arduino uno 2.4 tft lcd display shield touch panel ili9341 in stock
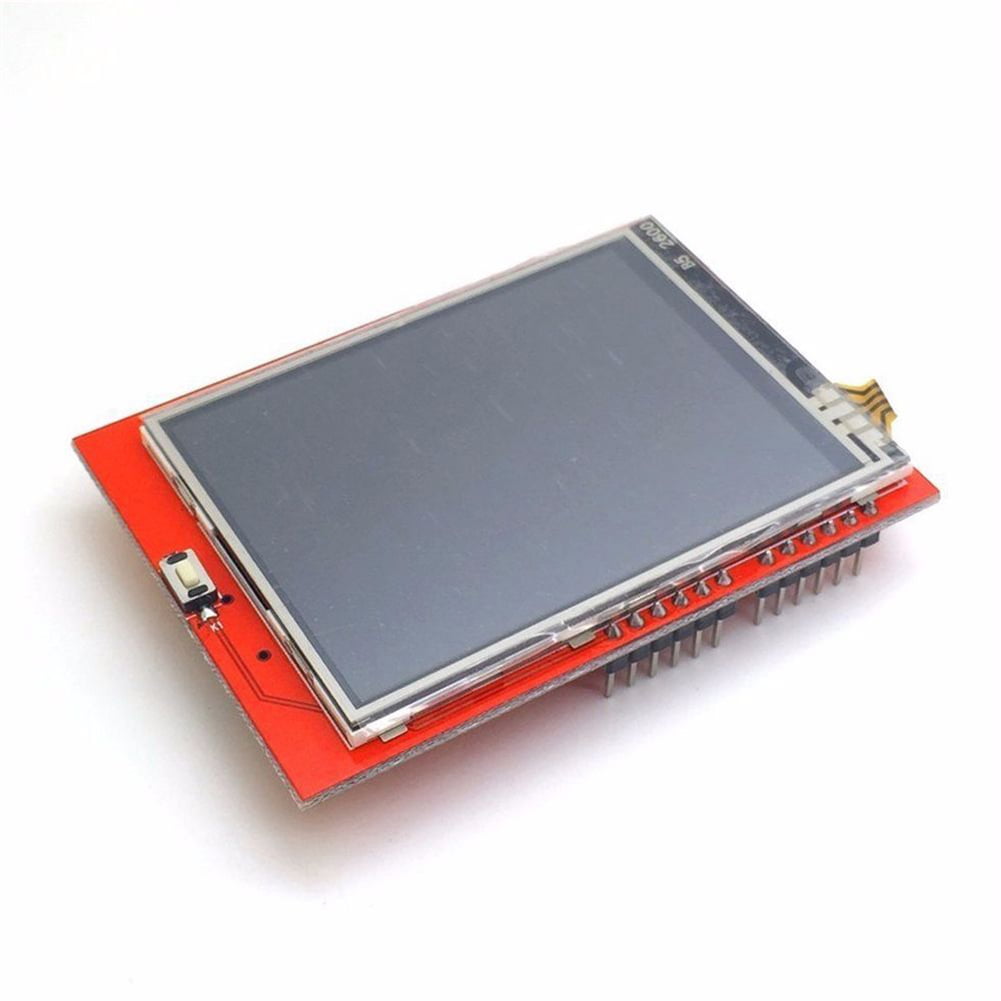

Features:2.4" diagonal LCD TFT Touch Panel displayBright, 4 white-LED backlight, on by default but you can connect the transistor to a digital pin for backlight controlColorful, 18-bit 262,000 different shades4-wire resistive touchscreen8 bit digital interface, plus 4 control linesUses digital pins 5-13 and analog 0-3. That means you can use digital pins 2, 3 and analog 4 and 5. Pin 12 is available if not using the micro SD5V compatible, use with 3.3V or 5V logicFor Arduino UNO R3 MEGA2560
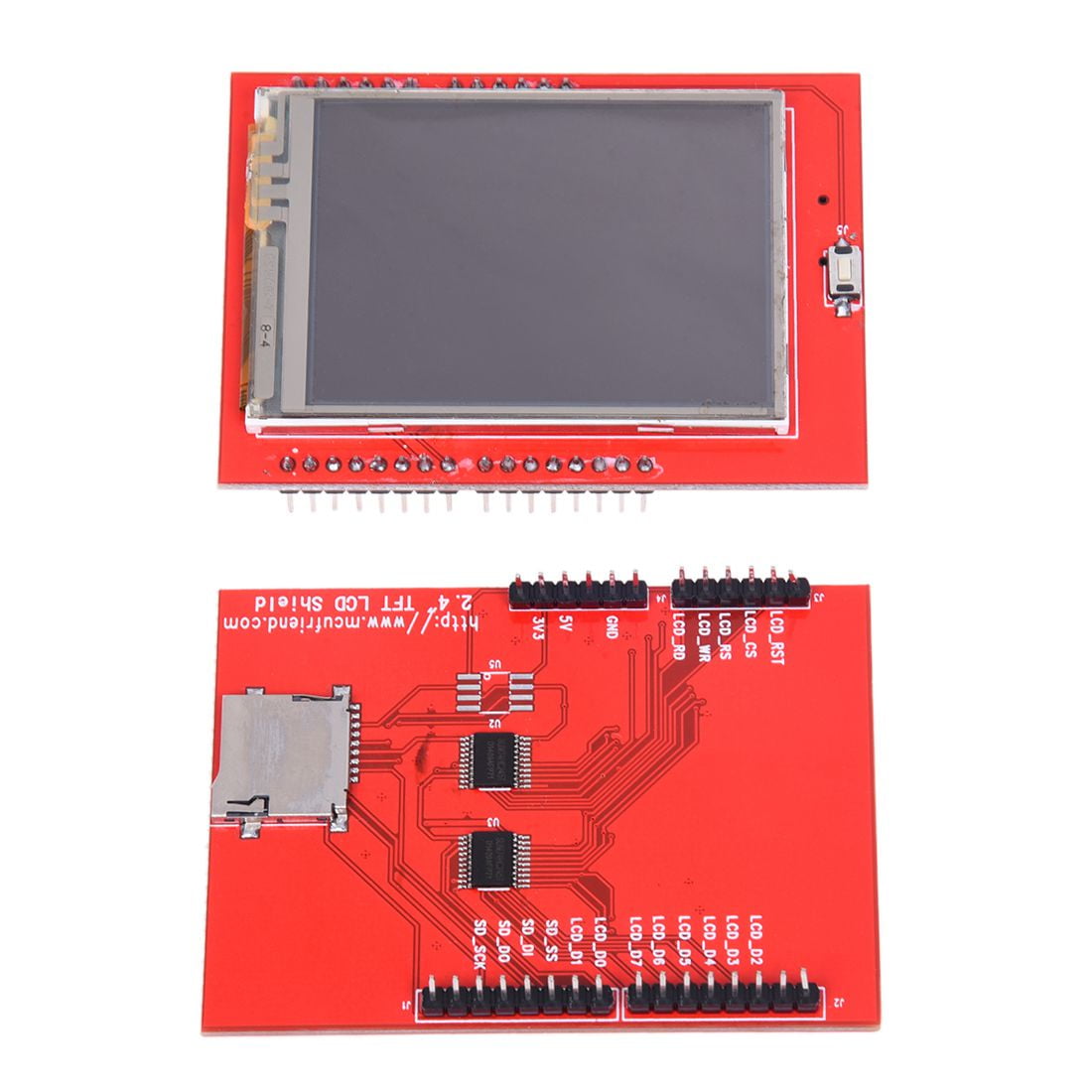
Spice up your Arduino project with a beautiful touchscreen display shield with built in microSD card connection. This TFT display is 2.4" diagonal and colorful (18-bit 262,000 different shades)! 240x320 pixels with individual pixel control. As a bonus, this display has a optional capacitive touch panel and resistive touch panel with controller XPT2046 attached by default.
The shield is fully assembled, tested and ready to go. No wiring, no soldering! Simply plug it in and load up our library - you"ll have it running in under 10 minutes! Works best with any classic Arduino (UNO/Due/Mega 2560).
This display shield has a controller built into it with RAM buffering, so that almost no work is done by the microcontroller. You can connect more sensors, buttons and LEDs.
Of course, we wouldn"t just leave you with a datasheet and a "good luck!" - we"ve written a full open source graphics library at the bottom of this page that can draw pixels, lines, rectangles, circles and text. We also have a touch screen library that detects x,y and z (pressure) and example code to demonstrate all of it. The code is written for Arduino but can be easily ported to your favorite microcontroller!
If you"ve had a lot of Arduino DUEs go through your hands (or if you are just unlucky), chances are you’ve come across at least one that does not start-up properly.The symptom is simple: you power up the Arduino but it doesn’t appear to “boot”. Your code simply doesn"t start running.You might have noticed that resetting the board (by pressing the reset button) causes the board to start-up normally.The fix is simple,here is the solution.

In this tutorial, you will learn how to use and set up 2.4″ Touch LCD Shield for Arduino. First, you’ll see some general information about this shield. And after learning how to set the shield up, you’ll see 3 practical projects.
The role of screens in electronic projects is very important. Screens can be of very simple types such as 7 Segment or character LCDs or more advanced models like OLEDs and TFT LCDs.
One of the most important features of this LCD is including a touch panel. If you are about to use the LCD, you need to know the coordinates of the point you touch. To do so, you should upload the following code on your Arduino board and open the serial monitor. Then touch your desired location and write the coordinates displayed on the serial monitor. You can use this coordination in any other project.
To display pictures on this LCD you should save the picture in 24bit BMP colored format and size of 240*320. Then move them to SD card and put the SD card in the LCD shield. we use the following function to display pictures. This function has 3 arguments; the first one stands for the pictures name, and the second and third arguments are for length and width coordinates of the top left corner of the picture.
If you want to display pictures without using an SD card, you can convert it to code and then display it. You can display even several photos sequentially without delay to create an animation. (Check this) But be aware that in this case, Arduino UNO may not be suitable (because of low processor speed). We recommend using the Arduino Mega or Arduino DUE.

ILI9341 is integrated inside the display. It drives the display and has nothing to do with touchscreen (Although the shield connects some pins of ILI9341 together with pins of the touchscreen).
ILI9341 interpretes input byte as command (if RS=0) or as data/parameter (RS=1). You have first to send a command to ILI and then write or read data/parameters. CS pin has to be LOW during the communication, WR rising from LOW to HIGH tells to ILI to read byte on data pins. To read a byte from ILI after sending a read command (e.g. 09h - Read Display Status) set RD from HIGH to LOW, so ILI9341 outputs data until RD returns HIGH.
To draw a rectangle (or just one pixel) on the screen you have to tell to ILI the area (start_column, end_column, start_row, end_row, commands 0x2Ah and 0x2Bh) you want to draw. Then command 0x2Ch. Then send in sequence for every single pixel in the area a value of the color to display. The color has 2 byte format.
The touch screen is attached on the surface of the display. It connects through 4 wires, which share arduino pins 8, 9, A2, A3 with ILI. So you can"t write to LCD display and read the touch screen in the same time.
Touch-screen devices using resistive technology, a two-dimensional membrane potentiometer provides x and y coordinates. The top layer is thin glass spaced close to a neighboring inner layer. The underside of the top layer has a transparent conductive coating; the surface of the layer beneath it has a transparent resistive coating. A finger or stylus deforms the glass to contact the underlying layer. Edges of the resistive layer have conductive contacts. Locating the contact point is done by applying a voltage to opposite edges, leaving the other two edges temporarily unconnected. The voltage of the top layer provides one coordinate. Disconnecting those two edges, and applying voltage to the other two, formerly unconnected, provides the other coordinate. Alternating rapidly between pairs of edges provides frequent position updates. An analog-to digital converter provides output data.
First we need to detect if there is a touch. So we connect both wires of one layer/membrane, e.g. X to ground (LOW from ardiuno pins set as output) and one wire from layer Y to pull-up resistor (setting corresponding arduino pin as INPUT_PULLUP). Reading the second wire of Y layer we get HIGH if there is no touch (because of pull-up) and LOW if there is a touch (because of contact with grounded X layer).
Then we need to read a position of a touch. So we set one of the X wires to HIGH (which one depends on on which side of touch screen we want to read min/max value; see variant A/B in the code) and we read analog value on Y. The value should be in the range 0-1023, but touchscreen I tested returns 110-910 (So it need to be calibrated - run ILI9341_7.ino). Then we apply LOW-HIGH on Y layer and read analog value on X.
Touchscreen I tested sometimes wrongly detects a touch, outside of the touched point. To prevent this I added some delays and the X and Y analog value is read repeatedly and touch is approved only if values do not differ (a lot).

The 2.4 inch TFT Touch Screen Module with micro SD card slot is now available as a SHIELD for Arduino UNO. It has a four wire resistive touch screen, a micro SD card socket, a reset switch and a convenient Arduino Uno shield footprint.

In this Arduino touch screen tutorial we will learn how to use TFT LCD Touch Screen with Arduino. You can watch the following video or read the written tutorial below.
For this tutorial I composed three examples. The first example is distance measurement using ultrasonic sensor. The output from the sensor, or the distance is printed on the screen and using the touch screen we can select the units, either centimeters or inches.
The third example is a game. Actually it’s a replica of the popular Flappy Bird game for smartphones. We can play the game using the push button or even using the touch screen itself.
As an example I am using a 3.2” TFT Touch Screen in a combination with a TFT LCD Arduino Mega Shield. We need a shield because the TFT Touch screen works at 3.3V and the Arduino Mega outputs are 5 V. For the first example I have the HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor, then for the second example an RGB LED with three resistors and a push button for the game example. Also I had to make a custom made pin header like this, by soldering pin headers and bend on of them so I could insert them in between the Arduino Board and the TFT Shield.
Here’s the circuit schematic. We will use the GND pin, the digital pins from 8 to 13, as well as the pin number 14. As the 5V pins are already used by the TFT Screen I will use the pin number 13 as VCC, by setting it right away high in the setup section of code.
I will use the UTFT and URTouch libraries made by Henning Karlsen. Here I would like to say thanks to him for the incredible work he has done. The libraries enable really easy use of the TFT Screens, and they work with many different TFT screens sizes, shields and controllers. You can download these libraries from his website, RinkyDinkElectronics.com and also find a lot of demo examples and detailed documentation of how to use them.
After we include the libraries we need to create UTFT and URTouch objects. The parameters of these objects depends on the model of the TFT Screen and Shield and these details can be also found in the documentation of the libraries.
Next we need to define the fonts that are coming with the libraries and also define some variables needed for the program. In the setup section we need to initiate the screen and the touch, define the pin modes for the connected sensor, the led and the button, and initially call the drawHomeSreen() custom function, which will draw the home screen of the program.
So now I will explain how we can make the home screen of the program. With the setBackColor() function we need to set the background color of the text, black one in our case. Then we need to set the color to white, set the big font and using the print() function, we will print the string “Arduino TFT Tutorial” at the center of the screen and 10 pixels down the Y – Axis of the screen. Next we will set the color to red and draw the red line below the text. After that we need to set the color back to white, and print the two other strings, “by HowToMechatronics.com” using the small font and “Select Example” using the big font.
Ok next is the RGB LED Control example. If we press the second button, the drawLedControl() custom function will be called only once for drawing the graphic of that example and the setLedColor() custom function will be repeatedly called. In this function we use the touch screen to set the values of the 3 sliders from 0 to 255. With the if statements we confine the area of each slider and get the X value of the slider. So the values of the X coordinate of each slider are from 38 to 310 pixels and we need to map these values into values from 0 to 255 which will be used as a PWM signal for lighting up the LED. If you need more details how the RGB LED works you can check my particular tutorialfor that. The rest of the code in this custom function is for drawing the sliders. Back in the loop section we only have the back button which also turns off the LED when pressed.
In order the code to work and compile you will have to include an addition “.c” file in the same directory with the Arduino sketch. This file is for the third game example and it’s a bitmap of the bird. For more details how this part of the code work you can check my particular tutorial. Here you can download that file:

This shield with graphic LCD 2.4 "" touchscreen is perfect for your projects. It has a resolution of 320x240 pixels. Shield contains a resistive touchscreen type. It contains a slot for SD cards that can load images in .bmp format to display them on display. Specifications 320 x 240 resolution Based on SPFD5408 controller (compatible with ILI9341) 8-bit digital interface control + 4 lines LDO voltage regulator 3.3 V Integrated Compatible with 5V microcontrollers and 3.3 V 18-bit color (up to 262,000 colors supported) SD card slot 4-wire resistive touchscreen

When autocomplete results are available use up and down arrows to review and enter to select. Touch device users, explore by touch or with swipe gestures.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey