arduino mini lcd display free sample

Adding a display to your Arduino can serve many purposes. Since a common use for microcontrollers is reading data from sensors, a display allows you to see this data in real-time without needing to use the serial monitor within the Arduino IDE. It also allows you to give your projects a personal touch with text, images, or even interactivity through a touch screen.
Transparent Organic Light Emitting Diode (TOLED) is a type of LED that, as you can guess, has a transparent screen. It builds on the now common OLED screens found in smartphones and TVs, but with a transparent display, offers up some new possibilities for Arduino screens.
Take for example this brilliant project that makes use of TOLED displays. By stacking 10 transparent OLED screens in parallel, creator Sean Hodgins has converted a handful of 2D screens into a solid-state volumetric display. This kind of display creates an image that has 3-dimensional depth, taking us one step closer to the neon, holographic screens we imagine in the future.
Crystalfontz has a tiny monochrome (light blue) 1.51" TOLED that has 128x56 pixels. As the technology is more recent than the following displays in this list, the cost is higher too. One of these screens can be purchased for around $26, but for certain applications, it might just be worth it.
The liquid crystal display (LCD) is the most common display to find in DIY projects and home appliances alike. This is no surprise as they are simple to operate, low-powered, and incredibly cheap.
This type of display can vary in design. Some are larger, with more character spaces and rows; some come with a backlight. Most attach directly to the board through 8 or 12 connections to the Arduino pins, making them incompatible with boards with fewer pins available. In this instance, buy a screen with an I2C adapter, allowing control using only four pins.
Available for only a few dollars (or as little as a couple of dollars on AliExpress with included I2C adapter), these simple displays can be used to give real-time feedback to any project.
The screens are capable of a large variety of preset characters which cover most use cases in a variety of languages. You can control your LCD using the Liquid Crystal Library provided by Arduino. The display() and noDisplay() methods write to the LCD, as shown in the official tutorial on the Arduino website.
Are you looking for something simple to display numbers and a few basic characters? Maybe you are looking for something with that old-school arcade feel? A seven-segment display might suit your needs.
These simple boards are made up of 7 LEDs (8 if you include the dot), and work much like normal LEDs with a common Anode or Cathode connection. This allows them to take one connection to V+ (or GND for common cathode) and be controlled from the pins of your Arduino. By combining these pins in code, you can create numbers and several letters, along with more abstract designs—anything you can dream up using the segments available!
Next on our list is the 5110 display, also affectionately known as the Nokia display due to its wide use in the beloved and nigh indestructible Nokia 3310.
These tiny LCD screens are monochrome and have a screen size of 84 x 48 pixels, but don"t let that fool you. Coming in at around $2 on AliExpress, these displays are incredibly cheap and usually come with a backlight as standard.
Depending on which library you use, the screen can display multiple lines of text in various fonts. It"s also capable of displaying images, and there is free software designed to help get your creations on screen. While the refresh rate is too slow for detailed animations, these screens are hardy enough to be included in long-term, always-on projects.
For a step up in resolution and functionality, an OLED display might be what you are looking for. At first glance, these screens look similar to the 5110 screens, but they are a significant upgrade. The standard 0.96" screens are 128 x 64 monochrome, and come with a backlight as standard.
They connect to your Arduino using I2C, meaning that alongside the V+ and GND pins, only two further pins are required to communicate with the screen. With various sizes and full color options available, these displays are incredibly versatile.
For a project to get you started with OLED displays, our Electronic D20 build will teach you everything you need to know -- and you"ll end up with the ultimate geeky digital dice for your gaming sessions!
These displays can be used in the same way as the others we have mentioned so far, but their refresh rate allows for much more ambitious projects. The basic monochrome screen is available on Amazon.
Thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal displays (TFT LCDs) are in many ways another step up in quality when it comes to options for adding a screen to your Arduino. Available with or without touchscreen functionality, they also add the ability to load bitmap files from an on-board microSD card slot.
Arduino have an official guide for setting up their non-touchscreen TFT LCD screen. For a video tutorial teaching you the basics of setting up the touchscreen version, YouTuber educ8s.tv has you covered:
With the touchscreen editions of these screens costing less than $10 on AliExpress, these displays are another great choice for when you need a nice-looking display for your project.
Looking for something a little different? An E-paper (or E-ink depending on who you ask) display might be right for you. These screens differ from the others giving a much more natural reading experience, it is no surprise that this technology is the cornerstone of almost every e-reader available.
The reason these displays look so good is down to the way they function. Each "pixel" contains charged particles between two electrodes. By switching the charge of each electrode, you can influence the negatively charged black particles to swap places with the positively charged white particles.
This is what gives e-paper such a natural feel. As a bonus, once the ink is moved to its location, it uses no power to keep it there. This makes these displays naturally low-power to operate.
This article has covered most options available for Arduino displays, though there are definitely more weird and wonderful ways to add feedback to your DIY devices.
Now that you have an idea of what is out there, why not incorporate a screen into your DIY smart home setup? If retro gaming is more your thing, why not create some retro games on Arduino?
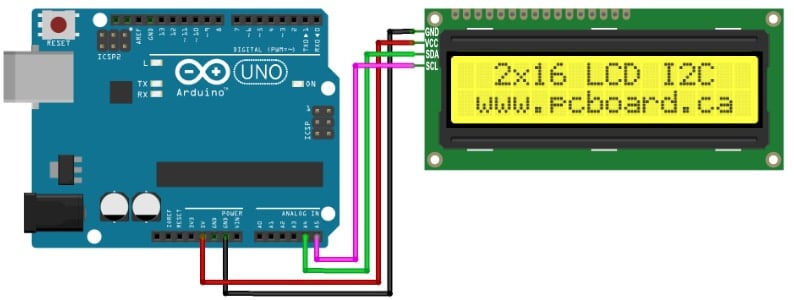
In this Arduino tutorial we will learn how to connect and use an LCD (Liquid Crystal Display)with Arduino. LCD displays like these are very popular and broadly used in many electronics projects because they are great for displaying simple information, like sensors data, while being very affordable.
You can watch the following video or read the written tutorial below. It includes everything you need to know about using an LCD character display with Arduino, such as, LCD pinout, wiring diagram and several example codes.
An LCD character display is a unique type of display that can only output individual ASCII characters with fixed size. Using these individual characters then we can form a text.
If we take a closer look at the display we can notice that there are small rectangular areas composed of 5×8 pixels grid. Each pixel can light up individually, and so we can generate characters within each grid.
The number of the rectangular areas define the size of the LCD. The most popular LCD is the 16×2 LCD, which has two rows with 16 rectangular areas or characters. Of course, there are other sizes like 16×1, 16×4, 20×4 and so on, but they all work on the same principle. Also, these LCDs can have different background and text color.
It has 16 pins and the first one from left to right is the Groundpin. The second pin is the VCCwhich we connect the 5 volts pin on the Arduino Board. Next is the Vo pin on which we can attach a potentiometer for controlling the contrast of the display.
Next, The RSpin or register select pin is used for selecting whether we will send commands or data to the LCD. For example if the RS pin is set on low state or zero volts, then we are sending commands to the LCD like: set the cursor to a specific location, clear the display, turn off the display and so on. And when RS pin is set on High state or 5 volts we are sending data or characters to the LCD.
Next comes the R/W pin which selects the mode whether we will read or write to the LCD. Here the write mode is obvious and it is used for writing or sending commands and data to the LCD. The read mode is used by the LCD itself when executing the program which we don’t have a need to discuss about it in this tutorial.
Next is the E pin which enables the writing to the registers, or the next 8 data pins from D0 to D7. So through this pins we are sending the 8 bits data when we are writing to the registers or for example if we want to see the latter uppercase A on the display we will send 0100 0001 to the registers according to the ASCII table. The last two pins A and K, or anode and cathode are for the LED back light.
After all we don’t have to worry much about how the LCD works, as the Liquid Crystal Library takes care for almost everything. From the Arduino’s official website you can find and see the functions of the library which enable easy use of the LCD. We can use the Library in 4 or 8 bit mode. In this tutorial we will use it in 4 bit mode, or we will just use 4 of the 8 data pins.
We will use just 6 digital input pins from the Arduino Board. The LCD’s registers from D4 to D7 will be connected to Arduino’s digital pins from 4 to 7. The Enable pin will be connected to pin number 2 and the RS pin will be connected to pin number 1. The R/W pin will be connected to Ground and theVo pin will be connected to the potentiometer middle pin.
We can adjust the contrast of the LCD by adjusting the voltage input at the Vo pin. We are using a potentiometer because in that way we can easily fine tune the contrast, by adjusting input voltage from 0 to 5V.
Yes, in case we don’t have a potentiometer, we can still adjust the LCD contrast by using a voltage divider made out of two resistors. Using the voltage divider we need to set the voltage value between 0 and 5V in order to get a good contrast on the display. I found that voltage of around 1V worked worked great for my LCD. I used 1K and 220 ohm resistor to get a good contrast.
There’s also another way of adjusting the LCD contrast, and that’s by supplying a PWM signal from the Arduino to the Vo pin of the LCD. We can connect the Vo pin to any Arduino PWM capable pin, and in the setup section, we can use the following line of code:
It will generate PWM signal at pin D11, with value of 100 out of 255, which translated into voltage from 0 to 5V, it will be around 2V input at the Vo LCD pin.
First thing we need to do is it insert the Liquid Crystal Library. We can do that like this: Sketch > Include Library > Liquid Crystal. Then we have to create an LC object. The parameters of this object should be the numbers of the Digital Input pins of the Arduino Board respectively to the LCD’s pins as follow: (RS, Enable, D4, D5, D6, D7). In the setup we have to initialize the interface to the LCD and specify the dimensions of the display using the begin()function.
The cursor() function is used for displaying underscore cursor and the noCursor() function for turning off. Using the clear() function we can clear the LCD screen.
In case we have a text with length greater than 16 characters, we can scroll the text using the scrollDisplayLeft() orscrollDisplayRight() function from the LiquidCrystal library.
We can choose whether the text will scroll left or right, using the scrollDisplayLeft() orscrollDisplayRight() functions. With the delay() function we can set the scrolling speed.
So, we have covered pretty much everything we need to know about using an LCD with Arduino. These LCD Character displays are really handy for displaying information for many electronics project. In the examples above I used 16×2 LCD, but the same working principle applies for any other size of these character displays.
I hope you enjoyed this tutorial and learned something new. Feel free to ask any question in the comments section below and don’t forget to check out my full collection of 30+ Arduino Projects.

The Arduino family of devices is features rich and offers many capabilities. The ability to interface to external devices readily is very enticing, although the Arduino has a limited number of input/output options. Adding an external display would typically require several of the limited I/O pins. Using an I2C interface, only two connections for an LCD character display are possible with stunning professional results. We offer both a 4 x 20 LCD.
The character LCD is ideal for displaying text and numbers and special characters. LCDs incorporate a small add-on circuit (backpack) mounted on the back of the LCD module. The module features a controller chip handling I2C communications and an adjustable potentiometer for changing the intensity of the LED backlight. An I2C LCD advantage is that wiring is straightforward, requiring only two data pins to control the LCD.
A standard LCD requires over ten connections, which can be a problem if your Arduino does not have many GPIO pins available. If you happen to have an LCD without an I2C interface incorporated into the design, these can be easily
The LCD displays each character through a matrix grid of 5×8 pixels. These pixels can display standard text, numbers, or special characters and can also be programmed to display custom characters easily.
Connecting the Arduino UNO to the I2C interface of the LCD requires only four connections. The connections include two for power and two for data. The chart below shows the connections needed.
The I2C LCD interface is compatible across much of the Arduino family. The pin functions remain the same, but the labeling of those pins might be different.
Located on the back of the LCD screen is the I2C interface board, and on the interface is an adjustable potentiometer. This adjustment is made with a small screwdriver. You will adjust the potentiometer until a series of rectangles appear – this will allow you to see your programming results.
The Arduino module and editor do not know how to communicate with the I2C interface on the LCD. The parameter to enable the Arduino to send commands to the LCD are in separately downloaded LiquidCrystal_I2C library.
Before installing LiquidCrystal_I2C, remove any other libraries that may reside in the Arduino IDE with the same LiquidCrystal_I2C name. Doing this will ensure that only the known good library is in use. LiquidCrystal_I2C works in combination with the preinstalled Wire.h library in the Arduino editor.
To install the LiquidCrystal_I2C library, use the SketchSketch > Include Library > Add .ZIP Library…from the Arduino IDE (see example). Point to the LiquidCrystal_I2C-master.zip which you previously downloaded and the Library will be installed and set up for use.
Several examples and code are included in the Library installation, which can provide some reference and programming examples. You can use these example sketches as a basis for developing your own code for the LCD display module.
There may be situations where you should uninstall the Arduino IDE. The reason for this could be due to Library conflicts or other configuration issues. There are a few simple steps to uninstalling the IDE.
The I2c address can be changed by shorting the address solder pads on the I2C module. You will need to know the actual address of the LCD before you can start using it.
Once you have the LCD connected and have determined the I2C address, you can proceed to write code to display on the screen. The code segment below is a complete sketch ready for downloading to your Arduino.
The code assumes the I2C address of the LCD screen is at 0x27 and can be adjusted on the LiquidCrystal_I2C lcd = LiquidCrystal_I2C(0x27,16,2); as required.
Similar to the cursor() function, this will create a block-style cursor. Displayed at the position of the next character to be printed and displays as a blinking rectangle.
This function turns off any characters displayed to the LCD. The text will not be cleared from the LCD memory; rather, it is turned off. The LCD will show the screen again when display() is executed.
Scrolling text if you want to print more than 16 or 20 characters in one line then the scrolling text function is convenient. First, the substring with the maximum of characters per line is printed, moving the start column from right to left on the LCD screen. Then the first character is dropped, and the next character is displayed to the substring. This process repeats until the full string has been displayed on the screen.
The LCD driver backpack has an exciting additional feature allowing you to create custom characters (glyph) for use on the screen. Your custom characters work with both the 16×2 and 20×4 LCD units.
A custom character allows you to display any pattern of dots on a 5×8 matrix which makes up each character. You have full control of the design to be displayed.
To aid in creating your custom characters, there are a number of useful tools available on Internet. Here is a LCD Custom Character Generator which we have used.

This tutorial shows how to use the I2C LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) with the ESP32 using Arduino IDE. We’ll show you how to wire the display, install the library and try sample code to write text on the LCD: static text, and scroll long messages. You can also use this guide with the ESP8266.
Additionally, it comes with a built-in potentiometer you can use to adjust the contrast between the background and the characters on the LCD. On a “regular” LCD you need to add a potentiometer to the circuit to adjust the contrast.
Before displaying text on the LCD, you need to find the LCD I2C address. With the LCD properly wired to the ESP32, upload the following I2C Scanner sketch.
After uploading the code, open the Serial Monitor at a baud rate of 115200. Press the ESP32 EN button. The I2C address should be displayed in the Serial Monitor.
Displaying static text on the LCD is very simple. All you have to do is select where you want the characters to be displayed on the screen, and then send the message to the display.
The next two lines set the number of columns and rows of your LCD display. If you’re using a display with another size, you should modify those variables.
Then, you need to set the display address, the number of columns and number of rows. You should use the display address you’ve found in the previous step.
To display a message on the screen, first you need to set the cursor to where you want your message to be written. The following line sets the cursor to the first column, first row.
Scrolling text on the LCD is specially useful when you want to display messages longer than 16 characters. The library comes with built-in functions that allows you to scroll text. However, many people experience problems with those functions because:
The messageToScroll variable is displayed in the second row (1 corresponds to the second row), with a delay time of 250 ms (the GIF image is speed up 1.5x).
In a 16×2 LCD there are 32 blocks where you can display characters. Each block is made out of 5×8 tiny pixels. You can display custom characters by defining the state of each tiny pixel. For that, you can create a byte variable to hold the state of each pixel.
In summary, in this tutorial we’ve shown you how to use an I2C LCD display with the ESP32/ESP8266 with Arduino IDE: how to display static text, scrolling text and custom characters. This tutorial also works with the Arduino board, you just need to change the pin assignment to use the Arduino I2C pins.
We hope you’ve found this tutorial useful. If you like ESP32 and you want to learn more, we recommend enrolling in Learn ESP32 with Arduino IDE course.

In this tutorial, I’ll explain how to set up an LCD on an Arduino and show you all the different ways you can program it. I’ll show you how to print text, scroll text, make custom characters, blink text, and position text. They’re great for any project that outputs data, and they can make your project a lot more interesting and interactive.
The display I’m using is a 16×2 LCD display that I bought for about $5. You may be wondering why it’s called a 16×2 LCD. The part 16×2 means that the LCD has 2 lines, and can display 16 characters per line. Therefore, a 16×2 LCD screen can display up to 32 characters at once. It is possible to display more than 32 characters with scrolling though.
The code in this article is written for LCD’s that use the standard Hitachi HD44780 driver. If your LCD has 16 pins, then it probably has the Hitachi HD44780 driver. These displays can be wired in either 4 bit mode or 8 bit mode. Wiring the LCD in 4 bit mode is usually preferred since it uses four less wires than 8 bit mode. In practice, there isn’t a noticeable difference in performance between the two modes. In this tutorial, I’ll connect the LCD in 4 bit mode.
Here’s a diagram of the pins on the LCD I’m using. The connections from each pin to the Arduino will be the same, but your pins might be arranged differently on the LCD. Be sure to check the datasheet or look for labels on your particular LCD:
Also, you might need to solder a 16 pin header to your LCD before connecting it to a breadboard. Follow the diagram below to wire the LCD to your Arduino:
All of the code below uses the LiquidCrystal library that comes pre-installed with the Arduino IDE. A library is a set of functions that can be easily added to a program in an abbreviated format.
In order to use a library, it needs be included in the program. Line 1 in the code below does this with the command #include
Now we’re ready to get into the programming! I’ll go over more interesting things you can do in a moment, but for now lets just run a simple test program. This program will print “hello, world!” to the screen. Enter this code into the Arduino IDE and upload it to the board:
There are 19 different functions in the LiquidCrystal library available for us to use. These functions do things like change the position of the text, move text across the screen, or make the display turn on or off. What follows is a short description of each function, and how to use it in a program.
TheLiquidCrystal() function sets the pins the Arduino uses to connect to the LCD. You can use any of the Arduino’s digital pins to control the LCD. Just put the Arduino pin numbers inside the parentheses in this order:
This function sets the dimensions of the LCD. It needs to be placed before any other LiquidCrystal function in the void setup() section of the program. The number of rows and columns are specified as lcd.begin(columns, rows). For a 16×2 LCD, you would use lcd.begin(16, 2), and for a 20×4 LCD you would use lcd.begin(20, 4).
This function clears any text or data already displayed on the LCD. If you use lcd.clear() with lcd.print() and the delay() function in the void loop() section, you can make a simple blinking text program:
Similar, but more useful than lcd.home() is lcd.setCursor(). This function places the cursor (and any printed text) at any position on the screen. It can be used in the void setup() or void loop() section of your program.
The cursor position is defined with lcd.setCursor(column, row). The column and row coordinates start from zero (0-15 and 0-1 respectively). For example, using lcd.setCursor(2, 1) in the void setup() section of the “hello, world!” program above prints “hello, world!” to the lower line and shifts it to the right two spaces:
You can use this function to write different types of data to the LCD, for example the reading from a temperature sensor, or the coordinates from a GPS module. You can also use it to print custom characters that you create yourself (more on this below). Use lcd.write() in the void setup() or void loop() section of your program.
The function lcd.noCursor() turns the cursor off. lcd.cursor() and lcd.noCursor() can be used together in the void loop() section to make a blinking cursor similar to what you see in many text input fields:
Cursors can be placed anywhere on the screen with the lcd.setCursor() function. This code places a blinking cursor directly below the exclamation point in “hello, world!”:
This function creates a block style cursor that blinks on and off at approximately 500 milliseconds per cycle. Use it in the void loop() section. The function lcd.noBlink() disables the blinking block cursor.
This function turns on any text or cursors that have been printed to the LCD screen. The function lcd.noDisplay() turns off any text or cursors printed to the LCD, without clearing it from the LCD’s memory.
This function takes anything printed to the LCD and moves it to the left. It should be used in the void loop() section with a delay command following it. The function will move the text 40 spaces to the left before it loops back to the first character. This code moves the “hello, world!” text to the left, at a rate of one second per character:
Like the lcd.scrollDisplay() functions, the text can be up to 40 characters in length before repeating. At first glance, this function seems less useful than the lcd.scrollDisplay() functions, but it can be very useful for creating animations with custom characters.
lcd.noAutoscroll() turns the lcd.autoscroll() function off. Use this function before or after lcd.autoscroll() in the void loop() section to create sequences of scrolling text or animations.
This function sets the direction that text is printed to the screen. The default mode is from left to right using the command lcd.leftToRight(), but you may find some cases where it’s useful to output text in the reverse direction:
This code prints the “hello, world!” text as “!dlrow ,olleh”. Unless you specify the placement of the cursor with lcd.setCursor(), the text will print from the (0, 1) position and only the first character of the string will be visible.
This command allows you to create your own custom characters. Each character of a 16×2 LCD has a 5 pixel width and an 8 pixel height. Up to 8 different custom characters can be defined in a single program. To design your own characters, you’ll need to make a binary matrix of your custom character from an LCD character generator or map it yourself. This code creates a degree symbol (°):

I recently received some free LCD samples from my friends at FocusLCDs.com. One of which is a 16x4 LCD; P/N: C164AXBSYLY6WT. It uses a ST7066U controller (see datasheet here) instead of the HD44780 commonly found in LCD shields. I am not so sure if it will work with an Arduino and its libraries, so I wanted to try it out.

– Arduino is an open-source platform used for building electronics projects. Arduino consists of both a physical programmable microcontroller and a piece of software, or IDE (Integrated Development Environment) that runs on your computer, used to write and upload computer code to the physical board.
– The Arduino platform unlike most previous programmable circuit boards, the Arduino does not need a separate programmer to load new code onto the board — you can simply use a USB cable. Additionally, the Arduino IDE uses a simplified version of C++, making it easier to learn to program.
– The open sources and extensible language: Arduino IDE is based on open source tool. The programming language used can be extended through the C++ library.
– The open source and expandable hardware: Arduino is based on Atmel’s ATMEGA 8-bit microcontrollers and its SAM3X8E and SAMD21 32-bit microcontrollers. Development boards and modules are planned to be released under the premise of following the “Creative Commons License Agreement”, so experienced circuit designers can make their own modules and carry out corresponding expansions and improvements. Even users who are relatively inexperienced can make a trial version of the basic Uno development board, which is easy to understand the principle of its operation and save costs.
– The Arduino hardware and software were designed for artists, designers, hobbyists, hackers, newbies, and anyone interested in creating interactive objects or environments. Arduino can interact with buttons, LEDs, motors, speakers, GPS units, cameras, the internet, and even your smart-phone or your TV.
Arduino Leonardo: Arduino’s first development board to use one microcontroller with built-in USB. It is cheaper and simpler. The code libraries allow the board to emulate a computer keyboard, mouse, and more.
LCD means liquid crystal display. Basically, any displays can be used with Arduino, including alphanumeric character LCD display, monochrome graphic LCD display, color TFT LCD display, IPS LCD display. It can also be used for non LCD displays like: PMOLED display, AMOLED display, E-ink (E-paper) displays. Orient Display developed easy interface (SPI, I2C) displays which can be easily used with Arduino.
LCD displays were first used for watches and calculators. Now, LCD display technology dominants the display world, it can be found in wearables, smart homes, mobile phones, TVs, laptops, monitors, kiosks, aircraft cockpit, digital cameras, lab instrument, power grid etc.
LCD itself can emit light itself. It has to utilize outside light sources. LCD display module normally includes LCD glass (or LCD panel), LCD driving circuitry ( can be COG, COB or TAB) and a backlight.
A LCD display 16*2 is actually a basic and simple to use LCD module. It includes LCD glass, COB (Chip on PCB Board) LCD control board, backlight, zebra to connect LCD glass and control board and a bezel to hold everything together. 16×2 LCD display can display 16 characters per line and there are two lines. Each character has 5×7 dot matrix pixels and the cursor underneath. All 16×2 LCD display originally used standard Hitachi HD44780 driver. Of course the legendary HD44780 controller had EOL long time ago. All the 16×2 LCD displays use HD44780 compatible LCD controllers. Some of them are drop replacement, some of them need to modify the initialization code a little.
Pin5 (Read/Write/Control Pin): This pin toggles the display among the read or writes operation, and it is connected to a microcontroller unit pin to get either 0 or 1 (0 = Write Operation, and 1 = Read Operation).
Pins 7-14 (Data Pins): These pins are used to send data to the display. These pins are connected in two-wire modes like 4-bit mode and 8-bit mode. In 4-wire mode, only four pins are connected to the microcontroller unit like 0 to 3, whereas in 8-wire mode, 8-pins are connected to microcontroller unit like 0 to 7.
A 16×2 LCD has two registers like data register and command register. The RS (register select) is mainly used to change from one register to another. When the register set is ‘0’, then it is known as command register. Similarly, when the register set is ‘1’, then it is known as data register.
Command Register: The main function of the command register is to store the instructions of command which are given to the display. So that predefined tasks can be performed such as clearing the display, initializing, set the cursor place, and display control. Here commands processing can occur within the register.
Data Register: The main function of the data register is to store the information which is to be exhibited on the LCD screen. Here, the ASCII value of the character is the information which is to be exhibited on the screen of LCD. Whenever we send the information to LCD, it transmits to the data register, and then the process will be starting there. When register set =1, then the data register will be selected.
All of the code below uses the LiquidCrystal library that comes pre-installed with the Arduino IDE. A library is a set of functions that can be easily added to a program in an abbreviated format. In order to use a library, it needs be included in the program. Line 1 in the code below does this with the command #include
Now we’re ready to get into the programming! I’ll go over more interesting things you can do in a moment, but for now let’s just run a simple test program. This program will print “hello, world!” to the screen. Enter this code into the Arduino IDE and upload it to the board:
There are 19 different functions in the LiquidCrystal library available for us to use. These functions do things like change the position of the text, move text across the screen, or make the display turn on or off. What follows is a short description of each function, and how to use it in a program.
The LiquidCrystal() function sets the pins the Arduino uses to connect to the LCD. You can use any of the Arduino’s digital pins to control the LCD. Just put the Arduino pin numbers inside the parentheses in this order:
This function sets the dimensions of the LCD. It needs to be placed before any other LiquidCrystal function in the void setup() section of the program. The number of rows and number of columns are specified as lcd.begin(columns, rows). For a 16×2 LCD, you would use lcd.begin(16, 2), and for a 20×4 LCD you would use lcd.begin(20, 4).
This function clears any text or data already displayed on the LCD. If you use lcd.clear() with lcd.print() and the delay() function in the void loop() section, you can make a simple blinking text program.
Similar, but more useful than lcd.home() is lcd.setCursor(). This function places the cursor (and any printed text) at any position on the screen. It can be used in the void setup() or void loop() section of your program.
The cursor position is defined with lcd.setCursor(column, row). The column and row coordinates start from zero (0-15 and 0-1 respectively). For example, using lcd.setCursor(2, 1) in the void setup() section of the “hello, world!” program above prints “hello, world!” to the lower line and shifts it to the right two spaces:
This function creates a block style cursor that blinks on and off at approximately 500 milliseconds per cycle. Use it in the void loop() section. The function lcd.noBlink() disables the blinking block cursor.
This function turns on any text or cursors that have been printed to the LCD screen. The function lcd.noDisplay() turns off any text or cursors printed to the LCD, without clearing it from the LCD’s memory.
This function takes anything printed to the LCD and moves it to the left. It should be used in the void loop() section with a delay command following it. The function will move the text 40 spaces to the left before it loops back to the first character. This code moves the “hello, world!” text to the left, at a rate of one second per character.
lcd.noAutoscroll() turns the lcd.autoscroll() function off. Use this function before or after lcd.autoscroll() in the void loop() section to create sequences of scrolling text or animations.
This function sets the direction that text is printed to the screen. The default mode is from left to right using the command lcd.leftToRight(), but you may find some cases where it’s useful to output text in the reverse direction.
This command allows you to create your own custom characters. Each character of a 16×2 LCD has a 5 pixel width and an 8 pixel height. Up to 8 different custom characters can be defined in a single program. To design your own characters, you’ll need to make a binary matrix of your custom character from an LCD character generator or map it yourself. This code creates a degree symbol (°).
The detailed LCD tutorial can be found in the article. ARDUINO LCD SET UP AND PROGRAMMING GUIDE or to check https://github.com/arduino-libraries/LiquidCrystal

The purpose of this guide is to get your 0.96″ color LCD display successfully operating with your Arduino, so you can move forward and experiment and explore further types of operation with the display. This includes installing the Arduino library, making a succesful board connection and running a demonstration sketch.
Although you can use the display with an Arduino Uno or other boad with an ATmega328-series microcontroller – this isn’t recommended for especially large projects. The library eats up a fair amount of flash memory – around 60% in most cases.
So if you’re running larger projects we recommend using an Arduino Mega or Due-compatible board due to the increased amount of flash memory in their host microcontrollers.
(As the display uses the ST7735S controller IC, you may be tempted to use the default TFT library included with the Arduino IDE – however it isn’t that reliable. Instead, please follow the instructions below).
The display uses the SPI data bus for communication, and is a 3.3V board. You can use it with an Arduino or other 5V board as the logic is tolerant of higher voltages.
The library used is based on the uTFT library by Henning Karlsen. You can find all the drawing and other commands in the user manual – so download the pdf and enjoy creating interesting displays.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey