tn tft display in stock

If none of these part numbers meet your requirements in terms of brightness, interface, or connection method, please email us at info@orientdisplay.com.
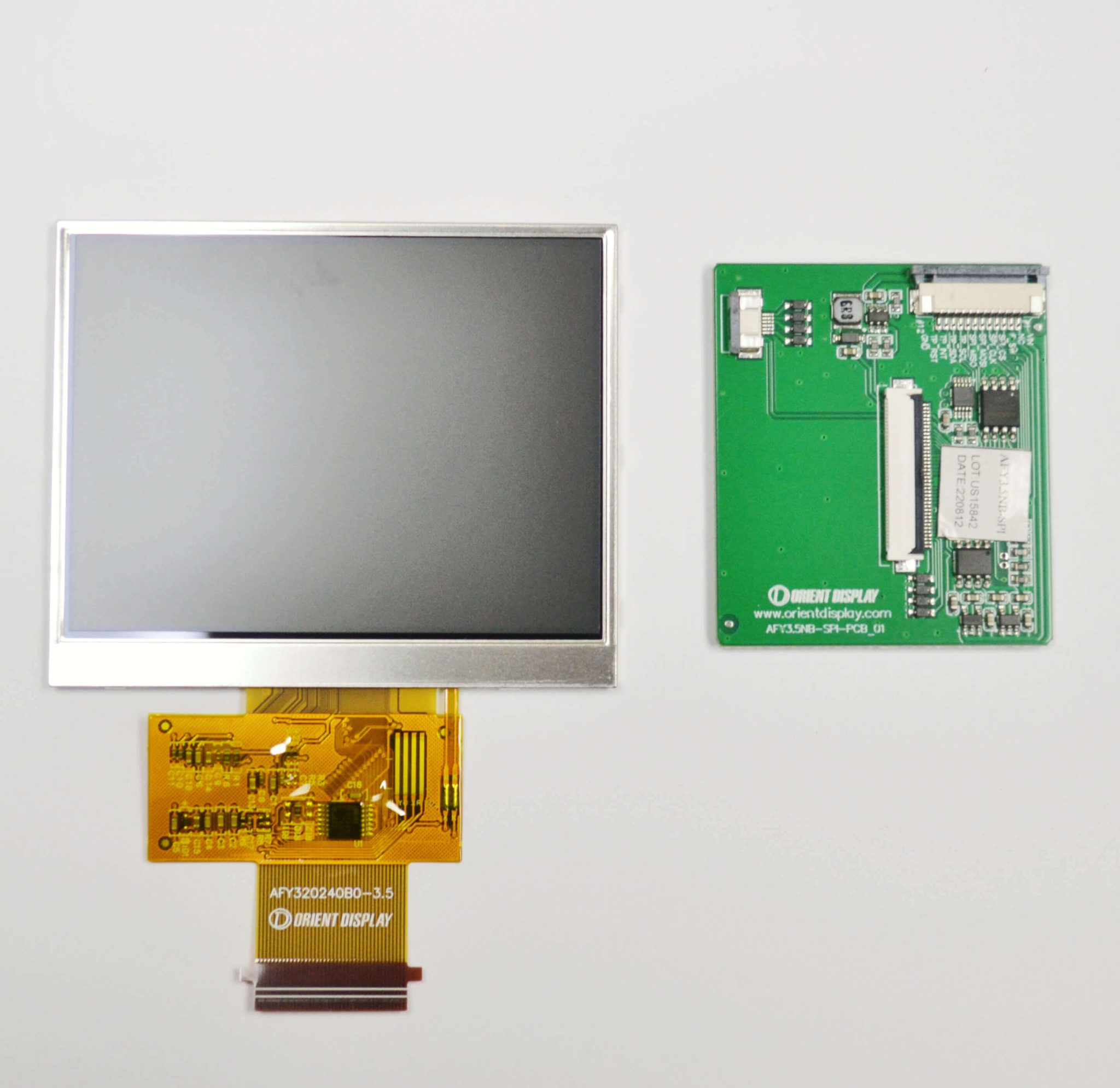
If none of these part numbers meet your requirements in terms of brightness, interface, or connection method, please email us at info@orientdisplay.com.

IPS (In-Plane Switching) lcd is still a type of TFT LCD, IPS TFT is also called SFT LCD (supper fine tft ),different to regular tft in TN (Twisted Nematic) mode, theIPS LCD liquid crystal elements inside the tft lcd cell, they are arrayed in plane inside the lcd cell when power off, so the light can not transmit it via theIPS lcdwhen power off, When power on, the liquid crystal elements inside the IPS tft would switch in a small angle, then the light would go through the IPS lcd display, then the display on since light go through the IPS display, the switching angle is related to the input power, the switch angle is related to the input power value of IPS LCD, the more switch angle, the more light would transmit the IPS LCD, we call it negative display mode.
The regular tft lcd, it is a-si TN (Twisted Nematic) tft lcd, its liquid crystal elements are arrayed in vertical type, the light could transmit the regularTFT LCDwhen power off. When power on, the liquid crystal twist in some angle, then it block the light transmit the tft lcd, then make the display elements display on by this way, the liquid crystal twist angle is also related to the input power, the more twist angle, the more light would be blocked by the tft lcd, it is tft lcd working mode.
A TFT lcd display is vivid and colorful than a common monochrome lcd display. TFT refreshes more quickly response than a monochrome LCD display and shows motion more smoothly. TFT displays use more electricity in driving than monochrome LCD screens, so they not only cost more in the first place, but they are also more expensive to drive tft lcd screen.The two most common types of TFT LCDs are IPS and TN displays.

US Micro Products manufactures a wide selection of TFT LCD (Active Matrix LCDs) displays to accommodate the needs of OEMs across many different industries, including medical, industrial, gaming, military and many more.
An array of available interfaces, brightness levels, and temperature ranges ensure that our TFT LCDs work well with your design and in the environment of your choice
If you can’t find what you are looking for, contact us at sales@usmicroproducts.com! We are a manufacturer of Custom Display Solutions and are experts in extreme applications.

TFT LCD Modules: The CFAF240320W-020T-TS IPS TFT boasts vibrant, full color images at 200 PPI (Pixels Per Inch) in a compact 2” package for crystal clear, sharp images and text perfect for small applications and up close viewing. This touchscreen IPS TFT display has a wider viewing angle than a TN TFT display.
The CFAF240320W-020T-TS connects to the host via a single 45-pin ZIF connector, allowing for quick and easy installation. The display supports a wide variety of interfaces, including parallel, SPI, and RGB DOT-CLK to work seamlessly with a large variety of host devices.

Heng Cheng Electronics Technology Co., Ltd, established in 2009, is a manufacturer and distributor of TFT Displays, Touch Panels, Controller Boards and related components of the business.
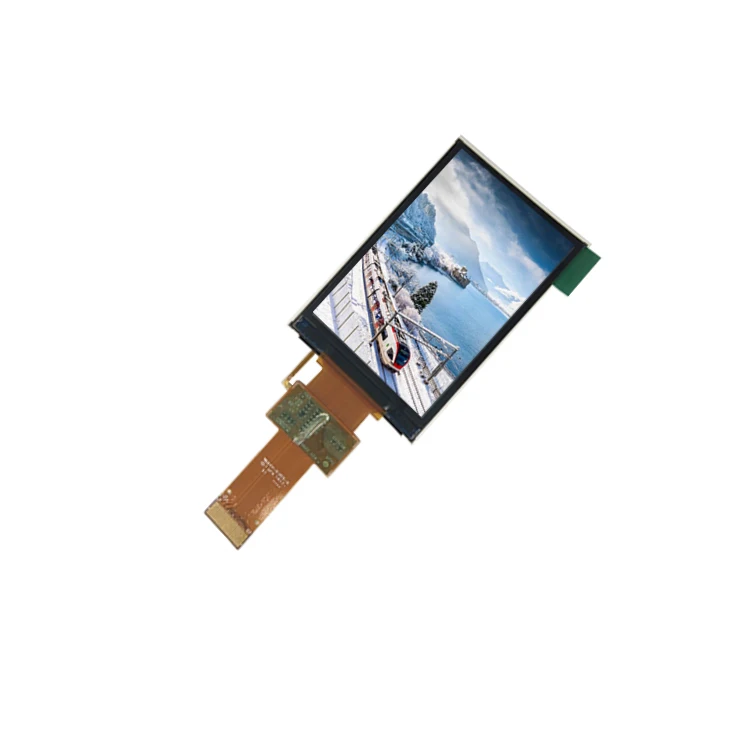
A TN-TFT display is a type of Liquid Crystal Displaywith thin film transistors for controlling the image formation. The TFT technology works by controlling brightness in red, green and blue sub-pixels through transistors for each pixel on the screen.
TFT-LCD technology is now fairly mature. As a result, manufacturing processes are efficient and production yields are high, leading to very competitive unit prices. Upgrading from a monochrome display to a TFT is now an affordable way to give your product an uplift.
As with all our displays, a variety of customisation options are availableto bring you a unique design that meets your application requirements and satisfies environmental challenges, including:
Here at Anders we don"t just strive to design a best in class display solution for your product, but we also want to make sure the display is driven with the right embedded system. We can help achieve a hardware solution that ensures your display works perfectly within your application. Hardware solutions include:
With ever increasing pressure in all of our lives, having easy to use and reliable home appliances plays a key role in easing those stresses. A cost effective colour TFT display is ideal for demanding user expectations, available in a variety of shapes and sizes..
Residential and commercial metering solutions are changing from monochrome to colour with a TN-TFT display offering an ideal cost effective solution to give your product the uplift it deserves. We can optimise these to suit your application including mechanical integration, coverlens design and backlight enhancements.
TN-TFT Displays are ideal for medical and personal healthcare devices. Both low power consumption and low cost solutions, they are available with wide viewing angles for challenging medical situations where the user may be at an acute angle to the device.
Putting your own stamp on your product is more than a logo on the start-up screen. Discover how we can help you design a unique display solution with our customisation services:
We aim to offer reliable and long-term solutions to our B2B customers. If you would like to discuss your display and/or embedded system requirements please contact us below.

Twisted Nematic (TN) panels are a rather inexpensive display technology in which each pixel consists of rod-shaped liquid crystals that are aligned horizontally to the image layer and allow light from the backlight to pass through. When a voltage is applied to the pixels, the orientation of the liquid crystals changes. The higher the voltage, the more perpendicular the rods are to the image layer, preventing the light from the backlight from "shining through". TN displays can be used, for example, in cash registers or kiosk systems where the user usually looks at the display from the front and for this reason an extended viewing angle from all directions is not required.
![]()
IPS, also known as In-Plane Switching, is a type of monitor display and screen technology that uses a voltage to control the alignment of liquid crystals, similar to TN technology. However, IPS displays use a different crystal orientation where the crystals are parallel to the glass substrates, hence the term ‘in-plane’. Rather than ‘twisting’ the crystals to modify the amount of light let through, IPS crystals are essentially rotated, which has a range of benefits. IPS displays offer the best color reproduction as well as the widest viewing angles compared to other LCD technologies.
While TN LCD’s support high refresh rates with low response times, they do come with sub-optimal viewing angles, and slightly diminished color reproduction. IPS panels address these downfalls with 80 degree viewing angles that eliminate color inversion and contrast diminishment. IPS technology is ideal for a wide array of applications such as medical, industrial, HVAC, Pool/Spa due to the ability to use the displays in both landscape and portrait mode while maintaining uniform viewing angles. This also allows for displays to be seen from different angles and heights, ideal for jacuzzi controls and thermostats that tend to require consideration of dynamic user parameters.

LCD is the abbreviation for liquid crystal display. An LCD basically consists of two glass plates with a special liquid between them. The special attribute of this liquid is that it rotates or “twists” the plane of polarized light. This effect is influenced by the creation of an electrical field. The glass plates are thus each coated with a very thin metallic film. To obtain polarized light, you apply a polarization foil, the polarizer, to the bottom glass plate. Another foil must be applied to the bottom glass plate, but this time with a plane of polarization twisted by 90°. This is referred to as the analyzer.
In the idle state, the liquid twists the plane of polarization of the incoming light by 90° so that it can pass the analyzer unhindered. The LCD is thus transparent. If a specific voltage is applied to the metallic film coating, the crystals rotate in the liquid. This twists the plane of polarization of the light by another 90°, for example: The analyzer prevents the light getting through, and the LCD thus becomes opaque.TN, STN, FSTN, blue mode, yellow-green mode
Liquids that twist the plane of polarized light by 90° are referred to as TN (Twisted Nematic). STN (Super Twisted Nematic) liquids twist the plane of polarized light by at least 180°. This gives the display improved contrast. However, this technology does color the display to a certain extent. The most common colors are referred to as yellow-green and blue mode. There is also a gray mode, which in practice is more blue than gray, however.
In order to counteract the undesired color effect, the FSTN technology uses an additional foil on the outer side, but this causes a loss of light and means that this technology is only effective with lit displays.
However, the different colors occur only in displays that are either not lit or that are lit with white light. If there is any color in the lighting (e.g. yellow-green LED lighting), it overrides the color of the display. A blue-mode LCD with yellow-green LED lighting will always appear yellow-green.Static or multiplex driving method
Small displays with a small viewing area are generally statically driven. Static displays have the best contrast and the largest possible angle of view. The TN technology fulfills its purpose to the full here (black and white display, reasonably priced). The bigger displays get, however, the more lines become necessary in static operation (e.g. graphics 128x64=8192 segments =8192 lines). Since there is not enough space on either the display or a driver IC for so many lines, multiplexing is used. The display is thus divided up into rows and columns, and there is a segment at each intersection (128+64=192 lines). Scanning takes place row by row (64x, in other words a multiplex rate of 1:64). Because only 1 row is ever active at any one time, however, the contrast and the angle of view suffer the higher the multiplex rate becomes. This makes it essential to use STN.Angle of view 6°°/12°°
Every LCD has a preferred angle of view at which the contrast of the display is at its optimum. Most displays are produced for the 6°° angle of view, which is also known as the bottom view (BV). This angle corresponds to that of a pocket calculator that is lying flat on a desktop.
12°° displays (top view, TV) are best built into a table-top unit. All displays can be read vertically from the front.Reflective, transflective, transmissive
However, the lighting also determines the optical impression made by the display, and the display mode; blue or yellow-green – does not always have an influence. Below you can see the EAP162-3N display with different types of lighting by way of example:Lighting
Standard LCDs have a temperature range of 0 to +50°C. High-temperature displays are designed for operation in the range from -20 to +70°C. In this case, however, additional supply voltage is generally required. Since the contrast of any LCD is dependent on the temperature, a special temperature-compensation circuit is needed in order to use the entire temperature range, and this is particularly true for high-temperature displays (-20 to +70°C). Manual adjustment is possible but rather impractical for the user.
However, the storage temperature of a display should never be exceeded under any circumstances. An excessively high temperature can destroy the display very quickly. Direct exposure to the sun, for example, can destroy an LCD: This is because an LCD becomes darker (in positive mode) as it gets hotter. As it gets darker, it absorbs more light and converts it to heat. As a result, the display becomes even hotter and darker... In this way, temperatures of over 100°C can quickly be reached.Dot-matrix, graphics and 7-segment displays
The first LCDs were 7-segment displays, and they are still found today in simple pocket calculators and digital watches. 7 segments allow all of the digits from 0 to 9 to be displayed.
Text displays require what is known as a dot matrix, an area consisting of 5x7=35 dots, in order to display all of the letters in the alphabet as well as various special characters. Graphics displays have a similar structure to text displays. In this case, however, there are no spaces between the lines and characters.Display drivers and controllers
The semiconductor industry now offers a very large range of LCD drivers. We generally distinguish between pure display drivers without intelligence of their own, controllers with a display memory and possibly a character set, and micro-controllers with integrated LC drivers.
Pure display drivers work in a similar way to a shift register. They generally have a serial input. They require an external pulse, and in multiplex operation with high frequency they require new display data continuously in order to achieve a refresh frequency that is as high as possible (MSM5219, UPD7225, HD44100, LC7942, etc.). An example of a genuine controller is theHD44780 for dot-matrix displays: Once it has received the ASCII code, the controller manages its character set, memory and multiplexing entirely on its own. The following controllers are widely used for graphics displays: HD61202/3, HD61830, SED1520, SED1330, T6963.
Many ask themselves, "What is the difference between an LCD display and a TFT display?" or "What is the difference between a TFT and an OLED display?". Here are these 3 sometimes extremely different display technologies briefly explained. LCD vs. TFT vs. OLED (comparison).
- The LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) is a passive display technology. The operation and the structure are described above. Passive means that an LCD can only darken or let out light. So it always depends on ambient light or a backlight. This can be an advantage because the power consumption of a LCD display is very, very low. Sometimes even less than the accumulated power consumption of an E-paper display, which in static operation requires absolutely no energy to maintain the content. To change the contents, however, a relatively large amount of power is required for an E-paper display.
LCDs can also be reflective, so they reflect incident light and are therefore legible even at maximum brightness (sunlight, surgical lighting). Compared to TFT and also OLED, they have an unbeatable advantage in terms of readability and power consumption :; the "formula" is: Sunlight = LCD.
- A TFT display (of Thin-Film Transistor) is usually a color display (RGB). From the construction and the technology it corresponds to the LCD. It is also passive, so it needs a backlight. This is in any case necessary except for a few, very expensive constructions. However, a TFT needs much more light than the monochrome relatives, because the additional structures on the glass as well as the additional color filters "swallow" light. So TFTs are not particularly energy-efficient, but can display in color and at the same time the resolution is much higher.
- OLED displays (by Organic-Light-Emitting-Diode) are as the name implies active displays - every pixel or sign generates light. This achieves an extremely wide viewing angle and high contrast values. The power consumption is dependent on the display content. Here OLEDs to TFTs and LCDs differ significantly, which have a nearly constant power consumption even with different display contents. Unfortunately, the efficiency of converting the electric current into light energy is still very poor. This means that the power consumption of OLEDs with normal content is sometimes higher than that of a TFT with the same size. Colored OLEDs are increasingly used in consumer devices, but for the industry, due to their availability and lifetime, currently only monochrome displays are suitable (usually in yellow color).
In the reaction time, the OLEDs beat each TFT and LCD by worlds. Trise and Tfall are about 10μs, which would correspond to a theoretical refresh rate of 50,000 Hz. Possibly an advantage in very special applications.
Finally the question "What is better, LCD, OLED or TFT?" Due to the physical differences you can not answer that blanket. Depending on the application, there are pros and cons to each individual technology. In addition to the above differences, there are many more details in the design and construction that need to be individually illuminated for each device. Write us an e-mail or call us: we have specialists with some 20- and 30-year experience. We are happy to compare different displays together with you.AACS and IPS technology




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey