clear lcd screen arduino manufacturer
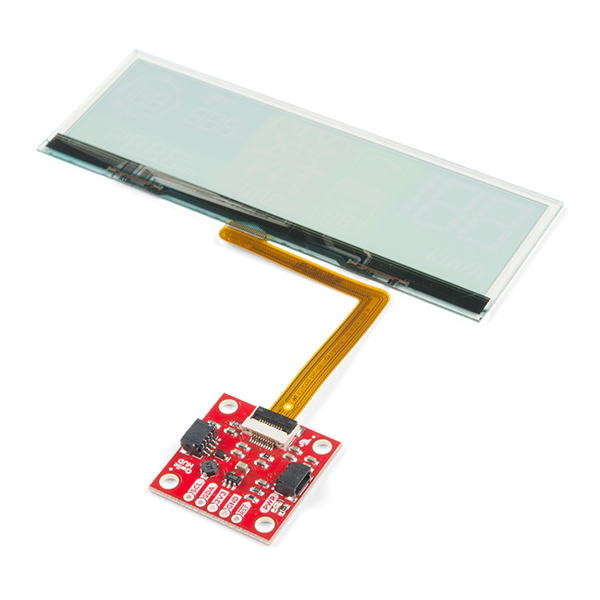

One of the most widely used information display elements in the Arduino world is the 16×2 LCD (Liquid Crystal Display). When manufacturing an electronic system, it can be interesting to have it give us some information about its status without having to connect it to a computer or to another system such as a smartphone. The 16×02 LCD screen is supplied with a large number of Arduino kits and is very sufficient for a large number of applications.
The 16×2 LCD screen can be found mounted on a shield with the bonus of a few buttons to create simple programmable interfaces to display values and control your Arduino project. All this while making the installation much easier.

I"m using serial communication to display the the data to my 4x20 lcd display. When I filled up all the lines of course I need to clear it. I"ve search over the net and found something like:
But it doesn"t work. I also found a solution like Serial.println(); but that solution (cheat as they called it) will only work on a serial monitor. So is there any possible solution to clear the display or delete a single character from the LCD?

This stems from the fact that the LCD controller itself does not inherently support the function and in fact treats the ASCII codes for and as displayable characters instead of control codes.
The fact that the LiquidCrystal library inherits from Print class and thus permits the use of println() essentially makes things worse. Instead of barfing and spitting out an error message it just happily displays two unrelated characters on the screen and the uninitiated have no idea of the cause.
In my opinion the basic LiquidCrystal library should concentrate on implementing all of the capabilities of the LCD controller and no more. If people want a library that more closely emulates a CRT (or LCD) terminal that is fine, but I think it should be done in a different library.

I put it to clear a certain part of the lcd where the millisecond counter is. It never cleared. When i replaced the lcd.print(""); with lcd.print("."); it displayed an period where I wanted the nothing.

Liquid Crystal displays or LCDs have been used in electronics equipment since the late 1970s. LCD displays have the advantage of consuming very little current And they are ideal for your Arduino projects.
In this article and in the accompanying video I’ll show you how easy it is to add an LCD display to your next Arduino design. I’ll also show you a very popular Arduino Shield that has a keypad which you can use in your projects as well.
Today LCD displays are used in a variety of items from test equipment to televisions. They’re inexpensive and versatile, this makes them ideal for all sorts of designs.
LCD displays do not emit light. Instead they block the passage of light, like little windows which open and shut the let light through. The liquid crystals used inside LCD displays are sandwiched between two layers of polarized material. By changing the orientation of the liquid crystals they allow light to pass or they block the light entirely.
Because transmissive LCD displays (the type we will be using) work by blocking light they require a backlight. Several methods have been used to create back lights including electroluminescent panels and fluorescent tubes. these days the most common form of backlight is an LED, in fact so-called LED televisions are usually just LCD screens with an LED backlight system.
Another type of LCD display, the passive-matrix display, does not require a backlight, it works using reflected light. This type of display is often found in digital watches.
The principles of liquid crystals were discovered in the late 1880s but work on Modern LCD displays did not begin until the mid-1960s. a number of patents were filed in the early 1970s and in 1973 the Sharp Corporation introduced LCD displays for calculators.
The first color LCD displays were developed in the early 1980s but production units were not commonly available until the mid-1990s. By the late 1990s LCD displays were quite common.
A number of LCD displays are available for experimenters. These low-cost monochrome displays are ideal for use with microcontrollers like the Arduino and micro computers like the Raspberry Pi.
The LCD1602 display module is a very popular and inexpensive LCD display. It is available in a number of different colors such as blue yellow and green and can easily be connected to an Arduino or Raspberry Pi.
Because the LCD module uses a parallel data input it requires 8 connections to the host microcontroller for the data alone. Add that to the other control pins and it consumes a lot of connections. On an Arduino Uno half of the I/O pins would be taken up by the display, which can be problematic if you want to use the I/O pins for other input or output devices.
We will begin our experiments by hooking up the LCD1602 to an Arduino Uno and running a few of the example sketches included with the Arduino IDE. This will allow you to get familiar with the display without needing to write any code.
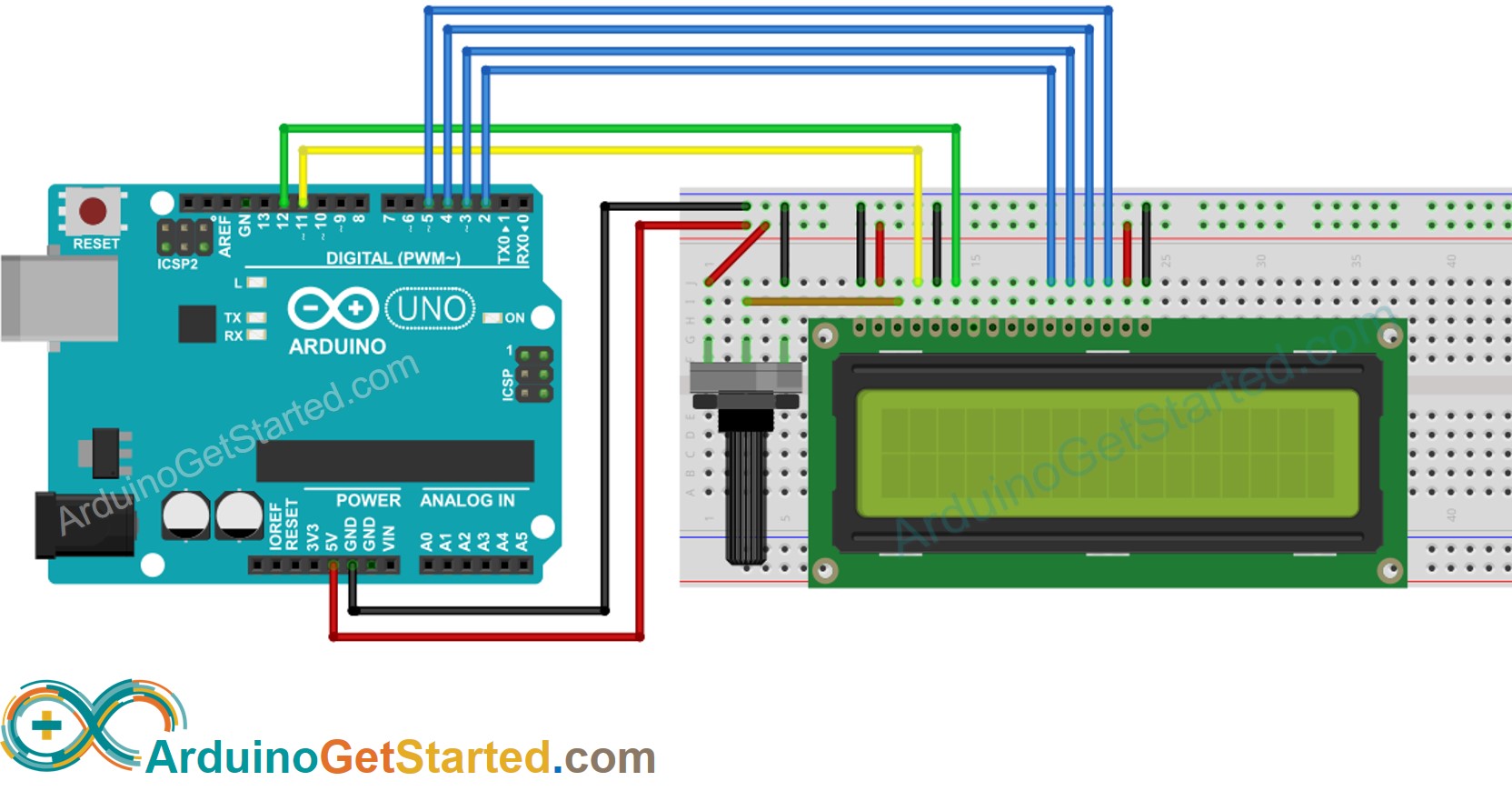
We need to hookup our LCD display to our Arduino. The display can use any of the Arduino digital I/O pins as it has no special requirements, but if you hook it up as I’ve illustrated here you can run the example sketches without needing to make any modifications.
In addition to the LCD1602 display ands the Arduino Uno you will need a 10K trimpot ot potentiometer, this is used a s a brightness control for the display. You’ll also need a 220 ohm resistor to drop the voltage for the displays LED backlight.
The Arduino IDE includestheLiquidCrystallibraryand this library has a number of example sketches. I’ll go over three of them here but you can also try the other ones.
The sketch starts with a number of credits and a description of the required hardware hookup. You’ll note that this is the same hookup you just performed on your Arduino and LCD module.
We then initialize an object that we call “lcd” using the pinouts of the LCD display. If you decide to hook up your display to different pins then you’ll need to modify this section.
That ends the loop, so we start back at the top of the loop and repeat. The result will be a counter on the second line that counts seconds from the htime the Arduino was last reset.
Load the sketch up to your Arduino and observe your display. If you don’t see anything try adjusting the brightness control that you wired to the display.
The second example we will try isthe Scroll sketch. Scrolling is a useful technique when you can’t get your text to fit on one line of the LCD display.
The Custom Character demonstration requires one additional component to be wired to the Arduino, a potentiometer (10K or greater) wired up to deliver a variable voltage to analog input pin A0.
As with the previous sketches we examined this one starts by loading theLiquidCrystallibrary and defining an object calledlcdwith the connection information for the display. It then moves on to define the custom characters.
Finally the setup routine ends by printing a line to the first row of the LCD display. The line makes use of two of the custom characters, the “heart” and the “smiley”.
We begin by reading the value of the voltage on pin A0 using the ArduinoanalogReadfunction. As the Arduino has a 10-bit analog to digital converter this will result in a reading ranging from 0 to 1023.
We then use an Arduinomapfunction to convert this reading into a range from 200 to 1000. This value is then assigned to an integer calleddelayTime, which as its name implies represents a time delay period.
One thing you may have noticed about using the LCD display module with the Arduino is that it consumes a lot of connections. Even in 4-wire mode there are still a total of seven connections made to the Arduino digital I/O pins. As an Arduino Uno has only 14 digital I/O pins that’s half of them used up for the display.
In other cases you would need to resort to using some of the analog pins as digital pins or even moving up to an Arduino Mega which has many more I/O pins.
But there is another solution. Use the I2C bus adapter for the LCD display and connect using I2C. This only consumes two I/O pins and they aren’t even part of the set of digital I/O pins.
The bus has evolved to be used as an ideal method of communicating between microcontrollers, integrated circuits, sensors and micro computers. You can use it to allow multiple Arduinos to talk to each other, to interface numerous sensors and output devices or to facilitate communications between a Raspberry Pi and one or more Arduinos.
In I2C communications there is the concept of Master and Slave devices. There can be multiples of each but there can only be one Master at any given moment. In most Arduino applications one Arduino is designated Master permanently while the other Arduinos and peripherals are the Slaves.
The I2C Adapter for the LCD display is a tiny circuit board with 16 male header pins soldered to it. These pins are meant to be connected directly to the 16-pin connection on the LCD1602 display (or onto other displays that use the same connection scheme).
The device also has a 4-pin connector for connection to the I2C bus. In addition there is a small trimpot on the board, this is the LCD display brightness control.
Most Arduino Unos also have some dedicated pins for I2C, these are internally connected to A4 and A5 and are usually located above the 14 digital I/O pins. Some models of the Uno have additional I2C connectors as well.
Note how much easier it is to use the I2C connection, which does not consume any of the Arduino Unos 14 digital I/O pins. Since A4 and A5 are being used for the I2C bus they can’t be used as analog inputs in this configuration.
Load this sketch into your Arduino then open your serial monitor. You’ll see the I2C address of your I2C LCD display adapter. You can then make note of this address and use it in the sketches we’ll be looking at now.
In order to run the subsequent sketches you’ll need to install another library. This is theNewLiquidCrystallibrarywhich, as its name implies, is an improved version of the LiquidCrystal library packaged with your Arduino IDE.
The sketch starts by loading the ArduinoWirelibrary. This is the Arduino library that facilitates communications over I2C and it’s part of your Arduino IDE installation.
On the next line we define the connections to the LCD display module from the I2C Adapter,. Note that these are NOT the connections from the Arduino, they are the connections used by the chip on the adapter itself.
Load the sketch and run it on your Arduino. If you can’t get it to work check out the address and connection information to be sure you have it right.
As you can see the DHT22 is connected with its output tied to pin 7 of the Arduino. The other two connections are 5 volts and ground. Note that pin 3 of the DHT22 is not used.
This sketch also makes use of theDHTlibrary from Adafruit. We used this library in a previous article, “Using the HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Distance Sensor with Arduino” so you may want to take a look at that one in order to get it installed.
The key thing to note is that this library is dependant upon another Adafruit library, theirUnified Sensorlibrary. Both can be installed using the Library Manager in your Arduino IDE.
The sketch is similar to our demo sketch in that it creates an “lcd” object with the I2C and display connection information. It also defines a couple of parameters for the DHT22 sensor, as well as some floating variables to hold the temperature and humidity values.
So far we have used the LCD1602 display module for all of our experiments. For our final demonstration we’ll switch to a popular Arduino shield that contains a LCD1602 along with some push buttons.
The LCD Keypad Shield is available from several different manufacturers. The device fits onto an Arduino Uno or an Arduino Mega and simplifies adding an LCD display to your project.
The Reset button is simply connected to the Arduino Reset pin and works just like the Reset button on the Arduino itself. This is common on many shields as the shields physically cover the Reset button.
Instead the buttons are connected to a resistor array that acts as a voltage divider. The entire array is connected to the Arduino’s analog A0 pin. One pin for five push buttons.
Note that the LCD is being used in 4-wire mode. The LCD itself is the same one used on the LCD1602 module, so all of the code for that module will work with the LCD Keypad Shield as well.
Now that you know how the LCD Keypad module works and which Arduino pins it uses all that remains is to install it onto your Arduino and load the demo sketch.
One thing – once the shield is installed on the Arduino you won’t have easy access to the unused I/O pins to connect any sensors or output devices you may want to use (although the demo sketch doesn’t need anything else connected). There are a couple of ways to get around this:
Use a shield that exposes the pins for prototyping before you install the LCD Keypad shield. In the video associated with this article I use a “Screw Shield” that brings all of the Arduino I/O pins out to a series of screw connectors. There are other similar shields. Using one of these shields is the easiest way to work with the LCD Keypad shield, as well as other Arduino shields.
The sketch begins by including theLiquidCrystallibrary. You can use the original one or the one includes with theNewLiquidCrystallibrary. We then set up an object with the LCD connections, note that these are just hard-coded as they won’t change.
Next we define a number of constants, one for each of the push buttons. Note that nothing is defined for the Reset button as it simply mimics the Arduino Reset button, however a constant is defined for the “none” condition.
After that we define a function calledread_LCD_buttons(). This function reads the value on analog port A0 and returns an integer corresponding to the button integers we defined earlier. Note that the function adds approximately 50 to each of the manufacturers specified values to account for intolerances in the resistors in the voltage divider.
We start the loop by placing the cursor 9 spaces over on the second line. We then use themillisfunction to display a counter that counts the time since the Arduino was reset. This is to test the Reset button.
We then call ourread_LCD_buttons()function and use it to display the value of the push button, right before the counter. Then we end the loop and do it again.
Load the code onto the Arduino and run it. You should see the value of each button as you press it, along with a counter that increments each second. If you press Reset the counter should reset itself back to zero.
As you can see LCD displays are pretty simple to use thanks to the availability of some excellent libraries for the Arduino. As these displays are also very inexpensive they will make an ideal addition to many of your Arduino projects.
And finally the LCD Keypad Shield is a convenient method of adding both a display and a simple keypad to your project, no wiring or soldering required.

i want to preserve video information for long time without communicating with arduino on lcd 1602, i"m tryng to use the command of liquidCrystal library noDisplay() but when i use it,this clear all display. On arduino website here is the description of this command "Turns off the LCD display, without losing the text currently shown on it." but i lose all on screen. Thanks for reply

Hi. I’m trying to find an optically clear (non-diffusing) display with which I can darken individual pixels – basically, a pixel-addressable Liquid Crystal Light Valve (LCLV) or an LCD that doesn’t have a backing. This would be used for modulating brightness of an image projected through the display, which is why it is important that the material not act as a diffuser. I want something under $100 that is easily interfaced to an Arduino (actually, probably an ESP32) and is roughly square, with a display area of at least about 25x25mm, and no more than about 100x100mm. Pixel resolution isn’t critical, but on the order of 128x128 would be nice. Pixels don’t need lots of tonal control; in fact, monochrome clear/black would suffice, although color would be ok too.
I had tried to separate a backlight from a TFT LCD, but that didn’t go well. Perhaps taking the shiny backing off a transflective LCD would be better? I’d really prefer not to have to do surgery on the display. Any suggestions?
PS: In case you’re wondering, I’m an ECE professor at the University of Kentucky and this is for a little side project involving computational photography research. There is a chance that in addition to open source release of the design, this might lead to a product… which is why peeling backings off LCDs doesn’t seem like a great solution.

The platforms mentioned above as supported is/are an indication of the module"s software or theoritical compatibility. We only provide software library or code examples for Arduino platform in most cases. It is not possible to provide software library / demo code for all possible MCU platforms. Hence, users have to write their own software library.
Step 4. Please follow below picture to select example HelloWorld and upload the arduino. If you do not know how to upload the code, please check how to upload code.
Step 1. Using a Grove cable connect Grove - LCD RGB Backlight to Seeeduino"s I2C port. If you are using Arduino, please take advantage of a Base Shield.
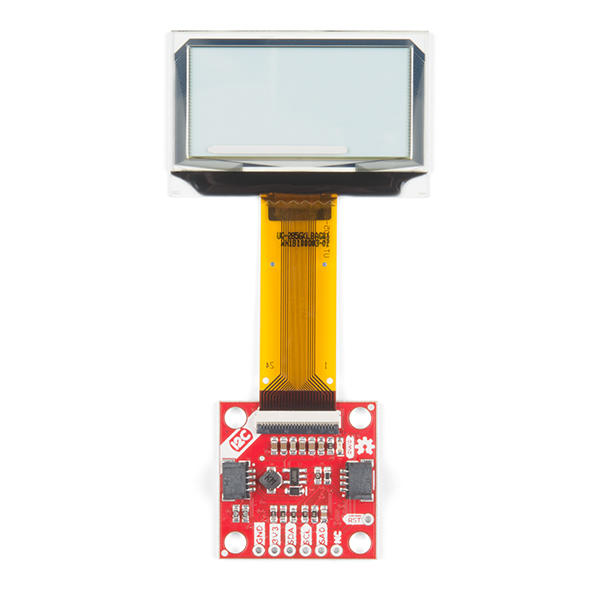
One of the most widely used information display elements in the Arduino world is the 16×2 LCD (Liquid Crystal Display). When manufacturing an electronic system, it can be interesting to have it give us some information about its status without having to connect it to a computer or to another system such as a smartphone. The 16×02 LCD screen is supplied with a large number of Arduino kits and is very sufficient for a large number of applications.
The 16×2 LCD screen can be found mounted on a shield with the bonus of a few buttons to create simple programmable interfaces to display values and control your Arduino project. All this while making the installation much easier.

Glass substrate with ITO electrodes. The shapes of these electrodes will determine the shapes that will appear when the LCD is switched ON. Vertical ridges etched on the surface are smooth.
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals combined with polarizers. Liquid crystals do not emit light directlybacklight or reflector to produce images in color or monochrome.seven-segment displays, as in a digital clock, are all good examples of devices with these displays. They use the same basic technology, except that arbitrary images are made from a matrix of small pixels, while other displays have larger elements. LCDs can either be normally on (positive) or off (negative), depending on the polarizer arrangement. For example, a character positive LCD with a backlight will have black lettering on a background that is the color of the backlight, and a character negative LCD will have a black background with the letters being of the same color as the backlight. Optical filters are added to white on blue LCDs to give them their characteristic appearance.
LCDs are used in a wide range of applications, including LCD televisions, computer monitors, instrument panels, aircraft cockpit displays, and indoor and outdoor signage. Small LCD screens are common in LCD projectors and portable consumer devices such as digital cameras, watches, digital clocks, calculators, and mobile telephones, including smartphones. LCD screens are also used on consumer electronics products such as DVD players, video game devices and clocks. LCD screens have replaced heavy, bulky cathode-ray tube (CRT) displays in nearly all applications. LCD screens are available in a wider range of screen sizes than CRT and plasma displays, with LCD screens available in sizes ranging from tiny digital watches to very large television receivers. LCDs are slowly being replaced by OLEDs, which can be easily made into different shapes, and have a lower response time, wider color gamut, virtually infinite color contrast and viewing angles, lower weight for a given display size and a slimmer profile (because OLEDs use a single glass or plastic panel whereas LCDs use two glass panels; the thickness of the panels increases with size but the increase is more noticeable on LCDs) and potentially lower power consumption (as the display is only "on" where needed and there is no backlight). OLEDs, however, are more expensive for a given display size due to the very expensive electroluminescent materials or phosphors that they use. Also due to the use of phosphors, OLEDs suffer from screen burn-in and there is currently no way to recycle OLED displays, whereas LCD panels can be recycled, although the technology required to recycle LCDs is not yet widespread. Attempts to maintain the competitiveness of LCDs are quantum dot displays, marketed as SUHD, QLED or Triluminos, which are displays with blue LED backlighting and a Quantum-dot enhancement film (QDEF) that converts part of the blue light into red and green, offering similar performance to an OLED display at a lower price, but the quantum dot layer that gives these displays their characteristics can not yet be recycled.
Since LCD screens do not use phosphors, they rarely suffer image burn-in when a static image is displayed on a screen for a long time, e.g., the table frame for an airline flight schedule on an indoor sign. LCDs are, however, susceptible to image persistence.battery-powered electronic equipment more efficiently than a CRT can be. By 2008, annual sales of televisions with LCD screens exceeded sales of CRT units worldwide, and the CRT became obsolete for most purposes.
Each pixel of an LCD typically consists of a layer of molecules aligned between two transparent electrodes, often made of Indium-Tin oxide (ITO) and two polarizing filters (parallel and perpendicular polarizers), the axes of transmission of which are (in most of the cases) perpendicular to each other. Without the liquid crystal between the polarizing filters, light passing through the first filter would be blocked by the second (crossed) polarizer. Before an electric field is applied, the orientation of the liquid-crystal molecules is determined by the alignment at the surfaces of electrodes. In a twisted nematic (TN) device, the surface alignment directions at the two electrodes are perpendicular to each other, and so the molecules arrange themselves in a helical structure, or twist. This induces the rotation of the polarization of the incident light, and the device appears gray. If the applied voltage is large enough, the liquid crystal molecules in the center of the layer are almost completely untwisted and the polarization of the incident light is not rotated as it passes through the liquid crystal layer. This light will then be mainly polarized perpendicular to the second filter, and thus be blocked and the pixel will appear black. By controlling the voltage applied across the liquid crystal layer in each pixel, light can be allowed to pass through in varying amounts thus constituting different levels of gray.
The chemical formula of the liquid crystals used in LCDs may vary. Formulas may be patented.Sharp Corporation. The patent that covered that specific mixture expired.
Most color LCD systems use the same technique, with color filters used to generate red, green, and blue subpixels. The LCD color filters are made with a photolithography process on large glass sheets that are later glued with other glass sheets containing a TFT array, spacers and liquid crystal, creating several color LCDs that are then cut from one another and laminated with polarizer sheets. Red, green, blue and black photoresists (resists) are used. All resists contain a finely ground powdered pigment, with particles being just 40 nanometers across. The black resist is the first to be applied; this will create a black grid (known in the industry as a black matrix) that will separate red, green and blue subpixels from one another, increasing contrast ratios and preventing light from leaking from one subpixel onto other surrounding subpixels.Super-twisted nematic LCD, where the variable twist between tighter-spaced plates causes a varying double refraction birefringence, thus changing the hue.
LCD in a Texas Instruments calculator with top polarizer removed from device and placed on top, such that the top and bottom polarizers are perpendicular. As a result, the colors are inverted.
The optical effect of a TN device in the voltage-on state is far less dependent on variations in the device thickness than that in the voltage-off state. Because of this, TN displays with low information content and no backlighting are usually operated between crossed polarizers such that they appear bright with no voltage (the eye is much more sensitive to variations in the dark state than the bright state). As most of 2010-era LCDs are used in television sets, monitors and smartphones, they have high-resolution matrix arrays of pixels to display arbitrary images using backlighting with a dark background. When no image is displayed, different arrangements are used. For this purpose, TN LCDs are operated between parallel polarizers, whereas IPS LCDs feature crossed polarizers. In many applications IPS LCDs have replaced TN LCDs, particularly in smartphones. Both the liquid crystal material and the alignment layer material contain ionic compounds. If an electric field of one particular polarity is applied for a long period of time, this ionic material is attracted to the surfaces and degrades the device performance. This is avoided either by applying an alternating current or by reversing the polarity of the electric field as the device is addressed (the response of the liquid crystal layer is identical, regardless of the polarity of the applied field).
Displays for a small number of individual digits or fixed symbols (as in digital watches and pocket calculators) can be implemented with independent electrodes for each segment.alphanumeric or variable graphics displays are usually implemented with pixels arranged as a matrix consisting of electrically connected rows on one side of the LC layer and columns on the other side, which makes it possible to address each pixel at the intersections. The general method of matrix addressing consists of sequentially addressing one side of the matrix, for example by selecting the rows one-by-one and applying the picture information on the other side at the columns row-by-row. For details on the various matrix addressing schemes see passive-matrix and active-matrix addressed LCDs.
LCDs, along with OLED displays, are manufactured in cleanrooms borrowing techniques from semiconductor manufacturing and using large sheets of glass whose size has increased over time. Several displays are manufactured at the same time, and then cut from the sheet of glass, also known as the mother glass or LCD glass substrate. The increase in size allows more displays or larger displays to be made, just like with increasing wafer sizes in semiconductor manufacturing. The glass sizes are as follows:
Until Gen 8, manufacturers would not agree on a single mother glass size and as a result, different manufacturers would use slightly different glass sizes for the same generation. Some manufacturers have adopted Gen 8.6 mother glass sheets which are only slightly larger than Gen 8.5, allowing for more 50 and 58 inch LCDs to be made per mother glass, specially 58 inch LCDs, in which case 6 can be produced on a Gen 8.6 mother glass vs only 3 on a Gen 8.5 mother glass, significantly reducing waste.AGC Inc., Corning Inc., and Nippon Electric Glass.
In 1922, Georges Friedel described the structure and properties of liquid crystals and classified them in three types (nematics, smectics and cholesterics). In 1927, Vsevolod Frederiks devised the electrically switched light valve, called the Fréedericksz transition, the essential effect of all LCD technology. In 1936, the Marconi Wireless Telegraph company patented the first practical application of the technology, "The Liquid Crystal Light Valve". In 1962, the first major English language publication Molecular Structure and Properties of Liquid Crystals was published by Dr. George W. Gray.RCA found that liquid crystals had some interesting electro-optic characteristics and he realized an electro-optical effect by generating stripe-patterns in a thin layer of liquid crystal material by the application of a voltage. This effect is based on an electro-hydrodynamic instability forming what are now called "Williams domains" inside the liquid crystal.
In the late 1960s, pioneering work on liquid crystals was undertaken by the UK"s Royal Radar Establishment at Malvern, England. The team at RRE supported ongoing work by George William Gray and his team at the University of Hull who ultimately discovered the cyanobiphenyl liquid crystals, which had correct stability and temperature properties for application in LCDs.
The idea of a TFT-based liquid-crystal display (LCD) was conceived by Bernard Lechner of RCA Laboratories in 1968.dynamic scattering mode (DSM) LCD that used standard discrete MOSFETs.
On December 4, 1970, the twisted nematic field effect (TN) in liquid crystals was filed for patent by Hoffmann-LaRoche in Switzerland, (Swiss patent No. 532 261) with Wolfgang Helfrich and Martin Schadt (then working for the Central Research Laboratories) listed as inventors.Brown, Boveri & Cie, its joint venture partner at that time, which produced TN displays for wristwatches and other applications during the 1970s for the international markets including the Japanese electronics industry, which soon produced the first digital quartz wristwatches with TN-LCDs and numerous other products. James Fergason, while working with Sardari Arora and Alfred Saupe at Kent State University Liquid Crystal Institute, filed an identical patent in the United States on April 22, 1971.ILIXCO (now LXD Incorporated), produced LCDs based on the TN-effect, which soon superseded the poor-quality DSM types due to improvements of lower operating voltages and lower power consumption. Tetsuro Hama and Izuhiko Nishimura of Seiko received a US patent dated February 1971, for an electronic wristwatch incorporating a TN-LCD.
In 1972, the concept of the active-matrix thin-film transistor (TFT) liquid-crystal display panel was prototyped in the United States by T. Peter Brody"s team at Westinghouse, in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania.Westinghouse Research Laboratories demonstrated the first thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display (TFT LCD).high-resolution and high-quality electronic visual display devices use TFT-based active matrix displays.active-matrix liquid-crystal display (AM LCD) in 1974, and then Brody coined the term "active matrix" in 1975.
In 1972 North American Rockwell Microelectronics Corp introduced the use of DSM LCDs for calculators for marketing by Lloyds Electronics Inc, though these required an internal light source for illumination.Sharp Corporation followed with DSM LCDs for pocket-sized calculators in 1973Seiko and its first 6-digit TN-LCD quartz wristwatch, and Casio"s "Casiotron". Color LCDs based on Guest-Host interaction were invented by a team at RCA in 1968.TFT LCDs similar to the prototypes developed by a Westinghouse team in 1972 were patented in 1976 by a team at Sharp consisting of Fumiaki Funada, Masataka Matsuura, and Tomio Wada,
In 1983, researchers at Brown, Boveri & Cie (BBC) Research Center, Switzerland, invented the passive matrix-addressed LCDs. H. Amstutz et al. were listed as inventors in the corresponding patent applications filed in Switzerland on July 7, 1983, and October 28, 1983. Patents were granted in Switzerland CH 665491, Europe EP 0131216,
The first color LCD televisions were developed as handheld televisions in Japan. In 1980, Hattori Seiko"s R&D group began development on color LCD pocket televisions.Seiko Epson released the first LCD television, the Epson TV Watch, a wristwatch equipped with a small active-matrix LCD television.dot matrix TN-LCD in 1983.Citizen Watch,TFT LCD.computer monitors and LCD televisions.3LCD projection technology in the 1980s, and licensed it for use in projectors in 1988.compact, full-color LCD projector.
In 1990, under different titles, inventors conceived electro optical effects as alternatives to twisted nematic field effect LCDs (TN- and STN- LCDs). One approach was to use interdigital electrodes on one glass substrate only to produce an electric field essentially parallel to the glass substrates.Germany by Guenter Baur et al. and patented in various countries.Hitachi work out various practical details of the IPS technology to interconnect the thin-film transistor array as a matrix and to avoid undesirable stray fields in between pixels.
Hitachi also improved the viewing angle dependence further by optimizing the shape of the electrodes (Super IPS). NEC and Hitachi become early manufacturers of active-matrix addressed LCDs based on the IPS technology. This is a milestone for implementing large-screen LCDs having acceptable visual performance for flat-panel computer monitors and television screens. In 1996, Samsung developed the optical patterning technique that enables multi-domain LCD. Multi-domain and In Plane Switching subsequently remain the dominant LCD designs through 2006.South Korea and Taiwan,
In 2007 the image quality of LCD televisions surpassed the image quality of cathode-ray-tube-based (CRT) TVs.LCD TVs were projected to account 50% of the 200 million TVs to be shipped globally in 2006, according to Displaybank.Toshiba announced 2560 × 1600 pixels on a 6.1-inch (155 mm) LCD panel, suitable for use in a tablet computer,transparent and flexible, but they cannot emit light without a backlight like OLED and microLED, which are other technologies that can also be made flexible and transparent.
In 2016, Panasonic developed IPS LCDs with a contrast ratio of 1,000,000:1, rivaling OLEDs. This technology was later put into mass production as dual layer, dual panel or LMCL (Light Modulating Cell Layer) LCDs. The technology uses 2 liquid crystal layers instead of one, and may be used along with a mini-LED backlight and quantum dot sheets.
Since LCDs produce no light of their own, they require external light to produce a visible image.backlight. Active-matrix LCDs are almost always backlit.Transflective LCDs combine the features of a backlit transmissive display and a reflective display.
CCFL: The LCD panel is lit either by two cold cathode fluorescent lamps placed at opposite edges of the display or an array of parallel CCFLs behind larger displays. A diffuser (made of PMMA acrylic plastic, also known as a wave or light guide/guiding plateinverter to convert whatever DC voltage the device uses (usually 5 or 12 V) to ≈1000 V needed to light a CCFL.
EL-WLED: The LCD panel is lit by a row of white LEDs placed at one or more edges of the screen. A light diffuser (light guide plate, LGP) is then used to spread the light evenly across the whole display, similarly to edge-lit CCFL LCD backlights. The diffuser is made out of either PMMA plastic or special glass, PMMA is used in most cases because it is rugged, while special glass is used when the thickness of the LCD is of primary concern, because it doesn"t expand as much when heated or exposed to moisture, which allows LCDs to be just 5mm thick. Quantum dots may be placed on top of the diffuser as a quantum dot enhancement film (QDEF, in which case they need a layer to be protected from heat and humidity) or on the color filter of the LCD, replacing the resists that are normally used.
WLED array: The LCD panel is lit by a full array of white LEDs placed behind a diffuser behind the panel. LCDs that use this implementation will usually have the ability to dim or completely turn off the LEDs in the dark areas of the image being displayed, effectively increasing the contrast ratio of the display. The precision with which this can be done will depend on the number of dimming zones of the display. The more dimming zones, the more precise the dimming, with less obvious blooming artifacts which are visible as dark grey patches surrounded by the unlit areas of the LCD. As of 2012, this design gets most of its use from upscale, larger-screen LCD televisions.
RGB-LED array: Similar to the WLED array, except the panel is lit by a full array of RGB LEDs. While displays lit with white LEDs usually have a poorer color gamut than CCFL lit displays, panels lit with RGB LEDs have very wide color gamuts. This implementation is most popular on professional graphics editing LCDs. As of 2012, LCDs in this category usually cost more than $1000. As of 2016 the cost of this category has drastically reduced and such LCD televisions obtained same price levels as the former 28" (71 cm) CRT based categories.
Monochrome LEDs: such as red, green, yellow or blue LEDs are used in the small passive monochrome LCDs typically used in clocks, watches and small appliances.
Today, most LCD screens are being designed with an LED backlight instead of the traditional CCFL backlight, while that backlight is dynamically controlled with the video information (dynamic backlight control). The combination with the dynamic backlight control, invented by Philips researchers Douglas Stanton, Martinus Stroomer and Adrianus de Vaan, simultaneously increases the dynamic range of the display system (also marketed as HDR, high dynamic range television or FLAD, full-area local area dimming).
The LCD backlight systems are made highly efficient by applying optical films such as prismatic structure (prism sheet) to gain the light into the desired viewer directions and reflective polarizing films that recycle the polarized light that was formerly absorbed by the first polarizer of the LCD (invented by Philips researchers Adrianus de Vaan and Paulus Schaareman),
Due to the LCD layer that generates the desired high resolution images at flashing video speeds using very low power electronics in combination with LED based backlight technologies, LCD technology has become the dominant display technology for products such as televisions, desktop monitors, notebooks, tablets, smartphones and mobile phones. Although competing OLED technology is pushed to the market, such OLED displays do not feature the HDR capabilities like LCDs in combination with 2D LED backlight technologies have, reason why the annual market of such LCD-based products is still growing faster (in volume) than OLED-based products while the efficiency of LCDs (and products like portable computers, mobile phones and televisions) may even be further improved by preventing the light to be absorbed in the colour filters of the LCD.
A pink elastomeric connector mating an LCD panel to circuit board traces, shown next to a centimeter-scale ruler. The conductive and insulating layers in the black stripe are very small.
A standard television receiver screen, a modern LCD panel, has over six million pixels, and they are all individually powered by a wire network embedded in the screen. The fine wires, or pathways, form a grid with vertical wires across the whole screen on one side of the screen and horizontal wires across the whole screen on the other side of the screen. To this grid each pixel has a positive connection on one side and a negative connection on the other side. So the total amount of wires needed for a 1080p display is 3 x 1920 going vertically and 1080 going horizontally for a total of 6840 wires horizontally and vertically. That"s three for red, green and blue and 1920 columns of pixels for each color for a total of 5760 wires going vertically and 1080 rows of wires going horizontally. For a panel that is 28.8 inches (73 centimeters) wide, that means a wire density of 200 wires per inch along the horizontal edge.
The LCD panel is powered by LCD drivers that are carefully matched up with the edge of the LCD panel at the factory level. The drivers may be installed using several methods, the most common of which are COG (Chip-On-Glass) and TAB (Tape-automated bonding) These same principles apply also for smartphone screens that are much smaller than TV screens.anisotropic conductive film or, for lower densities, elastomeric connectors.
Monochrome and later color passive-matrix LCDs were standard in most early laptops (although a few used plasma displaysGame Boyactive-matrix became standard on all laptops. The commercially unsuccessful Macintosh Portable (released in 1989) was one of the first to use an active-matrix display (though still monochrome). Passive-matrix LCDs are still used in the 2010s for applications less demanding than laptop computers and TVs, such as inexpensive calculators. In particular, these are used on portable devices where less information content needs to be displayed, lowest power consumption (no backlight) and low cost are desired or readability in direct sunlight is needed.
A comparison between a blank passive-matrix display (top) and a blank active-matrix display (bottom). A passive-matrix display can be identified when the blank background is more grey in appearance than the crisper active-matrix display, fog appears on all edges of the screen, and while pictures appear to be fading on the screen.
STN LCDs have to be continuously refreshed by alternating pulsed voltages of one polarity during one frame and pulses of opposite polarity during the next frame. Individual pixels are addressed by the corresponding row and column circuits. This type of display is called response times and poor contrast are typical of passive-matrix addressed LCDs with too many pixels and driven according to the "Alt & Pleshko" drive scheme. Welzen and de Vaan also invented a non RMS drive scheme enabling to drive STN displays with video rates and enabling to show smooth moving video images on an STN display.
Bistable LCDs do not require continuous refreshing. Rewriting is only required for picture information changes. In 1984 HA van Sprang and AJSM de Vaan invented an STN type display that could be operated in a bistable mode, enabling extremely high resolution images up to 4000 lines or more using only low voltages.
High-resolution color displays, such as modern LCD computer monitors and televisions, use an active-matrix structure. A matrix of thin-film transistors (TFTs) is added to the electrodes in contact with the LC layer. Each pixel has its own dedicated transistor, allowing each column line to access one pixel. When a row line is selected, all of the column lines are connected to a row of pixels and voltages corresponding to the picture information are driven onto all of the column lines. The row line is then deactivated and the next row line is selected. All of the row lines are selected in sequence during a refresh operation. Active-matrix addressed displays look brighter and sharper than passive-matrix addressed displays of the same size, and generally have quicker response times, producing much better images. Sharp produces bistable reflective LCDs with a 1-bit SRAM cell per pixel that only requires small amounts of power to maintain an image.
Segment LCDs can also have color by using Field Sequential Color (FSC LCD). This kind of displays have a high speed passive segment LCD panel with an RGB backlight. The backlight quickly changes color, making it appear white to the naked eye. The LCD panel is synchronized with the backlight. For example, to make a segment appear red, the segment is only turned ON when the backlight is red, and to make a segment appear magenta, the segment is turned ON when the backlight is blue, and it continues to be ON while the backlight becomes red, and it turns OFF when the backlight becomes green. To make a segment appear black, the segment is always turned ON. An FSC LCD divides a color image into 3 images (one Red, one Green and one Blue) and it displays them in order. Due to persistence of vision, the 3 monochromatic images appear as one color image. An FSC LCD needs an LCD panel with a refresh rate of 180 Hz, and the response time is reduced to just 5 milliseconds when compared with normal STN LCD panels which have a response time of 16 milliseconds.
Samsung introduced UFB (Ultra Fine & Bright) displays back in 2002, utilized the super-birefringent effect. It has the luminance, color gamut, and most of the contrast of a TFT-LCD, but only consumes as much power as an STN display, according to Samsung. It was being used in a variety of Samsung cellular-telephone models produced until late 2006, when Samsung stopped producing UFB displays. UFB displays were also used in certain models of LG mobile phones.
In-plane switching is an LCD technology that aligns the liquid crystals in a plane parallel to the glass substrates. In this method, the electrical field is applied through opposite electrodes on the same glass substrate, so that the liquid crystals can be reoriented (switched) essentially in the same plane, although fringe fields inhibit a homogeneous reorientation. This requires two transistors for each pixel instead of the single transistor needed for a standard thin-film transistor (TFT) display. The IPS technology is used in everything from televisions, computer monitors, and even wearable devices, especially almost all LCD smartphone panels are IPS/FFS mode. IPS displays belong to the LCD panel family screen types. The other two types are VA and TN. Before LG Enhanced IPS was introduced in 2001 by Hitachi as 17" monitor in Market, the additional transistors resulted in blocking more transmission area, thus requiring a brighter backlight and consuming more power, making this type of display less desirable for notebook computers. Panasonic Himeji G8.5 was using an enhanced version of IPS, also LGD in Korea, then currently the world biggest LCD panel manufacture BOE in China is also IPS/FFS mode TV panel.
In 2011, LG claimed the smartphone LG Optimus Black (IPS LCD (LCD NOVA)) has the brightness up to 700 nits, while the competitor has only IPS LCD with 518 nits and double an active-matrix OLED (AMOLED) display with 305 nits. LG also claimed the NOVA display to be 50 percent more efficient than regular LCDs and to consume only 50 percent of the power of AMOLED displays when producing white on screen.
This pixel-layout is found in S-IPS LCDs. A chevron shape is used to widen the viewing cone (range of viewing directions with good contrast and low color shift).
Vertical-alignment displays are a form of LCDs in which the liquid crystals naturally align vertically to the glass substrates. When no voltage is applied, the liquid crystals remain perpendicular to the substrate, creating a black display between crossed polarizers. When voltage is applied, the liquid crystals shift to a tilted position, allowing light to pass through and create a gray-scale display depending on the amount of tilt generated by the electric field. It has a deeper-black background, a higher contrast ratio, a wider viewing angle, and better image quality at extreme temperatures than traditional twisted-nematic displays.
Blue phase mode LCDs have been shown as engineering samples early in 2008, but they are not in mass-production. The physics of blue phase mode LCDs suggest that very short switching times (≈1 ms) can be achieved, so time sequential color control can possibly be realized and expensive color filters would be obsolete.
Some LCD panels have defective transistors, causing permanently lit or unlit pixels which are commonly referred to as stuck pixels or dead pixels respectively. Unlike integrated circuits (ICs), LCD panels with a few defective transistors are usually still usable. Manufacturers" policies for the acceptable number of defective pixels vary greatly. At one point, Samsung held a zero-tolerance policy for LCD monitors sold in Korea.ISO 13406-2 standard.
Dead pixel policies are often hotly debated between manufacturers and customers. To regulate the acceptability of defects and to protect the end user, ISO released the ISO 13406-2 standard,ISO 9241, specifically ISO-9241-302, 303, 305, 307:2008 pixel defects. However, not every LCD manufacturer conforms to the ISO standard and the ISO standard is quite often interpreted in different ways. LCD panels are more likely to have defects than most ICs due to their larger size. For example, a 300 mm SVGA LCD has 8 defects and a 150 mm wafer has only 3 defects. However, 134 of the 137 dies on the wafer will be acceptable, whereas rejection of the whole LCD panel would be a 0% yield. In recent years, quality control has been improved. An SVGA LCD panel with 4 defective pixels is usually considered defective and customers can request an exchange for a new one.
Some manufacturers, notably in South Korea where some of the largest LCD panel manufacturers, such as LG, are located, now have a zero-defective-pixel guarantee, which is an extra screening process which can then determine "A"- and "B"-grade panels.clouding (or less commonly mura), which describes the uneven patches of changes in luminance. It is most visible in dark or black areas of displayed scenes.
The zenithal bistable device (ZBD), developed by Qinetiq (formerly DERA), can retain an image without power. The crystals may exist in one of two stable orientations ("black" and "white") and power is only required to change the image. ZBD Displays is a spin-off company from QinetiQ who manufactured both grayscale and color ZBD devices. Kent Displays has also developed a "no-power" display that uses polymer stabilized cholesteric liquid crystal (ChLCD). In 2009 Kent demonstrated the use of a ChLCD to cover the entire surface of a mobile phone, allowing it to change colors, and keep that color even when power is removed.
In 2004, researchers at the University of Oxford demonstrated two new types of zero-power bistable LCDs based on Zenithal bistable techniques.e.g., BiNem technology, are based mainly on the surface properties and need specific weak anchoring materials.
Resolution The resolution of an LCD is expressed by the number of columns and rows of pixels (e.g., 1024×768). Each pixel is usually composed 3 sub-pixels, a red, a green, and a blue one. This had been one of the few features of LCD performance that remained uniform among different designs. However, there are newer designs that share sub-pixels among pixels and add Quattron which attempt to efficiently increase the perceived resolution of a display without increasing the actual resolution, to mixed results.
Spatial performance: For a computer monitor or some other display that is being viewed from a very close distance, resolution is often expressed in terms of dot pitch or pixels per inch, which is consistent with the printing industry. Display density varies per application, with televisions generally having a low density for long-distance viewing and portable devices having a high density for close-range detail. The Viewing Angle of an LCD may be important depending on the display and its usage, the limitations of certain display technologies mean the display only displays accurately at certain angles.
Temporal performance: the temporal resolution of an LCD is how well it can display changing images, or the accuracy and the number of times per second the display draws the data it is being given. LCD pixels do not flash on/off between frames, so LCD monitors exhibit no refresh-induced flicker no matter how low the refresh rate.
Color performance: There are multiple terms to describe different aspects of color performance of a display. Color gamut is the range of colors that can be displayed, and color depth, which is the fineness with which the color range is divided. Color gamut is a relatively straight forward feature, but it is rarely discussed in marketing materials except at the professional level. Having a color range that exceeds the content being shown on the screen has no benefits, so displays are only made to perform within or below the range of a certain specification.white point and gamma correction, which describe what color white is and how the other colors are displayed relative to white.
Brightness and contrast ratio: Contrast ratio is the ratio of the brightness of a full-on pixel to a full-off pixel. The LCD itself is only a light valve and does not generate light; the light comes from a backlight that is either fluorescent or a set of LEDs. Brightness is usually stated as the maximum light output of the LCD, which can vary greatly based on the transparency of the LCD and the brightness of the backlight. Brighter backlight allows stronger contrast and higher dynamic range (HDR displays are graded in peak luminance), but there is always a trade-off between brightness and power consumption.
Usually no refresh-rate flicker, because the LCD pixels hold their state between refreshes (which are usually done at 200 Hz or faster, regardless of the input refresh rate).
No theoretical resolution limit. When multiple LCD panels are used together to create a single canvas, each additional panel increases the total resolution of the display, which is commonly called stacked resolution.
As an inherently digital device, the LCD can natively display digital data from a DVI or HDMI connection without requiring conversion to analog. Some LCD panels have native fiber optic inputs in addition to DVI and HDMI.
As of 2012, most implementations of LCD backlighting use pulse-width modulation (PWM) to dim the display,CRT monitor at 85 Hz refresh rate would (this is because the entire screen is strobing on and off rather than a CRT"s phosphor sustained dot which continually scans across the display, leaving some part of the display always lit), causing severe eye-strain for some people.LED-backlit monitors, because the LEDs switch on and off faster than a CCFL lamp.
Only one native resolution. Displaying any other resolution either requires a video scaler, causing blurriness and jagged edges, or running the display at native resolution using 1:1 pixel mapping, causing the image either not to fill the screen (letterboxed display), or to run off the lower or right edges of the screen.
Fixed bit depth (also called color depth). Many cheaper LCDs are only able to display 262144 (218) colors. 8-bit S-IPS panels can display 16 million (224) colors and have significantly better black level, but are expensive and have slower response time.
Input lag, because the LCD"s A/D converter waits for each frame to be completely been output before drawing it to the LCD panel. Many LCD monitors do post-processing before displaying the image in an attempt to compensate for poor color fidelity, which adds an additional lag. Further, a video scaler must be used when displaying non-native resolutions, which adds yet more time lag. Scaling and post processing are usually done in a single chip on modern monitors, but each function that chip performs adds some delay. Some displays have a video gaming mode which disables all or most processing to reduce perceivable input lag.
Dead or stuck pixels may occur during manufacturing or after a period of use. A stuck pixel will glow with color even on an all-black screen, while a dead one will always remain black.
In a constant-on situation, thermalization may occur in case of bad thermal management, in which part of the screen has overheated and looks discolored compared to the rest of the screen.
Loss of brightness and much slower response times in low temperature environments. In sub-zero environments, LCD screens may cease to function without the use of supplemental heating.
The production of LCD screens uses nitrogen trifluoride (NF3) as an etching fluid during the production of the thin-film components. NF3 is a potent greenhouse gas, and its relatively long half-life may make it a potentially harmful contributor to global warming. A report in Geophysical Research Letters suggested that its effects were theoretically much greater than better-known sources of greenhouse gasses like carbon dioxide. As NF3 was not in widespread use at the time, it was not made part of the Kyoto Protocols and has been deemed "the missing greenhouse gas".
Kawamoto, H. (2012). "The Inventors of TFT Active-Matrix LCD Receive the 2011 IEEE Nishizawa Medal". Journal of Display Technology. 8 (1): 3–4. Bibcode:2012JDisT...8....3K. doi:10.1109/JDT.2011.2177740. ISSN 1551-319X.
Explanation of CCFL backlighting details, "Design News — Features — How to Backlight an LCD" Archived January 2, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Randy Frank, Retrieved January 2013.
Energy Efficiency Success Story: TV Energy Consumption Shrinks as Screen Size and Performance Grow, Finds New CTA Study; Consumer Technology Association; press release 12 July 2017; https://cta.tech/News/Press-Releases/2017/July/Energy-Efficiency-Success-Story-TV-Energy-Consump.aspx Archived November 4, 2017, at the Wayback Machine
LCD Television Power Draw Trends from 2003 to 2015; B. Urban and K. Roth; Fraunhofer USA Center for Sustainable Energy Systems; Final Report to the Consumer Technology Association; May 2017; http://www.cta.tech/cta/media/policyImages/policyPDFs/Fraunhofer-LCD-TV-Power-Draw-Trends-FINAL.pdf Archived August 1, 2017, at the Wayback Machine
New Cholesteric Colour Filters for Reflective LCDs; C. Doornkamp; R. T. Wegh; J. Lub; SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers; Volume 32, Issue 1 June 2001; Pages 456–459; http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1889/1.1831895/full
K. H. Lee; H. Y. Kim; K. H. Park; S. J. Jang; I. C. Park & J. Y. Lee (June 2006). "A Novel Outdoor Readability of Portable TFT-LCD with AFFS Technology". SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers. 37 (1): 1079–1082. doi:10.1889/1.2433159. S2CID 129569963.
Jack H. Park (January 15, 2015). "Cut and Run: Taiwan-controlled LCD Panel Maker in Danger of Shutdown without Further Investment". www.businesskorea.co.kr. Archived from the original on May 12, 2015. Retrieved April 23, 2015.
NXP Semiconductors (October 21, 2011). "UM10764 Vertical Alignment (VA) displays and NXP LCD drivers" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on March 14, 2014. Retrieved September 4, 2014.
"Samsung to Offer "Zero-PIXEL-DEFECT" Warranty for LCD Monitors". Forbes. December 30, 2004. Archived from the original on August 20, 2007. Retrieved September 3, 2007.
"Display (LCD) replacement for defective pixels – ThinkPad". Lenovo. June 25, 2007. Archived from the original on December 31, 2006. Retrieved July 13, 2007.
Explanation of why pulse width modulated backlighting is used, and its side-effects, "Pulse Width Modulation on LCD monitors", TFT Central. Retrieved June 2012.
An enlightened user requests Dell to improve their LCD backlights, "Request to Dell for higher backlight PWM frequency" Archived December 13, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Dell Support Community. Retrieved June 2012.
Oleg Artamonov (January 23, 2007). "Contemporary LCD Monitor Parameters: Objective and Subjective Analysis". X-bit labs. Archived from the original on May 16, 2008. Retrieved May 17, 2008.

– Arduino is an open-source platform used for building electronics projects. Arduino consists of both a physical programmable microcontroller and a piece of software, or IDE (Integrated Development Environment) that runs on your computer, used to write and upload computer code to the physical board.
– The Arduino platform unlike most previous programmable circuit boards, the Arduino does not need a separate programmer to load new code onto the board — you can simply use a USB cable. Additionally, the Arduino IDE uses a simplified version of C++, making it easier to learn to program.
– The open sources and extensible language: Arduino IDE is based on open source tool. The programming language used can be extended through the C++ library.
– The open source and expandable hardware: Arduino is based on Atmel’s ATMEGA 8-bit microcontrollers and its SAM3X8E and SAMD21 32-bit microcontrollers. Development boards and modules are planned to be released under the premise of following the “Creative Commons License Agreement”, so experienced circuit designers can make their own modules and carry out corresponding expansions and improvements. Even users who are relatively inexperienced can make a trial version of the basic Uno development board, which is easy to understand the principle of its operation and save costs.
– The Arduino hardware and software were designed for artists, designers, hobbyists, hackers, newbies, and anyone interested in creating interactive objects or environments. Arduino can interact with buttons, LEDs, motors, speakers, GPS units, cameras, the internet, and even your smart-phone or your TV.
Arduino Leonardo: Arduino’s first development board to use one microcontroller with built-in USB. It is cheaper and simpler. The code libraries allow the board to emulate a computer keyboard, mouse, and more.
LCD means liquid crystal display. Basically, any displays can be used with Arduino, including alphanumeric character LCD display, monochrome graphic LCD display, color TFT LCD display, IPS LCD display. It can also be used for non LCD displays like: PMOLED display, AMOLED display, E-ink (E-paper) displays. Orient Display developed easy interface (SPI, I2C) displays which can be easily used with Arduino.
LCD displays were first used for watches and calculators. Now, LCD display technology dominants the display world, it can be found in wearables, smart homes, mobile phones, TVs, laptops, monitors, kiosks, aircraft cockpit, digital cameras, lab instrument, power grid etc.
LCD itself can emit light itself. It has to utilize outside light sources. LCD display module normally includes LCD glass (or LCD panel), LCD driving circuitry ( can be COG, COB or TAB) and a backlight.
A LCD display 16*2 is actually a basic and simple to use LCD module. It includes LCD glass, COB (Chip on PCB Board) LCD control board, backlight, zebra to connect LCD glass and control board and a bezel to hold everything together. 16×2 LCD display can display




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey