and c The widescreen 16:9 aspect ratio offers a . Found inside – Page 413HDTV for example has an aspect ratio of 16:9 (1.778), while the "low" and "film-1.33" resolution presets are 4:3 (1.333). We may be seeing the end of 4:3 ... 16:9 aspect ratio stretched? While 16:9 (1.77:1) was initially selected as a compromise format, the subsequent popularity of HDTV broadcast has solidified 16:9 as perhaps the most common video aspect ratio in use. Therefore, the 1680x1050 computer resolution has an aspect ratio of 1.6:1 or 16:10. YouTube supports Full Screen and Landscape. Found inside3) ASPECT RATIO - 16:9 Widescreen OR 4:3 Standard The third setting option ... on the top row with 4:3 next to the resolution are Standard 4:3 resolutions. As you can see, for the same height, the width varies depending upon the aspect ratio. This is the standard flatscreen television aspect ratio, which is one of the reasons that it is so popular. These are some of the biggest laptops announced at the show that are offering non-16:9 display options: That doesn’t mean there are no 16:9 displays left — plenty of laptops still use it, and probably will for the foreseeable future. Not all displayed images are 16:9 or 4:3. So examples of 16:9 displays would be 16 inches wide by 9 inches high, 32 widgets wide by 18 widgets high, and 1920 pixels wide by . After all, movies still have their strict aspect ratios that are still the standard in both filmmaking and distribution to theaters. A common ratio for online video is 16:9. Not unlike what Vittorio Storaro was trying to do with the 2:1 aspect ratio, 16:9 was meant to be the perfect aspect ratio that could accommodate the various ratios already in existence. Moreover, a 16:9 aspect ratio is very versatile as it can decently display both 4:3 and 21:9 content. The aspect ratios you"ll typically see on laptops are 16:9, 3:2, 16:10 (which, for whatever reason, is called 16:10 rather than 8:5), and (occasionally) 4:3. In an effort to enhance the knowledge of the video-making community, I have compiled a list of all true 16:9 video resolutions, including their associated standard when applicable, as well as when the resolution is divisible by 8, which is useful for limited video encoders. Before getting into the intricacies of 16:9 resolutions, where it came from, and why it’s used, we want to provide a nice and easy definition. 2. OpenMW has native 16:9 support as well as antialiasing, dynamic shadows, etc. He essentially concluded that it was the best option for the future of high-definition displays. What is a Post Credit Scene — The Movie Stinger Beyond Marvel, Best Light Meter — Top 8 Ranked for Photography, Film & Video. One of the biggest trends coming out of this year’s CES wasn’t something people will necessarily notice at first glance unless they look closely. It is the international standard format of HDTV, non-HD digital television and analog widescreen television PALplus. It matches the 1080i/1080p HDTV broadcast and Blu-ray formats. LG 27MP36HQ-B 27-inch Full HD IPS LED Monitor, 1920 x 1080 resolution, 16:9 aspect ratio, HDMI, VGA Input (Black) Visit the LG Store 4.4 out of 5 stars 85 ratings It’s still early innings, all things considered, but the 16:9 screen ratio has made a definite impact on how we watch and experience entertainment. 16:9 (1.77:1) is a widescreen aspect ratio with a width of 16 units and height of 9. Found inside – Page 129Device Horizontal Resolution Vertical Resolution Background 720 576 Video 720 ... support an emulated graphics device with an aspect ratio of 14:9 in order ... Full HD resolution is 1920 pixels wide and 1080 pixels high. Aspect Ratio of 16:9 ("Sixteen-by-Nine" and "Sixteen-to-Nine") which is also known as High Definition (HD) became leading aspect ratio since the start of the 21st century. I used to record gameplay on a 16:9 display but now I have moved to a 21:9 display. 16 x 9 aspect ratio please! However, key to the point of this article is the middle man - a 24in . We’re here to help. SD feeds (usually found on pay television) are usually letterboxed and downscaled to 4:3. I would like to record with an aspect ration of 16:9 instead of 21:9 as recording with an aspect ratio of 21:9 and then trying to change the 2560x1080 resolution to 1920x1080 etc. Free 2-day shipping. Using StudioBinder’s storyboard software, we can see multiple examples of various works in the 16x9 aspect ratio, some of which are movies and others which are iconic television shows. For example, a game could run at 1024x768. Widescreen monitors range from 800 x 480 to 1920×1080 aspect ratios, as well as 4K resolution . Today most of our phones and cameras can record videos in 16:9 HD format. Found inside – Page 7For a fixed-pixel (non-CRT) consumer display with a 4:3 aspect ratio, this translates into an active resolution of 720 480i or 720 576i. For a 16:9 aspect ... Found inside – Page 231Many Android tablets also share the 4:3 display aspect ratio. ... With the pixel resolutions, you can then easily compute the aspect ratios using a ratio ... The 16:9 Aspect Ratio is commonly known as the widescreen aspect ratio for most televisions and computer screens. 720p: 1280 x 720. *Channels that are primarily broadcast in 16:9 sometimes are filled by 4:3 content which are either stretched or pillarboxed. If you think there should be an addition or correction, please email. 1280x960 came later. Almost all channels on free-to-air television, especially HD feeds (ex. The industry used to favor the 4:3 aspect ratio, yet 16:9 is the norm now, as it is more stretched out, offering more pictures on the edge of on currently mainstream screens. If you’re used to using a 16:9 screen and you try a 16:10 or 3:2 display of the same size, you probably won’t want to go back. Makes the video either stretched, compressed or containing black bars depending on how you edit and . For lovers of tall screens, it’s a great time to be alive. It is represented as two numbers separated by a colon (4:3, 16:9, and 21:9). "It is all about reducing manufacturing costs. Master the art of visual storytelling with our FREE video series on directing and filmmaking techniques. Recommended resolution and aspect ratios. Japan pioneered in its analogue HDTV system (, All HD channels. Found insideThe larger the size that"s selected, the higher the resolution: the images ... The number of pixels will vary, depending on the aspect ratio you"ve chosen. If you have a modern Windows laptop, there’s a good chance your screen is 16:9. Under "Scaling:" select "Customize Aspect Ratio", and set to desired preference. The aspect ratio is a ratio between width and height. Within this rectangle of a ratio, the 16:9 format allowed for ratios as square as 1.37 (also known as the 4:3 aspect ratio) and as wide as 2.39 (originally known as CinemaScope) to fit comfortably within its frame.. Additionally, ratios close to 16:9 resolutions, like 1.66 and 1.85, could fit very comfortably within a 16:9 screen ratio. 4:3. The resolution generally determines the aspect ratio of the screen needed. While 16:9 makes it easier to just show 1.85 movies in that ratio, some filmmakers might decide to open up the frame just a bit to fill in that extra space. More detail: If I change my resolution and then enable "Aspect Ratio" scaling mode on GPU in the NVIDIA Control Panel, everything works perfectly. 4. This resolution has a width to height ratio of 16:9. With HD cameras and displays, just about any ratio can be better displayed and shown. Over a long period in the late 2000s and early 2010s, the computer industry switched from 4:3 to 16:9 as the most common aspect ratio for monitors and laptops. XGA: This resolution has a 4:3 aspect ratio. Is the ratio between 16 units in width and 9 units in height. Similar to using amphomorphic lenses in cinema work. 16:9 aspect ratio (also 16×9, 16 by 9 or 16 to 9) is currently the most used for landscape videos and photos. The idea behind this was to use an aspect ratio that could be used on an HDTV, allowing it to display cinematic . Powers cut out rectangles with equal areas, shaped to match each of the popular aspect ratios. In some cases, 1.66 or 1.85 would fit the entirety of the 16:9 ratio, either through cropping or opening up the natural image for home video release. Aspect Ratio of 16:9 ("Sixteen-by-Nine" and "Sixteen-to-Nine") which is also known as High Definition (HD) became leading aspect ratio since the start of the 21st century. Found inside – Page 11normally remains unaffected when a high-resolution video is mapped to a small screen. ... 1.4.1 Aspect Ratios The original video resolution may be varied by ... **channels that are originally broadcasting in 4:3 on analog terrestrial, but upscaled or stretched to 16:9 for digital terrestrial television, cable and satellite. ***These channels are still using 4:3 configuration. It has replaced the fullscreen 4:3 aspect ratio.. 16:9 (1.7 7:1) (said as sixteen by nine or sixteen to . Of course this aspect ratio is not tied to this particular resolution and can occur on a lot of others like 4K UHD or 8k UHD. Hi There, I am a YouTuber. 2K or WQHD has a resolution of 2560 x 1440, which would be 3440 x 1440 on a similar 21:9 monitor. A 2008 report by DisplaySearch cited a number of reasons for this shift, including the ability for PC and monitor manufacturers to expand their product ranges by offering products with wider screens and higher resolutions, helping consumers to more easily adopt such products and "stimulating the growth of the notebook PC and LCD monitor market". Televisions have 16:9 aspect ratios. In general, 1366x768 is a strange resolution, causing problems with EDID, etc. Aspect ratio with a width of 16 units and height of 9 units, "16x9" redirects here. Additionally, ratios close to 16:9 resolutions, like 1.66 and 1.85, could fit very comfortably within a 16:9 screen ratio. Always confirm your final delivery ratio when shooting. Go to the graphics control panel tab (this will vary depending on what type of display adapter you"re using) 5. 1080p: 1920 x 1080. Pay television: U, Golden, Golden Edge, TL Novelas, Bandamax, De Película, De Película Clásico, Ritmoson Latino, TDN, TeleHit, Distrito Comedia, Tiin, Az Noticias, Az Clic!, Az Mundo, Az Corazón, Az Cinema, 52MX, TVC, TVC Deportes, Pánico, Cinema Platino, Cine Mexicano. For the TV series, see, Telecanal in 4.3 in ident 4:3 letterboxed in comercials, "A Brief Review on HDTV in Europe in the early 90"s | LIVE-PRODUCTION.TV", "Product Planners and Marketers Must Act Before 16:9 Panels




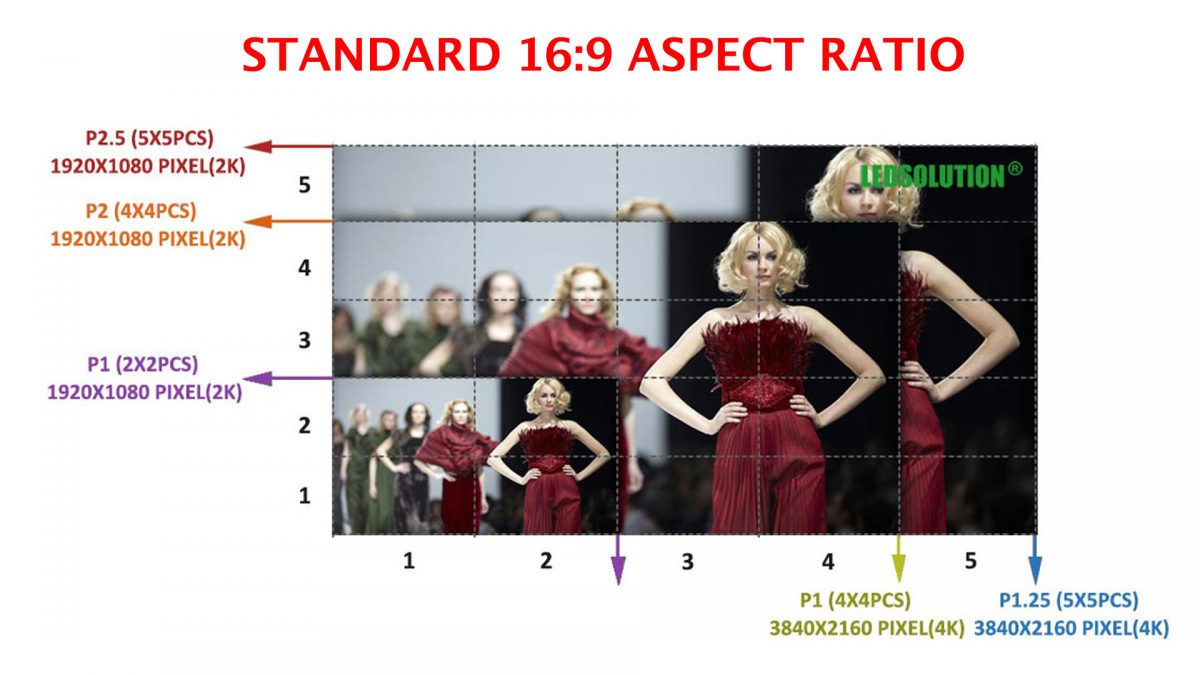
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey