tft lcd displays tft lcd vs oled price
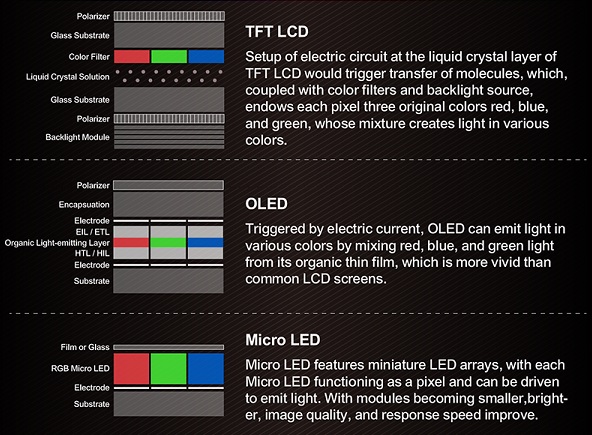
TFT LCD is a mature technology. OLED is a relatively new display technology, being used in more and more applications. As for Micro LED, it is a new generation technology with very promising future. Followings are the pros and cons of each display technology.
TFT Liquid Crystal Display is widely used these days. Since LCD itself doesn"t emit light. TFT LCD relies on white LED backlight to show content. This is an explanation of how TFT LCD works.
Relatively lower contrast:Light needs to pass through LCD glasses, liquid crystal layer, polarizers and color filters. Over 90% is lost. Also, LCD can not display pure black.
Organic Light-Emitting Diode is built from an electro-luminescent layer that contains organic compounds, which emit light in response to an electric current. There are two types of OLED, Passive Matrix OLED (PMOLED) and Active Matrix OLED (AMOLED). These driving methods are similar to LCD"s. PMOLED is controlled sequentially using a matrix addressing scheme, m + n control signals are required to address a m x n display. AMOLED uses a TFT backplane that can switch individual pixels on and off.
Low power consumption and flexible: OLED doesn"t rely on backlight and consumes less power. OLED is essentially created on plastic film. It is bendable and easy to process.
High contrast and vivid color: OLED emits light itself, can produce very bright image with beautiful color. And because OLED can be turned off, it can produce true black.
Stroboscopic effect: most OLED screen uses PWM dimming technology. Some people who are easy perceive stroboscopic frequency may have sore eyes and tears.
Micro LED, sometimes called μLED is made up of tiny LED, measure less than 100μm. Another way of looking at this is that MicroLEDs are simply traditional LEDs shrunk down and placed into an array.
Replacing organic material with inorganic GaN material eliminates the need of polarizing and encapsulation layer, found in OLED. Micro LED is smaller and thinner, consumes less power.
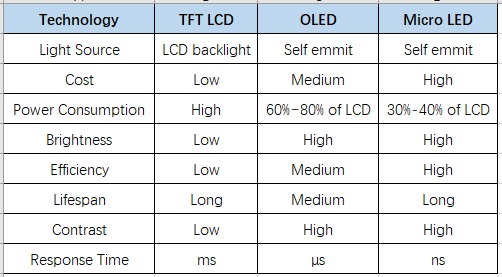
A new form of display technology called Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED) is sweeping the display world today. Let’s take a look at what TFT display VS OLED display and how it stacks up to TFTs.
OLED display uses a light-emitting diode (LED) that features an organic compound as its emissive electroluminescent layer. Electric current is applied to the diode, activating the organic compound film and giving off light as a result. The organic compound film is typically situated between two electrodes, one of which is transparent.
OLEDs are mostly used in smartphones and limited releases of high-end smart televisions. It can also be used in computer monitors and handheld game consoles.
OLED displays naturally emit light, so using them on a display panel doesn’t require a backlight. Meanwhile, LCDs need backlights because the liquid crystals cannot create light on their own. OLED’s natural light emission also paves the way for creating lighter screen devices than those using TFT LCD display.
LCD displays are brighter than OLED. This is due to the LCD’s use of backlights that can brightly light up the entire screen. While OLEDs emit good brightness levels from their light, they can never match the brightness that LCD backlights have.
OLED wins in the black levels feature. It’s because OLEDs can perfectly turn off a pixel, causing it to become completely black. LCDs can’t create perfect black screens even with their full-array local dimming feature. LCDs are also prone to blooming, where a bright part spoils the darkness of an adjacent black area.
OLED screens have better viewing angles than LCDs display. Some LCDs improve their viewing angles by using in-plane switching panels (IPS). However, the clarity of images and videos can’t match that of OLEDs when viewed from extreme side angles. This is because LCDs inherently block light due to their filtering layers, and that creates added depth which makes LCD viewing angles limited.
LCD displays are a bit more energy-efficient than OLEDs. Energy consumption in OLED displays depends on the screen brightness. Less brightness used means lower power consumption, but this may not be ideal because the contrast ratio will suffer when brightness is reduced. This is not ideal if, for instance, you’re using an OLED smartphone under bright sunlight.
Meanwhile, the backlights form the bulk of power consumption in TFT displays. Putting the backlight to a lower setting significantly improves the energy efficiency of TFT displays. For instance, reducing the backlight brightness of an LCD TV with a LED backlight won’t affect the picture quality but will draw less power consumption than an OLED TV.
Both OLED and LCD create high-quality images with a wide color gamut on a screen. OLED display wins over TFT display regarding blackness levels and viewing angle. However, the TFT display takes the cake for brightness and energy efficiency.
AMOLED is another emerging display technology lately. It stands for Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diodes. AMOLED is a type of OLED display used in several smartphones, digital cameras, televisions, and media players.
Thin film transistors (TFTs) and capacitors are attached to each pixel LED component of the panel. At least two TFTs are attached to one pixel – one to control the capacitor’s charging and another to give a voltage source.
AMOLED displays have better color accuracy than LCDs. What makes the color more accurate in AMOLED displays is largely due to the precise pixel control achieved by AMOLED panels.
Whites and blacks appear perfect in AMOLED displays. Whites produced by LCDs may carry a bluish tint due to the backlight. Blacks don’t completely appear dark in LCDs, too.
AMOLED provides a greater color gamut than LCDs. AMOLEDs (and all OLED displays in general) have additional blue and green saturation. While these hues greatly widen AMOLED’s color options, some people find the resulting colors a bit unnatural to look at.
Meanwhile, LCDs have subdued greens and quite compelling red hues. Its color gamutmay not be as wide as AMOLED’s, but many people still find it satisfying. That’s because LCD’s color range closely matches the Standard RBG color gamut profile, the one most utilized in videos and images.
LCD’s backlights help maintain the color balance of the entire screen. The backlights ensure that color balance remains consistent across the display. Meanwhile, AMOLED tends to suffer from very slight color balance drifts because of variances in the diodes’ light-emitting capacity over time.
LCDs often have a lower contrast ratio and are prone to light bleeds. That’s due to the backlights remaining open even if light has been blocked and the pixels are supposed to show black color. This is not a problem with AMOLED displays because the panel can simply switch off the pixel to create a pure black color. AMOLEDs have a better contrast ratio as exhibited by their pure black and white levels.
Since AMOLED displays do not require filtering layers and backlights, they’re more suited for use in handheld mobile devices such as smartphones and gaming consoles. LCD may be used in mobile devices as well, but the filtering layers and backlights tend to add a slight bulk to the device. Hence, many manufacturers are now switching to thinner and lighter AMOLED displays.
To sum up this part, AMOLED displays fare better than LCDs in terms of color gamut, accuracy, contrast, and mobile device suitability. However, LCDs have the potential for longer lifespans and carry a better color balance across the display device.
Display P3 is an Apple-developed color space heavily used in American films and digital movie projection. It allows devices to display richer, vibrant, and more lifelike colors that are demanded in videos and movies. It’s also created for adapting to computer displays.
Display P3 has a color space based on the DCI-P3 primaries. It uses the D65 white point which is typically used in color spaces for computer displays. Display P3 also utilizes the sRGB transfer curve in place of the DCI-P3’s 1/2.6 pure gamma curve.
If you compare color LCD vs Display P3, you’ll find a significantly wider color range in Display P3 than the typical sRGB used in color LCDs. LCD monitors, especially those used in computers and laptops, are configured to accurately represent the sRGB gamut as precisely as possible. Meanwhile, Display P3 has been consistently used in Apple products since 2015, starting with the iMac desktop.
That’s all the basic information you need to know about LCD display screens. And the difference between TFT Display VS OLED Display. Now, you know How LCD Works, its possible lifespan, components, and how it compares to other display technologies.
Armed with this information, you can better appreciate and take care of your LCD display devices. And in case you’re planning to add display devices to your business, the information you’ve learned will help you make educated choices regarding the display technologies you’ll utilize.

In market, LCD means passive matrix LCDs which increase TN (Twisted Nematic), STN (Super Twisted Nematic), or FSTN (Film Compensated STN) LCD Displays. It is a kind of earliest and lowest cost display technology.
LCD screens are still found in the market of low cost watches, calculators, clocks, utility meters etc. because of its advantages of low cost, fast response time (speed), wide temperature range, low power consumption, sunlight readable with transflective or reflective polarizers etc. Most of them are monochrome LCD display and belong to passive-matrix LCDs.
TFT LCDs have capacitors and transistors. These are the two elements that play a key part in ensuring that the TFT display monitor functions by using a very small amount of energy without running out of operation.
Normally, we say TFT LCD panels or TFT screens, we mean they are TN (Twisted Nematic) Type TFT displays or TN panels, or TN screen technology. TFT is active-matrix LCDs, it is a kind of LCD technologies.
TFT has wider viewing angles, better contrast ratio than TN displays. TFT display technologies have been widely used for computer monitors, laptops, medical monitors, industrial monitors, ATM, point of sales etc.
Actually, IPS technology is a kind of TFT display with thin film transistors for individual pixels. But IPS displays have superior high contrast, wide viewing angle, color reproduction, image quality etc. IPS screens have been found in high-end applications, like Apple iPhones, iPads, Samsung mobile phones, more expensive LCD monitors etc.
Both TFT LCD displays and IPS LCD displays are active matrix displays, neither of them can produce color, there is a layer of RGB (red, green, blue) color filter in each LCD pixels to make LCD showing colors. If you use a magnifier to see your monitor, you will see RGB color. With switch on/off and different level of brightness RGB, we can get many colors.
Neither of them can’t release color themselves, they have relied on extra light source in order to display. LED backlights are usually be together with them in the display modules as the light sources. Besides, both TFT screens and IPS screens are transmissive, it will need more power or more expensive than passive matrix LCD screens to be seen under sunlight. IPS screens transmittance is lower than TFT screens, more power is needed for IPS LCD display.

TFT displays are also known as an “Active Matrix TFT LCD module” and have an array of thin film transistors fabricated on the glass that makes the LCD. There is one of these transistors for each pixel on the LCD.
LCDs use voltage applied to a field of microscopic liquid crystals to change the crystal’s orientation, which in turn changes the polarization of the liquid crystal which creates light or dark pixels on the display.
Beautiful, complex images: All of our TFT modules are full-color graphic displays. Unlike standard monochrome character displays, you can create complex images for an imaginative user experience.
Thin and light: These are ideal display modules for handheld devices, communications equipment, information displays, and test and measurement equipment.
Single Supply: Most of the TFTs use an integrated controller with built-in voltage generation so only a single 3.3v supply is needed for both the panel power and logic voltage.
Many of our character LCD modules use a standard HD44780 controller, so they can be quickly integrated into a new product or used as a replacement in your existing products.
Many of the LCD controllers on board our graphic LCD display modules also include a CGROM (character generator ROM) which allows for easy character information as well as full bit-mapped graphic information to be shown.
Some of the graphic LCD displays have the ability to render graphics in grayscale, enabling you to show images and elements of your UI (user interface) with more depth and definition.
Because OLEDs are emissive, these displays can always be used in dark environments. There is usually a software command or hardware setting that will allow OLEDs to be dimmed.
Some OLED displays are bright enough to be sunlight readable–these models will typically take more current and may have a shorter rated lifetime. Additionally, OLEDs have extremely wide viewing angles.
What makes OLEDs useful for display construction is that they can be fabricated in bulk. Using OLED fabrication techniques, all the diodes can be made at the same time, at a much lower cost. OLEDs also come in a wide variety of colors.

AMOLED and TFT are two types of display technology used in smartphones. AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode) displays are made up of tiny organic light-emitting diodes, while TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) displays use inorganic thin-film transistors.
AMOLEDs are made from organic materials that emit light when an electric current is passed through them, while TFTs use a matrix of tiny transistors to control the flow of electricity to the display.
Refresh Rate: Another key difference between AMOLED and TFT displays is the refresh rate. The refresh rate is how often the image on the screen is updated. AMOLED screens have a higher refresh rate than TFT screens, which means that they can display images more quickly and smoothly.
Response Time: The response time is how long it takes for the pixels to change from one colour to another. AMOLED screens have a shorter response time than TFT screens..
Colour Accuracy/Display Quality: AMOLED screens are more accurate when it comes to displaying colours. This is because each pixel on an AMOLED screen emits its own light, which means that the colours are more pure and true to life. TFT screens, on the other hand, use a backlight to illuminate the pixels, which can cause the colours to appear washed out or less vibrant.
Viewing Angle: The viewing angle is the angle at which you can see the screen. AMOLED screens have a wider viewing angle than TFT screens, which means that you can see the screen from more angles without the colours looking distorted.
Power Consumption: One of the main advantages of AMOLED displays is that they consume less power than TFT displays. This is because the pixels on an AMOLED screen only light up when they need to, while the pixels on a TFT screen are always illuminated by the backlight.
Production Cost: AMOLED screens are more expensive to produce than TFT screens. This is because the manufacturing process for AMOLED screens is more complex, and the materials used are more expensive.
Availability: TFT screens are more widely available than AMOLED screens and have been around for longer. They are typically used in a variety of devices, ranging from phones to TVs.
Usage: AMOLED screens are typically used in devices where power consumption is a concern, such as phones and wearable devices. TFT screens are more commonly used in devices where image quality is a higher priority, such as TVs and monitors.
AMOLED and TFT are two different types of display technology. AMOLED displays are typically brighter and more vibrant, but they are more expensive to produce. TFT displays are cheaper to produce, but they are not as bright or power efficient as AMOLED displays.
The display technology that is best for you will depend on your needs and preferences. If you need a screen that is bright and vibrant, then an AMOLED display is a good choice. If you need a screen that is cheaper to produce, then a TFT display is a good choice. However, if you’re worried about image retention, then TFT may be a better option.
Nauticomp Inc.provides world-class fully customizable touchscreen displays for commercial and industrial settings. With features like sunlight readability, brightness adjustability, infrared lighting, full backlighting, all-weather capabilities, etc., our displays are second to none. Contact us today to learn more.

The viewfinder in the E-m10 mark II/III/IIIs/IV, Pen-F, and E-m5 mark III is an OLED viewfinder. The viewfinder in the E-m5 mark I/II, E-m1 mark I/II/II, E-m1x, Stylus-1, and the VF-2/VF-3/VF-4 viewfinders is a TFT LCD viewfinder. They have different characteristics:
In general an OLED viewfinder does not have issues if you look at the viewfinder while wearing polarized sunglasses and shooting in horizontal orientation. Most of the TFT LCD viewfinders have horizontal waves alternating between no distortion and heavy distortion (you can select the focus point if you concentrate on the areas where there is no distortion, but you would not be able to manually focus). However, the E-m5 mark II is different that when I"ve tried it, the viewfinder is completely opaque. Note, if you shoot in vertical orientation, there is not degradation.
In general, TFT viewfinders can refresh their images much faster that OLED displays can. I suspect this is the reason Olympus uses TFT viewfinders in the modern pro cameras.
Generally I find that the OLED viewfinder supersaturates the image compared to the TFT LCD viewfinder. This is great, many people like the supersaturation, but the picture that is recorded is not supersatured, and if you wanted the picture you saw in the viewfinder, you will need to bump up the levels somewhat in post processing.
In terms of computer monitors and TVs that use OLED displays compared to TFT LCD display, the OLED displays tend to fail sooner than the TFT displays. A particular failure mode is that often the OLED displays start losing color fidelity (particularly in the blue colors). However, I"m not sure it matters as much for a camera display. Most users probably don"t use their cameras enough for the monitor to fail. Those that do use their cameras day in and day typically replace their cameras every few years.
Also in terms of computer monitors and TVs that use OLED displays compared to TFT LCD displays, you can typically view an OLED screen at a wider angle than a TFT LCD screen. For a camera viewfinder, I suspect this is not an issue.
World wide, the cell phone market tends to consume most of the OLED displays. This leaves very few different displays that camera makers could use. TFT LCD display are older technology and there are likely different sources of the display.
I"m a migraine sufferer and I need to weark polarized sunglasses whenever I"m outdoors in daylight. So I now prefer cameras with OLED viewfinders over TFT LCD viewfinders.
I"ve run into other migraine sufferes that are sensitive to the refresh rate, but don"t need polarized glasses like I do. For them, the cameras with the TFT LCD finders are better because of the faster refresh rate.

It"s an organic light-emitting display. OLED display technology is different from the traditional LCD display mode, without backlight. It uses a very thin coating of organic materials and a glass substrate, which emit light when an electric current passes through. Moreover, OLED screen module can be made lighter and thinner, with larger viewing angle, and can significantly save power.
AMOLED is panel-self luminous. The TFT is illuminated on the LCD panel by backlight. AMOLED effect is more colorful and brighter. The screen can be seen clearly outside during the day. The most important is that the power consumption of AMOLED is much lower. AMOLED screen is more expensive than TFT LCD touch screen. The life of AMOLED screens is also longer.
AMOLED, after all, is a new technology, which has a bright future. TFT LCD touch screen can be thinned, and LTPS technology is still relatively stable. AMOLED module has low qualified rate and long lead time. So if the size and resolution are the same, buy the cheapest one.
Kingtech LCD is one of the leading TFT LCD OEM / ODM LCD display manufacturers in China. Customizing industrial equipment, medical, POS, logistics equipment, smart home applications and other projects is allowed.
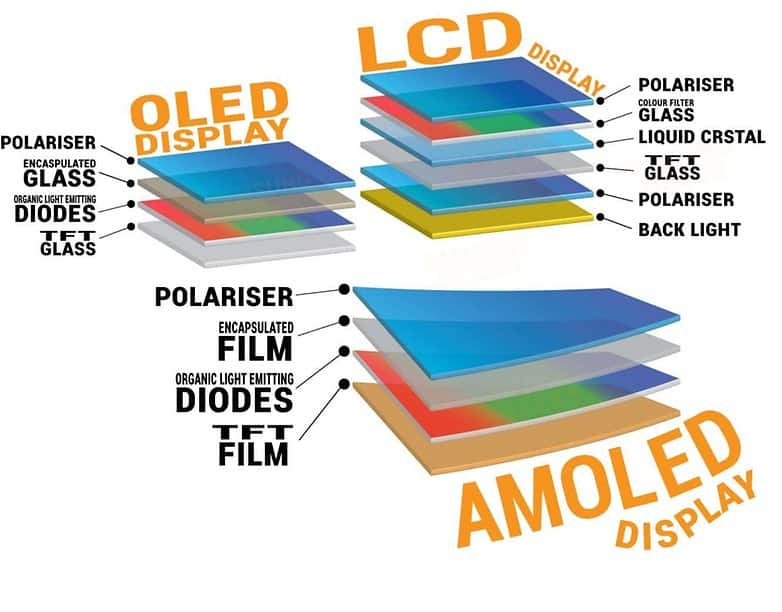
If you’re designing a display application or deciding what type of TV to get, you’ll probably have to choose between an OLED or LCD as your display type.
LCDs utilize liquid crystals that produce an image when light is passed through the display. OLED displays generate images by applying electricity to organic materials inside the display.OLED and LCD Main Difference:
graphics and images visible. This is the reason you’re still able to see light coming through on images that are meant to be dark on an LCD monitor, display, or television.
OLEDs by comparison, deliver a drastically higher contrast by dynamically managing their individual pixels. When an image on an OLED display uses the color black, the pixel shuts off completely and renders a much higher contrast than that of LCDs.OLED vs LCD - Who is better at contrast?
Having a high brightness level is important if your display is going to be used in direct sunlight or somewhere with high ambient brightness. The display"s brightness level isn"t as important if it’s going to be used indoors or in a low light setting.OLED vs LCD - Who is better at Brightness?
This means the display is much thinner than LCD displays and their pixels are much closer to the surface of the display, giving them an inherently wider viewing angle.
You’ll often notice images becoming distorted or losing their colors when tilting an LCD or when you view it from different angles. However, many LCDs now include technology to compensate for this – specifically In-Plane Switching (IPS).
LCDs with IPS are significantly brighter than standard LCDs and offer viewing angles that are on-par with OLEDs.OLED vs LCD - Who is better at Viewing Angles?
LCDs have been on the market much longer than OLEDs, so there is more data to support their longevity. On average LCDs have proven to perform for around 60,000 hours (2,500) days of operation.
With most LCDs you can expect about 7 years of consistent performance. Some dimming of the backlight has been observed but it is not significant to the quality of the display.
OLEDs are a newer technology in the display market, which makes them harder to fully review. Not only does OLED technology continue to improve at a rapid pace, but there also hasn’t been enough time to thoroughly observe their performance.
You must also consider OLED’s vulnerability to image burn-in. The organic material in these displays can leave a permanent afterimage on the display if a static image is displayed for too long.
So depending on how your OLED is used, this can greatly affect its lifespan. An OLED being used to show static images for long periods of time will not have the same longevity as one displaying dynamic, constantly moving images.OLED vs LCD - Which one last longer?
There is not yet a clear winner when it comes to lifespans between LCD and OLED displays. Each have their advantages depending on their use-cases. It’s a tie!
For a display application requiring the best colors, contrast, and viewing angles – especially for small and lightweight wearable devices – we would suggest an OLED display.

IPS (In-Plane Switching) lcd is still a type of TFT LCD, IPS TFT is also called SFT LCD (supper fine tft ),different to regular tft in TN (Twisted Nematic) mode, theIPS LCD liquid crystal elements inside the tft lcd cell, they are arrayed in plane inside the lcd cell when power off, so the light can not transmit it via theIPS lcdwhen power off, When power on, the liquid crystal elements inside the IPS tft would switch in a small angle, then the light would go through the IPS lcd display, then the display on since light go through the IPS display, the switching angle is related to the input power, the switch angle is related to the input power value of IPS LCD, the more switch angle, the more light would transmit the IPS LCD, we call it negative display mode.
The regular tft lcd, it is a-si TN (Twisted Nematic) tft lcd, its liquid crystal elements are arrayed in vertical type, the light could transmit the regularTFT LCDwhen power off. When power on, the liquid crystal twist in some angle, then it block the light transmit the tft lcd, then make the display elements display on by this way, the liquid crystal twist angle is also related to the input power, the more twist angle, the more light would be blocked by the tft lcd, it is tft lcd working mode.
A TFT lcd display is vivid and colorful than a common monochrome lcd display. TFT refreshes more quickly response than a monochrome LCD display and shows motion more smoothly. TFT displays use more electricity in driving than monochrome LCD screens, so they not only cost more in the first place, but they are also more expensive to drive tft lcd screen.The two most common types of TFT LCDs are IPS and TN displays.

Engineers should choose TFT vs OLED for new designs…and here’s why. OLED (organic light-emitting diode) technology continues to increase in popularity, but its growth has really exploded in the last few months due to such large-scale mass production of consumer products such as: e-cigarettes (personal vaporizers), smart-watches, cell phones and other wearables.
But these advantages have worked against OLEDs in new products as more and more new designs have incorporated OLEDs, increasing demand, while the supply side of this technology has failed to keep pace.
“There are only a handful of factories here in Shenzhen that produce OLED screens,” says Alex Liu, President of EC Supply Inc., a leading distributor of vape and electronic cigarette products. “These factories are extremely understaffed for the tens of millions of OLED screens that are in demand, yet everyone wants to jump on board the wearable technology craze. These factories simply lack the work force and raw materials to keep up with production of wearables, let alone fulfill relatively small orders for the vape industry in time for the holiday season.”
Adding to the OLED supply nightmare is the labor shortage in China coupled with many OEM customers increasing their order quantities in a race to beat the Chinese New year shut down.
“I strongly recommend customers purchase any MODs with OLED screens through a trusted source that can guarantee inventory.” – Alex Liu, President of EC Supply Inc.
TFT technology has been in production for several years and is here to stay. There are several TFT glass suppliers to support current demand and they have a great deal of capacity for increased demand.
Focus Displays carries TFT Displays as a standard stock item and can be shipped the same day from our online store as well as from distributor: Allied Electronics
LCD: liquid crystal display. Works by adjusting the amount of light blocked. Usually has a backlight but might not (clocks, calculators, Nintendo Gameboy). The green-black ones can be very cheap and are a mature technology. Response time can be slow.
TFT: is a type of LCD with a thin film transistor attached to each pixel. All computer LCD screens are TFT since early 2000s; older ones had slower response times and poorer colour. Cost is now very good; power consumption is fairly good but dominated by the backlight. Has to be manufactured out of glass.
LED: light emitting diode. As the name suggests, emits light rather than blocking it like LCD. Used for red/green/blue/white indicator lights everywhere.
Some manufacturers advertise "LED" displays that are TFT screens with a white LED backlight, which is just confusing. Ones that are real LED screens are usually OLED.
OLED: organic LED (rather than silicon or germanium based like regular LEDs). Comparatively recent technology, so cost still quite variable and not available in really large sizes. In theory can be printed on plastic, resulting in lighter flexible displays with good brightness, good power consumption and good response time.

Choosing a circular display could really set you apart from your competition. From 1" to 4.2" in TFT, PMOLED and AMOLED, we have something to suit every application.
The industrial marketplace is demanding circular displays, to differentiate product design. They offer an opportunity to grab customers attention in a range of applications. Modules are available with rotary switches for quick and easy selection of features.
Starting from 1” modules, you can choose Passive or Active Matrix OLED with an extremely thin profile, stunning colour clarity and true black appearance when off – ideal for home appliances and home heating controls.
Our circular displays are available from 1" to 4.2" and a great solution to give your product design a modern feel.. To further enhance the displays where environmental challenges including sunlight, extreme temperatures, water or steam can be an issue we have a number of
Circular come at a surprising affordable price. We can offer displays, with or without touchscreen and if certain design elements of the display in our standard range don’t quite fit, we can offer you a customization service at an affordable NRE/tooling fee that will help you to turn your concept to reality.
With increased consumer choice, home appliance products need to stand out from the crowd and what better way than switching to a circular display. With choices from small size, ultra thin OLED displays to larger TFT models, we can optimise to suit your application including coverlens design, touch and backlight enhancements.
The increased rise of the IOT revolution means heating controls or smart meters not only need to be functional but also aesthetically pleasing. To make your product stand out, why not switch to a circular display. Available with both OLED and TFT technology, these displays can be optimised to suit any application requirements.
Replacing mechanical gauges or rectangular displays in your instrument clusters with Circular TFT Displays is now possible at a cost recently seen as prohibitive. These stunning but tough displays are available in a range of sizes and can withstand extreme temperatures, water and salt spray and have superior readability in strong sunlight.
Our Circular displays come in sizes up to 4.2" and are ideal for replacing analogue gauges in instrument clusters. For harsh environments, such as Marine, where the displays are exposed to extreme temperatures, water or salt, we can ensure the displays are robustand continue to deliver outstanding performance with our Design Services. Browse our solutions below.
TFT displays are full color LCDs providing bright, vivid colors with the ability to show quick animations, complex graphics, and custom fonts with different touchscreen options. Available in industry standard sizes and resolutions. These displays come as standard, premium MVA, sunlight readable, or IPS display types with a variety of interface options including HDMI, SPI and LVDS. Our line of TFT modules include a custom PCB that support HDMI interface, audio support or HMI solutions with on-board FTDI Embedded Video Engine (EVE2).

TFT LCD Monitors are primarily discussed in our previous blogs. TFT LCDs are an everyday landscape, with TFT LCD being an extensively used display in different ways looking, from medical equipment, automobiles or advertisements, and smartphones.
One of our blogs, TFT LCD MONITOR: WHAT YOUR BUSINESS NEEDS TO KNOW, clearly mentioned how customers value Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) for the clear, high-quality images it produces. However, industry professionals are increasingly incorporating new technology into creating LCD screens. New inventions have recently taken the tech world by storm, replacing outdated LCD versions, such as the TFT LCD Monitor.
For businesses, open frame displays are a wonderful option. They are long-lasting and simple to install. Open frame displays can be available in a wide variety of sizes.
Compared to CRT (cathode ray tube) monitors, flatscreen monitors are much thinner and lighter. The technology also enables more transparent images, higher resolutions, and flicker-free displays, which are easier on the eyes, require less energy, and emit no electromagnetic radiation.
In today’s cars, there are a growing number of displays. This article explains the most important trends in automotive displays that you must know in 2022.
Nowadays, electromechanical switches and controls are being increasingly replaced by electronic controls, which include touchscreen displays. Even smaller controls, such as those to control the air conditioning, the position of a car’s exterior mirrors, or the buttons on the multifunction steering wheel, are involved.
The terms reflective, transmissive, and transflective describe how LCD modules illuminate. Compared to emissive display technologies such as OLED displays (organic light-emitting diode) and VFDs (vacuum fluorescent displays), LCDs need an ambient light source like the sun, artificial light, or a merged backlight.
Some displays use ambient lighting instead of backlights. This mode of operation is termed reflective. A mirror is installed behind the liquid crystal layer in this mode, which is either on the LCD cell or the rear polarizer...Read More
LVDS signaling is considered ideal for large displays, e.g., TV, laptops, and other computers. Its capability of transferring large pixels in less time makes it a popular and favorable choice for developing PMOLED, AMOLED, TFT, and different types of displays.
Today, there is a high demand for electronic devices featuring high brightness displays. Liquid Crystal Display Technology (LCD) is one of the most popular display technologies in use today. They are found in various electronic devices right from mobile phones, computer monitors, tablets, touchscreen displays, tablets, television sets, and more. Over the years, there have been variations to these displays. TFT LCDs have gained immense popularity in recent years. These are thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal displays, which utilize thin-film transistors to optimize image qualities. These LCD displays are nowadays available in different configurations. Of these, 10.25 inch TFT LCD displays offered by Microtips USA have gained popularity in recent years due to various reasons...Read More
TFT, which stands for thin film transistor, is an advanced offshoot of the LCD technology. These are active matrix LCDs, which immensely improve the quality of color, contrast, image clarity, and more. This is one reason why TFTs are used in displays of many electronic devices, along with capacitors. The 3.9-inch bar type color TFT LCD display comes with such amazing quality and features in terms of the resolution, size, interface, and so on. This display finds applications in many industrial equipment, marine equipment, point of sale (POS) terminals, automobiles, advertising displays, server systems, and so on. There are many 3.9-inch TFT LCD module manufacturers making this display although features may slightly differ based on the manufacturer...Read More
TFT or thin film transistor is a variant of the LCD technology. TFTs are active matrix LCDs, which help improve contrast, color, and picture quality. Thin film transistors are used along with capacitors to improve image quality in many electronic devices. Owing to their several advantages, these TFT displays are available in various specifications. The 4.3 inch TFT display is one of the most popular among them. The 4.3-inch TFT LCD display module touch screen has a resolution of 480X272 with an RGB interface. This display finds applications in mobile phones, cars, embedded systems, and certain industrial equipment among others. There are many 4.3-inch TFT LCD module manufacturers making this display; however, certain features may slightly differ based on the manufacturer...Read More
Over the years, various display technologies have gained popularity across the world and the liquid –crystal display technology, abbreviated as LCD, stands tall among them. This technology has become a choice for manufacturers of electronic devices such as mobile phones, televisions, computers, and more, owing to several advantages offered by them. However, the advances in this technology have opened new options for device manufacturers. Thin-film-transistor is one of the most popular types of LCDs used by electronics manufacturers all over the world. Today, it is produced in various specifications to meet your application requirements. However, the 12.3 inch TFT LCD display by Microtips Technology has gained the attention of electronic device manufacturers...Read More

AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode) and TFT (Thin Film Transistor) are the two types of displays that are used in mobile phones. TFT is actually a process of producing the displays and is used even by AMOLED but for most purposes, TFT is used to refer to LCD displays. The difference between them is the material as AMOLED uses organicmaterials, mainly carbon, while TFT does not.
There are differences between the two that are quite tangible. For starters, AMOLED generates its own light rather than relying on a backlight like a TFT-LCD does. This consequently means that AMOLED displays are much thinner than LCD displays; due to the absence of a backlight. It also results in much better colors than a TFT is capable of producing. As each pixel’s color and light intensity can be regulated independently and no light seeps from adjacent pixels. A side by side comparison of the two displays with the same picture should confirm this. Another effect of the lack of a backlight is the much lower power consumption of the device. This is very desirable when it comes to mobile phones where every single feature competes for the limited capacity of the battery. As the screen is on 90% of the time that the device is being used, it is very good that AMOLED displays consume less. Just how much of a difference is not very fixed though as it really depends on the color and intensity of the image. Having a black background with white text consumes much less energy than having black text on a white background.
The biggest disadvantage that AMOLED has is the shorter lifespan of the screen compared to TFT. Each pixel in the display degrades with each second that it is lit and even more so the brighter it is. Â Despite improvements on the lifetime of AMOLED displays, AMOLED still only lasts a fraction of the lifetime of a TFT display. With that said, an AMOLED display is able to outlast the usable lifetime of the device before parts of it start to degrade.
The main hindrance to the massive adaptation of AMOLED is the low production numbers. TFT has been in production for much longer and the infrastructure is already there to meet the demands.

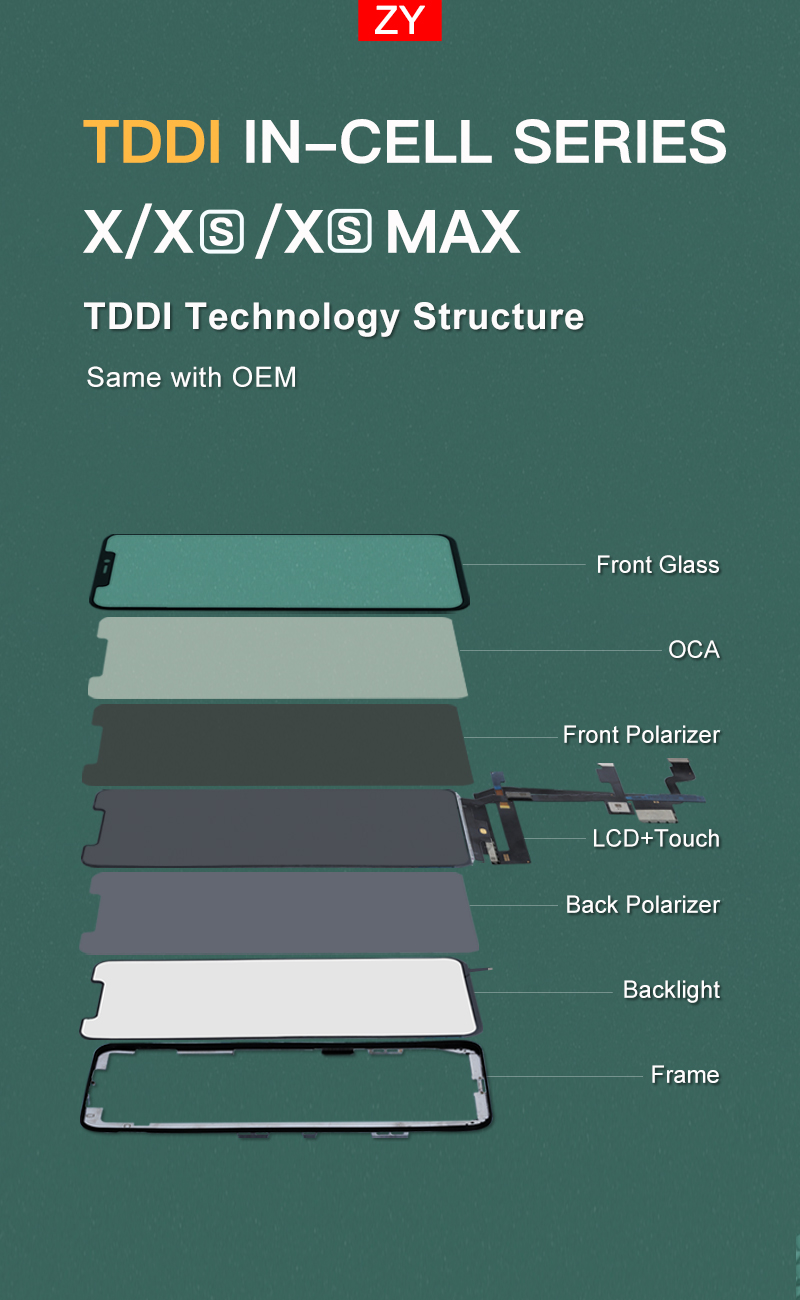
Thin-Film Transistor Liquid Crystal Displays use thin-film transistors to control the voltage applied to the liquid crystal layer at a sub-pixel level. The structure of TFT LCDs consists of a TFT “sandwich” and a BLU (Backlight Unit). A typical configuration is shown in the schematic diagram below.
Firstly, between the back and front polarizers, TFT LCD cells are made with two glass substrates – one for color filters, the other for a TFT array – and a liquid crystal layer sandwiched in between.
For normally black TFT LCDs, if we follow along a piece of light setting off from its backlight source, it will bea)guided uniformly by LGP;b)reflected and enhanced by BEF and DBEF;c)polarized by the back polarizer;d)polarization changed by twisted LC under the voltage applied by TFT arrays;e)“tinted” red/green/blue by corresponding color filter of the subpixel;f)let through the front polarizer by matched polarization; andg)finally, it will reach the surface and appears in viewer’s eyes.
Normally black LCDs have higher contrast and wider viewing angles without grayscale inversion phenomenon compared to their normally white relatives. And whether TFT LCDs are normally black or white depends on their LC switching mode:

TFT and LCD are two different types of electronic displays used in computers, TVs, and smartphones. However, they are not as different as you might think. Let’s start with what those abbreviations mean.
A key weakness of TFT panels is that they do not have wide viewing angles, so they are better suited to displays that require you to view head-on. This can be a good or a bad thing, depending on your needs. For example, the narrower viewing angles mean people sitting or standing around you are less likely to be able to snoop on what you are doing on your mobile phone.
TFT panels are cheaper to manufacture, but they also consume much more power than regular LCD panels. Lastly, they have poorer sunlight visibility. You will find TFT displays on feature phones, smart feature phones, and low-end Android phones.
LCD: This is an abbreviation for “liquid crystal display”. It is a flat panel display with wider viewing angles compared to TFT. They also have lower power consumption and so deliver much better battery life than their TFT counterparts.
In summary, while TFT panels have some distinct advantages, they fall short in other areas and so their use have been limited to low end phones, from feature phones to entry-level Android phones. Plastic feels inferior to touch than glass, which means that TFT screens don’t get to feature much on mid-range and premium devices.
As we see improvements to TFT technology, we will see them deployed on higher end devices over time. In 2022, Samsung used TFT displays in its mid-range Galaxy A13 and Galaxy A23. Perhaps those improvements are happening already.
For now, LCD is the most widely used display type in modern smartphones. At the very top end, we have premium flagships using OLED and AMOLED displays.
TFT displays are higher quality components than regular LCD displays. TFT displays are sharper, brighter, and refresh better than LCD panels. However, they have weaknesses that make them unsuitable for higher end phones.
AMOLED panels have all the benefits of OLED screens, which means they are better than LCD panels. They are expensive though, and so are used in high-end smartphones only.
These are improved versions of AMOLED screens and were developed by Samsung. They are also thinner. The name explains it: think of Super AMOLED as AMOLED on steroids.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey