tft lcd screen fritzing price
The LCD display you choose doesn’t really matter either. Sparkfun makes great products and they work. I guess my thoughts on the display was based on the cost. I use 2.8" TFT LCD displays with touchscreens for half the cost of that character display.
The LCD display you choose doesn’t really matter either. Sparkfun makes great products and they work. I guess my thoughts on the display was based on the cost. I use 2.8" TFT LCD displays with touchscreens for half the cost of that character display.

I don’t think inkscape is quirky, I get along with it quite well considering I am a newbie at it. I think the inkscape to Fritzing interaction needs work and I think most of the problems can be solved on the inkscape side of things.
This is slightly misleading in that copper1 is actually under copper0 not silkscreen, but the order should be silkscreen, copper1 with copper0 as a group under copper1 (at present copper1 and copper0 are reversed.) I don’t know of any problem this causes other than Fritzing will prefer to select silkscreen if it is the lowest group (thus a warning rather than an error.)
While this shows as an error (because in schematic it likely is one), in this case it is ignorable, because Fritzing will use the center of the pin as the termination point as was intended. Technically you can and should remove the connectorxterminal elements in breadboard, but it won’t hurt anything. repeats for all the pins on breadboard.
With that done and no major problems, load the part in to Fritzing and test it. This is to catch errors that the script can not (such as a terminalId existing but being in the wrong place). Here is a sketch of a typical test:

Download each library and unzip the folders. Rename them to "Adafruit_ST7735" and "Adafruit_GFX" and place each folder inside your Arduino Libraries folder. I"ve attached a screenshot of the libraries in the correct folder. Once installed, you are ready to operate the screen! Inside the Adafruit ST7735 library is a file called graphicstest.ino which you can upload to your Arduino and it will run through a number of functions that draw objects to the screen. However, this file will need some altering to adapt the pins to your layout.

The SparkFun TFT LCD Breakout is a versatile, colorful, and easy way to experiment with graphics or create a user interface for your project. With a 4-wire SPI interface and microSD card holder, you can use this breakout to easily add visual display/interface capabilities to a project as well as providing all the storage you might need for multimedia files.
Out of the box, the SparkFun TFT LCD Breakout will come with a large backing PCB that makes it easy to securely mount the display in a project. If you need a more flexible solution you can remove the display module, snap off half the backing board, and then re-insert the display module. When this is done you"ll be left with the bare minimum frame around the display to more seamlessly integrate with your project.
Sometimes it is handy to have a small screen in your Arduino project. The 0.96 inch IPS color diplay is perfect for this. You can get the original Adafruit Color TFT display with SD card readerfor this for $20 (excluding shipping costs), but you can also find a clone on Chinese reseller websites or eBay. Mine did not include a SD card reader, but it was $3 (including shipping).
To make your project better to understand, you can also add board diagrams. This can be done using Fritzing. Just download the version supported by your OS. I have used the Windows 64-bit version and just needed to unzip it and start Fritzing.exe.
In my case I also needed a part that was not in the Fritzing database. Luckily there is a community that submits parts. It is located on the forum page. Adafruit also has parts on their Github page. To import the part just click the icon in the Parts frame and select Import...
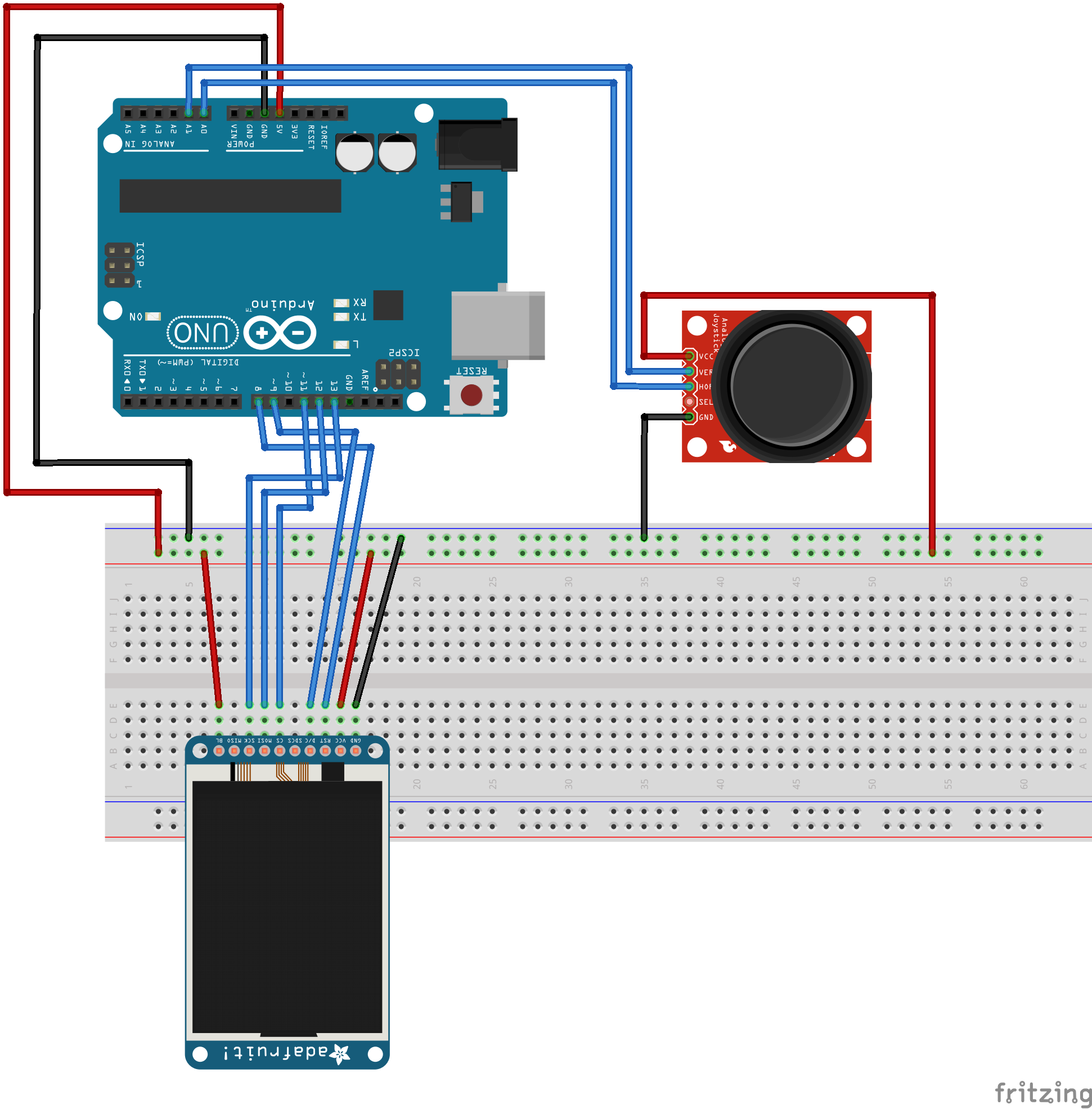
I was now able to create the breadboard diagram. Below you see the breadboard diagram created with Fritzing app of how to connect the display to Arduino Nano.
The display part is Adafruit based, but I have created a table on how to translate the Original Adafruit 0.96" 160x80 Color TFT Display to Chinese Clone IPS 0.96 inch 7P SPI ST7735 module
Adafruit_ST7735 is the library we need to pair with the graphics library for hardware specific functions of the ST7735 TFT Display/SD-Card controller.
Basically, besides the obvious backlight, we tell the controller first what we are talking to with the CS pins. CS(TFT) selects data to be for the Display, and CS(SD) to set data for the SD-Card. Data is written to the selected device through SDA (display) or MOSI (SD-Card). Data is read from the SD-Card through MISO.
You can name your BMP file “parrot.bmp” or modify the Sketch to have the proper filename (in “spitftbitmap” line 70, and in “soft_spitftbitmap” line 74).
#define SD_CS 4 // Chip select line for SD card#define TFT_CS 10 // Chip select line for TFT display#define TFT_DC 9 // Data/command line for TFT#define TFT_RST 8 // Reset line for TFT (or connect to +5V)
#define SD_CS 4 // Chip select line for SD card#define TFT_CS 10 // Chip select line for TFT display#define TFT_DC 9 // Data/command line for TFT#define TFT_RST 8 // Reset line for TFT (or connect to +5V)
However, if your application needs your screen sideways, then you’d want to rotate the screen 90 degrees, effectively changing the display from a 128×160 pixel (WxH) screen to a 160×128 pixel display. Valid values are: 0 (0 degrees), 1 (90 degrees), 2 (180 degrees) and 3 (270 degrees).
tft.print("Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Curabitur adipiscing ante sed nibh tincidunt feugiat. Maecenas enim massa, fringilla sed malesuada et, malesuada sit amet turpis. Sed porttitor neque ut ante pretium vitae malesuada nunc bibendum. Nullam aliquet ultrices massa eu hendrerit. Ut sed nisi lorem. In vestibulum purus a tortor imperdiet posuere. ");




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey