lcd display schematic diagram quotation

In this tutorial, I’ll explain how to set up an LCD on an Arduino and show you all the different ways you can program it. I’ll show you how to print text, scroll text, make custom characters, blink text, and position text. They’re great for any project that outputs data, and they can make your project a lot more interesting and interactive.
The display I’m using is a 16×2 LCD display that I bought for about $5. You may be wondering why it’s called a 16×2 LCD. The part 16×2 means that the LCD has 2 lines, and can display 16 characters per line. Therefore, a 16×2 LCD screen can display up to 32 characters at once. It is possible to display more than 32 characters with scrolling though.
The code in this article is written for LCD’s that use the standard Hitachi HD44780 driver. If your LCD has 16 pins, then it probably has the Hitachi HD44780 driver. These displays can be wired in either 4 bit mode or 8 bit mode. Wiring the LCD in 4 bit mode is usually preferred since it uses four less wires than 8 bit mode. In practice, there isn’t a noticeable difference in performance between the two modes. In this tutorial, I’ll connect the LCD in 4 bit mode.
BONUS: I made a quick start guide for this tutorial that you can download and go back to later if you can’t set this up right now. It covers all of the steps, diagrams, and code you need to get started.
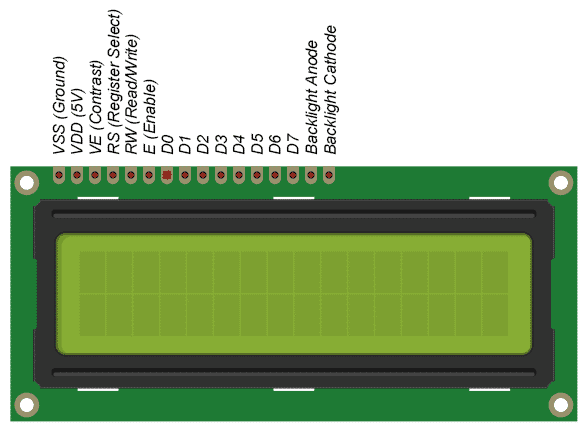
Here’s a diagram of the pins on the LCD I’m using. The connections from each pin to the Arduino will be the same, but your pins might be arranged differently on the LCD. Be sure to check the datasheet or look for labels on your particular LCD:
Also, you might need to solder a 16 pin header to your LCD before connecting it to a breadboard. Follow the diagram below to wire the LCD to your Arduino:
The resistor in the diagram above sets the backlight brightness. A typical value is 220 Ohms, but other values will work too. Smaller resistors will make the backlight brighter.
There are 19 different functions in the LiquidCrystal library available for us to use. These functions do things like change the position of the text, move text across the screen, or make the display turn on or off. What follows is a short description of each function, and how to use it in a program.
TheLiquidCrystal() function sets the pins the Arduino uses to connect to the LCD. You can use any of the Arduino’s digital pins to control the LCD. Just put the Arduino pin numbers inside the parentheses in this order:
This function sets the dimensions of the LCD. It needs to be placed before any other LiquidCrystal function in the void setup() section of the program. The number of rows and columns are specified as lcd.begin(columns, rows). For a 16×2 LCD, you would use lcd.begin(16, 2), and for a 20×4 LCD you would use lcd.begin(20, 4).
This function clears any text or data already displayed on the LCD. If you use lcd.clear() with lcd.print() and the delay() function in the void loop() section, you can make a simple blinking text program:
Similar, but more useful than lcd.home() is lcd.setCursor(). This function places the cursor (and any printed text) at any position on the screen. It can be used in the void setup() or void loop() section of your program.
The cursor position is defined with lcd.setCursor(column, row). The column and row coordinates start from zero (0-15 and 0-1 respectively). For example, using lcd.setCursor(2, 1) in the void setup() section of the “hello, world!” program above prints “hello, world!” to the lower line and shifts it to the right two spaces:
You can use this function to write different types of data to the LCD, for example the reading from a temperature sensor, or the coordinates from a GPS module. You can also use it to print custom characters that you create yourself (more on this below). Use lcd.write() in the void setup() or void loop() section of your program.
The function lcd.noCursor() turns the cursor off. lcd.cursor() and lcd.noCursor() can be used together in the void loop() section to make a blinking cursor similar to what you see in many text input fields:
Cursors can be placed anywhere on the screen with the lcd.setCursor() function. This code places a blinking cursor directly below the exclamation point in “hello, world!”:
This function creates a block style cursor that blinks on and off at approximately 500 milliseconds per cycle. Use it in the void loop() section. The function lcd.noBlink() disables the blinking block cursor.
This function turns on any text or cursors that have been printed to the LCD screen. The function lcd.noDisplay() turns off any text or cursors printed to the LCD, without clearing it from the LCD’s memory.
This function takes anything printed to the LCD and moves it to the left. It should be used in the void loop() section with a delay command following it. The function will move the text 40 spaces to the left before it loops back to the first character. This code moves the “hello, world!” text to the left, at a rate of one second per character:
Like the lcd.scrollDisplay() functions, the text can be up to 40 characters in length before repeating. At first glance, this function seems less useful than the lcd.scrollDisplay() functions, but it can be very useful for creating animations with custom characters.
lcd.noAutoscroll() turns the lcd.autoscroll() function off. Use this function before or after lcd.autoscroll() in the void loop() section to create sequences of scrolling text or animations.
This function sets the direction that text is printed to the screen. The default mode is from left to right using the command lcd.leftToRight(), but you may find some cases where it’s useful to output text in the reverse direction:
This code prints the “hello, world!” text as “!dlrow ,olleh”. Unless you specify the placement of the cursor with lcd.setCursor(), the text will print from the (0, 1) position and only the first character of the string will be visible.
This command allows you to create your own custom characters. Each character of a 16×2 LCD has a 5 pixel width and an 8 pixel height. Up to 8 different custom characters can be defined in a single program. To design your own characters, you’ll need to make a binary matrix of your custom character from an LCD character generator or map it yourself. This code creates a degree symbol (°):
This tutorial includes everything you need to know about controlling a character LCD with Arduino. I have included a wiring diagram and many example codes. These displays are great for displaying sensor data or text and they are also fairly cheap.
The first part of this article covers the basics of displaying text and numbers. In the second half, I will go into more detail on how to display custom characters and how you can use the other functions of the LiquidCrystal Arduino library.
As you will see, you need quite a lot of connections to control these displays. I therefore like to use them with an I2C interface module mounted on the back. With this I2C module, you only need two connections to control the LCD. Check out the tutorial below if you want to use an I2C module as well:
These LCDs are available in many different sizes (16×2 1602, 20×4 2004, 16×1 etc.), but they all use the same HD44780 parallel interface LCD controller chip from Hitachi. This means you can easily swap them. You will only need to change the size specifications in your Arduino code.
For more information, you can check out the datasheets below. The 16×2 and 20×4 datasheets include the dimensions of the LCD and in the HD44780 datasheet you can find more information about the Hitachi LCD driver.
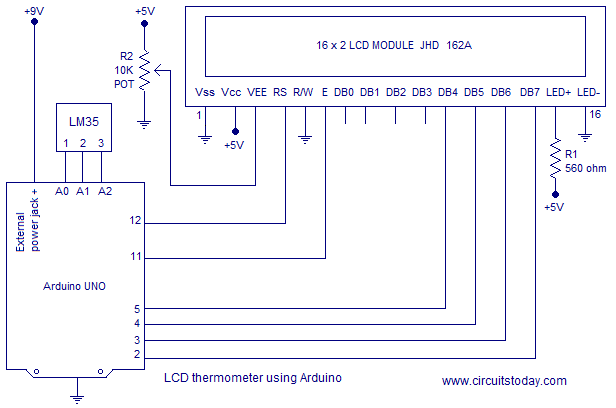
Most LCDs have a built-in series resistor for the LED backlight. You should find it on the back of the LCD connected to pin 15 (Anode). If your display doesn’t include a resistor, you will need to add one between 5 V and pin 15. It should be safe to use a 220Ω resistor, but this value might make your display a bit dim. You can check the datasheet for the maximum current rating of the backlight and use this to select an appropriate resistor value.
After you have wired up the LCD, you will need to adjust the contrast of the display. This is done by turning the 10 kΩ potentiometer clockwise or counterclockwise.
Plug in the USB connector of the Arduino to power the LCD. You should see the backlight light up. Now rotate the potentiometer until one (16×2 LCD) or 2 rows (20×4 LCD) of rectangles appear.
In order to control the LCD and display characters, you will need to add a few extra connections. Check the wiring diagram below and the pinout table from the introduction of this article.
We will be using the LCD in 4-bit mode, this means you don’t need to connect anything to D0-D3. The R/W pin is connected to ground, this will pull the pin LOW and set the LCD to WRITE mode.
To control the LCD we will be using the LiquidCrystal library. This library should come pre-installed with the Arduino IDE. You can find it by going to Sketch > Include Library > LiquidCrystal.
The example code below shows you how to display a message on the LCD. Next, I will show you how the code works and how you can use the other functions of the LiquidCrystal library.
After including the library, the next step is to create a new instance of the LiquidCrystal class. The is done with the function LiquidCrystal(rs, enable, d4, d5, d6, d7). As parameters we use the Arduino pins to which we connected the display. Note that we have called the display ‘lcd’. You can give it a different name if you want like ‘menu_display’. You will need to change ‘lcd’ to the new name in the rest of the sketch.
In the loop() the cursor is set to the third column and first row of the LCD with lcd.setCursor(2,0). Note that counting starts at 0, and the first argument specifies the column. If you do not specify the cursor position, the text will be printed at the default home position (0,0) if the display is empty, or behind the last printed character.
Next, the string ‘Hello World!’ is printed with lcd.print("Hello World!"). Note that you need to place quotation marks (” “) around the text. When you want to print numbers or variables, no quotation marks are necessary.
Clears the LCD screen and positions the cursor in the upper-left corner (first row and first column) of the display. You can use this function to display different words in a loop.
This function turns off any text or cursors printed to the LCD. The text/data is not cleared from the LCD memory. This means it will be shown again when the function display() is called.
Scrolls the contents of the display (text and cursor) one space to the left. You can use this function in the loop section of the code in combination with delay(500), to create a scrolling text animation.
This function turns on automatic scrolling of the LCD. This causes each character output to the display to push previous characters over by one space. If the current text direction is left-to-right (the default), the display scrolls to the left; if the current direction is right-to-left, the display scrolls to the right. This has the effect of outputting each new character to the same location on the LCD.
The following example sketch enables automatic scrolling and prints the character 0 to 9 at the position (16,0) of the LCD. Change this to (20,0) for a 20×4 LCD.
With the function createChar() it is possible to create and display custom characters on the LCD. This is especially useful if you want to display a character that is not part of the standard ASCII character set.
Technical info: LCDs that are based on the Hitachi HD44780 LCD controller have two types of memories: CGROM and CGRAM (Character Generator ROM and RAM). CGROM generates all the 5 x 8 dot character patterns from the standard 8-bit character codes. CGRAM can generate user-defined character patterns.
/* Example sketch to create and display custom characters on character LCD with Arduino and LiquidCrystal library. For more info see www.www.makerguides.com */
After including the library and creating the LCD object, the custom character arrays are defined. Each array consists of 8 bytes, 1 byte for each row. In this example 8 custom characters are created.
In this article I have shown you how to use an alphanumeric LCD with Arduino. I hope you found it useful and informative. If you did, please share it with a friend that also likes electronics and making things!
I would love to know what projects you plan on building (or have already built) with these LCDs. If you have any questions, suggestions, or if you think that things are missing in this tutorial, please leave a comment down below.

On home appliances, it is often necessary to display numbers and words to convey information, such as the current time displayed on the clock, the current temperature information on the kettle… etc. The two most commonly used displays are LED displays and LCD displays, this article will compare the advantages and disadvantages of LED displays and LCD displays, and provide a two-step quick way to quickly determine whether this product is an LCD or LED display.
LCD displays are the most common displays in daily life, from your mobile phone screen to home appliances, you can use LCD displays, but whether it is a color or black and white LCD display, in fact, the principle is the same. There are two main components within the LCD display:Backlight module
Black-and-white LCD displays are widely used in a variety of low-cost products, and the picture above is a black-and-white LCD display used in science calculator.
Advantages of monochrome LCD displays:Can show very compact information.Each display point of the calculator as shown below is very close to each other, and high-resolution text can be displayed
Power savingBlack and white LCD displays can operated without a lot of power compared to full-color LCD, when products that do not require full-color demand and need to control power consumption are often used.
CheapIf you just want to display a set of numbers or a few ICONs, the price of using a black-and-white LCD display is much cheaper than that of a full-color LCD, and it is often used in a large number of consumer products.
Disadvantages of monochrome LCD displays:Small viewing angle, not easy to use for outdoor application.Usually black and white liquid crystal display in the front view, the display is the clearest, but due to the LCD panel characteristics, as long as the side view, the clarity will be declined, outdoor will be affected by strong light, the viewing angle is not large, the clarity is not enough, LED display due to the word luminescence characteristics, there is no viewing angle problem.
Can only be used in monochromeIf you need multi-color applications, you can only upgrade to a full-color LCD display that is many times more expensive, and the LED display can simply add different colors to the LED display without significantly increasing the cost
The structure and basic introduction of the display in this article this article, compared with LCD displays, self-illumination characteristics, so that LED displays in the outdoor visibility is high, high brightness, but also no viewing angle problem. LED displays are the same as black and white LCD liquid crystals, and the display information must be designed in advance and cannot be arbitrarily transformed. The price of LED displays is between full-color LCDs and monochrome LCDs, and if properly designed, they can save the cost of achieving display performance.
This article briefly introduces the basic principles and advantages and disadvantages of two common LCD displays, and provides two steps to quickly determine whether the display in hand is an LED display, and product designers can follow these two steps to understand which display the product is used when observing the product.

Our 64128L monochrome graphic LCD module has a viewing area of approximately 60 x 30 mm. This LCD is suitable for a wide variety of applications and is available with several different backlight colors. The COG IC is the Sitronix ST7565R. This LCD has a THRU-HOLE PIN interface.
The ST7565R is a single-chip dot matrix LCD driver that can be connected directly to a microprocessor bus. 8-bit parallel or 4-line SPI display data sent from the microprocessor is stored in the internal display data RAM and the chip generates a LCD drive signal independent of the microprocessor. Because the chips in the ST7565R contain 65x132 bits of display data RAM and there is a 1-to-1 correspondence between the LCD panel pixels and the internal RAM bits, these chips enable displays with a high degree of freedom. The ST7565R chips contain 65 common output circuits and 132 segment output circuits, so that a single chip can drive a 65x132 dot display (capable of displaying 8 columns x 4 rows of a 16x16 dot kanji font).

Since the Company’s inception by a team of enterprising academics at the University of Hong Kong in 1978, Varitronix have grown to become one of the leading manufacturers of Liquid Crystal Displays through years of innovation in research, design, production scalability, and technology advancement.
Through the following years of finding local success, Varitronix envisioned a much larger scale operation for the ever-increasing demand for displays. The trajectory plan eventually led the Company to be officially listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange in 1991 (HKSE code: 710), continuing its influence and strong presence to serve customers at the local, national, and global levels.
Nearly half a century later, BOE Varitronix continues its time-honored tradition in providing the one stop shop for the latest display technologies, backed up by solid research and commitment to quality, customized to the individual needs, and delivered economically and efficiently.
To evaluate the performance of display devices, several metrics are commonly used, such as response time, CR, color gamut, panel flexibility, viewing angle, resolution density, peak brightness, lifetime, among others. Here we compare LCD and OLED devices based on these metrics one by one.
The last finding is somehow counter to the intuition that a LCD should have a more severe motion picture image blur, as its response time is approximately 1000 × slower than that of an OLED (ms vs. μs). To validate this prediction, Chen et al.
If we want to further suppress image blur to an unnoticeable level (MPRT<2 ms), decreasing the duty ratio (for LCDs, this is the on-time ratio of the backlight, called scanning backlight or blinking backlight) is mostly adopted
As Figure 6 depicts, there are two types of surface reflections. The first one is from a direct light source, i.e., the sun or a light bulb, denoted as A1. Its reflection is fairly specular, and in practice, we can avoid this reflection (i.e., strong glare from direct sun) by simply adjusting the display position or viewing direction. However, the second reflection, denoted as A2, is quite difficult to avoid. It comes from an extended background light source, such as a clear sky or scattered ceiling light. In our analysis, we mainly focus on the second reflection (A2).
To investigate the ACR, we have to clarify the reflectance first. A large TV is often operated by remote control, so touchscreen functionality is not required. As a result, an anti-reflection coating is commonly adopted. Let us assume that the reflectance is 1.2% for both LCD and OLED TVs. For the peak brightness and CR, different TV makers have their own specifications. Here, without losing generality, let us use the following brands as examples for comparison: LCD peak brightness=1200 nits, LCD CR=5000:1 (Sony 75″ X940E LCD TV); OLED peak brightness=600 nits, and OLED CR=infinity (Sony 77″ A1E OLED TV). The obtained ACR for both LCD and OLED TVs is plotted in Figure 7a. As expected, OLEDs have a much higher ACR in the low illuminance region (dark room) but drop sharply as ambient light gets brighter. At 63 lux, OLEDs have the same ACR as LCDs. Beyond 63 lux, LCDs take over. In many countries, 60 lux is the typical lighting condition in a family living room. This implies that LCDs have a higher ACR when the ambient light is brighter than 60 lux, such as in office lighting (320–500 lux) and a living room with the window shades or curtain open. Please note that, in our simulation, we used the real peak brightness of LCDs (1200 nits) and OLEDs (600 nits). In most cases, the displayed contents could vary from black to white. If we consider a typical 50% average picture level (i.e., 600 nits for LCDs vs. 300 nits for OLEDs), then the crossover point drops to 31 lux (not shown here), and LCDs are even more favorable. This is because the on-state brightness plays an important role to the ACR, as Equation (2) shows.
Calculated ACR as a function of different ambient light conditions for LCD and OLED TVs. Here we assume that the LCD peak brightness is 1200 nits and OLED peak brightness is 600 nits, with a surface reflectance of 1.2% for both the LCD and OLED. (a) LCD CR: 5000:1, OLED CR: infinity; (b) LCD CR: 20 000:1, OLED CR: infinity.
Recently, an LCD panel with an in-cell polarizer was proposed to decouple the depolarization effect of the LC layer and color filtersFigure 7b. Now, the crossover point takes place at 16 lux, which continues to favor LCDs.
For mobile displays, such as smartphones, touch functionality is required. Thus the outer surface is often subject to fingerprints, grease and other contaminants. Therefore, only a simple grade AR coating is used, and the total surface reflectance amounts to ~4.4%. Let us use the FFS LCD as an example for comparison with an OLED. The following parameters are used in our simulations: the LCD peak brightness is 600 nits and CR is 2000:1, while the OLED peak brightness is 500 nits and CR is infinity. Figure 8a depicts the calculated results, where the intersection occurs at 107 lux, which corresponds to a very dark overcast day. If the newly proposed structure with an in-cell polarizer is used, the FFS LCD could attain a 3000:1 CRFigure 8b), corresponding to an office building hallway or restroom lighting. For reference, a typical office light is in the range of 320–500 luxFigure 8 depicts, OLEDs have a superior ACR under dark ambient conditions, but this advantage gradually diminishes as the ambient light increases. This was indeed experimentally confirmed by LG Display
Calculated ACR as a function of different ambient light conditions for LCD and OLED smartphones. Reflectance is assumed to be 4.4% for both LCD and OLED. (a) LCD CR: 2000:1, OLED CR: infinity; (b) LCD CR: 3000:1, OLED CR: infinity. (LCD peak brightness: 600 nits; OLED peak brightness: 500 nits).
For conventional LCDs employing a WLED backlight, the yellow spectrum generated by YAG (yttrium aluminum garnet) phosphor is too broad to become highly saturated RGB primary colors, as shown in Figure 9aTable 2. The first choice is the RG-phosphor-converted WLEDFigure 9b, the red and green emission spectra are well separated; still, the green spectrum (generated by β-sialon:Eu2+ phosphor) is fairly broad and red spectrum (generated by K2SiF6:Mn4+ (potassium silicofluoride, KSF) phosphor) is not deep enough, leading to 70%–80% Rec. 2020, depending on the color filters used.
Recently, a new LED technology, called the Vivid Color LED, was demonstratedFigure 9d), which leads to an unprecedented color gamut (~98% Rec. 2020) together with specially designed color filters. Such a color gamut is comparable to that of laser-lit displays but without laser speckles. Moreover, the Vivid Color LED is heavy-metal free and shows good thermal stability. If the efficiency and cost can be further improved, it would be a perfect candidate for an LCD backlight.
As mentioned earlier, TFT LCDs are a fairly mature technology. They can be operated for >10 years without noticeable performance degradation. However, OLEDs are more sensitive to moisture and oxygen than LCDs. Thus their lifetime, especially for blue OLEDs, is still an issue. For mobile displays, this is not a critical issue because the expected usage of a smartphone is approximately 2–3 years. However, for large TVs, a lifetime of >30 000 h (>10 years) has become the normal expectation for consumers.
Here we focus on two types of lifetime: storage and operational. To enable a 10-year storage lifetime, according to the analysis−6 g (m2-day)−1 and 1 × 10−5 cm3 (m2-day)−1, respectively. To achieve these values, organic and/or inorganic thin films have been developed to effectively protect the OLED and lengthen its storage lifetime. Meanwhile, it is compatible to flexible substrates and favors a thinner display profile
Power consumption is equally important as other metrics. For LCDs, power consumption consists of two parts: the backlight and driving electronics. The ratio between these two depends on the display size and resolution density. For a 55″ 4K LCD TV, the backlight occupies approximately 90% of the total power consumption. To make full use of the backlight, a dual brightness enhancement film is commonly embedded to recycle mismatched polarized light
The power efficiency of an OLED is generally limited by the extraction efficiency (ηext~20%). To improve the power efficiency, multiple approaches can be used, such as a microlens array, a corrugated structure with a high refractive index substrateFigure 11 shows the power efficiencies of white, green, red and blue phosphorescent as well as blue fluorescent/TTF OLEDs over time. For OLEDs with fluorescent emitters in the 1980s and 1990s, the power efficiency was limited by the IQE, typically <10 lm W−1(Refs. 41, 114, 115, 116, 117, 118). With the incorporation of phosphorescent emitters in the ~2000 s, the power efficiency was significantly improved owing to the materials and device engineering−1 was demonstrated in 2011 (Ref. 127), which showed a >100 × improvement compared with that of the basic two-layer device proposed in 1987 (1.5 lm W−1 in Ref. 41). A white OLED with a power efficiency >100 lm W−1 was also demonstrated, which was comparable to the power efficiency of a LCD backlight. For red and blue OLEDs, their power efficiencies are generally lower than that of the green OLED due to their lower photopic sensitivity function, and there is a tradeoff between color saturation and power efficiency. Note, we separated the performances of blue phosphorescent and fluorescent/TTF OLEDs. For the blue phosphorescent OLEDs, although the power efficiency can be as high as ~80 lm W−1, the operation lifetime is short and color is sky-blue. For display applications, the blue TTF OLED is the favored choice, with an acceptable lifetime and color but a much lower power efficiency (16 lm W−1) than its phosphorescent counterpartFigure 11 shows.
To compare the power consumption of LCDs and OLEDs with the same resolution density, the displayed contents should be considered as well. In general, OLEDs are more efficient than LCDs for displaying dark images because black pixels consume little power for an emissive display, while LCDs are more efficient than OLEDs at displaying bright images. Currently, a ~65% average picture level is the intersection point between RGB OLEDs and LCDs
Flexible displays have a long history and have been attempted by many companies, but this technology has only recently begun to see commercial implementations for consumer electronics
In addition to the aforementioned six display metrics, other parameters are equally important. For example, high-resolution density has become a standard for all high-end display devices. Currently, LCD is taking the lead in consumer electronic products. Eight-hundred ppi or even >1000 ppi LCDs have already been demonstrated and commercialized, such as in the Sony 5.5″ 4k Smartphone Xperia Z5 Premium. The resolution of RGB OLEDs is limited by the physical dimension of the fine-pitch shadow mask. To compete with LCDs, most OLED displays use the PenTile RGB subpixel matrix scheme
The viewing angle is another important property that defines the viewing experience at large oblique angles, which is quite critical for multi-viewer applications. OLEDs are self-emissive and have an angular distribution that is much broader than that of LCDs. For instance, at a 30° viewing angle, the OLED brightness only decreases by 30%, whereas the LCD brightness decrease exceeds 50%. To widen an LCD’s viewing angle, three options can be used. (1) Remove the brightness-enhancement film in the backlight system. The tradeoff is decreased on-axis brightness
In addition to brightness, color, grayscale and the CR also vary with the viewing angle, known as color shift and gamma shift. In these aspects, LCDs and OLEDs have different mechanisms. For LCDs, they are induced by the anisotropic property of the LC material, which could be compensated for with uniaxial or biaxial films
Cost is another key factor for consumers. LCDs have been the topic of extensive investigation and investment, whereas OLED technology is emerging and its fabrication yield and capability are still far behind LCDs. As a result, the price of OLEDs is about twice as high as that of LCDs, especially for large displays. As more investment is made in OLEDs and more advanced fabrication technology is developed, such as ink-jet printing

Liquid Crystal Displays or more commonly known as LCDs are one of the most common electronic components which help us interact with an equipment or a device. Most personal portable equipment and even gigantic industrial equipment utilize a custom segment display to display data. For many portable consumer electronics, a segment LCD display is one of the biggest contributors to the overall cost of the device, hence designing a custom segment display can drive the cost down while also utilizing the display area in the most optimum manner. These displays have the lowest cost per piece, low power requirements, and a low tooling fee too.
At first thought, designing a custom segment LCD might look like a Herculean task, but trust me that it is easier than it seems. In this article, we have summarised and compared the display types and available technologies which are required to construct a custom segment LCD. We have also provided a flowchart that can act as a step-by-step guide while you design your own custom LCD. We have also provided the process we followed, a require gathering sheet we used for communicating our needs to the manufacturer, and a few other data and the quotation we received from the manufacturer.
Icons: A silhouette of any shape can be placed on the glass which enhances the ability to display data. For example, a symbol of a heart can be made to denote heart rate or an icon for a low battery to show that the battery needs to be charged. Icons are counted as a single pixel or segment and can give a lot more details than similar-sized text.
LCD Bias– It denotes the number of different voltage levels used in driving the segments, static drives (explained later in this article) only have 2 voltage levels or 2 bias voltage while multiplex drives have multiple voltage levels. For example, 1/3 will have 4 bias voltages.
LCDs utilizes the light modulating properties of liquid crystals which can be observed by using polarizing filters. Polarizing filters are special materials that have their molecules aligned in the same direction. If the light waves passing through polarisers have the same orientation as the filter, then the molecules of lights are absorbed by the filter, hence reducing the intensity of light passing through it, making it visible.
A custom LCD is important for maximizing the efficiency of the display area by adding custom symbols and characters. It also helps in reducing the cost and improving energy efficiency of the product. A higher number of custom symbols and specified placement of numerical and alphanumerical characters make the display more informative and readable for the user. This makes it look better than the plain old boring displays we get in the market. Furthermore, we can specify the viewing angle, contrast, and other specifications which can increase durability or give a better value for money for our intended usage. A typical Custom Segment display is shown below, we will also show you how to design and fabricate the same further in the article.
The LCD display doesn’t emit any light of its own, therefore it requires an external source of illumination or reflector to be readable in dark environments.
While designing a custom segment LCD display, we have the leverage of choosing a lot of parameters that affect the final product. From the color of the display to the illumination technique and color of illumination as well as the type of input pins. Some important considerations we need to take while designing a custom 7 segment display are - the type of display, i.e. positive or negative, illumination method, driving technique, polarising type, and connection method. All these design criteria are explained below:
Positive and negative displays can be easily distinguished by the colour of the background and characters. Some common differences between the positive and negative displays are:
So, which one should you choose? When the displays are to be used in areas with higher ambient light, we should select positive segment LCD display as it has better visibility than negative segment LCD displays without using a backlight.
As we know that LED displays don’t emit any light, hence to illuminate it and make it visible in a dark environment, we can use different methods of illumination. The most common LCD Illumination methods are compared below:
For displays that need to be used for budget-friendly devices that should be small and rugged, LED lights are preferred for the displays due to the high durability and low cost of operations. For high brightness, CCFL and Incandescent lights can be used.
A polarizer film is the most important component of an LCD display, which makes it possible to display characters by controlling the light. There are 3 types of polarizers that can be used in the LCD display, the properties and difference are given below:
Displays can be categorized into two types, passive displays, and active display, passive displays are simpler to construct as they have 2 connections at each segment, the conductors comprise of an Indium Tin Oxide to create an image, whereas the active displays use thin-film transistors (TFT) arranged in a grid. The name is due to its ability to control each pixel individually.
If your displays have fewer segments, then static LCD drive is preferred as it is easier to control and cheaper to construct, and has a better contrast ratio. But let’s say that if the number of segments in the display are more than 30-40 then a multiplex LCD drive should be preferred as it has multiple common pins, hence reducing the total number of pins required to drive the display.
Choosing a connector type!!! For the prototyping phase or if you need to connect your LCD display on a Microcontroller directly, a pin type connector is the best and most economical option you have. If you need to connect your LCD display in a final product with a high volume of production which also requires to be extremely durable, but at the same time should not take up a lot of space, a Flex type LCD Connector will work best for you
LCDs have limited viewing angles and when seen from an angle they lose contrast and are difficult to be observed. The viewing angle is defined by the angles perpendicular to the center of the display towards its right, left, up, and down which are denoted by the notations 3:00, 9:00, 12:00, and 6:00 respectively. The viewing angle of LCD can be defined as the angle w.r.t. to the bias angle at which the contrast of segments is legible.
To improve the viewing angle in an LCD, a Bias is incorporated in the design which shifts the nominal viewing angle with an offset. Another technique is to increase the Voltage, it affects the bias angle, making the display crisper when viewed from a direction.
For example, the viewing angle of a TN type TFT LCD is 45-65 degrees. Extra-wide polarising film (EWP) can increase the viewing angle by 10 degrees, using an O film polariser can make the viewing angles 75 degrees but these come at a cost of reduced contrast.
LCD Control chip or LCD driver chips can be mounted on the flex cable, display, or externally on a PCB. The placement of LCD control chip can affect the cost and size of the display. The 2 most common methods of chip placement are-Chip of Board (COB)and Chip on Glass(COG) which are described below:
We planned to design an air quality monitoring system for which we needed a custom segment LCD panel for an air quality monitoring device. Our product needs to display the following data: 2.5-micron and 10-micron particulate matter (PM) suspended in the air; the units should be in parts per million (PPM). CO2 in the air in PPM along with total volatile organic compounds present in the air in parts per billion (PPB). To make the product more usable, we included time in 24-hour format, Temperature in ºC, Battery status, loudspeaker status, Bluetooth status, and Wi-Fi status. And for some personal touch, we also added how good the air quality in the room is by using 3 different smileys.
We realized that it was impossible to provide all these data in a generic LCD available in the market, thus decided to build a custom LCD for our project.
A step-by-step flowchart is shown below to walk you through each and every step of selecting components and getting your custom segment LCD manufactured.
We started by listing down our requirements and drew a mock-up of the display on paper. After finalizing the placement of all the segments and icons on the prototype sketch of the display, we then decided which all icons and segments have to be kept on for the whole time and which needs to be driven. Realizing that there are too many segments, characters and icons, hence we selected a multiplex drive with 8 common pins which helped us bring down the total pins from an estimated 180 pins to less than 40 pins.
Since the device was meant to be used inside houses and offices, which are more often than not well lit and protected from environmental conditions, we opted for a positive mode display. For superior contrast ratio and better viewing angle, we chose a Film Super Twisted Nematic Display (FSTN) with a drive condition of 1/8 Duty and bias of 1/4.
Usually, the displays are mounted at a height of 4.5 feet from the ground, thus the viewing direction was selected to be 12"O clock with an operating frequency of 64Hz. We selected a Transmissive polarizer for the front glass and a reflective polarizer for the rear glass so that the natural light can pass through the front panel and the display can achieve the maximum contrast without the need for backlighting and we opted for the pin type connectors as they are easy for prototyping and are suitable for harsh environment with a lot of vibrations and shocks which best suited our purpose.
In the above image of a custom display design, we sent to the manufacturer, the red lines over multiple characters indicate that all these are considered as a single segment. For the sake of simplicity, we added test like T, S, U, B to denote Text, Symbols, Units, and Battery respectively. These characters were followed by numbers to simplify communication between us and the manufacturer. For example, if we needed any particular text or symbol to remain on, we can easily specify that to the manufacturer by using the corresponding text for that segment.
We mailed our requirements to multiple LCD manufacturers, (you will find a lot of LCD manufacturers on the Internet). Most LCD manufacturers have competitive pricing, and reply within a week. A sample requirement sheet is shown above which a customer needs to fill to specify all the details to the manufacturer.
This is a sample Custom Segment LCD quotation we got from one of the manufacturers. As you can see, the cost is based on the quantity. Higher the quantity, lower the cost. Apart from the cost per quantity, there is one more component called tooling fees. Tooling fee is a one-time fee charged by the manufacturer. It is for the technical design, support, and customization of the product. Customization of PCB or tooling of LCD can drive the tooling price higher or lower.
A custom segment LCD can help you personalize your product while also saving the overall cost of your product. The whole process will take you around 2-3 months, which will include the designing phase, prototyping phase, and getting your custom segment LCDs delivered to your doorstep. Higher ordering quantity will reduce the cost per piece of each unit, thus driving down the cost of your final product.

PG Technologies supplies Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) Technology to a variety of industries. Using the latest production processes, our manufacturing facility has developed a wide range of products capable of meeting today’s market demands.
We can assist with design and development of all types of custom LCD panels and modules, e.g. TFT, TN, HTN, STN, FSTN and COG types. All products are manufactured in a state of the art manufacturing facility with an annual output and volume now standing at 42,000,000 panels and 1,170,000 modules. Diverse production processes provide flexibility to address all of your prototype, short runs to large production requirements.
At PG Technologies, a sharp focus is placed on continuous product and process improvement. We are continually introducing new custom and standard LCD’s platforms for both the domestic and international markets. If you are interested in any of our products, or have a customized need to fill, please contact us. Our world-class pricing and flexible manufacturing lead-times are among the most competitive in the industry. We look forward to working with you on your LCD needs.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey