arduino 2.4'' tft lcd touch shield code pricelist

Spice up your Arduino project with a beautiful touchscreen display shield with built in microSD card connection. This TFT display is 2.4" diagonal and colorful (18-bit 262,000 different shades)! 240x320 pixels with individual pixel control. As a bonus, this display has a optional capacitive touch panel and resistive touch panel with controller XPT2046 attached by default.
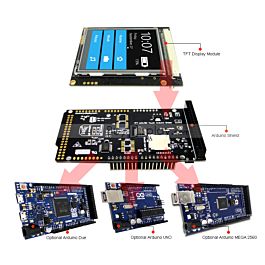
The shield is fully assembled, tested and ready to go. No wiring, no soldering! Simply plug it in and load up our library - you"ll have it running in under 10 minutes! Works best with any classic Arduino (UNO/Due/Mega 2560).
This display shield has a controller built into it with RAM buffering, so that almost no work is done by the microcontroller. You can connect more sensors, buttons and LEDs.
Of course, we wouldn"t just leave you with a datasheet and a "good luck!" - we"ve written a full open source graphics library at the bottom of this page that can draw pixels, lines, rectangles, circles and text. We also have a touch screen library that detects x,y and z (pressure) and example code to demonstrate all of it. The code is written for Arduino but can be easily ported to your favorite microcontroller!
If you"ve had a lot of Arduino DUEs go through your hands (or if you are just unlucky), chances are you’ve come across at least one that does not start-up properly.The symptom is simple: you power up the Arduino but it doesn’t appear to “boot”. Your code simply doesn"t start running.You might have noticed that resetting the board (by pressing the reset button) causes the board to start-up normally.The fix is simple,here is the solution.

Find many great new & used options and get the best deals for 2.4" TFT LCD Display Shield Touch Panel Module 240×320 for Arduino UNO Ili9341 at the best online prices at eBay! Free shipping for many products!
It worked with examples of the UTFT-Library, but now I try to write an own program and the screen is only white. When I use myGLCD.getDisplayXSize(), it gives me the right value.

Idea was to build small environment controller on due + tft lcd touch. I succeed with sensors, next step for me to make all necessary data to be on display.
i got mcufriend 2.4" TFT LCD shield and arduino lcd. I decided to start from 2.4" tried a lot of libraries sketches but everywhere i got failure(( some sketches just didn"t compile because ave/arm difference, some compile but display stay blank, and just being white, later i decided that I"m to stupid for this one, and for sure with arduino lcd should follow a lot of tutorials for due, but again fail)) all i found is bunch of stuff for other boards but not due.
I already built a 2.4 LCD TFT library for Due with parallel HX8347A chip controller. The video section is working OK but the external touch controller (ADS7843) had some issues thus I decided to buy a 3.2" with touch embedded. I expect to receive the 3.2 in a couple of weeks and continue my post.

In this Arduino touch screen tutorial we will learn how to use TFT LCD Touch Screen with Arduino. You can watch the following video or read the written tutorial below.
For this tutorial I composed three examples. The first example is distance measurement using ultrasonic sensor. The output from the sensor, or the distance is printed on the screen and using the touch screen we can select the units, either centimeters or inches.
The third example is a game. Actually it’s a replica of the popular Flappy Bird game for smartphones. We can play the game using the push button or even using the touch screen itself.
As an example I am using a 3.2” TFT Touch Screen in a combination with a TFT LCD Arduino Mega Shield. We need a shield because the TFT Touch screen works at 3.3V and the Arduino Mega outputs are 5 V. For the first example I have the HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor, then for the second example an RGB LED with three resistors and a push button for the game example. Also I had to make a custom made pin header like this, by soldering pin headers and bend on of them so I could insert them in between the Arduino Board and the TFT Shield.
Here’s the circuit schematic. We will use the GND pin, the digital pins from 8 to 13, as well as the pin number 14. As the 5V pins are already used by the TFT Screen I will use the pin number 13 as VCC, by setting it right away high in the setup section of code.
As the code is a bit longer and for better understanding I will post the source code of the program in sections with description for each section. And at the end of this article I will post the complete source code.
I will use the UTFT and URTouch libraries made by Henning Karlsen. Here I would like to say thanks to him for the incredible work he has done. The libraries enable really easy use of the TFT Screens, and they work with many different TFT screens sizes, shields and controllers. You can download these libraries from his website, RinkyDinkElectronics.com and also find a lot of demo examples and detailed documentation of how to use them.
After we include the libraries we need to create UTFT and URTouch objects. The parameters of these objects depends on the model of the TFT Screen and Shield and these details can be also found in the documentation of the libraries.
Next we need to define the fonts that are coming with the libraries and also define some variables needed for the program. In the setup section we need to initiate the screen and the touch, define the pin modes for the connected sensor, the led and the button, and initially call the drawHomeSreen() custom function, which will draw the home screen of the program.
So now I will explain how we can make the home screen of the program. With the setBackColor() function we need to set the background color of the text, black one in our case. Then we need to set the color to white, set the big font and using the print() function, we will print the string “Arduino TFT Tutorial” at the center of the screen and 10 pixels down the Y – Axis of the screen. Next we will set the color to red and draw the red line below the text. After that we need to set the color back to white, and print the two other strings, “by HowToMechatronics.com” using the small font and “Select Example” using the big font.
Ok next is the RGB LED Control example. If we press the second button, the drawLedControl() custom function will be called only once for drawing the graphic of that example and the setLedColor() custom function will be repeatedly called. In this function we use the touch screen to set the values of the 3 sliders from 0 to 255. With the if statements we confine the area of each slider and get the X value of the slider. So the values of the X coordinate of each slider are from 38 to 310 pixels and we need to map these values into values from 0 to 255 which will be used as a PWM signal for lighting up the LED. If you need more details how the RGB LED works you can check my particular tutorialfor that. The rest of the code in this custom function is for drawing the sliders. Back in the loop section we only have the back button which also turns off the LED when pressed.
In order the code to work and compile you will have to include an addition “.c” file in the same directory with the Arduino sketch. This file is for the third game example and it’s a bitmap of the bird. For more details how this part of the code work you can check my particular tutorial. Here you can download that file:

In this tutorial, you will learn how to use and set up 2.4″ Touch LCD Shield for Arduino. First, you’ll see some general information about this shield. And after learning how to set the shield up, you’ll see 3 practical projects.
The role of screens in electronic projects is very important. Screens can be of very simple types such as 7 Segment or character LCDs or more advanced models like OLEDs and TFT LCDs.
One of the most important features of this LCD is including a touch panel. If you are about to use the LCD, you need to know the coordinates of the point you touch. To do so, you should upload the following code on your Arduino board and open the serial monitor. Then touch your desired location and write the coordinates displayed on the serial monitor. You can use this coordination in any other project.
To display pictures on this LCD you should save the picture in 24bit BMP colored format and size of 240*320. Then move them to SD card and put the SD card in the LCD shield. we use the following function to display pictures. This function has 3 arguments; the first one stands for the pictures name, and the second and third arguments are for length and width coordinates of the top left corner of the picture.
If you want to display pictures without using an SD card, you can convert it to code and then display it. You can display even several photos sequentially without delay to create an animation. (Check this) But be aware that in this case, Arduino UNO may not be suitable (because of low processor speed). We recommend using the Arduino Mega or Arduino DUE.

Displays are one of the best ways to provide feedback to users of a particular device or project and often the bigger the display, the better. For today’s tutorial, we will look on how to use the relatively big, low cost, ILI9481 based, 3.5″ Color TFT display with Arduino.
This 3.5″ color TFT display as mentioned above, is based on the ILI9481 TFT display driver. The module offers a resolution of 480×320 pixels and comes with an SD card slot through which an SD card loaded with graphics and UI can be attached to the display. The module is also pre-soldered with pins for easy mount (like a shield) on either of the Arduino Mega and Uno, which is nice since there are not many big TFT displays that work with the Arduino Uno.
The module is compatible with either of the Arduino Uno or the Arduino Mega, so feel free to choose between them or test with both. As usual, these components can be bought via the links attached to them.
One of the good things about this module is the ease with which it can be connected to either of the Arduino Mega or Uno. For this tutorial, we will use the Arduino Uno, since the module comes as a shield with pins soldered to match the Uno’s pinout. All we need to do is snap it onto the top of the Arduino Uno as shown in the image below, thus no wiring required.
This ease of using the module mentioned above is, however, one of the few downsides of the display. If we do not use the attached SD card slot, we will be left with 6 digital and one analog pin as the module use the majority of the Arduino pins. When we use the SD card part of the display, we will be left with just 2 digital and one analog pin which at times limits the kind of project in which we can use this display. This is one of the reasons while the compatibility of this display with the Arduino Mega is such a good news, as the “Mega” offers more digital and analog pins to work with, so when you need extra pins, and size is not an issue, use the Mega.
To easily write code to use this display, we will use the GFX and TFT LCD libraries from “Adafruit” which can be downloaded here. With the library installed we can easily navigate through the examples that come with it and upload them to our setup to see the display in action. By studying these examples, one could easily learn how to use this display. However, I have compiled some of the most important functions for the display of text and graphics into an Arduino sketch for the sake of this tutorial. The complete sketch is attached in a zip file under the download section of this tutorial.
As usual, we will do a quick run through of the code and we start by including the libraries which we will use for the project, in this case, the Adafruit GFX and TFT LCD libraries.
With this done, the Void Setup() function is next. We start the function by issuing atft.reset() command to reset the LCD to default configurations. Next, we specify the type of the LCD we are using via the LCD.begin function and set the rotation of the TFT as desired. We proceed to fill the screen with different colors and display different kind of text using diverse color (via the tft.SetTextColor() function) and font size (via the tft.setTextSize() function).
The Adafruit library helps reduce the amount of work one needs to do while developing the code for this display, leaving the quality of the user interface to the limitations of the creativity and imagination of the person writing the code.
In this guide we’re going to show you how you can use the 1.8 TFT display with the Arduino. You’ll learn how to wire the display, write text, draw shapes and display images on the screen.
The 1.8 TFT is a colorful display with 128 x 160 color pixels. The display can load images from an SD card – it has an SD card slot at the back. The following figure shows the screen front and back view.
This module uses SPI communication – see the wiring below . To control the display we’ll use the TFT library, which is already included with Arduino IDE 1.0.5 and later.
The TFT display communicates with the Arduino via SPI communication, so you need to include the SPI library on your code. We also use the TFT library to write and draw on the display.
The 1.8 TFT display can load images from the SD card. To read from the SD card you use the SD library, already included in the Arduino IDE software. Follow the next steps to display an image on the display:
In this guide we’ve shown you how to use the 1.8 TFT display with the Arduino: display text, draw shapes and display images. You can easily add a nice visual interface to your projects using this display.

2.4 inch TFT LCD Touch Screen Shield for Arduino UNO R3 Mega2560The shield is fully assembled, tested and ready to go. No wielding, no solder! Simply plug it in and load up our library - you"ll have it running in under 10 minutes! Works best with any classic UNO. This shield does work with the Mega but its going to be half the speed of the Uno-type boards because of the way the Mega rearranges all the pins (there is no way to get around this!) This shield is Leonardo-compatible
Description:Spice up your project with a beautiful large touchscreen display shield with built in microSD card connection. This TFT display is big (2.4 inch diagonal) bright (4 white-LED backlight) and colorful (18-bit 262,000 different shades)! 240x320 pixels with individual pixel control. It has way more resolution than a black and white 128x64 display. As a bonus, this display has a resistive touchscreen attached to it already, so you can detect finger presses anywhere on the screen.color: redMaterial: comprehensive material
Technical Details:2.4 inch diagonal LCD TFT display240x320 resolution, 18-bit (262,000) colorspfd5408 controller with built in video RAM buffer8 bit digital interface, plus 4 control linesUses digital pins 5-13 and analog 0-3. That means you can use digital pins 2, 3 and analog 4 and 5. Pin 12 is available if using the microSDWorks with any "328 or Mega (Leonardo supported yet)5V compatible! Use with 3.3V or 5V logicOnboard 3.3V 300mA LDO regulator4 white LED backlight. On by default but you can connect the transistor to a digital pin for backlight control4-wire resistive Press screenPackage Contents:1* 2.4 inch TFT LCD screen1* Pen

NMLCD-24240320-CLBis a colour active matrix LCD module incorporating amorphous silicon TFT (Thin Film Transistor). It is composed of a colour TFT-LCD panel, driver IC, FPC and a back light unit and without a Touch Panel (TP), with a Cover Lens Bezel (CLB). The module display area contains 240 x 320 pixels. This product accords with RoHS environmental criterion.
Shenzhen SLS Industrial Co.,ltd established in 2003, is a professional LCD module manufacturer and solution provider. We have 1 full-auto COG assembly line, 2 semi-auto assembly line, backlight assembly line, no dust TP bonding line and manufacturing tech support, we can provide unique, innovative and cost effective LCD module development and manufacturing. Our product range includes: middle-small size TFT LCD, industrial capacitive touch panel... Our LCD products have been widely used in communications, GPS, Equipment, electronic audio-visual, instrumentation, household appliances, PDA and other industries.

// For better pressure precision, we need to know the resistance // between X+ and X- Use any multimeter to read it // For the one we"re using, its 300 ohms across the X plate TouchScreen ts = TouchScreen(XP, YP, XM, YM, 300);
tft.fillRect(0, 0, BOXSIZE, BOXSIZE, RED); tft.fillRect(BOXSIZE, 0, BOXSIZE, BOXSIZE, YELLOW); tft.fillRect(BOXSIZE*2, 0, BOXSIZE, BOXSIZE, GREEN); tft.fillRect(BOXSIZE*3, 0, BOXSIZE, BOXSIZE, CYAN); tft.fillRect(BOXSIZE*4, 0, BOXSIZE, BOXSIZE, BLUE); tft.fillRect(BOXSIZE*5, 0, BOXSIZE, BOXSIZE, MAGENTA); // tft.fillRect(BOXSIZE*6, 0, BOXSIZE, BOXSIZE, WHITE); tft.drawRect(0, 0, BOXSIZE, BOXSIZE, WHITE); currentcolor = RED; pinMode(13, OUTPUT); }
void loop() { digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // Recently Point was renamed TSPoint in the TouchScreen library // If you are using an older version of the library, use the // commented definition instead. Point p = ts.getPoint(); // TSPoint p = ts.getPoint(); digitalWrite(13, LOW);
// if sharing pins, you"ll need to fix the directions of the touchscreen pins //pinMode(XP, OUTPUT); pinMode(XM, OUTPUT); pinMode(YP, OUTPUT); //pinMode(YM, OUTPUT);
if (p.z > MINPRESSURE && p.z < MAXPRESSURE) { /* Serial.print("X = "); Serial.print(p.x); Serial.print("\tY = "); Serial.print(p.y); Serial.print("\tPressure = "); Serial.println(p.z); */ if (p.y < (TS_MINY-5)) { Serial.println("erase"); // press the bottom of the screen to erase tft.fillRect(0, BOXSIZE, tft.width(), tft.height()-BOXSIZE, BLACK); } // scale from 0->1023 to tft.width p.x = tft.width()-(map(p.x, TS_MINX, TS_MAXX, tft.width(), 0)); p.y = tft.height()-(map(p.y, TS_MINY, TS_MAXY, tft.height(), 0)); /* Serial.print("("); Serial.print(p.x); Serial.print(", "); Serial.print(p.y); Serial.println(")"); */ if (p.y < BOXSIZE) { oldcolor = currentcolor;
if (p.x < BOXSIZE) { currentcolor = RED; tft.drawRect(0, 0, BOXSIZE, BOXSIZE, WHITE); } else if (p.x < BOXSIZE*2) { currentcolor = YELLOW; tft.drawRect(BOXSIZE, 0, BOXSIZE, BOXSIZE, WHITE); } else if (p.x < BOXSIZE*3) { currentcolor = GREEN; tft.drawRect(BOXSIZE*2, 0, BOXSIZE, BOXSIZE, WHITE); } else if (p.x < BOXSIZE*4) { currentcolor = CYAN; tft.drawRect(BOXSIZE*3, 0, BOXSIZE, BOXSIZE, WHITE); } else if (p.x < BOXSIZE*5) { currentcolor = BLUE; tft.drawRect(BOXSIZE*4, 0, BOXSIZE, BOXSIZE, WHITE); } else if (p.x < BOXSIZE*6) { currentcolor = MAGENTA; tft.drawRect(BOXSIZE*5, 0, BOXSIZE, BOXSIZE, WHITE); }
if (oldcolor != currentcolor) { if (oldcolor == RED) tft.fillRect(0, 0, BOXSIZE, BOXSIZE, RED); if (oldcolor == YELLOW) tft.fillRect(BOXSIZE, 0, BOXSIZE, BOXSIZE, YELLOW); if (oldcolor == GREEN) tft.fillRect(BOXSIZE*2, 0, BOXSIZE, BOXSIZE, GREEN); if (oldcolor == CYAN) tft.fillRect(BOXSIZE*3, 0, BOXSIZE, BOXSIZE, CYAN); if (oldcolor == BLUE) tft.fillRect(BOXSIZE*4, 0, BOXSIZE, BOXSIZE, BLUE); if (oldcolor == MAGENTA) tft.fillRect(BOXSIZE*5, 0, BOXSIZE, BOXSIZE, MAGENTA); } } if (((p.y-PENRADIUS) > BOXSIZE) && ((p.y+PENRADIUS) < tft.height())) { tft.fillCircle(p.x, p.y, PENRADIUS, currentcolor); } } }




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey