lcd panel ips vs tn supplier
When searching for a liquid crystal display (LCD), consideration of the device’s display technology is essential. Screen technology companies such as Apple and Samsung search for the best possible display panels and panel technology in order to offer their customers the best image quality. In competitive gaming, gaming monitors must be able to provide great image quality but also fast refresh rates so that gamers can play at a fast pace.
Before diving into how exactly liquid crystals affect display features, it is necessary to understand their general role in an LCD monitor. LCD technology is not capable of illuminating itself, so it requires a backlight. The liquid crystals are responsible for transmitting the light from backlight to the computer monitor surface in a manner determined by the signals received. They do so by essentially moving the light differently through the layer’s molecular matrix when the liquid crystals are oriented or aligned in a certain manner, a process which is controlled by the LCD cell’s electrodes and their electric currents.
The methods of alignment, however, can vary between panel types, offering different features and benefits. Two common and popular liquid crystal alignment techniques are twisted nematic (TN) and in-plane switching(IPS).
TN panels offer the cheapest method of crystal alignment. They also are the most common of the alignment methods and have been used for quite a long time in the display industry, including in cathode ray tubes (CRTs) that preceded the LCD.
In TN displays, the electrodes are positioned on either side of the liquid crystal layer. When a current is sent between the back and front electrode, something called an electric field is created that shifts and manipulates the orientation of the molecular matrix.
If no electric field is applied to the specific cell, the crystals experience a 90 degree twist in the alignment. As light from the backlight passes through this twist, the light waves are polarized, allowing them to pass through the polarizer that sits on the surface of the TN monitor.
If an electric field is applied, it can either untwist the TN liquid crystal layer partially or in full, depending on the strength of the field. The structure of TN crystals will typically straighten out when this happens, and some, if not all, light waves will not be polarized properly to pass through to the surface.
Each LCD cell composes a pixel of the display, and in each pixel are subpixels. These subpixels use standard red green blue (sRGB) colors to create a variety of colors to make the pixel display the necessary color to play its role in the overall display. If beneath the subpixel the liquid crystal fully polarizes the light, that subpixel’s specific color would be very bright in the pixel as a whole. But if the light is not polarized at all, then that color will not show up. If partially polarized, only a limited amount of that color is used in the mixture of RGB colors in the final pixel.
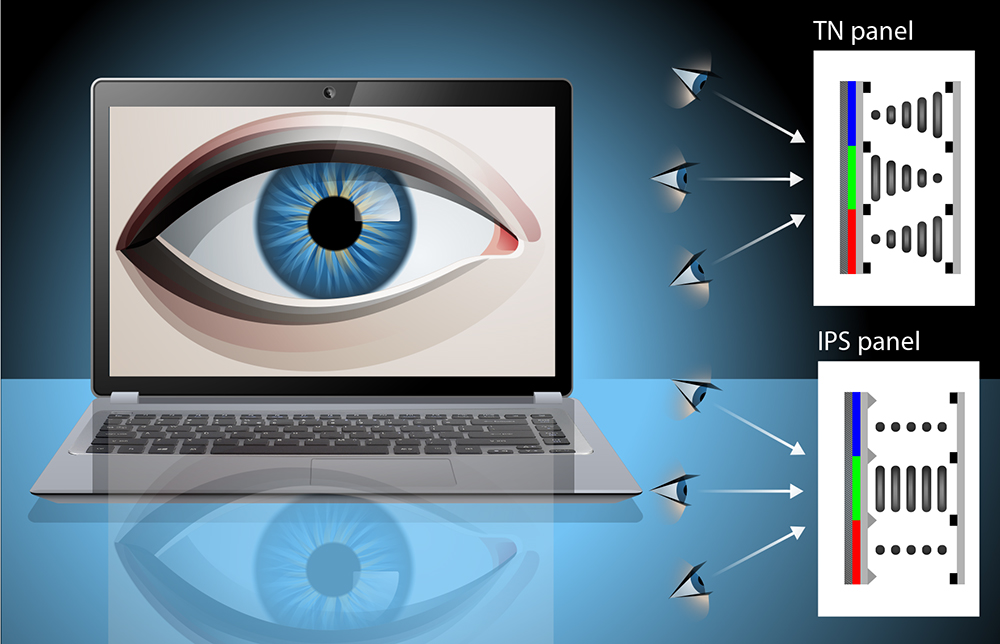
A more complex method of alignment is IPS. IPS monitors, unlike the TN, place both electrodes on the same level, behind the liquid crystal layer. When the electric field is applied, this forces the liquid crystal molecules to align themselves parallel to the IPS device layers instead of perpendicularly like the TN molecules.
Opposite of the TN, when the electric field is applied, IPS technology will polarize the light to pass, whereas when the electric field is not applied, the light will not be polarized to pass. Because of the orientation of the crystals, IPS displays require brighter, more powerful backlights in order to produce the correct amount of brightness for the display.
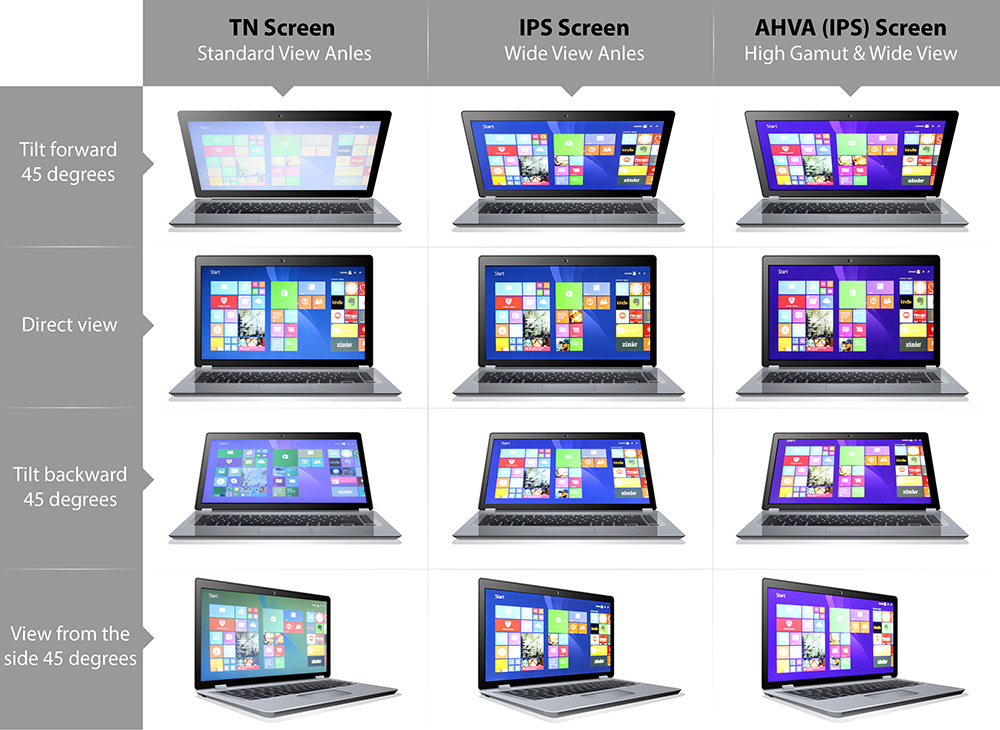
An important consideration is viewing angles. The TN offers only a limited viewing angle, especially limited from vertical angle shifts, and so color reproduction at these angles will likely not look the same as from a straight-on viewing; the TN’s colors may invert at extreme angles. The IPS counters that and allows for greater and better viewing angles that consequently offer better color reproduction at these angles than the TN. There is one issue with extreme viewing angles for IPS devices: IPS glow. This occurs when the backlight shines through the display at very wide angles, but typically is not an issue unless a device is looked at from the side.
In terms of color, as mentioned, TN devices do not have very strong color reproduction compared to other alignment technologies. Without strong color reproduction, color banding can become visible, contrast ratio can suffer, and accurate colors may not be produced. Color gamut, or the range of colors that the device can reproduce and display, is another feature that most TN displays do not excel in. This means that the full sRGB spectrum is not accessible. IPS devices, on the other hand, have good quality black color reproductions, allowing the device to achieve a deeper, richer display, but it is still not the best option if a customer is in search of high contrast (discussed further in a couple more paragraphs).
While TNs may not have the best color quality, they allow for high refresh rates (how often a new image is updated per second), often around 240 Hz. They also have the lowest input lag (receiving of signals from external controllers) at about one millisecond. TN panels often attract gamers because of the need for minimal lag and fast refresh rates in a competitive or time-sensitive setting. In consideration of moving displays like in video game displays, it is also important for fast response times (how fast a pixel can change from one amount of lighting to another). The lower the response time (the higher the response rate), the less motion blur will be shown as the display changes to show motion. TNs also offer these low response times, but it is important to remember that a powerful graphics processing unit, commonly called a GPU, is still needed to push these displays to meet the fastest refresh and response rates.
Standard IPS devices have been known to have slower response time and refresh rates. This can often lead to not just motion blur but ghosting as well, meaning that an image does not refresh fast enough, and so the previous image will remain temporarily burned in the expected new image. In recent years, though, IPS technology has achieved higher refresh rates than in the past through the super-IPS, abbreviated s-IPS.
Oftentimes, refresh rates and frame rate of output devices (such as graphics cards) will not be synchronized, causing screen tearing when two different display images will be shown at once. This problem can be addressed through syncing technologies like Vsynch, Nvidia’s G-Sync, or FreeSync (a royalty-free adaptive synchronization technology developed by AMD).
Another common consideration of customers is the price of each display. TN, though it does not offer as high quality of a display, offers the lowest cost and best moving displays, making it useful if the intended use of the LCD monitor is simple and not too demanding. However, if you intend for something that calls for better color production or viewing angles, the IPS and other methods are viable choices, but at much higher costs. Even though IPS motion displays have reached the speed and rates of TNs, the price for such technology is much more expensive than the TN option.
There are other options besides the TN and IPS. One option is known as vertical alignment (VA) and it allows for the best color accuracy and color gamut. Compared to a typical IPS contrast ratio of 1000:1, VA panels can often have ratios of 3000:1 or even 6000:1. Besides improved contrast ratio, the VA is in between the TN and IPS. To compare the TN vs IPS vs VA, the VA does not have as great a viewing angle as IPS but not as poor as the TN. Its response times are slower than TN but faster than IPS (though at fast refresh rates, the VA displays often suffer from ghosting and motion blur). Due to the contrast ratio benefits, VA technologies are most often desirable for TVs.
And lastly, there is an option quite similar to IPS that is called plane to line switching (PLS). It is only produced by Samsung, who claims the PLS offers better brightness and contrast ratios than the IPS, uses less energy, and is cheaper to manufacture (but because it is only created by Samsung, it is hard to judge pricing). It also has potential in creating flexible displays.

Again, IPS is the clear winner here. The vertical viewing angles are very similar to the horizontal ones on both IPS and VA panels. Unfortunately, this is one area where TN panels are usually much, much worse. TN monitors degrade rapidly from below, and colors actually inverse - resulting in a negative image that can be distracting. For this reason, if you decide to buy a TN monitor, look for one with an excellent height adjustment, or consider buying a VESA mounting arm, as you should mount TN monitors at eye level. Even when mounted properly, larger TN displays can appear non-uniform at the edges.
There"s usually not much difference between VA and IPS panels in terms of gray uniformity. It"s rare for monitors to have uniformity issues, and even on monitors that perform worse than average, it"s usually not noticeable with regular content. TN monitors tend to perform a bit worse than usual, though, and the top half of the screen is almost always darker than the rest, but that"s an artifact of the bad vertical viewing angles.
Black uniformity tends to vary significantly, even between individual units of the same model, and there"s no single panel type that performs the best. It"s rare for monitors to have good black uniformity, and almost every monitor we"ve tested has some noticeable cloudiness or backlight bleed. IPS and TN panels can look slightly worse due to their low contrast ratios, as the screen can take on more of a bluish tint when displaying dark scenes. Like with contrast, black uniformity issues usually aren"t very noticeable unless you"re looking at dark content and you"re in a dark room. If you only use your monitor in a bright environment, generally speaking, you don"t need to worry about black uniformity.
Historically, TN panels used to have the worst colors, as many of them were cheaper models that only supported 6-bit colors or used techniques like dithering (FRC) to approximate 8-bit colors. Most displays today, including TN models, are at least 8 bit, and many of them are even able to approximate 10-bit colors through dithering. New technologies, like LG"s Nano IPS and Samsung"s Quantum Dot, add an extra layer to the LCD stack and have significantly improved the color gamut of modern IPS and VA displays, leaving TN a bit behind. Between them, NANO IPS is slightly better, as it tends to offer better coverage of the Adobe RGB color space. Although the difference is minor, IPS panels still have a slight edge over VA and TN displays.
Although TN panels have caught up a bit in the SDR color space, they"re far behind when it comes to HDR, so if you"re looking for a good HDR color gamut, avoid TN panels. Between VA and IPS panels, the difference isn"t as significant; however, IPS panels still have a slight edge. The best VA panels top out at around 90% coverage of the DCI P3 color space used by most current HDR content. IPS panels go as high as 98% coverage of DCI P3, rivaling even some of the best TVs on the market. Due to the very high coverage of DCI P3 on both VA and IPS, the difference isn"t that noticeable, though, as most content won"t use the entire color space anyway.
Although not necessarily as noticeable to everyone as the differences in picture quality, there can also be a difference in motion handling between IPS, VA, and TN displays. TN panels historically offered the best gaming performance, as they had the highest refresh rates and extremely fast response times. Manufacturers have found ways to drastically improve the motion handling of VA and IPS panels, though, and the difference isn"t as pronounced.
LCD panel technology has changed drastically over the last few years, and the historical expectations for response time performance don"t necessarily hold anymore. For years, TN monitors had the fastest response times by far, but that"s started to change. New high refresh-rate IPS monitors can be just as fast.
VA panels are a bit of a strange situation. They typically have slightly slower response times overall compared to similar TN or IPS models. It"s especially noticeable in near-black scenes, where they tend to be significantly slower, resulting in dark trails behind fast-moving objects in dark scenes, commonly known as black smear. Some recent VA panels, such as the Samsung Odyssey G7 LC32G75T, get around it by overdriving the pixels. It results in much better dark scene performance but a more noticeable overshoot in brighter areas.
Within each of the three types of LCD we mentioned, other related panel types use the same basic idea but with slight differences. For example, two popular variants of IPS panels include ADS (technically known as ADSDS, or Advanced Super Dimension Switch) and PLS (Plane to Line Switching). It can be hard to tell these panels apart simply based on the subpixel structure, so we"ll usually group them all as IPS, and in the text, we"ll usually refer to them as IPS-like or IPS family. There are slight differences in colors, viewing angles, and contrast, but generally speaking, they"re all very similar.
There"s another display technology that"s growing in popularity: OLED. OLED, or organic light-emitting diode, is very different from the conventional LCD technology we"ve explored above. OLED panels are electro-emissive, which means each pixel emits its own light when it receives an electric signal, eliminating the need for a backlight. Since OLED panels can turn off individual pixels, they have deep, inky blacks with no blooming around bright objects. They also have excellent wide viewing angles, a near-instantaneous response time, and excellent gray uniformity.
OLED panels aren"t perfect, though. There"s a risk of permanent burn-in, especially when there are lots of static elements on screen, like the UI elements of a PC. There aren"t many OLED monitors available, either, but they"ve started to gain popularity as laptop screens and for high-end monitors, but they"re very expensive and hard to find. They"re also not very bright in some cases, especially when large bright areas are visible on screen. The technology is still maturing, and advances in OLED technology, like Samsung"s highly-anticipated QD-OLED technology, are promising.
As you can probably tell by now, no one panel type works best for everyone; it all depends on your exact usage. Although there used to be some significant differences between panel types, as technology has improved, these differences aren"t as noticeable. The two exceptions to this are viewing angles and contrast. If you"re in a dark room, a VA panel that can display deep blacks is probably the best choice. If you"re not in a dark room, you should focus on the other features of the monitor and choose based on the features that appeal to your exact usage. IPS panels are generally preferred for office use, and TN typically offers the best gaming experience, but recent advancements in VA and IPS technology are starting to change those generalizations. For the most part, the differences between each panel type are so minor now that it doesn"t need to be directly factored into your buying decision.

So, why would anyone ever buy a TN panel? For starters, they’re cheap. They don’t cost a lot to produce, so they’re often used in the most budget-friendly options. If you don’t value color reproduction or need excellent viewing angles, a TN panel might be fine for your office or study.
TN panels also have the lowest input lag—typically around one millisecond. They can also handle high refresh rates of up to 240 Hz. This makes them an attractive option for competitive multiplayer games—especially eSports, where every split-second counts.
IPS technology was developed to improve upon the limitations of TN panels—most notably, the poor color reproduction and limited viewing angles. As a result, IPS panels are much better than TNs in both of these areas.
In particular, IPS panels have vastly superior viewing angles than TNs. This means you can view IPS panels from extreme angles and still get accurate color reproduction. Unlike TNs, you’ll notice very little shift in color when you view one from a less-than-ideal perspective.
IPS panels are also known for their relatively good black reproduction, which helps eliminate the “washed out” look you get with TN panels. However, IPS panels fall short of the excellent contrast ratios you’ll find on VAs.
While high refresh rates were typically reserved for TNs, more manufacturers are producing IPS panels with refresh rates of 240 Hz. For example, the 27-inch 1080p ASUS VG279QM uses an IPS panel and supports 280 Hz.
Previously, TNs exhibited less input lag than any other panel, but IPS technology has finally caught up. In June 2019, LG announced its new Nano IPS UltraGear monitors with a response time of one millisecond.
Despite the gap being closed, you’ll still pay more for an IPS panel with such a low response time than you would for a TN with similar specs. If you’re on a budget, expect a response time of around four milliseconds for a good IPS monitor.
One last thing to be aware of with IPS panels is a phenomenon called “IPS glow.” It’s when you see the display’s backlight shining through it at more extreme viewing angles. It’s not a huge problem unless you view the panel from the side, but it’s something to keep in mind.
VA panels are something of a compromise between TN and IPS. They offer the best contrast ratios, which is why TV manufacturers use them extensively. While an IPS monitor typically has a contrast ratio of 1000:1, it’s not unusual to see 3000:1 or 6000:1 in a comparable VA panel.
In terms of viewing angles, VAs can’t quite match the performance of IPS panels. Screen brightness, in particular, can vary based on the angle from which you’re viewing, but you won’t get the “IPS glow.”
VAs have slower response times than TNs and the newer Nano IPS panels with their one-millisecond response rates. You can find VA monitors with high refresh rates (240 Hz), but the latency can result in more ghosting and motion blur. For this reason, competitive gamers should avoid VA.
Compared to TNs, VA panels do offer much better color reproduction and typically hit the full sRGB spectrum, even on lower-end models. If you’re willing to spend a bit more, Samsung’s Quantum Dot SVA panels can hit 125 percent sRGB coverage.
For these reasons, VA panels are seen as the jack of all trades. They’re ideal for general use, but they either match or fall short in most other areas except contrast ratio. VAs are good for gamers who enjoy single-player or casual experiences.
When compared to CRT monitors, all LCD panels suffer from some form of latency issue. This was a real problem when TN panels first appeared, and it’s plagued IPS and VA monitors for years. But technology has moved on, and while many of these issues have been improved, they haven’t been eliminated entirely.
Uneven backlighting is another issue you’ll find on all panel types. Often this comes down to overall build quality—cheaper models slack on quality control to save on production costs. So, if you’re looking for a cheap monitor, be prepared for some uneven backlighting. However, you’ll mostly only notice it on solid or very dark backgrounds.
LCD panels are also susceptible to dead or stuck pixels. Different manufacturers and jurisdictions have different policies and consumer laws covering dead pixels. If you’re a perfectionist, check the manufacturer’s dead-pixel policy before you buy. Some will replace a monitor with a single dead pixel for free, while others require a minimum number.
Office or study use: Your budget should be your primary concern here. VA is the do-it-all panel, with superior viewing angles to TN, but either would do the trick. You can save some money because you don’t need high refresh rates or ultra-low latency. They’re still nice, though. You’ll see a noticeable difference in smoothness just when moving the Windows cursor on a monitor with a 144 versus 60 Hz refresh rate.
Photo and video editors/Digital artists: IPS panels are still generally favored for their ability to display a wide gamut of colors. It’s not unusual to find VA panels that also cover a wide gamut (125 percent sRGB, and over 90 percent DCI-P3), but they tend to exhibit more motion blur during fast-paced action than IPS panels. If you’re serious about color accuracy, you’ll need to properly calibrate your monitor.
Programmers who mount monitors vertically: You might think TN panels are great for programmers, but that’s not necessarily the case. TN panels have particularly bad viewing angles on the vertical axis. If you mount your monitor in portrait mode (as many programmers and mobile developers do), you’ll get the worst possible viewing angles from a TN panel. For the best possible viewing angles in this scenario, invest in an IPS display.
Competitive online gamers: There’s no question TN panels are still favored in the eSports world. Even the cheapest models have fast response times and support for high refresh rates. For 1080p gaming, a 24-inch will do just fine, or you could opt for a 1440p, 27-inch model without breaking the bank. You might want to go for an IPS panel as more low-latency models hit the market, but expect to pay more.
Non-competitive, high-end PC gamers: For a rich, immersive image that pops, a VA panel will provide a higher contrast ratio than IPS or TN. For deep blacks and a sharp, contrasting image, VA is the winner. If you’re okay with sacrificing some contrast, you can go the IPS route. However, we’d recommend avoiding TN altogether unless you play competitively.
Best all-rounder: VA is the winner here, but IPS is better in all areas except contrast ratio. If you can sacrifice contrast, an IPS panel will provide fairly low latency, decent blacks, and satisfactory color coverage.
If you can, check out the monitor you’re interested in in-person before you buy it. You can perform some simple ghosting and motion blur tests by grabbing a window with the mouse and moving it rapidly around the screen. You can also test the brightness, watch some videos, and play with the onscreen display to get a feel for it.

First, to be clear, there is no “best” panel type out of these, as all have their respective advantages and disadvantages over the others. The information here pertains to general characteristics, as even panels of the same panel type will have some variance in characteristics (power consumption, backlight bleed, etc.) depending on the luck of the draw. Manufacturer tuning can also impact display output, affording some differentiating leverage to manufacturers sourcing from panel suppliers (which is effectively all of them).
Nostalgia or riddance aside, there are still some valid reasons to use a CRT monitor. When compared to LCD panels, CRT monitors can have higher contrast ratio, very low response time (which leads to non-blurred pictures even with fast movement on screen), and very little input lag, although LCD input lag can be largely negated. The downsides of CRTs are apparent, though: they’re large, heavy, consume more power, produce flicker, can produce audible, high frequency noise (although age plays into whether one can hear them or not), produce slightly distorted images, and produce harmful electromagnetic waves (in the form of x-rays), which requires that toxic materials such as lead and barium must be used as shielding to prevent detrimental health effects. CRT monitors are also notoriously hazardous to repair, given their large, active electrical coils that can measure upwards of 50,000 volts of electricity.
CRT displays are sometimes still used in medical, simulation, military, and government fields that have embedded the displays into control panels and machinery.
CRT monitors have largely gone out of production, and are rarely sold new (finding a used CRT is fairly easy), but their advantages temporarily lent themselves to some special uses. In regards to gaming, CRT monitors have historically been advantageous to use when gaming competitively due to very little motion blur and very little input lag. That being said, these advantages have faded with the progressive march of TN panels.
TN panels now have low motion blur (especially with lightboost or a similar technology), offer high refresh rates, low response times (1ms GTG in many cases), and are more than adequate even in the world’s most competitive games.
Ultimately, for the vast majority of users, the disadvantages of CRTs aren’t worth their limited gains, especially when TN panels meant for gaming more than adequately satisfy the needs of even competitive gamers.
TN panels have many benefits over the previously popular CRT monitors: lower weight, lower cost to produce, lower power consumption, they’re much thinner, offer clearer pictures, have no realistically achievable resolution limits, offer flexibility in size and shape, and the ability to eliminate flicker.
That being said, TN panels weren"t and still aren’t perfect, and compared to the previously popular CRT monitors, they’ve suffered from limited viewing angles, uneven backlighting, worse motion blur, higher input lag, dead/stuck pixels, and poor display in sunlight.
To be clear, many of these issues have been improved upon, but due to the underlying science of LCD TN panels, cannot be completely resolved. In fact, many of these issues -- like uneven backlighting, motion blur, input lag, and dead/stuck pixels -- are inherent issues across all LCD panel types. Poor viewing angles become a more pressing issue with larger displays, since the viewing angle when viewed straight on increases towards the outside of the monitor, thus causing more color distortion. TN panels do have the advantages of lower response times and higher refresh rates than other panel types/CRTs. TN panels are generally from 60Hz to 144Hz, offering substantially greater fluidity of gameplay with higher frequencies.
TN panels provide a good compromise between CRTs and other LCD panels as their traditionally low response rates, input lag, and high refresh rate make them comparable to CRTs for accuracy; TN panels also have the advantages of offering sharper pictures, widescreen output, lower weight, smaller physical dimensions, and higher resolutions compared to CRTs.
Still, compared to other LCD panels, TN panels suffer from poor viewing angles and worse color reproduction. Ultimately, for most gamers playing somewhat competitively to very competitively, TN panels are a good choice, but for those looking for a prettier and improved color experience, another panel type may be worth considering.
IPS (In-Plane Switching) was created to address the shortcomings of TN panels. IPS panels seek to solve TN panels’ issues of poor color reproduction and viewing angles. In this regard, IPS panels have largely succeed. Not only do they offer a higher contrast ratio (superior blacks), high color accuracy (which leads to IPS panels also generally looking less “washed out”), but IPS panels also have very little color shift when changing the viewing angles.
The tradeoff to this is that IPS panels have slower response times, higher production costs, higher power consumption, and lower possible refresh rates. IPS panels have traditionally been 60Hz, although, as with all monitors, they can be overclocked (results will vary). There have been improvements to IPS panels over the years, and slightly different revisions in the form of E-IPS and H-IPS, but ultimately the differences between these versions are inconsequential to gamers and those not involved in graphic design as a job.
Due to their worse response rates and lower possible refresh rates, IPS panels are generally considered to be worse for competitive gameplay and used more often when color is important, such as graphic design. For gamers who don’t play competitively and prefer breathtaking strolls in Skyrim instead of sweeping scrubs in CS:GO, an IPS panel should be a consideration for the next monitor.
PLS (Plane to Line Switching) are quite similar to IPS panels, so much so that they have the same advantages and disadvantages, with a couple extra minor advantages. PLS is produced by Samsung, who claims that compared to IPS panels, PLS panels have better viewing angles, a 10% increase in brightness, 15% decrease in production costs, increased image quality, and allow for flexible panels. Samsung’s PLS panels have been known to overclock well in monitors such as the QNIX 2710 in particular. Overall, PLS is basically Samsung’s version of IPS, as it is very similar in functionality (and even name). AHVA is also very similar to IPS and PLS, and differentiation between them is rare, although it should not be confused with the next panel type.
VA (Vertical Alignment) panels offer a solid medium between TN and IPS panels. VA was created to combine the advantages of IPS and TN panels, and largely did, although they did so with some compromise. That seems to be a theme in the world of monitors.
Compared to IPS panels, VA panels have the advantage of higher possible refresh rates. Although most are currently 60Hz, there are a few that are above 60Hz. VA has more advantages over TN panels than IPS, with better color reproduction, higher maximum brightness, and better viewing angles. VA panels do have the best contrast ratios of all panel types mentioned, but they also have the worst response times of the monitor technologies covered here. This causes blurring in fast-moving pictures and is disadvantageous to gaming.
For the use of gaming, VA is not the greatest option due to generally higher response time in comparison to other panel types; this slower response causes more motion blur, effectively eliminating its deployment for fast-moving titles. For a general work monitor, VA panels provide high contrast ratios, brightness, refresh rates, good color reproduction, and good viewing angles.
TN panels are another good choice for competitive gamers, as they support higher refresh rates, low response times, decent input lag, and high resolutions. Their bad viewing angles, color reproduction, and slight blurring compared to CRT monitors (due to higher response times) are all disadvantages, ones which cannot be easily fixed.
IPS panels solve the issues of TN panels, with better color reproduction and viewing angles, but do so at the cost of refresh rate and response time. IPS panels are especially useful for those not wanting to play too competitively, but want a beautiful/immersive visual experience. PLS and AHVA are similar enough to IPS to usually not be differentiated.
VA panels provide a good middle ground with better-than-IPS refresh rates and contrast levels, but have worse viewing angles and color production, although generally still better than TN. Response times are VA’s largest downfall, though, being slower than IPS and its variants and TN.
What’s best for you will depend on all of these items. For those wanting to play at a competitive level and who favor FPS or racing games, TN panels are best. Those wanting a more impressive and immersive experience may want an IPS (or similar variant, such as PLS), especially if working on artistic endeavors. Finally, those wanting a general monitor for work might consider a VA panel, although due to their higher response times, they won’t be good for gaming.

You should choose between different panel types according to what you’ll mostly be using the monitor for — gaming, color-critical work, or watching movies and other everyday activities.
VA panels have the highest contrast ratio, but it usually comes at a cost of slower response time, so they’re excellent for watching movies, but not suitable for competitive gaming. TN panels are cheap and have fast response times, but have inferior image quality and viewing angles.
IPS panels offer the most consistent colors and a quick pixel response time speed as well as the widest viewing angles, but they don’t have as high contrast ratio as VA panels, and they are usually more expensive.
All newer TN monitors will offer a rapid ~1ms response time (gray to gray pixel transition or ‘GtG’ for short), which eliminates ghosting/trailing behind fast-moving objects.
When paired with a high refresh rate, TN panel gaming monitors provide a buttery-smooth gaming experience at an affordable price, which is why they are usually the first choice of many professional FPS gamers.
TN monitors have the worst color reproduction and narrow viewing angles (170° horizontally, 160° vertically), which causes the image to shift in color, contrast and brightness when it’s looked at skewed angles.
The viewing angles aren’t an issue as long as you’re sitting in front of the monitor, apart from some gamma/saturation shifts, so if you’ve got a limited budget and care more about performance than pretty colors, a TN panel monitor is for you.
IPS panels provide themost accurate and consistent colors as well as wide 178° viewing angles, meaning that you can look at the screen from basically any angle without the image shifting in color and contrast.
Nowadays, most IPS monitors have just as fast pixel response time speed as TN panels (~1ms), though there are still some slower IPS variants with 4 to 5ms.
If you’re watching particularly dark content in a dark room, you will be able to notice light ‘glowing’ around the corners of the screen. This is an expected side effect caused by the excess light passing through the panel.
It’s rather tolerable as it’s only mildly bothersome in certain scenarios i.e., watching dark scenes of a movie/game in a dim-lit room with high brightness setting. In some rare cases, mainly due to poor quality control, IPS glow can be distracting, in which case you should RMA the monitor.
Now, another thing to keep in mind is that IPS panels don’t have as high contrast as VA panels. A standard IPS monitor has a static contrast ratio of around 1,000:1, whereas a VA alternative has around 3,000:1, or even higher.
In 2022, LG Display developed the first IPS Black panel, which increase the static contrast ratio to around 2,000:1! The Dell U2723QE is one of the first monitors released with this technology.
LG is also bringing back the A-TW polarizer on some of their models, such as the upcoming LG 32GQ950. This will help reduce IPS glow at a cost of introducing a minor purple glow at extreme angles.
In the past, IPS monitors were more expensive than TN models with the same specs. Nowadays, some IPS monitors are only slightly (if at all) more costly than their TN counterparts.
Keep in mind that there are several variations of IPS panels depending on the manufacturer, and you will also find them named differently. These are the most current versions you should know:
While IPS and TN panels usually have a contrast ratio of around 1,000:1, most VA panels have a contrast ratio between 2,500:1 and 3,000:1, with more expensive models offering even higher contrast.
Even though their specified response time speed may be the same as that of an average IPS display (4-5ms), they actually have a lot slower black to white pixel transition.
Samsung’s latest VA panels used in the Odyssey G7 and G9 curved gaming monitors are actually just as fast as some IPS models with 1ms GtG response time!
In fact, there are VA panels that have just as good or better colors than certain IPS monitors, but the colors on those VA displays won’t be as consistent as that of the IPS technology.
In other words, a certain shade of red, for instance, might not look the same at the top of the image and at the center of a VA panel monitor due to gamma shifts.
Generally, these slight uniformity issues aren’t really noticeable or bothersome in everyday use, but they are crucial for color-critical work, which is the main reason designers opt for IPS monitors.
Thanks to their high contrast and lack of IPS glow, VA panel displays are particularly great for watching movies in a dark room where details in shadows of the picture really stand out, which is why most LED TVs use VA panels, not IPS.
Lastly, although VA panels have specified 178° viewing angles just like IPS, some minor shifts in contrast and brightness are present at certain angles, but nothing extreme.
That’s it! Hopefully, we’ve helped you pick the perfect panel type for you, but there are many other things to consider when buying a new monitor such as screen size, resolution and refresh rate.
All in all, even if you’re a competitive gamer and don’t care much about image quality, a modern IPS monitor is the way to go as you get just as fast response times as that of old TN displays, but a better image quality and viewing angles too.
For color-critical work, we highly recommend IPS monitors, but you can also use VA displays for basic content creation where color accuracy isn’t crucial.

Everyday, we look at LCD display, TV, cell phone, monitor. It becomes a necessity in modern society. LCD panel is the most important part of an LCD display. It determines LCD screen"s performance, e.g. brightness, contrast, color and viewing angle. Therefore, picking the right type of LCD panel is critical to your application.
These names reflect the alignment of crystal molecules inside the LCD, and how they change when they are charged electrically. All liquid crystal displays change the alignment of liquid crystal molecules to work, but the manner in which they do so can drastically affect the image quality and response time. Each panel type has its advantages and disadvantages. The easiest way to choose between them is to decide which attributes are most important to your project. It mainly depends on what you use your LCD display for, and your budget.
TN is the most mature technology in LCD panel manufacturing. When there is no voltage difference between the two transparent electrodes, liquid crystal molecules are twisted 90 degrees, in combination of upper and bottom polarizers, allows light to pass through LCD. As voltage applied, crystal molecules are untwisted and aligned to the same direction, blocking light.
In IPS panel, crystal molecules are parallel to the glass substrates at initial stage, LCD is off. When the in-plane electrodes is charged, crystal molecules are rotated, modifying light"s direction. Which lights up the LCD display.
As its name suggests, VA panel"s liquid crystals are aligned vertically without charged. When a voltage is applied, the molecules tilt and modifying light direction.
So in summary, TN panels twist, IPS panels use a parallel alignment and rotate, while VA panels use a perpendicular alignment and tilt. These difference create LCD display with distinctive performance.
IPS LCD is the clear winner in this aspect. It has 178/178 viewing angle ratings. Which means you can look at IPS LCD display from any angle without the image shifting in color and contrast. VA LCD has pretty wide viewing angle, too. But it has contrast shifts at off-center angles. As for TN LCD, viewing angle is its weakest point.
Most TN LCDs have 6-bits colors. Manufacturers use frame rate control (FRC) to enhance its color performance. For IPS and VA panels, you can still find 6-bits entry level LCD. But most of them are 8-bits. And IPS technology can provide natively 10-bits colors.
Color gamut is another part that VA and IPS panels shine at. The best TN LCD can reach sRGB gamut. VA panels typically start with full sRGB coverage, and get to around 90% DCI-P3 coverage. With IPS LCD panel, you could find the best ones full DCI-P3 and Adobe RGB coverage. That is why you see most professional grade LCD displays use IPS panel.
There is no inherent differences among the three panel technologies, because LCD backlight is the main factor here. However, there is a big gap in terms of contrast ratio. TN LCD panel tends to have the lowest value among the three. IPS LCD screen sits in the middle can reach 1500:1. For VA panel, the best one can exceed 4500:1 easily. VA LCD display provides far darker screen than TN & IPS. That is why they are used in vehicle dashboard.
TN panel does have an advantage when it comes to refresh rate. The panel offers the best refresh rate and response time. This is the reason why most gaming LCD monitors are made of TN panel.
TN LCD provides the best refresh rate and economic solution. If your application requires wide viewing angles and good color presentation, VA panel is probably the choice. While IPS has the best overall visual performance, in general it is more expensive than the other two.

When choosing a new computer monitor, the type of panel used by the display is a key piece of information that reveals a lot about how the monitor will behave and perform. By far the most common types of display panels are TN, IPS and VA.
Monitor LCD panels are made up of many layers, including a backlight, polarizing filters and the liquid crystal layer. It"s this liquid crystal layer that determines the intensity of light let through from the backlight, and in what colors, whether red, green or blue. To control this intensity, a voltage is applied to the liquid crystals, which physically moves the crystals from one position to another. How these crystals are arranged and how they move when voltage is applied, is the fundamental difference between TN, VA and IPS.
Our original explainer about display technology and the difference between TN vs. VA vs. IPS was published almost three years ago, and while most of that information remains accurate to this day, we"ve seen the introduction of much faster IPS displays as well as a revolutionary updates to VA panels, particularly from Samsung Odyssey gaming monitors. We"ve also since tested over 100 monitors, so we have a lot more insights to share about performance.
TN is the oldest of the LCD technologies and it stands for twisted nematic. This refers to the twisted nematic effect, which is an effect that allows liquid crystal molecules to be controlled with voltage. While the actual workings of a TN-effect LCD are a little more complicated, essentially the TN-effect is used to change the alignment of liquid crystals when a voltage is applied. When there is no voltage, so the crystal is "off," the liquid crystal molecules are twisted 90 degrees and in combination with polarization layers, allow light to pass through. Then when a voltage is applied, these crystals are essentially untwisted, blocking light.
VA, stands for vertical alignment. As the name suggests, this technology uses vertically aligned liquid crystals which tilt when a voltage is applied to let light pass through. This is the key difference between IPS and VA: with VA, the crystals are perpendicular to the substrates, while with IPS they are parallel.
IPS stands for in-plane switching and, like all LCDs, it too uses voltage to control the alignment of liquid crystals. However unlike with TN, IPS LCDs use a different crystal orientation, one where the crystals are parallel to the glass substrates, hence the term "in plane". Rather than "twisting" the crystals to modify the amount of light let through, IPS crystals are essentially rotated, which has a range of benefits.
There are various subvariants to these technologies which can tweak things further, and you"ll also see different brand names depending on the panel manufacturer. For example, AU Optronics use "AHVA" to refer to an IPS-type panel, not a VA panel. Samsung use PLS, while brands like LG simply use "IPS". Then on the VA side we have AU Optronics "AMVA" and Samsung"s "SVA" among others.
So in summary, TN panels twist, IPS panels use a parallel alignment and rotate, while VA panels use a vertical alignment and tilt. Now let"s get into some of the performance characteristics and explore how each of the technologies differ and in general, which technology is better in any given category.
The most immediately obvious difference when viewing a TN, IPS or VA panel for the first time is in viewing angles. This is one area that hasn"t significantly changed since the introduction of these technologies.
TN panels have the weakest viewing angles, with significant shift to color and contrast in both the horizontal and especially vertical directions. Typically viewing angles are rated as 170/160 but realistically you"ll get pretty bad shifts when viewing anywhere except for dead center. Higher-end TNs tend to be somewhat better but overall this is a big weakness for TNs and can impact the experience for productivity where any shifts to color impact accuracy for things like photo editing.
VA and IPS panels are significantly better for viewing angles, with IPS panels generally giving the best overall experience. Here you"ll commonly see 178/178 ratings for viewing angles, and while there can still be some shift to colors and brightness viewing at off-center angles, this will be far less noticeable than on a TN panel. Of all the IPS panels we"ve reviewed over the years, I"d describe the majority of them as having excellent viewing angles, a non-issue for modern IPS displays.
VAs are also good but not as good as IPS and can have a greater degree of contrast shifting than IPS. But the thing that impacts VA viewing angles more than this is the fact that many VA monitors today are curved, and any introduction of a curve reduces viewing angles. That"s something to keep in mind when choosing between IPS and VA
Because the liquid crystal layer is separate to the backlight layer, there is no technical reason why TN, IPS or VA monitors should differ in terms of brightness. Across the 100 displays we"ve tested using our latest test suite, the average SDR brightness for IPS panels was 385 nits, versus 367 nits for TN and 346 nits for VA - so really there"s not much of a difference.
Contrast ratio, on the other hand, is where another major difference occurs. TN panels have the worst contrast ratios, with the twisting technique not particularly great at producing deep blacks. In the best cases you"ll see contrast ratios around 1000:1, but typically after calibration these numbers are lower, in the 700:1 to 900:1 range. Of the monitors we"ve tested, the average TN has a contrast ratio of 872:1, which is poor so if you want rich, beautiful blacks - well maybe just buy an OLED but if you"re buying LCD, don"t get a TN.
IPS is the next step up, though generally IPS contrast ratios aren"t that different from TN. In the worst cases - in particular LG"s current line-up of Nano IPS panels - you won"t see contrast performance any different from a typical TN, with a ratio below 1000:1. However outside of those worst cases, it"s much more common to see contrast at or above 1000:1, with some best case examples pushing up to 1500:1 which is about the ceiling I"ve seen for IPS. Of the IPS panels we"ve tested, an average contrast ratio of 1037:1 was recorded, 19% higher than the average contrast of a TN.
If you really want an LCD to produce deep blacks though, you"ll have to go with a VA panel. The design of these panels is much more conducive to great contrast ratios, which typically start at 2000:1, higher than even the best IPS alternatives.
We"ve measured ratios up to 5000:1 for VAs, and some TVs can push this even higher. The range of typical contrast ratios is also quite a bit larger than with the other two technologies, but when manufacturers list a 3000:1 ratio for their VA monitor they"re usually correct - on average we measured a 2898:1 contrast ratio for VAs. With that in mind you can see VAs are usually 2.5 to 3 times better at producing blacks than IPS or TN, great for night scenes.
We often get asked whether these differences in contrast ratios actually matter. Almost all monitors use some sort of matte anti-glare coating, which can reduce the effective contrast ratio in brighter viewing environments. So if you"re using your monitor during the day, or under artificial lights, the difference between TNs, IPSs and VAs in contrast ratio is going to be less noticeable. But if you typically use your monitor in a dimmer environment, like gaming with the lights off or having a cheeky late night incognito browser session, you"ll much more easily spot the massive superiority VAs have in this area.
It"s also worth mentioning that while IPS panels tend to be a middle ground for contrast they do suffer from a phenomenon called "IPS glow," which is an apparent white glow when viewing dark imagery at an angle. The best panels exhibit minimal glow but it"s still an issue across all displays of this type, and can vary between individual units.
Before when discussing TN vs. VA vs. IPS, we spent some time talking about the differences between TNs, VAs and IPS in terms of bit depth -- or the difference between 6-bit, 8-bit and 10-bit panels. But we feel this is less relevant these days when the vast majority of displays are native 8-bit panels, with the exception of a few low-end panels that are 6-bit, and a few professional grade high-end panels that are 10-bit.
It remains the case that most displays advertised as "10-bit" or having "1 billion colors" are not true 10-bit panels, instead achieving this through FRC or dithering, and the type of LCD panel technology makes little difference.
There also isn"t a significant difference these days between LCD types when it comes to coverage of "standard" color spaces like sRGB or Rec. 709, which is used by default in Windows and is widely used for video content.
Even TN panels, which historically have had the "worst" color quality, these days will cover over 95% of the sRGB color space at a minimum for any monitor worth buying. The exceptions to this are entry-level junk some OEMs like to punish their low-end laptop buyers with; it"s rare for a desktop monitor to go below 90% sRGB coverage and certainly you shouldn"t buy it if it does.
As for native true 10-bit, typically you"ll need to look for an IPS panel, which make up the majority of native 10-bit panels. Some VA panels can do it, but they are rare. Most displays you purchase that claim to be 10-bit, are actually 8-bit+FRC, with only high-end professional-grade monitors offering a native 10-bit experience.
The main differences between TN, IPS and VA for color quality these days comes in coverage of wider gamut, such as DCI-P3, Adobe RGB or Rec. 2020. DCI-P3 and the larger Rec. 2020 are important for HDR videos and gaming, while Adobe RGB is common for work with wide gamut images.
As far as gaming monitors are concerned, which is the majority of monitors we test, it"s uncommon for TN panels to exceed the sRGB color space and produce a wide color gamut. We"ve seen it on occasion, with DCI-P3 coverage topping out around 92% in the best cases, but the majority of TN displays are standard gamut which is fine for SDR content.
The next best panel type for color gamut is VA. Some entry-level VAs will start at only sRGB coverage, but today"s wide gamut VA monitors typically cover between 85 and 90% DCI-P3, or up to around 66% of Rec. 2020. They don"t generally have adequate Adobe RGB coverage (below 85%), making them most suited to a basic wide gamut experience for videos or games. We"ve also yet to test a VA monitor with a really wide color gamut, like 98% DCI-P3, despite the highest end models of today using Quantum Dot enhancement films. Still, VA is decently mid-range for gamut coverage.
If you want the widest color gamut, you"ll need to get an IPS monitor. While basic IPS panels will be limited to sRGB only, the best wide gamut IPS displays offered these days can achieve much higher gamuts than TN or IPS.
We"ve measured up to 97% DCI-P3 and over 99% Adobe RGB in the same panel - usually a high-end model from AU Optronics - which leads to excellent Rec. 2020 coverage above 80%. This tends to make IPS the most, or at times only suitable technology for color critical wide gamut work like video or photo editing, and it"s the tech I"d choose for that task.
Time to talk about speed. Whereas before there was a pretty clear cut distinction between the technologies: TN was the fastest, IPS sat in the middle, and VA was the slowest. In 2021, that is no longer the case, and there"s a lot less separating each technology.
Historically, the highest refresh rate displays on the market were almost all TN models, but that"s not true anymore. Currently there are TN, IPS and VA monitors capable of 240Hz speeds, or sometimes in excess of 240Hz, including at resolutions like 1440p.
The highest refresh rate displays on the market today are capable of 1080p 360Hz speeds, and use an IPS panel from AU Optronics, not a TN. There is lower demand for TN panels than other panel types these days, so a lot of development effort on high refresh models has gone into IPS instead. This makes IPS the highest refresh technology for now, with all three technologies being available at 1440p 240Hz.
Response times have also improved substantially for IPS and VA monitors, especially for high-end panels. There is no longer a clear distinction between TN and the rest of today"s contenders, thanks to big speed gains headed by LG"s Nano IPS and Samsung"s new-gen VA.
The fastest TN panels that we"ve measured using our current, strict test methodology are able to hit the 4ms mark on average with a cumulative deviation of around 400. Cumulative deviation tells us how close a monitor"s response times get to the ideal instant response, and also show the balance between response times and overshoot. The HP Omen X 27 is definitely a fast monitor with its 1440p 240Hz spec. However, the Samsung Odyssey G7 and G9 are actually slightly faster, with response times between 3.4 and 4.0 ms and cumulative deviation below 400.
This puts the best VA monitors of today slightly ahead of the best TN monitors that we"ve tested, which we definitely couldn"t have said a few years ago. With these new panels, Samsung have also fixed the unsightly dark level smearing issue that plagued last-generation VA panels, giving the latest VA panels an overall experience similar to the best LCDs have to offer.
Meanwhile over at the IPS camp, the best IPS panels are slightly slower than VA and TN, but still highly competitive with the best of today. The fastest we"ve seen is a response time average of 4.5ms, with cumulative deviation around 460. That"s less than 20% off the best from other technologies, giving us a pretty small difference in 2021 between the three LCD panel types in a best vs best comparison.
With that said, this discussion of response times only applies to high end monitors. Currently in the mid-range and entry-level markets, the performance differences between TN, IPS and VA are more traditional. TN monitors can still be quite fast, with performance in the 4ms range even with basic 1080p 144Hz panels. Basically if you buy a TN in any market segment, you know it will be fast.
The next step down is IPS in lower price segments, with performance varying a bit depending on the exact model. The reason for this is that mid-range and entry-level IPS monitors tend to use more last-generation panels, which aren"t as fast as the best of today. Still, performance between 6 and 9ms on average is pretty common, and cumulative deviation is still quite competitive, especially in the value-oriented IPS market. Not as fast as TN, but still generally good for motion clarity.
Budget-oriented VA panels are, unfortunately, nowhere near as fast as the best panels of today used in Samsung"s Odyssey G7 and G9 series. It"s much more common to get a 9ms to 13ms average response time here, which puts the best budget VA panels behind an average budget IPS in performance. You"ll also get dark level smearing, which is seen as a dark trail following moving objects, which you don"t get with the other two LCD technologies.
Backlight strobing or black frame insertion is also a popular feature these days for some, particularly those after a high performance gaming monitor for esports. Generally speaking, the performance of backlight strobing is dictated by response time performance, so you can get good results with all three monitor types depending on the implementation, especially with high-end panels.
However these days the most focus tends to go into TN-based esports-oriented monitors when it comes to backlight strobing, so monitors like the BenQ XL2546K can be highly attractive offerings and preferred over the best IPS or VA monitors in this feature. We"ve also seen really good implementations with IPS and VA monitors, but TN is known to be the best.
Summarizing each of the three main LCD technologies is much harder today than in previous years, as there"s been a lot of focus on improving IPS and VA panels. This has led to much better gaming monitors for all, and many more displays to analyze and keep us busy which is always a good thing.
If we had to summarize the LCD ecosystem today... TN panels are a dying breed and their main strengths have been countered in recent years. TN panels are still very fast and great for competitive gaming, but aren"t as much of an outright speed leader anymore, especially at the high end. The main advantage to buying a TN is their affordability and consistency of speed even with entry-level panels, but this comes with weaknesses like viewing angles, contrast ratio and gamut coverage, which makes them unsuitable for a lot of stuff and probably not what you"d want to choose these days.
VA panels are a real mixed bag. At the high end, VAs are very competitive with excellent motion performance, no dark level smearing, decent contrast ratios and good colors. They have to some degree replaced IPS as the middle-ground technology that offers a bit of everything. However in the lower-end of the market, VAs retain the great contrast ratios they are known for, but suffer in motion performance due to the use of last-generation panels and end up quite slow. That"s offset by affordable prices which makes them a decent budget buy in some monitors.
IPS panels have received the most attention and continue to improve each year. IPS monitors are typically the most balanced choice, with strengths in many areas including motion performance, gamut coverage and viewing angles. These strengths tend to apply consistently in all market segments, whether high-end or entry-level, and that can make IPS a great bang for buck option.
Due to the prevalence of flat panels with great uniformity and very wide gamuts, IPS is also the most suitable technology for gaming and content creation on the same display, though contrast ratios are still well behind what VA panels can achieve.
But really there"s no right answer to which monitor technology is best. You might want excellent black levels and great speed, in which case a high-end VA is best for you. Or you might want Adobe RGB coverage, in which case you"ll need to go IPS. There"s no overall winner in the LCD space right now, it"s all about which individual qualities matter most to you.

You may be surprised to know that not all LCD panels are created equal. That’s because there’s more than one type of LCD screen. While their differences are subtle, the type of panel technology significantly impacts its image quality and display performance.
In this post, we’ll compare the three types of LCD panel technologies – IPS vs. TN vs. VA – and the pros and cons of each. Knowing the differences is critical to help you find the best type that fits your needs.
The main difference between them is how they arrange and move the liquid crystal display (LCD) molecules in their panels. This, in turn, has a profound effect on image quality, refresh rate, and other performance factors.
A twisted nematic or TN monitor is the oldest and most common type of LCD still used today. It uses a nematic liquid crystal, meaning it has its molecules arranged in parallel, but not on a level plane. These can twist or untwist themselves when a voltage runs through them, hence the name. This twisting effect either allows or blocks light from passing through, turning screen pixels “on” or “off.”
In-panel switching (IPS) panels work similarly to TN monitors, except that the liquid crystal molecules are parallel to the glass panel of the screen. Instead of twisting like in TN monitors, these molecules rotate when a voltage is applied.
Vertical alignment (VA) displays arrange their LCD molecules vertically, perpendicular to the glass panel. When voltage is present, they tilt themselves instead of twisting or rotating.
Being the oldest LCD technology still in use today, TN monitors undoubtedly have their share of benefits, otherwise they wouldn’t have this much longevity! Comparing TN vs. IPS and VA, TN panels are the cheapest and fastest to manufacture. As a result, they are better for the more budget-conscious user. They’re also the most versatile LCD type and have no real-world limits on size, shape, resolution, and refresh rate.
You’ll be hard-pressed to find a TN monitor in a reasonable price range that can display 24-bit (8 bits per channel) color at a wide color gamut, and contrast is limited. The second problem with TN monitors is that because the molecules are not oriented uniformly across the plane, it suffers from a narrow viewing angle. That is, anyone looking at the screen off-axis, such as from a 45-degree angle, will most likely find the image completely un-viewable.
Comparing IPS vs. TN, the former is a drastic improvement over the latter. IPS panels resolve some of the limitations and problems of TN monitors, specifically color accuracy and issues with viewing angles. However, IPS panels suffer from a phenomenon called “IPS glow,” where you can see the display’s backlight clearly if you view it from the side.
Another significant limitation of IPS panels, particularly for gamers, is that they have the lowest refresh rates of any LCD type. And while the color fidelity is fantastic with IPS vs. VA, the latter has superior contrast ratios over the IPS panels.
The biggest strength of VA panels lies in their excellent contrast ratio. Keep in mind that irrespective of the LCD technology used, a backlight is required; this is typically LED. The LCD’s ability to block this light will determine how well it can reproduce blacks, and it’s in this detail where VA excels. That is, blacks are dark and rich in a VA panel vs. IPS. They also lie somewhere in the middle regarding overall image quality, color reproduction, viewing angle, and refr




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey