tft lcd driver code brands

In these videos, the SPI (GPIO) bus is referred to being the bottleneck. SPI based displays update over a serial data bus, transmitting one bit per clock cycle on the bus. A 320x240x16bpp display hence requires a SPI bus clock rate of 73.728MHz to achieve a full 60fps refresh frequency. Not many SPI LCD controllers can communicate this fast in practice, but are constrained to e.g. a 16-50MHz SPI bus clock speed, capping the maximum update rate significantly. Can we do anything about this?
The fbcp-ili9341 project started out as a display driver for the Adafruit 2.8" 320x240 TFT w/ Touch screen for Raspberry Pi display that utilizes the ILI9341 controller. On that display, fbcp-ili9341 can achieve a 60fps update rate, depending on the content that is being displayed. Check out these videos for examples of the driver in action:
Good old interlacing is added into the mix: if the amount of pixels that needs updating is detected to be too much that the SPI bus cannot handle it, the driver adaptively resorts to doing an interlaced update, uploading even and odd scanlines at subsequent frames. Once the number of pending pixels to write returns to manageable amounts, progressive updating is resumed. This effectively doubles the maximum display update rate. (If you do not like the visual appearance that interlacing causes, it is easy to disable this by uncommenting the line #define NO_INTERLACING in file config.h)
This driver does not utilize the notro/fbtft framebuffer driver, so that needs to be disabled if active. That is, if your /boot/config.txt file has lines that look something like dtoverlay=pitft28r, ..., dtoverlay=waveshare32b, ... or dtoverlay=flexfb, ..., those should be removed.
This program neither utilizes the default SPI driver, so a line such as dtparam=spi=on in /boot/config.txt should also be removed so that it will not cause conflicts.
If you have been running existing fbcp driver, make sure to remove that e.g. via a sudo pkill fbcp first (while running in SSH prompt or connected to a HDMI display), these two cannot run at the same time. If /etc/rc.local or /etc/init.d contains an entry to start up fbcp at boot, that directive should be deleted.
When using one of the displays that stack on top of the Pi that are already recognized by fbcp-ili9341, you don"t need to specify the GPIO pin assignments, but fbcp-ili9341 code already has those. Pass one of the following CMake directives for the hats:
-DPIRATE_AUDIO_ST7789_HAT=ON: If specified, targets a Pirate Audio 240x240, 1.3inch IPS LCD display HAT for Raspberry Pi with ST7789 display controller
-DKEDEI_V63_MPI3501=ON: If specified, targets a KeDei 3.5 inch SPI TFTLCD 480*320 16bit/18bit version 6.3 2018/4/9 display with MPI3501 display controller.
-DGPIO_TFT_DATA_CONTROL=number: Specifies/overrides which GPIO pin to use for the Data/Control (DC) line on the 4-wire SPI communication. This pin number is specified in BCM pin numbers. If you have a 3-wire SPI display that does not have a Data/Control line, set this value to -1, i.e. -DGPIO_TFT_DATA_CONTROL=-1 to tell fbcp-ili9341 to target 3-wire ("9-bit") SPI communication.
-DGPIO_TFT_RESET_PIN=number: Specifies/overrides which GPIO pin to use for the display Reset line. This pin number is specified in BCM pin numbers. If omitted, it is assumed that the display does not have a Reset pin, and is always on.
-DGPIO_TFT_BACKLIGHT=number: Specifies/overrides which GPIO pin to use for the display backlight line. This pin number is specified in BCM pin numbers. If omitted, it is assumed that the display does not have a GPIO-controlled backlight pin, and is always on. If setting this, also see the #define BACKLIGHT_CONTROL option in config.h.
In addition to the above CMake directives, there are various defines scattered around the codebase, mostly in config.h, that control different runtime options. Edit those directly to further tune the behavior of the program. In particular, after you have finished with the setup, you may want to build with -DSTATISTICS=0 option in CMake configuration line.
Here is a full example of what to type to build and run, if you have the Adafruit 2.8" 320x240 TFT w/ Touch screen for Raspberry Pi with ILI9341 controller:
These lines hint native applications about the default display mode, and let them render to the native resolution of the TFT display. This can however prevent the use of the HDMI connector, if the HDMI connected display does not support such a small resolution. As a compromise, if both HDMI and SPI displays want to be used at the same time, some other compatible resolution such as 640x480 can be used. See Raspberry Pi HDMI documentation for the available options to do this.
On the other hand, it is desirable to control how much CPU time fbcp-ili9341 is allowed to use. The default build settings are tuned to maximize the display refresh rate at the expense of power consumption on Pi 3B. On Pi Zero, the opposite is done, i.e. by default the driver optimizes for battery saving instead of maximal display update speed. The following options can be controlled to balance between these two:
The main option to control CPU usage vs performance aspect is the option #define ALL_TASKS_SHOULD_DMA in config.h. Enabling this option will greatly reduce CPU usage. If this option is disabled, SPI bus utilization is maximized but CPU usage can be up to 80%-120%. When this option is enabled, CPU usage is generally up to around 15%-30%. Maximal CPU usage occurs when watching a video, or playing a fast moving game. If nothing is changing on the screen, CPU consumption of the driver should go down very close to 0-5%. By default #define ALL_TASKS_SHOULD_DMA is enabled for Pi Zero, but disabled for Pi 3B.
The CMake option -DUSE_DMA_TRANSFERS=ON should always be enabled for good low CPU usage. If DMA transfers are disabled, the driver will run in Polled SPI mode, which generally utilizes a full dedicated single core of CPU time. If DMA transfers are causing issues, try adjusting the DMA send and receive channels to use for SPI communication with -DDMA_TX_CHANNEL=
The option #define RUN_WITH_REALTIME_THREAD_PRIORITY can be enabled to make the driver run at realtime process priority. This can lock up the system however, but still made available for advanced experimentation.
If USE_GPU_VSYNC is disabled, then a busy spinning GPU frame snapshotting thread is used to drive the updates. This will produce smoother animation in content that does not maintain a fixed 60Hz rate. Especially in OpenTyrian, a game that renders at a fixed 36fps and has slowly scrolling scenery, the stuttering caused by USE_GPU_VSYNC is particularly visible. Running on Pi 3B without USE_GPU_VSYNC enabled produces visually smoother looking scrolling on an Adafruit 2.8" ILI9341 PiTFT set to update at 119Hz, compared to enabling USE_GPU_VSYNC on the same setup. Without USE_GPU_VSYNC, the dedicated frame polling loop thread "finds" the 36Hz update rate of the game, and then pushes pixels to the display at this exact rate. This works nicely since SPI displays disregard vsync - the result is that frames are pushed out to the SPI display immediately as they become available, instead of pulling them at a fixed 60Hz rate like HDMI does.
The codebase captures screen framebuffers by snapshotting via the VideoCore vc_dispmanx_snapshot() API, and the obtained pixels are then routed on to the SPI-based display. This kind of polling is performed, since there does not exist an event-based mechanism to get new frames from the GPU as they are produced. The result is inefficient and can easily cause stuttering, since different applications produce frames at different paces. Ideally the code would ask the VideoCore API to receive finished frames in callback notifications immediately after they are rendered, but this kind of functionality does not exist in the current GPU driver stack. In the absence of such event delivery mechanism, the code has to resort to polling snapshots of the display framebuffer using carefully timed heuristics to balance between keeping latency and stuttering low, while not causing excessive power consumption. These heuristics keep continuously guessing the update rate of the animation on screen, and they have been tuned to ensure that CPU usage goes down to 0% when there is no detected activity on screen, but it is certainly not perfect. This GPU limitation is discussed at raspberrypi/userland#440. If you"d like to see fbcp-ili9341 operation reduce latency, stuttering and power consumption, please throw a (kind!) comment or a thumbs up emoji in that bug thread to share that you care about this, and perhaps Raspberry Pi engineers might pick the improvement up on the development roadmap. If this issue is resolved, all of the #define USE_GPU_VSYNC, #define SAVE_BATTERY_BY_PREDICTING_FRAME_ARRIVAL_TIMES and #define SELF_SYNCHRONIZE_TO_GPU_VSYNC_PRODUCED_NEW_FRAMES hacks from the previous section could be deleted from the driver, hopefully leading to a best of all worlds scenario without drawbacks.
At the moment fbcp-ili9341 is only likely to work on 32-bit OSes, on Raspbian/Ubuntu/Debian family of distributions, where Broadcom and DispmanX libraries are available. 64-bit operating systems do not currently work (see issue #43). It should be possible to port the driver to 64-bit and other OSes, though the amount of work has not been explored.
The fbcp part in the name means framebuffer copy; specifically for the ILI9341 controller. fbcp-ili9341 is not actually a framebuffer copying driver, it does not create a secondary framebuffer that it would copy bytes across to from the primary framebuffer. It is also no longer a driver only for the ILI9341 controller. A more appropriate name might be userland-raspi-spi-display-driver or something like that, but the original name stuck.
I don"t know, I don"t currently have any to test. Perhaps the code does need some model specific configuration, or perhaps it might work out of the box. I only have Pi 3B, Pi 3B+, Pi Zero W and a Pi 3 Compute Module based systems to experiment on. Pi 2 B has been reported to work by users (#17).
If fbcp-ili9341 does not support your display controller, you will have to write support for it. fbcp-ili9341 does not have a "generic SPI TFT driver routine" that might work across multiple devices, but needs specific code for each. If you have the spec sheet available, you can ask for advice, but please do not request to add support to a display controller "blind", that is not possible.
Perhaps. This is a more recent experimental feature that may not be as stable, and there are some limitations, but 3-wire ("9-bit") SPI display support is now available. If you have a 3-wire SPI display, i.e. one that does not have a Data/Control (DC) GPIO pin to connect, configure it via CMake with directive -DGPIO_TFT_DATA_CONTROL=-1 to tell fbcp-ili9341 that it should be driving the display with 3-wire protocol.
No. Those are completely different technologies altogether. It should be possible to port the driver algorithm to work on I2C however, if someone is interested.
At the moment one cannot utilize the XPT2046/ADS7846 touch controllers while running fbcp-ili9341, so touch is mutually incompatible with this driver. In order for fbcp-ili9341 to function, you will need to remove all dtoverlays in /boot/config.txt related to touch.
In this kind of mode, you would probably strip the DispmanX bits out of fbcp-ili9341, and recast it as a static library that you would link to in your drawing application, and instead of snapshotting frames, you can then programmatically write to a framebuffer in memory from your C/C++ code.
double check that the display controller is really what you expected. Trying to drive with the display with wrong initialization code usually results in the display not reacting, and the screen stays white,
This suggests that the power line or the backlight line might not be properly connected. Or if the backlight connects to a GPIO pin on the Pi (and not a voltage pin), then it may be that the pin is not in correct state for the backlight to turn on. Most of the LCD TFT displays I have immediately light up their backlight when they receive power. The Tontec one has a backlight GPIO pin that boots up high but must be pulled low to activate the backlight. OLED displays on the other hand seem to stay all black even after they do get power, while waiting for their initialization to be performed, so for OLEDs it may be normal for nothing to show up on the screen immediately after boot.
If the backlight connects to a GPIO pin, you may need to define -DGPIO_TFT_BACKLIGHT=
This suggests same as above, increase SPI bus divisor or troubleshoot disabling DMA. If DMA is detected to be the culprit, try changing up the DMA channels. Double check that /boot/config.txt does not have any dtoverlays regarding other SPI display drivers or touch screen controllers, and that it does NOT have a dtparam=spi=on line in it - fbcp-ili9341 does not use the Linux kernel SPI driver.
Double check the Data/Command (D/C) GPIO pin physically, and in CMake command line. Whenever fbcp-ili9341 refers to pin numbers, they are always specified in BCM pin numbers. Try setting a higher -DSPI_BUS_CLOCK_DIVISOR= value to CMake. Make sure no other fbcp programs or SPI drivers or dtoverlays are enabled.
As the number of supported displays, Raspberry Pi device models, Raspbian/Retropie/Lakka OS versions, accompanied C++ compiler versions and fbcp-ili9341 build options have grown in number, there is a combinatorial explosion of all possible build modes that one can put the codebase through, so it is not easy to keep every possible combo tested all the time. Something may have regressed or gotten outdated. Stay calm, and report a bug.
All the ILI9341 displays work nice and super fast at ~70-80MHz. My WaveShare 3.5" 320x480 ILI9486 display runs really slow compared to its pixel resolution, ~32MHz only. See fbcp-ili9341 ported to ILI9486 WaveShare 3.5" (B) SpotPear 320x480 SPI display for a video of this display in action. Adafruit"s 320x480 3.5" HX8357D PiTFTs is ~64% faster in comparison.
The Tontec MZ61581 controller based 320x480 3.5" display on the other hand can be driven insanely fast at up to 140MHz! These seem to be quite hard to come by though and they are expensive. Tontec seems to have gone out of business and for example the domain itontec.com from which the supplied instructions sheet asks to download original drivers from is no longer registered. I was able to find one from eBay for testing.
Port fbcp-ili9341 to work as a static code library that one can link to another application for CPU-based drawing directly to display, bypassing inefficiencies and latency of the general purpose Linux DispmanX/graphics stack.
Optimize ALL_TASKS_SHOULD_DMA mode to be always superior in performance and CPU usage so that the non-ALL_TASKS_SHOULD_DMA path can be dropped from the codebase. (probably requires the above chaining to function efficiently)
This driver is licensed under the MIT License. See LICENSE.txt. In nonlegal terms, it"s yours for both free and commercial projects, DIY packages, kickstarters, Etsys and Ebays, and you don"t owe back a dime. Feel free to apply and derive as you wish.

After execution, the driver will be installed. The system will automatically restart, and the display screen will rotate 90 degrees to display and touch normally.
( " XXX-show " can be changed to the corresponding driver, and " 90 " can be changed to 0, 90, 180 and 270, respectively representing rotation angles of 0 degrees, 90 degrees, 180 degrees, 270 degrees)
The majority of LCD displays contain a built in LCD controller. The exception to this is a segment, or glass-only, LCD that uses a multiplex method to drive the segments. All other display technologies such as: TFT, OLED, character, graphic, UWVD and FSC contain a built-in LCD controller.
The LCD controller is a small microprocessor that converts the customer’s software code (aka firmware) to information that the LCD can understand. The LCD screen then displays graphics, characters, images and numbers to be seen by the end user.
Each LCD requires only one controller/driver chip. Depending on the number of segments that need to be driven, additional driver chips may be required if there are a large number of segments to drive/refresh.
One key advantage of a LCD controller is that it provides a variety of standard bus interfaces that make it easy to program. These include SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface), i2C (I squared C), Parallel (4 bit, 8 bit, 16 bit) and LVDS (Low-voltage differential signaling).
The controller is chosen by the LCD supplier. Our goal is to choose a chip that will be in production for many years. It is possible to use a controller that is preferred by the customer, but we do not recommend this since some controllers have higher cost and longer lead-times than other controllers.
If you need to drive additional segments beyond the capability of the LCD controller/driver chip, you can add an additional driver chip, but there is always just one controller.
Do you need help with a new design and not sure which LCD or controller to choose? Make some coffee and pick up the phone to call FocusLCDs.com at 480-503-4295 or contact us. We’d be happy to help and assist you.

There are a few common TFT display drivers on the electronics hobbyist market, and a handful of libraries that work with them. TFT displays are high resolution and full color, unlike the OLED or ePaper displays mentioned in this repository. Most libraries for color TFT displays implement the usual 24-bit RGB color space, where 0xFF0000 is red, 0x00FF00 is green, and 0x0000FF is blue.
TFT displays can be slow to update. Therefore, it’s sometimes usefil to draw only part of the display at once. Adafruits GFX library includes a Canvas class, which lets you update elements offscreen and then draw them. It doesn’t speed up the display, but it can simplify drawing a subset of the screen. See this example to see it in use. Other libraries don’t include a canvas, but you can draw a filled rectangle over part of the screen and then draw on top of it, as shown in this example for the ILI9225.
Most TFT displays tend to have an SPI interface, with some extra pins, as explained on the main page of this repo. Some displays, like MakerFocus’ 1.3” TFT, do not implement the CS pin. For this board and others like it, initializing them with SPI_MODE3 works.
MakerFocus 1.3” LCD Display, no MicroSD, Amazon link - This display does not have a CS pin, so it can’t be used with other SPI devices at the same time. It works with the Adafruit_ST7789 library, but you have to change the init() function to include the SPI mode like so:
There’s no standard library for TFT screens, unfortunately. Vendors tend to support the displays they make in their own breakout boards, and not others. As with other types of displays, a well-supported library like the Adafruit libraries makes the display worth more, but limits you to the types of displays that vendor offers. Display manufacturers like Ilitek and Sitronix do not appear to release their own libraries for their displays.
The TFT_22_ILI9225 library works with this display, and its methods are well documented. Its graphics API is different than some of the other graphics libraries, and doesn’t implement the Printable API, so you can’t use commands like print() and println() with it. It has its own drawText() method instead, which takes an Arduino String object. It comes with a few built-in fonts, and includes many of the Adafruit GFX fonts, and you can generate your own fonts using the The squix.ch custom font generator. Set the settings to

As a 2inch IPS display module with a resolution of 240 * 320, it uses an SPI interface for communication. The LCD has an internal controller with basic functions, which can be used to draw points, lines, circles, and rectangles, and display English, Chinese as well as pictures.
The 2inch LCD uses the PH2.0 8PIN interface, which can be connected to the Raspberry Pi according to the above table: (Please connect according to the pin definition table. The color of the wiring in the picture is for reference only, and the actual color shall prevail.)
The LCD supports 12-bit, 16-bit, and 18-bit input color formats per pixel, namely RGB444, RGB565, and RGB666 three color formats, this demo uses RGB565 color format, which is also a commonly used RGB format.
For most LCD controllers, the communication mode of the controller can be configured, usually with an 8080 parallel interface, three-wire SPI, four-wire SPI, and other communication methods. This LCD uses a four-wire SPI communication interface, which can greatly save the GPIO port, and the communication speed will be faster.
2. The module_init() function is automatically called in the INIT () initializer on the LCD, but the module_exit() function needs to be called by itself
Python has an image library PIL official library link, it do not need to write code from the logical layer like C, can directly call to the image library for image processing. The following will take 1.54inch LCD as an example, we provide a brief description for the demo.

The RPi LCD can be driven in two ways: Method 1. install driver to your Raspbian OS. Method 2. use the Ready-to-use image file of which LCD driver was pre-installed.
3) Connect the TF card to the Raspberry Pi, start the Raspberry Pi. The LCD will display after booting up, and then log in to the Raspberry Pi terminal,(You may need to connect a keyboard and HDMI LCD to Pi for driver installing, or log in remotely with SSH)
1. Executing apt-get upgrade will cause the LCD to fail to work properly. In this case, you need to edit the config.txt file in the SD card and delete this sentence: dtoverlay=ads7846.
This LCD can be calibrated through the xinput-calibrator program. Note: The Raspberry Pi must be connected to the network, or else the program won"t be successfully installed.

In this article, you will learn how to use TFT LCDs by Arduino boards. From basic commands to professional designs and technics are all explained here.
There are several components to achieve this. LEDs, 7-segments, Character and Graphic displays, and full-color TFT LCDs. The right component for your projects depends on the amount of data to be displayed, type of user interaction, and processor capacity.
TFT LCD is a variant of a liquid-crystal display (LCD) that uses thin-film-transistor (TFT) technology to improve image qualities such as addressability and contrast. A TFT LCD is an active matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven LCDs with a few segments.
In Arduino-based projects, the processor frequency is low. So it is not possible to display complex, high definition images and high-speed motions. Therefore, full-color TFT LCDs can only be used to display simple data and commands.
There are several components to achieve this. LEDs, 7-segments, Character and Graphic displays, and full-color TFT LCDs. The right component for your projects depends on the amount of data to be displayed, type of user interaction, and processor capacity.
TFT LCD is a variant of a liquid-crystal display (LCD) that uses thin-film-transistor (TFT) technology to improve image qualities such as addressability and contrast. A TFT LCD is an active matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven LCDs with a few segments.
In Arduino-based projects, the processor frequency is low. So it is not possible to display complex, high definition images and high-speed motions. Therefore, full-color TFT LCDs can only be used to display simple data and commands.
After choosing the right display, It’s time to choose the right controller. If you want to display characters, tests, numbers and static images and the speed of display is not important, the Atmega328 Arduino boards (such as Arduino UNO) are a proper choice. If the size of your code is big, The UNO board may not be enough. You can use Arduino Mega2560 instead. And if you want to show high resolution images and motions with high speed, you should use the ARM core Arduino boards such as Arduino DUE.
In electronics/computer hardware a display driver is usually a semiconductor integrated circuit (but may alternatively comprise a state machine made of discrete logic and other components) which provides an interface function between a microprocessor, microcontroller, ASIC or general-purpose peripheral interface and a particular type of display device, e.g. LCD, LED, OLED, ePaper, CRT, Vacuum fluorescent or Nixie.
The display driver will typically accept commands and data using an industry-standard general-purpose serial or parallel interface, such as TTL, CMOS, RS232, SPI, I2C, etc. and generate signals with suitable voltage, current, timing and demultiplexing to make the display show the desired text or image.
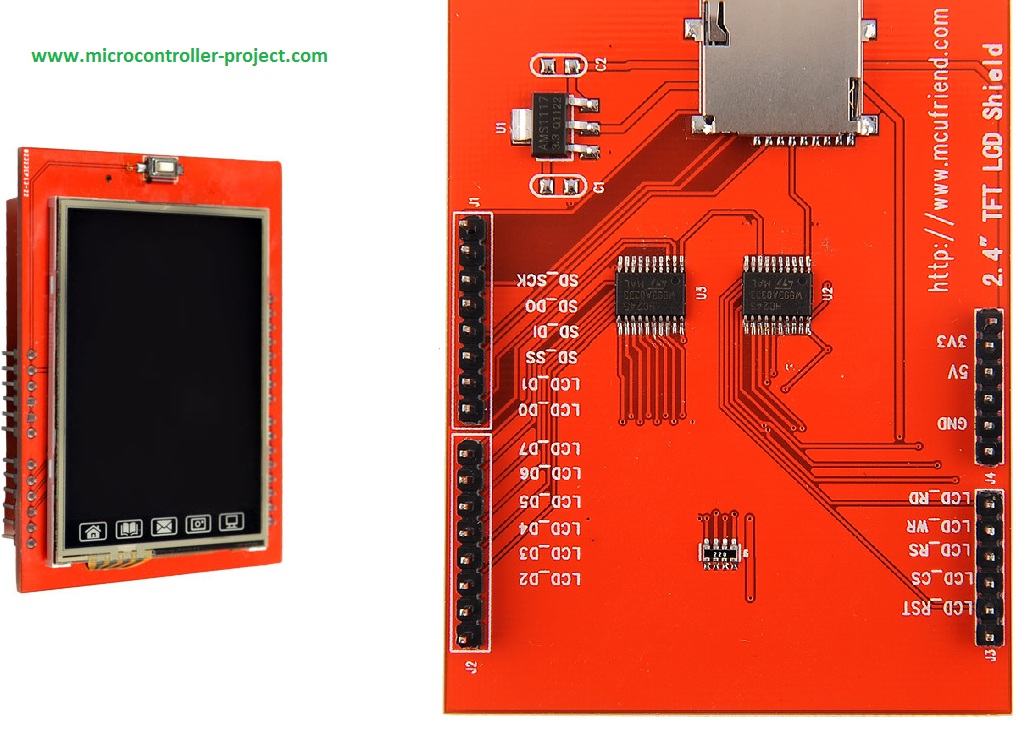
The LCDs manufacturers use different drivers in their products. Some of them are more popular and some of them are very unknown. To run your display easily, you should use Arduino LCDs libraries and add them to your code. Otherwise running the display may be very difficult. There are many free libraries you can find on the internet but the important point about the libraries is their compatibility with the LCD’s driver. The driver of your LCD must be known by your library. In this article, we use the Adafruit GFX library and MCUFRIEND KBV library and example codes. You can download them from the following links.
You must add the library and then upload the code. If it is the first time you run an Arduino board, don’t worry. Just follow these steps:Go to www.arduino.cc/en/Main/Software and download the software of your OS. Install the IDE software as instructed.
By these two functions, You can find out the resolution of the display. Just add them to the code and put the outputs in a uint16_t variable. Then read it from the Serial port by Serial.println(); . First add Serial.begin(9600); in setup().
First you should convert your image to hex code. Download the software from the following link. if you don’t want to change the settings of the software, you must invert the color of the image and make the image horizontally mirrored and rotate it 90 degrees counterclockwise. Now add it to the software and convert it. Open the exported file and copy the hex code to Arduino IDE. x and y are locations of the image. sx and sy are sizes of image. you can change the color of the image in the last input.
Upload your image and download the converted file that the UTFT libraries can process. Now copy the hex code to Arduino IDE. x and y are locations of the image. sx and sy are size of the image.
In this template, We just used a string and 8 filled circles that change their colors in order. To draw circles around a static point ,You can use sin(); and cos(); functions. you should define the PI number . To change colors, you can use color565(); function and replace your RGB code.
In this template, We converted a .jpg image to .c file and added to the code, wrote a string and used the fade code to display. Then we used scroll code to move the screen left. Download the .h file and add it to the folder of the Arduino sketch.
In this template, We used sin(); and cos(); functions to draw Arcs with our desired thickness and displayed number by text printing function. Then we converted an image to hex code and added them to the code and displayed the image by bitmap function. Then we used draw lines function to change the style of the image. Download the .h file and add it to the folder of the Arduino sketch.
In this template, We added a converted image to code and then used two black and white arcs to create the pointer of volumes. Download the .h file and add it to the folder of the Arduino sketch.
while (a < b) { Serial.println(a); j = 80 * (sin(PI * a / 2000)); i = 80 * (cos(PI * a / 2000)); j2 = 50 * (sin(PI * a / 2000)); i2 = 50 * (cos(PI * a / 2000)); tft.drawLine(i2 + 235, j2 + 169, i + 235, j + 169, tft.color565(0, 255, 255)); tft.fillRect(200, 153, 75, 33, 0x0000); tft.setTextSize(3); tft.setTextColor(0xffff); if ((a/20)>99)
while (b < a) { j = 80 * (sin(PI * a / 2000)); i = 80 * (cos(PI * a / 2000)); j2 = 50 * (sin(PI * a / 2000)); i2 = 50 * (cos(PI * a / 2000)); tft.drawLine(i2 + 235, j2 + 169, i + 235, j + 169, tft.color565(0, 0, 0)); tft.fillRect(200, 153, 75, 33, 0x0000); tft.setTextSize(3); tft.setTextColor(0xffff); if ((a/20)>99)
In this template, We just display some images by RGBbitmap and bitmap functions. Just make a code for touchscreen and use this template. Download the .h file and add it to folder of the Arduino sketch.
The speed of playing all the GIF files are edited and we made them faster or slower for better understanding. The speed of motions depends on the speed of your processor or type of code or size and thickness of elements in the code.

The new line of 3.5” TFT displays with IPS technology is now available! Three touchscreen options are available: capacitive, resistive, or without a touchscreen.
I got my hands on a 3.5Inch TFT LCD Screen Module for Arduino Mega and Uno on Amazon, and I was wondering whether I could make it work with a Raspberry Pi 4, and ultimately a CM4. Here is a picture of the connectors available on the module:

I just purchased a 2.8" TFT Touch Shield (PID 1651) and a metro board (PID 50) as well as an Arduino mega. The shield will not work with either of the arduinos. I have checked and set (and unset!) the #define in Adafruit_tftlcd.h and nothing changes. When I run the graphics test I get the following on the monitor :
I also have the FTDI driver installed (or it would not upload). This is on a new MacBook Pro with a fresh copy of the Arduino studio and the port/board are set correctly
Started off on the ardu-phone page, followed it to the TFT tutorial page and loaded the libraries from there. Should I delete the TFT library and only use the ILI9341 ?
8-Bit Library InstallWe have example code ready to go for use with these TFTs. It"s written for Arduino, which should be portable to any microcontroller by adapting the C++ source.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey