line lcd display free sample

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.
If you already know how to use these images.For viewing the images off-line (120 kB ZIP).All images, but with the color profiles stripped, in case you

We come across Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) displays everywhere around us. Computers, calculators, television sets, mobile phones, and digital watches use some kind of display to display the time.
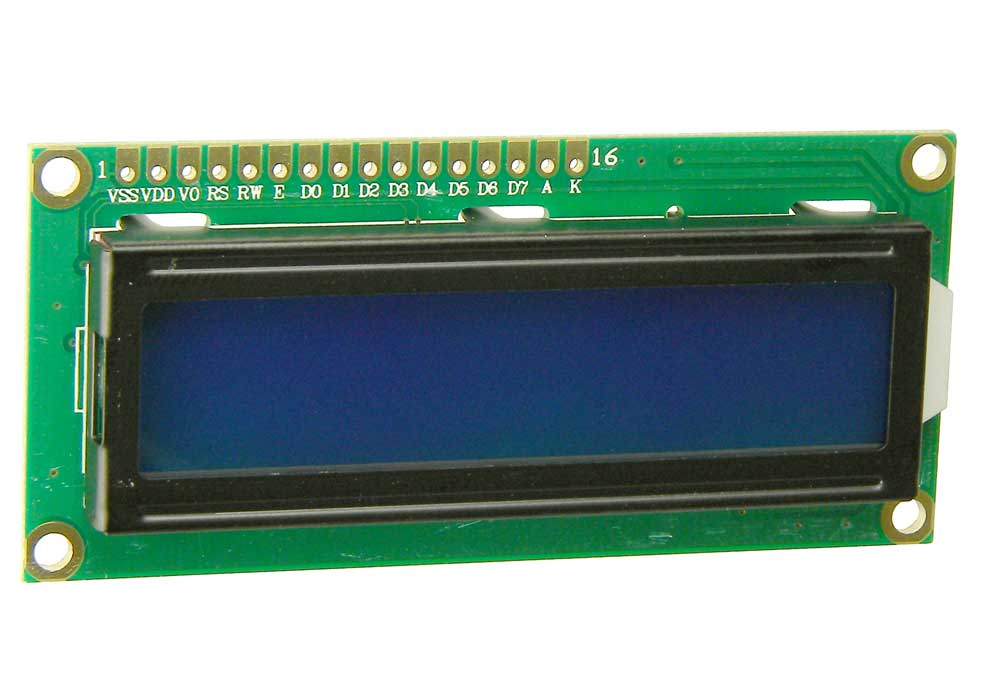
An LCD screen is an electronic display module that uses liquid crystal to produce a visible image. The 16×2 LCD display is a very basic module commonly used in DIYs and circuits. The 16×2 translates a display of 16 characters per line in 2 such lines. In this LCD, each character is displayed in a 5×7 pixel matrix.
Contrast adjustment; the best way is to use a variable resistor such as a potentiometer. The output of the potentiometer is connected to this pin. Rotate the potentiometer knob forward and backward to adjust the LCD contrast.
A 16X2 LCD has two registers, namely, command and data. The register select is used to switch from one register to other. RS=0 for the command register, whereas RS=1 for the data register.
Command Register: The command register stores the command instructions given to the LCD. A command is an instruction given to an LCD to do a predefined task. Examples like:
Data Register: The data register stores the data to be displayed on the LCD. The data is the ASCII value of the character to be displayed on the LCD. When we send data to LCD, it goes to the data register and is processed there. When RS=1, the data register is selected.
Generating custom characters on LCD is not very hard. It requires knowledge about the custom-generated random access memory (CG-RAM) of the LCD and the LCD chip controller. Most LCDs contain a Hitachi HD4478 controller.
CG-RAM address starts from 0x40 (Hexadecimal) or 64 in decimal. We can generate custom characters at these addresses. Once we generate our characters at these addresses, we can print them by just sending commands to the LCD. Character addresses and printing commands are below.
LCD modules are very important in many Arduino-based embedded system designs to improve the user interface of the system. Interfacing with Arduino gives the programmer more freedom to customize the code easily. Any cost-effective Arduino board, a 16X2 character LCD display, jumper wires, and a breadboard are sufficient enough to build the circuit. The interfacing of Arduino to LCD display is below.
The combination of an LCD and Arduino yields several projects, the most simple one being LCD to display the LED brightness. All we need for this circuit is an LCD, Arduino, breadboard, a resistor, potentiometer, LED, and some jumper cables. The circuit connections are below.

This tutorial shows how to use the I2C LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) with the ESP32 using Arduino IDE. We’ll show you how to wire the display, install the library and try sample code to write text on the LCD: static text, and scroll long messages. You can also use this guide with the ESP8266.
Additionally, it comes with a built-in potentiometer you can use to adjust the contrast between the background and the characters on the LCD. On a “regular” LCD you need to add a potentiometer to the circuit to adjust the contrast.
Before displaying text on the LCD, you need to find the LCD I2C address. With the LCD properly wired to the ESP32, upload the following I2C Scanner sketch.
After uploading the code, open the Serial Monitor at a baud rate of 115200. Press the ESP32 EN button. The I2C address should be displayed in the Serial Monitor.
Displaying static text on the LCD is very simple. All you have to do is select where you want the characters to be displayed on the screen, and then send the message to the display.
The next two lines set the number of columns and rows of your LCD display. If you’re using a display with another size, you should modify those variables.
Then, you need to set the display address, the number of columns and number of rows. You should use the display address you’ve found in the previous step.
To display a message on the screen, first you need to set the cursor to where you want your message to be written. The following line sets the cursor to the first column, first row.
Scrolling text on the LCD is specially useful when you want to display messages longer than 16 characters. The library comes with built-in functions that allows you to scroll text. However, many people experience problems with those functions because:
The messageToScroll variable is displayed in the second row (1 corresponds to the second row), with a delay time of 250 ms (the GIF image is speed up 1.5x).
In a 16×2 LCD there are 32 blocks where you can display characters. Each block is made out of 5×8 tiny pixels. You can display custom characters by defining the state of each tiny pixel. For that, you can create a byte variable to hold the state of each pixel.
In summary, in this tutorial we’ve shown you how to use an I2C LCD display with the ESP32/ESP8266 with Arduino IDE: how to display static text, scrolling text and custom characters. This tutorial also works with the Arduino board, you just need to change the pin assignment to use the Arduino I2C pins.

The Biomaker Stage-2 component pack contains a liquid crystal display (LCD) capable of displaying 2 lines of 16 characters (right). The device is equipped with an I2C interface backpack, that allows serial communication with the device. (This is the black-coloured circuit board soldered to the back of the green-coloured LCD board). The I2C interface allows communication with the LCD screen through two wires plus power supply, rather than 8+ wires required by a parallel port device. The I2C protocol allows comunication with multiple devices on the same 2 wire bus. Each device needs a unique address, usually set in the hardware.
The LCD display is powered by a 5V supply and draws about 25mA with the backlight on, and 2mA without. The green coloured backlight sits behind black coloured characters. The characters are formed in two lines of 16 characters in 5x7 dot matrices.
The display should be connected to the microcontroller via the Vcc (5V), Gnd (ground), SDA (data) and SCL (clock) wires. Because it is common to use multiple I2C devices, it is generally easier to connect through the breadboard, which allows multiple devices to share the I2C signals and power from the relevant sockets on the yellow connector on the microcontroller board.
XOD provides the software node text-lcd-16x2-i2c, that allows direct communication with the display, with inputs for each line of the display (see below). The address of the i2C device should be set at 27h using the ADDR parameter.
The text display can be a very useful tool for following program behaviour. In addition, XOD provides the watch node, a number of which can be connected to the outputs of key nodes, and provide real-time output of values as a programme is run in debug mode.
Advanced use: If you which to use multiple LCD displays on the I2C bus, you can add solder bridges to the jumpers A0, A1 and A2 on the I2C backpack - in order to change the address of each device, and allow them to be individually addressed. The supplied I2C backpack has a PCF8574T chip: and the IC address is (high order first) 0100 A2 A1 A0. When shipped, A2~A0 are all vacant. The default I2C address therefore: 0100 111 (0x27). If you want to modify the address yourself add the relevant jumpers, noting that floating address pad is 1, and the short circuit is 0 after adding a solder bridge.
Important: There is a potentiometer that controls the contrast setting of the display. It is a controlled by a black plastic wheel at the front left edge of the LCD screen. (Contrast can also be adjusted using the blue potentiometer on the I2C backpack). The contrast setting requires fine adjustment, and the screen will appear blank and unresponsive if badly adjusted. If, on first use, you want to check that the LCD screen is correctly connected (i.e. are using the correct I2C address), use a XOD node to switch the backlight on and off. If that works, load some text into the screen, and adjust the contrast for best legibility.
In this tutorial, I’ll explain how to set up an LCD on an Arduino and show you all the different ways you can program it. I’ll show you how to print text, scroll text, make custom characters, blink text, and position text. They’re great for any project that outputs data, and they can make your project a lot more interesting and interactive.
The display I’m using is a 16×2 LCD display that I bought for about $5. You may be wondering why it’s called a 16×2 LCD. The part 16×2 means that the LCD has 2 lines, and can display 16 characters per line. Therefore, a 16×2 LCD screen can display up to 32 characters at once. It is possible to display more than 32 characters with scrolling though.
The code in this article is written for LCD’s that use the standard Hitachi HD44780 driver. If your LCD has 16 pins, then it probably has the Hitachi HD44780 driver. These displays can be wired in either 4 bit mode or 8 bit mode. Wiring the LCD in 4 bit mode is usually preferred since it uses four less wires than 8 bit mode. In practice, there isn’t a noticeable difference in performance between the two modes. In this tutorial, I’ll connect the LCD in 4 bit mode.
Here’s a diagram of the pins on the LCD I’m using. The connections from each pin to the Arduino will be the same, but your pins might be arranged differently on the LCD. Be sure to check the datasheet or look for labels on your particular LCD:
Also, you might need to solder a 16 pin header to your LCD before connecting it to a breadboard. Follow the diagram below to wire the LCD to your Arduino:
In order to use a library, it needs be included in the program. Line 1 in the code below does this with the command #include
There are 19 different functions in the LiquidCrystal library available for us to use. These functions do things like change the position of the text, move text across the screen, or make the display turn on or off. What follows is a short description of each function, and how to use it in a program.
TheLiquidCrystal() function sets the pins the Arduino uses to connect to the LCD. You can use any of the Arduino’s digital pins to control the LCD. Just put the Arduino pin numbers inside the parentheses in this order:
This function sets the dimensions of the LCD. It needs to be placed before any other LiquidCrystal function in the void setup() section of the program. The number of rows and columns are specified as lcd.begin(columns, rows). For a 16×2 LCD, you would use lcd.begin(16, 2), and for a 20×4 LCD you would use lcd.begin(20, 4).
This function clears any text or data already displayed on the LCD. If you use lcd.clear() with lcd.print() and the delay() function in the void loop() section, you can make a simple blinking text program:
Similar, but more useful than lcd.home() is lcd.setCursor(). This function places the cursor (and any printed text) at any position on the screen. It can be used in the void setup() or void loop() section of your program.
The cursor position is defined with lcd.setCursor(column, row). The column and row coordinates start from zero (0-15 and 0-1 respectively). For example, using lcd.setCursor(2, 1) in the void setup() section of the “hello, world!” program above prints “hello, world!” to the lower line and shifts it to the right two spaces:
You can use this function to write different types of data to the LCD, for example the reading from a temperature sensor, or the coordinates from a GPS module. You can also use it to print custom characters that you create yourself (more on this below). Use lcd.write() in the void setup() or void loop() section of your program.
The function lcd.noCursor() turns the cursor off. lcd.cursor() and lcd.noCursor() can be used together in the void loop() section to make a blinking cursor similar to what you see in many text input fields:
Cursors can be placed anywhere on the screen with the lcd.setCursor() function. This code places a blinking cursor directly below the exclamation point in “hello, world!”:
This function creates a block style cursor that blinks on and off at approximately 500 milliseconds per cycle. Use it in the void loop() section. The function lcd.noBlink() disables the blinking block cursor.
This function turns on any text or cursors that have been printed to the LCD screen. The function lcd.noDisplay() turns off any text or cursors printed to the LCD, without clearing it from the LCD’s memory.
This function takes anything printed to the LCD and moves it to the left. It should be used in the void loop() section with a delay command following it. The function will move the text 40 spaces to the left before it loops back to the first character. This code moves the “hello, world!” text to the left, at a rate of one second per character:
Like the lcd.scrollDisplay() functions, the text can be up to 40 characters in length before repeating. At first glance, this function seems less useful than the lcd.scrollDisplay() functions, but it can be very useful for creating animations with custom characters.
lcd.noAutoscroll() turns the lcd.autoscroll() function off. Use this function before or after lcd.autoscroll() in the void loop() section to create sequences of scrolling text or animations.
This function sets the direction that text is printed to the screen. The default mode is from left to right using the command lcd.leftToRight(), but you may find some cases where it’s useful to output text in the reverse direction:
This code prints the “hello, world!” text as “!dlrow ,olleh”. Unless you specify the placement of the cursor with lcd.setCursor(), the text will print from the (0, 1) position and only the first character of the string will be visible.
This command allows you to create your own custom characters. Each character of a 16×2 LCD has a 5 pixel width and an 8 pixel height. Up to 8 different custom characters can be defined in a single program. To design your own characters, you’ll need to make a binary matrix of your custom character from an LCD character generator or map it yourself. This code creates a degree symbol (°):

The Arduino family of devices is features rich and offers many capabilities. The ability to interface to external devices readily is very enticing, although the Arduino has a limited number of input/output options. Adding an external display would typically require several of the limited I/O pins. Using an I2C interface, only two connections for an LCD character display are possible with stunning professional results. We offer both a 4 x 20 LCD.
The character LCD is ideal for displaying text and numbers and special characters. LCDs incorporate a small add-on circuit (backpack) mounted on the back of the LCD module. The module features a controller chip handling I2C communications and an adjustable potentiometer for changing the intensity of the LED backlight. An I2C LCD advantage is that wiring is straightforward, requiring only two data pins to control the LCD.
A standard LCD requires over ten connections, which can be a problem if your Arduino does not have many GPIO pins available. If you happen to have an LCD without an I2C interface incorporated into the design, these can be easily
The LCD displays each character through a matrix grid of 5×8 pixels. These pixels can display standard text, numbers, or special characters and can also be programmed to display custom characters easily.
Connecting the Arduino UNO to the I2C interface of the LCD requires only four connections. The connections include two for power and two for data. The chart below shows the connections needed.
The I2C LCD interface is compatible across much of the Arduino family. The pin functions remain the same, but the labeling of those pins might be different.
Located on the back of the LCD screen is the I2C interface board, and on the interface is an adjustable potentiometer. This adjustment is made with a small screwdriver. You will adjust the potentiometer until a series of rectangles appear – this will allow you to see your programming results.
The Arduino module and editor do not know how to communicate with the I2C interface on the LCD. The parameter to enable the Arduino to send commands to the LCD are in separately downloaded LiquidCrystal_I2C library.
Several examples and code are included in the Library installation, which can provide some reference and programming examples. You can use these example sketches as a basis for developing your own code for the LCD display module.
The I2c address can be changed by shorting the address solder pads on the I2C module. You will need to know the actual address of the LCD before you can start using it.
Once you have the LCD connected and have determined the I2C address, you can proceed to write code to display on the screen. The code segment below is a complete sketch ready for downloading to your Arduino.
The code assumes the I2C address of the LCD screen is at 0x27 and can be adjusted on the LiquidCrystal_I2C lcd = LiquidCrystal_I2C(0x27,16,2); as required.
Similar to the cursor() function, this will create a block-style cursor. Displayed at the position of the next character to be printed and displays as a blinking rectangle.
This function turns off any characters displayed to the LCD. The text will not be cleared from the LCD memory; rather, it is turned off. The LCD will show the screen again when display() is executed.
Scrolling text if you want to print more than 16 or 20 characters in one line then the scrolling text function is convenient. First, the substring with the maximum of characters per line is printed, moving the start column from right to left on the LCD screen. Then the first character is dropped, and the next character is displayed to the substring. This process repeats until the full string has been displayed on the screen.
The LCD driver backpack has an exciting additional feature allowing you to create custom characters (glyph) for use on the screen. Your custom characters work with both the 16×2 and 20×4 LCD units.
A custom character allows you to display any pattern of dots on a 5×8 matrix which makes up each character. You have full control of the design to be displayed.
To aid in creating your custom characters, there are a number of useful tools available on Internet. Here is a LCD Custom Character Generator which we have used.

Liquid Crystal Display(LCDs) provide a cost effective way to put a text output unit for a microcontroller. As we have seen in the previous tutorial, LEDs or 7 Segments do no have the flexibility to display informative messages.
This display has 2 lines and can display 16 characters on each line. Nonetheless, when it is interfaced with the micrcontroller, we can scroll the messages with software to display information which is more than 16 characters in length.
The LCD is a simple device to use but the internal details are complex. Most of the 16x2 LCDs use a Hitachi HD44780 or a compatible controller. Yes, a micrcontroller is present inside a Liquid crystal display as shown in figure 2.
It takes a ASCII value as input and generate a patter for the dot matrix. E.g., to display letter "A", it takes its value 0X42(hex) or 66(dec) decodes it into a dot matrix of 5x7 as shown in figure 1.
Power & contrast:Apart from that the LCD should be powered with 5V between PIN 2(VCC) and PIN 1(gnd). PIN 3 is the contrast pin and is output of center terminal of potentiometer(voltage divider) which varies voltage between 0 to 5v to vary the contrast.

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

Text LCD displays are among the simplest. They are popular for their ease of operation and programming thanks to the HD44780 LCD controller and their analogs with the built-in set of characters including ASCII characters. Text displays consist of a matrix of dots combined into rows and columns. Formats of rows and columns are standardized by manufacturers and can be 8x1, 8x2, 10x1, 10x2, 16x1, 16x2, 16x4, 20x1, 20x2, 20x4, 24x1, 24x2. Each LCD controller is capable of operating up to 80 characters so the text LCD display with the 20x4 format is the largest. There are even larger text LCD displays such as 40x4 using several LCD controllers but they are too rare.
Initially, text LCD displays communicate with microcontrollers such as Arduino using parallel 4 or 8-bit interfaces. Some manufacturers add shift registers and port expanders to the display, making it possible to control via I2C or SPI bus. It is done for connecting convenience and reducing the number of mounting wires.
These nodes contain everything you need to start working with displays. You only have to connect your display to the microcontroller and set up proper connection parameters.
If the display communicates via an I2C bus the input parameter is the device address. Put the I2C address value of the byte type to the ADDR pin field.
If the display is controlled using a parallel interface fill in the pin values RS, EN, D4, D5, D6, D7 according to the microcontroller ports through which the display is connected.
The L input pins of the string type have indexes from 1 to 4 and correspond to the lines on your text display. The boolean value at the ACT pin is responsible for updating the display screen if the incoming string values change. Versions controlled by the I2C bus have an additional BL pin which turns on and off the display backlight.
Here is a simple example of using quick start nodes. For the example we use a 16x2 format display controlled by I2C. Connect the display to the microcontroller. Create an empty patch and put the text-lcd-i2c-16x2 quick start node onto it. The LCD screen from this example has the 38 I2C address so we put the 38h value to the ADDR pin.
Let’s print the “HELLO” word on the first line of the text display. Add a constant-string node onto the patch, fill it with the "HELLO" string value, and then link it with the L1 input pin of the quickstart node denoting the first line of the display.
A text can be entered directly into a value field of the input pin. To demonstrate it, let’s print the “WORLD” word on the second line of the display. Put the "WORLD" string value into the L2 pin of the text-lcd-i2c-16x2 quick start node.
Try a more dynamic example. Let’s display the system time, it is the time that has passed since the start of the program. To obtain the time value use the system-time node from the core library.
Remove the "WORLD" value from the L2 pin of the quickstart node and change the text inside of the constant string node to "Time: ". In XOD you can add different strings together or combine a string with a value of another data type using concat or join nodes. Put the concat node onto the patch to unite the static "Time: " text with a value received from the system-time node. To display the combined string on the first line of the display link the output pin of the concat node with the L1 pin of the quickstart node.
If the quickstart node doesn’t suit your task or the display is of a non-common format try to operate some developer nodes from the library xod-dev/text-lcd library.
Define the display you want to use to start working with it in XOD. Find out how your display communicates and place the appropriate device node from the xod-dev/text-lcd library. These nodes construct and output an lcd-device custom type value which is necessary for further work.
Use the text-lcd-parallel-device node if the display is controlled using a parallel interface. This node allows the display connection only through a 4-bit parallel interface. Here enter the pin values RS, EN, D4, D5, D6, D7. These values correspond to the microcontroller ports through which the display is connected.
Use the text-lcd-i2c-device node if the display communicates via an I2C bus. For this node, the input parameter is the device address. Enter the I2C address of your display to the ADDR pin value.
When the device is initialized, you can display text on it. To output text, use the print-at node. It fits any type of LCD device because it is generic.
The input values of the print-at nodes determine what text to display and where it should be on the display screen. Text to display is set at the VAL pin value. The ROW and POS field values set the cell coordinates on the display for the first character. That’s the place where your text begins. The LEN pin value sets the number of character cells for the text to reserve. The text can’t go beyond the boundaries you specify. It is useful, for example, when the length of your text changes during the program or you want to organize free space between several text parts. Printing is performed when the DO pin receives a pulse.
At first, let’s make a patch to print the "HELLO" text. Put the text-lcd-i2c-device node onto the patch and fill it with parameters. According to the format of the display, the number of columns is 20 and the number of rows is 4. The I2C address of the used display is 0x39 so put the 39h byte to the ADDR pin. Add the print-at node and link it with the device node. Put the HELLO to the VAL input pin.
Add one more print-at node and link with the LCD device bus. Put the "WORLD" word into the VAL field. The new text is on the same line as the previous one so set the ROW value to 1. The POS value now should be calculated. The “HELLO” word begins from the cell with index 4 and occupies 5 cells. By adding one empty cell for space and the “HELLO” word length to the previous text position you can get the POS for the new text: it is 10. Link the input DO pin of the new node with output DONE pin of the previous to execute printing sequentially.
Also, it is necessary to change the LEN value for the “HELLO” text. It is equal to +Inf which means that the “HELLO” text reserves all the free space in the line after itself. Set it to 5 to reserve only the required number of cells for a given word.
Text displays contain a table of images for each character in their memory. These tables are used to generate letters, numbers and other symbols. Almost always a full list of all available characters can be found in the manufacturer’s datasheet. To display a specific symbol, it is necessary to transfer its hexadecimal number from the sign generator table. Use the \x## sequence to embed the character code in the string.
For example, the display that is used for this example contains five symbols which can indicate a battery capacity level. Hexadecimal codes for these symbols are 9B,9C,9D,9E, and 9F. Let’s try to display these symbols on the 3rd line of the display. Let’s change the previous example patch. Leave one print-at node and set up new printing coordinates. Put the 2 value into the ROW pin and let the POS be 7. Then, put the "\x9B\x9C\x9D\x9E\x9F" sequence of the character codes into the VAL pin…
Make your project or device more attractive and informative with a text display. Get started with quickstart nodes from the xod-dev/text-lcd library. Combine strings using concat. For non-standard cases, dive deeper into the library. Use a device node together with various action nodes, such as set-backlight and clear.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey