tn vs ips lcd panel made in china

It becomes a necessity in modern society. LCD panel is the most important part of an LCD display. It determines LCD screen"s performance, e.g. brightness, contrast, color and viewing angle. Therefore, picking the right type of LCD panel is critical to your application.
These names reflect the alignment of crystal molecules inside the LCD, and how they change when they are charged electrically. All liquid crystal displays change the alignment of liquid crystal molecules to work, but the manner in which they do so can drastically affect the image quality and response time. Each panel type has its advantages and disadvantages. The easiest way to choose between them is to decide which attributes are most important to your project. It mainly depends on what you use your LCD display for, and your budget.
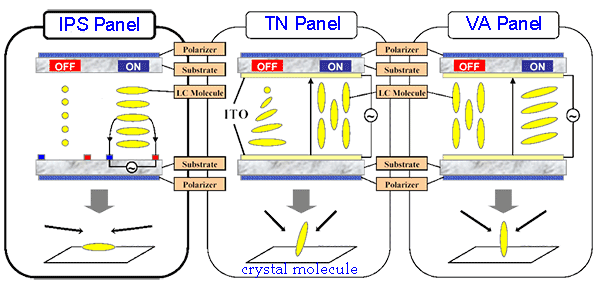
“TN and IPS are the most common LCD panel types. TN LCDs have advantage in cost and can meet severe environment challenge, while IPS LCDs have excellent performance in wide viewing angle and color restoration.
As early as the CRT display, given its unique imaging principle, the color, brightness, and contrast from the display can maintain good visual quality no matter from any viewing angle around the screen. However, its bulky structure has limited the design and application of displays for many applicants. As technology develops, flat panel displays take over the mainstream in the display market.
LCD is one of the main flat-panel display technologies. When it was just launched and the price was too high, it was difficult for the public to accept, so the LCD panel factories launched the affordable version, TN LCD.
To reduce the cost, the structure of TN LCD is simplified and the arrangement of liquid crystal molecules changes. It comes with the natural defects of the low color display quality and small effective viewing angle. When we look at the screen beyond the effective viewing angle, we will notice obvious image distortion.
In 1995, Hitachi was the first to introduce the IPS technology in LCD and put it into mass production in 1996. Ever since, the technology has undergone continuous innovation through Super-IPS, Advanced-SuperIPS, IPS-Pro, and still going on.
When the IPS display is on, the liquid crystal molecules of the panel rotate in a similar direction as in TN panels. However, when the display is off, they still rotate horizontally but change from the original spiral to layers.
By changing the electric field direction from vertical to horizontal, IPS technology can keep the liquid crystals stay parallel to the screen regardless the display is on or off. In addition, with the improvement of the structure, the viewing angle is enlarged significantly.
The liquid crystal molecules of the TN panel lay in the vertical direction, in consequence, the light can emit around the vertical area. Therefore, we can only get better visual quality at a very limited angle and notice the obvious color distortion in tilting angles.
In contrast, in IPS panels, the horizontal arrangement of the LC benefits the light emission at any angle, which enables a wide effective viewing angle. It can reach 170 to nearly 180 degrees both vertically and horizontally, so we also call the IPS LCD an “all viewing angle” display.
Due to the high contrast ratio and wide color gamut of HD, IPS panels take more time to respond than TN panels. In particular, in showing the dynamic HD pictures IPS are easy to appear ghosts and jitters. However, the phenomenon has greatly improved in recent years.
Compared to the TN panels, IPS panels have more gray levels, the imaging performance is more delicate, and can restore the color image in fine and vivid effect. As figure 4 shows, the image display on the TN panel appears only black in all four corners, with no details. While the IPS can show multiple color layers.
Due to the horizontal layout of liquid crystal molecules, under external pressure, the restoration speed of the IPS is about 10 times faster than TN which molecules in a vertical layout.
In addition, the surface of the IPS LCD is protected by a transparent resin film with high hardness, so it can remain the same when touched and there are no water ripples created on the screen surface. If we look at the screen with a magnifier, we can see that the pixels distribute towards the left like fish-scaled.
In contrast, when pressing the TN panel with a finger, there are water ripples on the surface, but the surface can restore quickly when the pressure is released. In addition, if it is bonded with a capacitive touchscreen, the cover of the CTP is normally hard (glass or hard plastic), which can release the pressure in touch.
When it comes todisplay technologies such asprojectorsand panels, factors such as resolution and refresh rate are often discussed. But the underlying technology is equally, if not more, important. There are tons of different types of screens, from OLED and LED to TN, VA, and IPS. Learn about the various monitor and television types, from operation to pros and cons!
1)Film layer that polarizes light entering2)glass substrate that dictates the dark shapes when the LCD screen is on3)Liquid crystal layer4)glass substrate that lines up with the horizontal filter5)Horizontal film filter letting light through or blocking it6)Reflective surface transmitting an image to the viewer
The most common form of monitor or TV on the market is LCD or Liquid Crystal Display. As the name suggests, LCDs use liquid crystals that alter the light to generate a specific colour. So some form of backlighting is necessary. Often, it’s LED lighting. But there are multiple forms of backlighting.
LCDs have utilized CCFLs or cold cathode fluorescent lamps. An LCD panel lit with CCFL backlighting benefits from extremely uniform illumination for a pretty even level of brightness across the entire screen. However, this comes at the expense of picture quality. Unlike an LED TV, cold cathode fluorescent lamp LCD monitors lack dimming capabilities. Since the brightness level is even throughout the entire array, a darker portion of scenes might look overly lit or washed out. While that might not be as obvious in a room filled with ambient light, under ideal movie-watching conditions, or in a dark room, it’s noticeable. LED TVs have mostly replaced CCFL.
An LCD panel is transmissive rather than emissive. Composition depends on the specific form of LCD being used, but generally, pixels are made up of subpixel layers that comprise the RGB (red-green-blue) colour spectrum and control the light that passes through. A backlight is needed, and it’s usually LED for modern monitors.
While many newer TVs and monitors are marketed as LED TVs, it’s sort of the same as an LCD TV. Whereas LCD refers to a display type, LED points to the backlighting in liquid crystal display instead. As such, LED TV is a subset of LCD. Rather than CCFLs, LEDs are light-emitting diodes or semiconductor light sources which generate light when a current passes through.
LED TVs boast several different benefits. Physically, LED television tends to be slimmer than CCFL-based LCD panels, and viewing angles are generally better than on non-LED LCD monitors. So if you’re at an angle, the picture remains relatively clear nonetheless. LEDs are also extremely long-lasting as well as more energy-efficient. As such, you can expect a lengthy lifespan and low power draw. Chances are you’ll upgrade to a new telly, or an internal part will go out far before any LEDs cease functioning.
Further segmenting LED TVs down, you’ll find TN panels. A TN display or Twisted Nematic display offers a low-cost solution with low response time and low input lag. TN monitors sport high refresh rates, so 100Hz, 144Hz, or higher. Thus, many monitors marketed toward gamers feature TN technology. Unfortunately, while an affordable, fast panel may sound ideal, TN panels suffer from inferior colour reproduction and horrible viewing angles. A TN panel works so that liquid crystal molecules point at the viewer, and light polarizers are oriented at 90-degree angles.
Like TN, IPS or In-plane Switching displays are a subset of LED panels. IPS monitors tend to boast accurate colour reproduction and great viewing angles. Price is higher than on TN monitors, but in-plane switching TVs generally feature a better picture when compared with twisted nematic sets. Latency and response time can be higher on IPS monitors meaning not all are ideal for gaming.
An IPS display aligns liquid crystals in parallel for lush colours. Polarizing filters have transmission axes aligned in the same direction. Because the electrode alignment differs from TN panels, black levels, viewing angles, and colour accuracy is much better. TN liquid crystals are perpendicular.
A VA or vertical alignment monitor features excellent contrast ratios, colour reproduction, and viewing angles. It’s a type of LED monitor with crystals perpendicular to the polarizers at right angles like TN monitors. Pricing varies, but response time isn’t as high as a TN monitor.
A quantum dot LED TV or QLED is yet another form of LED television. But it’s drastically different from other LED variants. Whereas most LED panels use a white backlight, quantum dot televisions opt for blue lights. In front of these blue LEDs sits a thin layer of quantum dots. These quantum dots in a screen glow at specific wavelengths of colour, either red, green, or blue, therefore comprising the entire RGB (red-green-blue) colour spectrum required to create a colour TV image.
QLED TV sets are thus able to achieve many more local dimming zones than other LED TVs. As opposed to uniform backlighting, local dimming zones can vary backlighting into zones for adjustable lighting to show accurate light and dark scenes. Quantum Dot displays maintain an excellent, bright image with precise colour reproduction.
An OLED or organic light-emitting diode display isn’t another variation of LED. OLEDs use negatively and positively charged ions for illuminating individual pixels. By contrast, LCD/LED TVs use a backlight that can make an unwanted glow. In OLED display, there are several layers, including a substrate, anode, hole injection layer, hole transport layer, an emissive layer, blocking layer, electron transport layer, and cathode. The emissive layer comprised of an electroluminescent layer of film is nestled between an electron-injecting cathode and an electron removal layer, the anode. OLEDs benefit from darker blacks and eschew any unwanted screen glow. Because OLED panels are made up of millions of individual subpixels, the pixels themselves emit light, and it’s, therefore, an emissive display as opposed to a transmissive technology like LCD/LED panels where a backlight is required behind the pixels themselves.
Image quality is top-notch. OLED TVs feature superb local dimming capabilities. The contrast ratio is unrivalled, even by the best of QLEDs, since pixels not used may be turned off. There’s no light bleed, black levels are incredible, excellent screen uniformity, and viewing angles don’t degrade the picture. Unfortunately, this comes at a cost. OLEDs are pricey, and the image isn’t as bright overall when compared to LED panels. For viewing in a darkened room, that’s fine, but ambient lighting isn’t ideal for OLED use.
As you can see, there are tons of different types of displays, each with their advantages and disadvantages. Although many monitors and TVs are referred to by different names like LED, IPS, VA, TN, or QLED, many are variations of LCD panels. However, specific technology such as the colour of backlighting and alignment of pixels dictates the picture quality. OLED is an entirely different form of display that’s not LED. Now that you understand the various types of monitors and televisions on the market, you can select the best TV to fit your needs!

Everyday, we look at LCD display, TV, cell phone, monitor. It becomes a necessity in modern society. LCD panel is the most important part of an LCD display. It determines LCD screen"s performance, e.g. brightness, contrast, color and viewing angle. Therefore, picking the right type of LCD panel is critical to your application.
These names reflect the alignment of crystal molecules inside the LCD, and how they change when they are charged electrically. All liquid crystal displays change the alignment of liquid crystal molecules to work, but the manner in which they do so can drastically affect the image quality and response time. Each panel type has its advantages and disadvantages. The easiest way to choose between them is to decide which attributes are most important to your project. It mainly depends on what you use your LCD display for, and your budget.
TN is the most mature technology in LCD panel manufacturing. When there is no voltage difference between the two transparent electrodes, liquid crystal molecules are twisted 90 degrees, in combination of upper and bottom polarizers, allows light to pass through LCD. As voltage applied, crystal molecules are untwisted and aligned to the same direction, blocking light.
In IPS panel, crystal molecules are parallel to the glass substrates at initial stage, LCD is off. When the in-plane electrodes is charged, crystal molecules are rotated, modifying light"s direction. Which lights up the LCD display.
As its name suggests, VA panel"s liquid crystals are aligned vertically without charged. When a voltage is applied, the molecules tilt and modifying light direction.
So in summary, TN panels twist, IPS panels use a parallel alignment and rotate, while VA panels use a perpendicular alignment and tilt. These difference create LCD display with distinctive performance.
IPS LCD is the clear winner in this aspect. It has 178/178 viewing angle ratings. Which means you can look at IPS LCD display from any angle without the image shifting in color and contrast. VA LCD has pretty wide viewing angle, too. But it has contrast shifts at off-center angles. As for TN LCD, viewing angle is its weakest point.
Most TN LCDs have 6-bits colors. Manufacturers use frame rate control (FRC) to enhance its color performance. For IPS and VA panels, you can still find 6-bits entry level LCD. But most of them are 8-bits. And IPS technology can provide natively 10-bits colors.
Color gamut is another part that VA and IPS panels shine at. The best TN LCD can reach sRGB gamut. VA panels typically start with full sRGB coverage, and get to around 90% DCI-P3 coverage. With IPS LCD panel, you could find the best ones full DCI-P3 and Adobe RGB coverage. That is why you see most professional grade LCD displays use IPS panel.
There is no inherent differences among the three panel technologies, because LCD backlight is the main factor here. However, there is a big gap in terms of contrast ratio. TN LCD panel tends to have the lowest value among the three. IPS LCD screen sits in the middle can reach 1500:1. For VA panel, the best one can exceed 4500:1 easily. VA LCD display provides far darker screen than TN & IPS. That is why they are used in vehicle dashboard.
TN panel does have an advantage when it comes to refresh rate. The panel offers the best refresh rate and response time. This is the reason why most gaming LCD monitors are made of TN panel.
TN LCD provides the best refresh rate and economic solution. If your application requires wide viewing angles and good color presentation, VA panel is probably the choice. While IPS has the best overall visual performance, in general it is more expensive than the other two.

When searching for a liquid crystal display (LCD), consideration of the device’s display technology is essential. Screen technology companies such as Apple and Samsung search for the best possible display panels and panel technology in order to offer their customers the best image quality. In competitive gaming, gaming monitors must be able to provide great image quality but also fast refresh rates so that gamers can play at a fast pace.
Before diving into how exactly liquid crystals affect display features, it is necessary to understand their general role in an LCD monitor. LCD technology is not capable of illuminating itself, so it requires a backlight. The liquid crystals are responsible for transmitting the light from backlight to the computer monitor surface in a manner determined by the signals received. They do so by essentially moving the light differently through the layer’s molecular matrix when the liquid crystals are oriented or aligned in a certain manner, a process which is controlled by the LCD cell’s electrodes and their electric currents.
The methods of alignment, however, can vary between panel types, offering different features and benefits. Two common and popular liquid crystal alignment techniques are twisted nematic (TN) and in-plane switching(IPS).
TN panels offer the cheapest method of crystal alignment. They also are the most common of the alignment methods and have been used for quite a long time in the display industry, including in cathode ray tubes (CRTs) that preceded the LCD.
In TN displays, the electrodes are positioned on either side of the liquid crystal layer. When a current is sent between the back and front electrode, something called an electric field is created that shifts and manipulates the orientation of the molecular matrix.
If no electric field is applied to the specific cell, the crystals experience a 90 degree twist in the alignment. As light from the backlight passes through this twist, the light waves are polarized, allowing them to pass through the polarizer that sits on the surface of the TN monitor.
If an electric field is applied, it can either untwist the TN liquid crystal layer partially or in full, depending on the strength of the field. The structure of TN crystals will typically straighten out when this happens, and some, if not all, light waves will not be polarized properly to pass through to the surface.
Each LCD cell composes a pixel of the display, and in each pixel are subpixels. These subpixels use standard red green blue (sRGB) colors to create a variety of colors to make the pixel display the necessary color to play its role in the overall display. If beneath the subpixel the liquid crystal fully polarizes the light, that subpixel’s specific color would be very bright in the pixel as a whole. But if the light is not polarized at all, then that color will not show up. If partially polarized, only a limited amount of that color is used in the mixture of RGB colors in the final pixel.
A more complex method of alignment is IPS. IPS monitors, unlike the TN, place both electrodes on the same level, behind the liquid crystal layer. When the electric field is applied, this forces the liquid crystal molecules to align themselves parallel to the IPS device layers instead of perpendicularly like the TN molecules.
Opposite of the TN, when the electric field is applied, IPS technology will polarize the light to pass, whereas when the electric field is not applied, the light will not be polarized to pass. Because of the orientation of the crystals, IPS displays require brighter, more powerful backlights in order to produce the correct amount of brightness for the display.
An important consideration is viewing angles. The TN offers only a limited viewing angle, especially limited from vertical angle shifts, and so color reproduction at these angles will likely not look the same as from a straight-on viewing; the TN’s colors may invert at extreme angles. The IPS counters that and allows for greater and better viewing angles that consequently offer better color reproduction at these angles than the TN. There is one issue with extreme viewing angles for IPS devices: IPS glow. This occurs when the backlight shines through the display at very wide angles, but typically is not an issue unless a device is looked at from the side.
In terms of color, as mentioned, TN devices do not have very strong color reproduction compared to other alignment technologies. Without strong color reproduction, color banding can become visible, contrast ratio can suffer, and accurate colors may not be produced. Color gamut, or the range of colors that the device can reproduce and display, is another feature that most TN displays do not excel in. This means that the full sRGB spectrum is not accessible. IPS devices, on the other hand, have good quality black color reproductions, allowing the device to achieve a deeper, richer display, but it is still not the best option if a customer is in search of high contrast (discussed further in a couple more paragraphs).
While TNs may not have the best color quality, they allow for high refresh rates (how often a new image is updated per second), often around 240 Hz. They also have the lowest input lag (receiving of signals from external controllers) at about one millisecond. TN panels often attract gamers because of the need for minimal lag and fast refresh rates in a competitive or time-sensitive setting. In consideration of moving displays like in video game displays, it is also important for fast response times (how fast a pixel can change from one amount of lighting to another). The lower the response time (the higher the response rate), the less motion blur will be shown as the display changes to show motion. TNs also offer these low response times, but it is important to remember that a powerful graphics processing unit, commonly called a GPU, is still needed to push these displays to meet the fastest refresh and response rates.
Standard IPS devices have been known to have slower response time and refresh rates. This can often lead to not just motion blur but ghosting as well, meaning that an image does not refresh fast enough, and so the previous image will remain temporarily burned in the expected new image. In recent years, though, IPS technology has achieved higher refresh rates than in the past through the super-IPS, abbreviated s-IPS.
Oftentimes, refresh rates and frame rate of output devices (such as graphics cards) will not be synchronized, causing screen tearing when two different display images will be shown at once. This problem can be addressed through syncing technologies like Vsynch, Nvidia’s G-Sync, or FreeSync (a royalty-free adaptive synchronization technology developed by AMD).
Another common consideration of customers is the price of each display. TN, though it does not offer as high quality of a display, offers the lowest cost and best moving displays, making it useful if the intended use of the LCD monitor is simple and not too demanding. However, if you intend for something that calls for better color production or viewing angles, the IPS and other methods are viable choices, but at much higher costs. Even though IPS motion displays have reached the speed and rates of TNs, the price for such technology is much more expensive than the TN option.
There are other options besides the TN and IPS. One option is known as vertical alignment (VA) and it allows for the best color accuracy and color gamut. Compared to a typical IPS contrast ratio of 1000:1, VA panels can often have ratios of 3000:1 or even 6000:1. Besides improved contrast ratio, the VA is in between the TN and IPS. To compare the TN vs IPS vs VA, the VA does not have as great a viewing angle as IPS but not as poor as the TN. Its response times are slower than TN but faster than IPS (though at fast refresh rates, the VA displays often suffer from ghosting and motion blur). Due to the contrast ratio benefits, VA technologies are most often desirable for TVs.
And lastly, there is an option quite similar to IPS that is called plane to line switching (PLS). It is only produced by Samsung, who claims the PLS offers better brightness and contrast ratios than the IPS, uses less energy, and is cheaper to manufacture (but because it is only created by Samsung, it is hard to judge pricing). It also has potential in creating flexible displays.
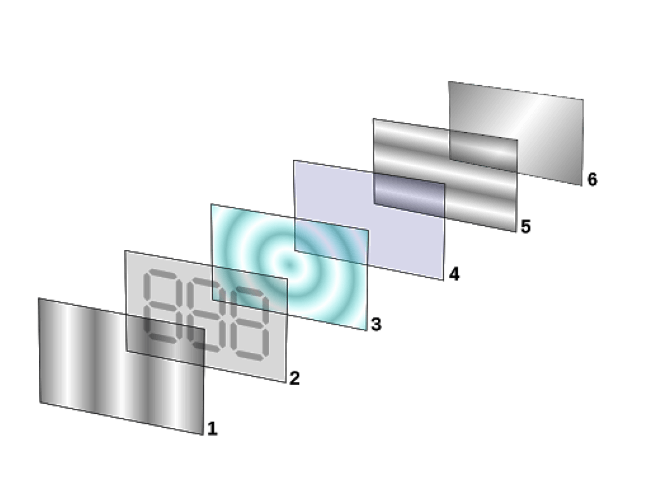
You may be surprised to know that not all LCD panels are created equal. That’s because there’s more than one type of LCD screen. While their differences are subtle, the type of panel technology significantly impacts its image quality and display performance.
In this post, we’ll compare the three types of LCD panel technologies – IPS vs. TN vs. VA – and the pros and cons of each. Knowing the differences is critical to help you find the best type that fits your needs.
The main difference between them is how they arrange and move the liquid crystal display (LCD) molecules in their panels. This, in turn, has a profound effect on image quality, refresh rate, and other performance factors.
A twisted nematic or TN monitor is the oldest and most common type of LCD still used today. It uses a nematic liquid crystal, meaning it has its molecules arranged in parallel, but not on a level plane. These can twist or untwist themselves when a voltage runs through them, hence the name. This twisting effect either allows or blocks light from passing through, turning screen pixels “on” or “off.”
In-panel switching (IPS) panels work similarly to TN monitors, except that the liquid crystal molecules are parallel to the glass panel of the screen. Instead of twisting like in TN monitors, these molecules rotate when a voltage is applied.
Vertical alignment (VA) displays arrange their LCD molecules vertically, perpendicular to the glass panel. When voltage is present, they tilt themselves instead of twisting or rotating.
Being the oldest LCD technology still in use today, TN monitors undoubtedly have their share of benefits, otherwise they wouldn’t have this much longevity! Comparing TN vs. IPS and VA, TN panels are the cheapest and fastest to manufacture. As a result, they are better for the more budget-conscious user. They’re also the most versatile LCD type and have no real-world limits on size, shape, resolution, and refresh rate.
You’ll be hard-pressed to find a TN monitor in a reasonable price range that can display 24-bit (8 bits per channel) color at a wide color gamut, and contrast is limited. The second problem with TN monitors is that because the molecules are not oriented uniformly across the plane, it suffers from a narrow viewing angle. That is, anyone looking at the screen off-axis, such as from a 45-degree angle, will most likely find the image completely un-viewable.
Comparing IPS vs. TN, the former is a drastic improvement over the latter. IPS panels resolve some of the limitations and problems of TN monitors, specifically color accuracy and issues with viewing angles. However, IPS panels suffer from a phenomenon called “IPS glow,” where you can see the display’s backlight clearly if you view it from the side.
Another significant limitation of IPS panels, particularly for gamers, is that they have the lowest refresh rates of any LCD type. And while the color fidelity is fantastic with IPS vs. VA, the latter has superior contrast ratios over the IPS panels.
The biggest strength of VA panels lies in their excellent contrast ratio. Keep in mind that irrespective of the LCD technology used, a backlight is required; this is typically LED. The LCD’s ability to block this light will determine how well it can reproduce blacks, and it’s in this detail where VA excels. That is, blacks are dark and rich in a VA panel vs. IPS. They also lie somewhere in the middle regarding overall image quality, color reproduction, viewing angle, and refresh rate. Overall, VA is a good compromise between TN and IPS.
A drawback of VA vs. IPS and TN is it exhibits an relatively high response time. As such, VA displays are more prone to motion blur and ghosting if you’re viewing fast-moving visuals on a screen, such as when you’re playing a racing game.
It’s worth noting that there is no universal “right” choice for choosing a type of LCD panel. Which one you pick depends on your budget, your intended use, and your expected outcome.
A TN monitor is best if you’re looking for a low-cost, readily available display for tasks that don’t rely on contrast and color accuracy, such as sending emails or typing a document or spreadsheet. They are also the best choice for competitive gamers who want the best refresh rates and response times to give them an edge in online multiplayer games, despite a technically lower image quality.
With their superior color reproduction, IPS panels are best for graphic designers, film editors, photographers, and other visual design professionals. For them, image quality including contrast and color accuracy are more important than refresh rates. IPS panels are also fantastic for casual gamers who want the best visuals and don’t mind the compromise in refresh rate or response time.
Whichever LCD type you choose, make sure you get the right cable, a Premium High Speed HDMI® Cable, or an Ultra High Speed HDMI® Cable to ensure delivery of all the HDMI 2.1 features. Doing this ensures that you’ll get the best experience on your screen.

When buying a gaming monitor, most consumers are not even aware of the existence of LCD panel technology. LCD display panels have different specs that can have a radical impact on the user experience. Based on how you plan to use your LCD monitor, you may choose among three main gaming monitor panel types: TN, IPS, and VA.
At first, choosing the right monitor panel may seem tricky. In this article, we will present the pros and cons of each LCD display panel. After finishing reading this post, you will be knowledgeable enough to challenge any sellers and choose the most appropriate gaming monitor for your next playing section.
Let’s begin with the most popular LCD display panel on the market today. TN panels are generally installed in most gaming monitors, especially in those with a high refresh rate. These kinds of LCD monitors are specially designed for very competitive video games.
One of the advantages of these panels is their relatively lower price compared to their counterparts. Another quality that makes TN panels a top pick is their fast response time. This means that there is a much lower delay between a click of the mouse or a keyboard touch and the command reproduced on the screen. This feature makes the TN panels ideal for those who love action shooters and video games that require very fast reactions. Besides, there are other benefits to having a shorter response time. Overall, there are fewer unpleasant phenomena such as blurring and ghosting. As a result, the final image is much clearer and sharper.
When buying TN panels, you will probably hear the terms ‘black-to-black’ or ‘grey-to-grey’ (GTG). Black-to-black is the standard response time measure. BTB refers to the amount of time it takes a pixel to go from black to white and then back to black. This indicator is considered among the most accurate to evaluate the response time of a device.
Monitors with IPS panels, rely on high colors definition. Looking at this type of LCDs, the quality that stands out the most is the exceptional color accuracy coupled with the wide viewing angles. The wide angularity makes these monitors more suitable for jobs that require a high intensity of colors displayed such as photo and video editing. In gaming, IPS panels are often preferred for RPGs with astonishing visuals.
IPS panels allow you to look at the screen perfectly from any position. These screens do not have the usual problems of changing colors or contrast as with most monitors. Unfortunately, to reach such a high definition of images, the response time must be sacrificed. When compared to TN panels, the response rate is much lower. Technology has undoubtedly updated itself in recent years leading to newest iteration improvements. Besides, most people do not encounter lag problems when playing video games on these screens.
Ultimately, for many casual gamers, image quality is much more important than a couple of milliseconds of delay in the panel’s overall response time. A disadvantage that we have to mention though is the high price. This is one of the critical aspects that turns costumers away from IPS to buying a TN solution.
Finally, there are the VA or Vertical Alignment panels. Much more similar to IPS, there are many types of VA panels, but the ones we will focus on are MVA (Multi-domain Vertical Alignment) panels and AMVA (Advanced MVA) panels.
MVA panels were initially designed to be in the middle between TN and IPS displays, as they offered a better viewing angle than TN screens and a higher contrast ratio and deeper blacks than IPS displays. However, their color accuracy is not as precise as the one of IPS monitors, and they do not have a particularly fast response time.
AMVA panels, on the other hand, focus precisely on a higher color definition. As a matter of fact, they have better color accuracy while preserving ultra-high contrast ratios and deep blacks. Their viewing angle is not as wide as that of IPS panels, and their response time is still a bit slow.
Consequently, monitors with VA panels can be seen as a good compromise among all the market monitors. Their flagship features are the excellent black levels – which is the best in the category of gaming monitors – and their amazing contrast ratio. Moreover, compared to TN panels, they have a better viewing angle and greater color accuracy.
On the downsides, despite apparently trying to correct and eliminate the weaknesses of their competitors, VA solutions do not have a color accuracy comparable to that of IPS panels or a response rate higher than TN screens.
To sum it up, for competitive online gamers, we would suggest TN panels. For non-competitive PC games, VA panels will work much better. If you just want to focus on visuals, IPS displays are a better choice. At Aiwa, we are dedicated to providing the best user experience to our customers.
If you are interested in LCD display panels and screens, you need to go any further. Hopefully, this guide was helpful in sharing more useful information for your next purchase. Come to check our solutions or contact us at any time!

IPS (In-Plane Switching) lcd is still a type of TFT LCD, IPS TFT is also called SFT LCD (supper fine tft ),different to regular tft in TN (Twisted Nematic) mode, theIPS LCD liquid crystal elements inside the tft lcd cell, they are arrayed in plane inside the lcd cell when power off, so the light can not transmit it via theIPS lcdwhen power off, When power on, the liquid crystal elements inside the IPS tft would switch in a small angle, then the light would go through the IPS lcd display, then the display on since light go through the IPS display, the switching angle is related to the input power, the switch angle is related to the input power value of IPS LCD, the more switch angle, the more light would transmit the IPS LCD, we call it negative display mode.
The regular tft lcd, it is a-si TN (Twisted Nematic) tft lcd, its liquid crystal elements are arrayed in vertical type, the light could transmit the regularTFT LCDwhen power off. When power on, the liquid crystal twist in some angle, then it block the light transmit the tft lcd, then make the display elements display on by this way, the liquid crystal twist angle is also related to the input power, the more twist angle, the more light would be blocked by the tft lcd, it is tft lcd working mode.
A TFT lcd display is vivid and colorful than a common monochrome lcd display. TFT refreshes more quickly response than a monochrome LCD display and shows motion more smoothly. TFT displays use more electricity in driving than monochrome LCD screens, so they not only cost more in the first place, but they are also more expensive to drive tft lcd screen.The two most common types of TFT LCDs are IPS and TN displays.

Panel type names are based on the molecule arrangement on a liquid crystal display - LCD monitor - and the changes that occur upon voltage application. LCD monitors - see also LED vs LCD review - adjust the molecule positioning to function, though the way the changes occur immensely impacts your response time and image quality.
While it is the oldest panel technology, a TN panel still has some advantages over the newer VA and IPS panel technologies (see QLED and IPS). For one, they are the cheapest and suitable if you want budget-friendly options . If the extent of color reproduction or better viewing angles is not essential, a TN screen might suit you.
Moreover, TN panels have the least input lag of about one millisecond. A TN computer can operate at fast refresh rates reaching 240 Hz (see 1440p - 240Hz monitors review). For this reason, they are ideal for competitive players seeking gaming monitors (check out the best monitors for Xbox One X and Xbox Series X) that enable them to take advantage of each second. The Benefits of a good monitor for gaming are shown also in our review of monitors for League of Legends.
Nevertheless, TN display technology has notable disadvantages starting with the small viewing angles on the perpendicular axis. The changing of your TN computer"s colors is common when seated at extreme angles.
TN screens also have poor color reproduction. Most TN displays cannot function at 24-bit true color, so they depend on interpolation for accurate shade simulation. This performance can lead to color banding and lower contrast ratios than VA and IPS panel technologies.
TN panels also have a relatively lower color gamut. Only high-end TN monitors display wide color ranges. Many lack a wide-gamut and therefore are unideal for color grading, web design, photo and video editing, or other usages demanding color accuracy.
With their much wider viewing angles compared to TN screens, IPS panels allow you to sit at extreme angles while getting accurate color displays. Those characteristics are also the reason why IPS displays are good for touchscreens in tablets and portable monitors suh as this ZenScreen Touch monitor from Asus or this from Elecrow, an open hardware facilitation company based in China. Unlike a TN screen, you"ll hardly notice a color shift when looking at the screen from an unideal perspective.
IPS panels also have excellent performance in black reproduction, vital in eliminating the washed-out displays typical on TN panels. Regardless, IPS monitors don"t have as high contrast ratios as VA panels.
While TN panels dominate in terms of the refresh rate, IPS panels are now available that support refresh rates even over 240 Hz. For instance, the ASUS TUF VG259QM 24.5-Inch has a 280 Hz refresh rate and features an IPS monitor (see also this 23.8-inch monitor from HP).
TN displays previously had lower lagging than any other panel type, but IPS displays are now at per. LG launched their Nano IPS UltraGear screens boasting of the fastest response times on IPS at one millisecond. Moreover, Samsung"s quantum dot technologies, which will be covered in another post, are more energy-efficient and offer enhanced color accuracy over IPS, as well.
Despite measuring up, you"ll still spend more to get an IPS screen with a one millisecond response time than a similar-rated TN monitor. If you want to benefit from IPS technology at a budget cost, expect an LCD panel at approximately four milliseconds. Dell S2318HN here has gone a step further though, combining IPS and LED - see also "What is OLED?" - technology for some great results.
Another notable demerit dominant in IPS panels is the IPS glow. If this phenomenon occurs, your screen"s backlight shines and blurs your view when sitting at extreme viewing angles. While not the biggest issue, it is something to consider if you like sitting on the side. On the other hand, these types of monitors are thin and lightweight (see "Auzai"s portable monitor", or this Desklab monitor), as well as energy-efficient. Speaking of portability, ASUS mb168b monitor and AOC e1659fwu are also easy to carry and offer good quality at an affordable price.
VA panels form a middle ground between IPS and TN monitors. They have the highest contrast ratios, making them a go-to option for TV manufacturers. While an IPS screen can have 1000:1, comparable VA alternatives may reach up to 3000:1 or 6000:1 contrast ratios.
A VA monitor won"t offer you as good of a performance as an IPS screen in viewing angles (see Lenovo Thinkvision m14). Depending on your sitting arrangement, you may experience some brightness, though not as glaring as the IPS glow.
VA panels feature slower response times than TN and IPS monitors at their best performance. While some VA monitors refresh at up to 240 Hz, they tend to have latency that can cause motion blur and ghosting.
As a result, if you are in a VS vs IPS monitor dilemma, it is wise to refrain from VA displays for competitive gaming, and go for top gamers" choice displays like in these monitors for CS: GO or these monitors for racing games.
Compared to TN panels, VA screens provide better color reproduction, often supporting full sRGB spectrum even on budget options (see the best monitors under $200 review).
Because of their attributes, VA panels are suitable for general use. However, these panels tend to perform lower in most specs apart from the contrast ratio. VA monitors are pretty excellent in single-player action, flight simulations, or casual gaming.
Media professionals prefer IPS panels to VA panels, given their wider color gamut, though professionals like music producers require different features in their monitors.

In order to understand this problem, we first need to know the panel type of LCD. At present, the LCD panels are mainly divided into three categories, which are TN, VA and IPS.
TN panel, full name Twisted Nematic (twist nematic), because the production cost is relatively low, so it is the first popular panel in LCD. The advantage of TN panel is that the response time of GTG panel is very fast, and the gray scale response time of GTG is often up to 1ms, which is the lowest among all LCD panels, so many e-sports / game monitors use TN panel.
However, the shortcomings of the TN panel are also obvious, such as less output gray scale, white color, small visual angle and so on. 1080p is the most common resolution in the TN panel, and there are also some 27-inch QHD panels, and the latest panel can do 28-inch UHD. At present, the main manufacturers of TN panels are Samsung display (Samsung Display), LG, Youda Optoelectronics, Qunchuang Optoelectronics, China Picture Tube and so on.
Let"s talk about the VA panel. VA panel full name Vertical Alignment (vertical arrangement), its advantage lies in the contrast, VA panel is the highest contrast of all LCD panels, usually can reach 3000 VA 1, while the contrast of TN, IPS is only about 1000 VA 1, the intuitive feeling of high contrast is that black looks purer and the picture is more layered.
The gray scale response time of VA panel is faster than that of IPS, and some of them even reach the same 1ms as TN, while the visual angle of TN is much better than that of TN, which is consistent with the visual angle of IPS panel, and there is no light leakage problem of VA panel.
Finally, let"s talk about the IPS panel. IPS full name In-Plane Switching (plane conversion), its advantage is that the color performance is relatively good, and the visual angle is also relatively wide, horizontal and vertical visual angle can reach 178°, but the contrast is not as good as VA panel, and the problem of light leakage is also more prominent.
From the above carding, it is not difficult to see that each panel has its own advantages, but also some inherent shortcomings. For example, TN panel is better than fast response time, but the color and visual angle is not good; VA panel contrast is high, but there are still some differences in response time and color; IPS color is good, but there are long response time and light leakage problems.
So which panel to choose depends on the specific requirements, you can"t simply think that IPS must be better than VA, or VA must be better than TN. For example, heavy players of FPS games who value response time can choose the display of TN panel, designers who value visual angle and have certain requirements for color can choose the display of IPS panel, and friends who like to watch some high-contrast and more powerful pictures can choose the display of VA panel.

Chinese manufacturers are expected to raise their market share from 39% this year to 52% next year in the monitor panel market, and 36% to 39% in the notebook panel market
Chinese manufacturers are expected to raise their market share from 39% this year to 52% next year in the monitor panel market, and 36% to 39% in the notebook panel market, according to TrendForce’s preliminary shipment forecast of panel makers for 2021. As such, these manufacturers are expected to maintain their plans of transitioning some production capacities from TV panel manufacturing to IT panel manufacturing in spite of the TV panel shortage in 2H20 caused by various factors such as the closedown of SDC’s LCD panel manufacturing operations, the rise of the stay-at-home economy, and the stimulus policies instituted by governments worldwide.
TrendForce indicates that, with regards to the standing of Chinese manufacturers in the IT panel industry, BOE has long established itself as the market leader, while CSOT and HKC are each also catching up fast. After acquiring SDC’s Suzhou-based Gen 8.5 fab, CSOT will possess even more production capacities for monitor panels. At the same time, HKC currently maintains three Gen 8.6 fabs, located in Chongqing, Chuzhou, and Mianyang, and plans to capture additional shares in the monitor panel and notebook panel markets.
Chinese panel makers have been gradually transitioning their current panel capacities to monitor panel production. Most significantly, as more Gen 10.5 production lines become available, TV panel production will most likely take place in Gen 10.5 fabs instead of Gen 8.5 fabs in the future, while the existing Gen 8.5 and Gen 8.6 production lines will be reallocated to monitor panel production in order to expend the excess capacity made available after TV panel production moves to Gen 10.5 fabs. In addition, after SDC’s forecasted closing of LCD panel manufacturing operations at the end of this year, CSOT and HKC will look to capture the resultant supply share of SDC’s absence in the market. On the other hand, since both TCL, which is CSOT’s parent company, and HKC possess monitor ODM operations, should the two companies decide to vertically integrate by making panels for their own monitor products, they will be able to effectively optimize their cost structures.
Although CSOT’s Wuhan-based T3 LTPS Gen 6 production line is primarily dedicated to smartphone and notebook panel manufacturing, the considerable reduction of LTPS smartphone panel demand from Huawei caused by U.S. sanctions means CSOT is expected to make plans for an increase in notebook panel shipment in order to make up for the shortfall. As well, thanks to high demand for TV panels this year, HKC’s production lines have been operating at maximum capacity utilization rates, in turn slowing down its notebook panel business. However, in light of the fact that the COVID-19 pandemic has brought about a rapid surge in TN notebook panel demand, HKC is therefore looking to TN panels as a new commercial opportunity in the notebook display market and subsequently prioritizing TN panel development over IPS panel development as its product strategy. Not only will this reprioritization allow HKC to align its strategy with the current market trend, but it will also quickly raise the yield rate of HKC’s Mianyang-based fab, which had never manufactured NB panels, by instead having the fab manufacture TN panels, which have a relatively simpler manufacturing process.
TrendForce analyst Jeff Yang indicates that, despite Chinese panel makers’ strong intention to enter the IT panel manufacturing business, success in the IT panel market is not solely decided by a company’s production capacity. For instance, with regards to monitor panels, CSOT’s technical competency is mostly focused on VA panels, meaning the company is constrained in its product mixes due to its lack of mainstream IPS offerings. Although HKC is equipped with both IPS and VA technologies, it lacks experience in manufacturing curved VA panels, leading its clients to take on a wait-and-see approach before placing additional orders. For notebook panels, although CSOT is primarily focusing on the mid-range and high-end LTPS notebook panel market, it faces intense competition from Samsung’s OLED notebook panels, which are gradually extending from the high-end segment to the mid-range segment as well. Likewise, HKC will have to take time in order to make headways in the notebook panel market, since it has not reached any production milestones, and it requires time to cultivate a significant client base.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey