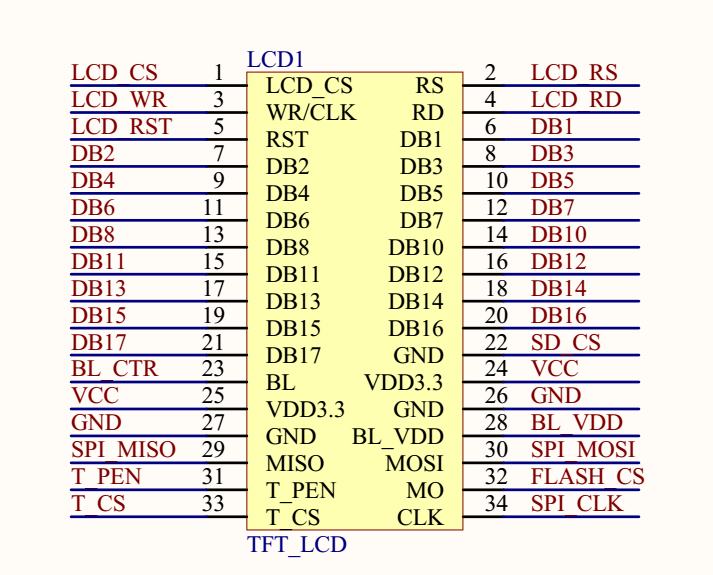
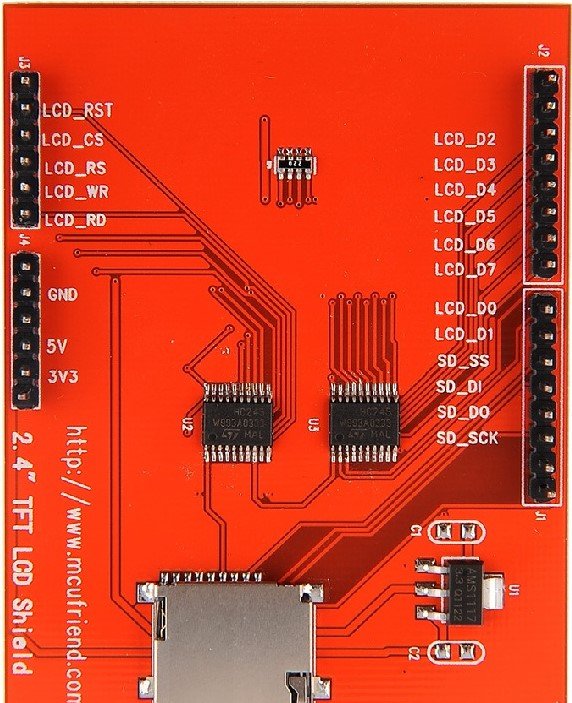
tft lcd pin description factory

A thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display (TFT LCD) is a variant of a liquid-crystal display that uses thin-film-transistor technologyactive matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven (i.e. with segments directly connected to electronics outside the LCD) LCDs with a few segments.
In February 1957, John Wallmark of RCA filed a patent for a thin film MOSFET. Paul K. Weimer, also of RCA implemented Wallmark"s ideas and developed the thin-film transistor (TFT) in 1962, a type of MOSFET distinct from the standard bulk MOSFET. It was made with thin films of cadmium selenide and cadmium sulfide. The idea of a TFT-based liquid-crystal display (LCD) was conceived by Bernard Lechner of RCA Laboratories in 1968. In 1971, Lechner, F. J. Marlowe, E. O. Nester and J. Tults demonstrated a 2-by-18 matrix display driven by a hybrid circuit using the dynamic scattering mode of LCDs.T. Peter Brody, J. A. Asars and G. D. Dixon at Westinghouse Research Laboratories developed a CdSe (cadmium selenide) TFT, which they used to demonstrate the first CdSe thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display (TFT LCD).active-matrix liquid-crystal display (AM LCD) using CdSe TFTs in 1974, and then Brody coined the term "active matrix" in 1975.high-resolution and high-quality electronic visual display devices use TFT-based active matrix displays.
The circuit layout process of a TFT-LCD is very similar to that of semiconductor products. However, rather than fabricating the transistors from silicon, that is formed into a crystalline silicon wafer, they are made from a thin film of amorphous silicon that is deposited on a glass panel. The silicon layer for TFT-LCDs is typically deposited using the PECVD process.
Polycrystalline silicon is sometimes used in displays requiring higher TFT performance. Examples include small high-resolution displays such as those found in projectors or viewfinders. Amorphous silicon-based TFTs are by far the most common, due to their lower production cost, whereas polycrystalline silicon TFTs are more costly and much more difficult to produce.
The twisted nematic display is one of the oldest and frequently cheapest kind of LCD display technologies available. TN displays benefit from fast pixel response times and less smearing than other LCD display technology, but suffer from poor color reproduction and limited viewing angles, especially in the vertical direction. Colors will shift, potentially to the point of completely inverting, when viewed at an angle that is not perpendicular to the display. Modern, high end consumer products have developed methods to overcome the technology"s shortcomings, such as RTC (Response Time Compensation / Overdrive) technologies. Modern TN displays can look significantly better than older TN displays from decades earlier, but overall TN has inferior viewing angles and poor color in comparison to other technology.
The transmittance of a pixel of an LCD panel typically does not change linearly with the applied voltage,sRGB standard for computer monitors requires a specific nonlinear dependence of the amount of emitted light as a function of the RGB value.
Less expensive PVA panels often use dithering and FRC, whereas super-PVA (S-PVA) panels all use at least 8 bits per color component and do not use color simulation methods.BRAVIA LCD TVs offer 10-bit and xvYCC color support, for example, the Bravia X4500 series. S-PVA also offers fast response times using modern RTC technologies.
When the field is on, the liquid crystal molecules start to tilt towards the center of the sub-pixels because of the electric field; as a result, a continuous pinwheel alignment (CPA) is formed; the azimuthal angle rotates 360 degrees continuously resulting in an excellent viewing angle. The ASV mode is also called CPA mode.
TFT dual-transistor pixel or cell technology is a reflective-display technology for use in very-low-power-consumption applications such as electronic shelf labels (ESL), digital watches, or metering. DTP involves adding a secondary transistor gate in the single TFT cell to maintain the display of a pixel during a period of 1s without loss of image or without degrading the TFT transistors over time. By slowing the refresh rate of the standard frequency from 60 Hz to 1 Hz, DTP claims to increase the power efficiency by multiple orders of magnitude.
Due to the very high cost of building TFT factories, there are few major OEM panel vendors for large display panels. The glass panel suppliers are as follows:
External consumer display devices like a TFT LCD feature one or more analog VGA, DVI, HDMI, or DisplayPort interface, with many featuring a selection of these interfaces. Inside external display devices there is a controller board that will convert the video signal using color mapping and image scaling usually employing the discrete cosine transform (DCT) in order to convert any video source like CVBS, VGA, DVI, HDMI, etc. into digital RGB at the native resolution of the display panel. In a laptop the graphics chip will directly produce a signal suitable for connection to the built-in TFT display. A control mechanism for the backlight is usually included on the same controller board.
The low level interface of STN, DSTN, or TFT display panels use either single ended TTL 5 V signal for older displays or TTL 3.3 V for slightly newer displays that transmits the pixel clock, horizontal sync, vertical sync, digital red, digital green, digital blue in parallel. Some models (for example the AT070TN92) also feature input/display enable, horizontal scan direction and vertical scan direction signals.
New and large (>15") TFT displays often use LVDS signaling that transmits the same contents as the parallel interface (Hsync, Vsync, RGB) but will put control and RGB bits into a number of serial transmission lines synchronized to a clock whose rate is equal to the pixel rate. LVDS transmits seven bits per clock per data line, with six bits being data and one bit used to signal if the other six bits need to be inverted in order to maintain DC balance. Low-cost TFT displays often have three data lines and therefore only directly support 18 bits per pixel. Upscale displays have four or five data lines to support 24 bits per pixel (truecolor) or 30 bits per pixel respectively. Panel manufacturers are slowly replacing LVDS with Internal DisplayPort and Embedded DisplayPort, which allow sixfold reduction of the number of differential pairs.
Kawamoto, H. (2012). "The Inventors of TFT Active-Matrix LCD Receive the 2011 IEEE Nishizawa Medal". Journal of Display Technology. 8 (1): 3–4. Bibcode:2012JDisT...8....3K. doi:10.1109/JDT.2011.2177740. ISSN 1551-319X.
K. H. Lee; H. Y. Kim; K. H. Park; S. J. Jang; I. C. Park & J. Y. Lee (June 2006). "A Novel Outdoor Readability of Portable TFT-LCD with AFFS Technology". SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers. AIP. 37 (1): 1079–82. doi:10.1889/1.2433159. S2CID 129569963.
Showcase high quality graphics and images on our 800 x 480 7” TFT display! The DT070CTFT LCD module is an upgraded version to our DT070ATFT module. Compared to the previous model, this new 7 inch display offers improved viewing angle and brighter LEDs. The DT070CTFT also uses the Himax HX8264E + HX8664B display drivers. This LCD display is available with a resistive or capacitive touchscreen panel.

TFT displays are full color LCDs providing bright, vivid colors with the ability to show quick animations, complex graphics, and custom fonts with different touchscreen options. Available in industry standard sizes and resolutions. These displays come as standard, premium MVA, sunlight readable, or IPS display types with a variety of interface options including HDMI, SPI and LVDS. Our line of TFT modules include a custom PCB that support HDMI interface, audio support or HMI solutions with on-board FTDI Embedded Video Engine (EVE2).

-Select-AfghanistanAlbaniaAlgeriaAmerican SamoaAndorraAngolaAnguillaAntigua and BarbudaArgentinaArmeniaArubaAustraliaAustriaAzerbaijan RepublicBahamasBahrainBangladeshBarbadosBelarusBelgiumBelizeBeninBermudaBhutanBoliviaBosnia and HerzegovinaBotswanaBrazilBritish Virgin IslandsBrunei DarussalamBulgariaBurkina FasoBurundiCambodiaCameroonCanadaCape Verde IslandsCayman IslandsCentral African RepublicChadChileChinaColombiaComorosCongo, Democratic Republic of theCongo, Republic of theCook IslandsCosta RicaCroatia, Republic ofCyprusCzech RepublicCôte d"Ivoire (Ivory Coast)DenmarkDjiboutiDominicaDominican RepublicEcuadorEgyptEl SalvadorEquatorial GuineaEritreaEstoniaEthiopiaFalkland Islands (Islas Malvinas)FijiFinlandFranceFrench GuianaFrench PolynesiaGabon RepublicGambiaGeorgiaGermanyGhanaGibraltarGreeceGreenlandGrenadaGuadeloupeGuamGuatemalaGuernseyGuineaGuinea-BissauGuyanaHaitiHondurasHong KongHungaryIcelandIndiaIndonesiaIraqIrelandIsraelItalyJamaicaJapanJerseyJordanKazakhstanKenyaKiribatiKorea, SouthKuwaitKyrgyzstanLaosLatviaLebanonLesothoLiberiaLibyaLiechtensteinLithuaniaLuxembourgMacauMacedoniaMadagascarMalawiMalaysiaMaldivesMaliMaltaMarshall IslandsMartiniqueMauritaniaMauritiusMayotteMexicoMicronesiaMoldovaMonacoMongoliaMontenegroMontserratMoroccoMozambiqueNamibiaNauruNepalNetherlandsNetherlands AntillesNew CaledoniaNew ZealandNicaraguaNigerNigeriaNiueNorwayOmanPakistanPalauPanamaPapua New GuineaParaguayPeruPhilippinesPolandPortugalPuerto RicoQatarReunionRomaniaRwandaSaint HelenaSaint Kitts-NevisSaint LuciaSaint Pierre and MiquelonSaint Vincent and the GrenadinesSan MarinoSaudi ArabiaSenegalSerbiaSeychellesSierra LeoneSingaporeSlovakiaSloveniaSolomon IslandsSomaliaSouth AfricaSpainSri LankaSurinameSwazilandSwedenSwitzerlandTaiwanTajikistanTanzaniaThailandTogoTongaTrinidad and TobagoTunisiaTurkeyTurkmenistanTurks and Caicos IslandsTuvaluUgandaUnited Arab EmiratesUnited KingdomUnited StatesUruguayUzbekistanVanuatuVatican City StateVenezuelaVietnamVirgin Islands (U.S.)Wallis and FutunaWestern SaharaWestern SamoaYemenZambiaZimbabwe
This 2.0”LCD display adopts T7789V driver chip and has 320*240 color pixels (RGB565). It uses IPS TFT display and can display 18-bit color(16-bit is basically used). The module performs excellently in displaying color bitmap. Besides, there is an onboard MicroSD card slot for displaying more pictures. There are two connection ways for this module: pin headers and GDI. Only one fpc cable is needed when working with main-cotnrollers with GDI, which greatly reduces the complexity of wiring.

A TFT LCD display module consists of a TFT LCD panel, one or more COG (chip-on-glass) or COB (chip-on-board) driver ICs, a backlight, and an interface. Several TFT display interface technologies exist today. Picking the right interface depends on specific end-product concerns. There are several types of TFT display interfaces which have been designed in the last number of years for various screen sizes, including LVDS, (Low-Voltage Differential Signaling) parallel, SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) RGB and so on. Here is an overview of these display interfaces to give you a better idea of the variety of TFT LCD displays that are taking center stage.
SPI LCD Interface: Serial Peripheral Interface allows serial (one bit at a time) exchange of data between two devices. It has an advantage over parallel ones, that of simpler wiring. SPI also can have longer cables, since there is much less interaction or crosstalk in the cable. The downside of SPI is that you can"t read from the TFT LCD display, you can only write on it and it is slow. That"s why you normally see smaller TFT LCD screens use SPI.
MCU Parallel Interface: Many modern MCUs have built-in LCD controller function. There are two types that are commonly used, 6800 and 8080. Generally, MCU/Parallel interface consist of data signal(4/8/9/16 bits) and control signal. MCU interface is simple, but requires display RAM.
RGB Interface: RGB interface is a special kind of parallel interface. It requires no display RAM. MCU directly updates the TFT screen, sending Red Green & Blue sub-pixel data (16/18/24 bits) and timing signals. RGB interface provides high speed communication to TFT LCD, but it needs more data wires and controlling is more complex.
LVDS Interface: Low-voltage differential signaling is an electrical digital signaling standard. Devices with LVDS interface can communicate at very high speeds over inexpensive twisted-pair copper cables. It is much less susceptible to EMI and crosstalk issues, allowing the transmitting device to be located farther from TFT LCD display.
UART/RS232/RS485: These serial interfaces are used in Topway"s Smart TFT LCD display module. Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART) is a block of circuitry responsible for implementing serial communication. Essentially, the UART acts as an intermediary between parallel and serial interfaces. On one end of UART is a bus of eight-or-so data lines (plus some control pins), on the other is the two serial wires – RX and TX.
To choose your product"s TFT LCD interface, besides above technical considerations, target use environment and bandwidth are two main factors as well. You can read more about how to choose LCD interfaces here, or consult with us. Topway has been manufacturing TFT LCD in the past 20s years. Our TFT LCD modules cover full spectrum of interfaces. And we surely can suggest a TFT LCD display that suits your use case.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey