arduino lcd screen pinout made in china

@Railroader Thanks for your advice, although I felt that it was a little patronising. But I guess that since the Arduino is primarily targeted at schoolchildren and for educational purposes, that"s a fair enough assumption of my age and career.
I am aware that there are better alternatives for screens that can be found for under £15. I was curious what was in a £15 quid projector and bought it for that reason. Disassembling it was fun and has already netted me lenses, heatsinks, and LEDs etc. for other projects which is worth more than its cost. The reason I asked was because a) I am loathe to bin the LCD and hence contribute to our electronic waste problems, and b) I am specifically looking for LEDs (most of the displays on eBay and Amazon are OLEDs) as I want to make an ESP32-controlled projector as a project. Non-OLEDs are difficult to find on eBay/Amazon nowadays. Hence I was asking on the off-chance that this screen might be similar to something else in Occidental part of the world that I could use.
From what you say it feels its very unlikely for there to be a shortcut and I"ll have decode the signals manually. Designing and manufacturing (or finding a 30 pin adapter) is not a problem but I can"t justify to myself spending the better part of my weekends in a month to decode the signals just to use it when I can spend £10 buying an SPI LCD from eBay which does the exact same thing. I"ll probably bite the bullet and do that.
Shame about having to bin the screen though. I have found the schematics for the GM8284DD chip and probably with a magnifying glass would be able to make out the LCD connections (RGB input etc.) on the circuit board but again, I"m not sure if its that cost-efficient spending that many weekends working on it...

I found that the one I have uses ILI9335 and after some hacking I was able to make it work with UTFT (it uses a non standard pinout using PB[0:1] and PD[2:7] and needs LCD_RD at HIGH) but so far so good.
"C:\\Users\\David Prentice\\AppData\\Local\\Arduino15\\packages\\STM32\\tools\\arm-none-eabi-gcc\\6-2017-q2-update/bin/arm-none-eabi-size" -A "C:\\Users\\DAVIDP~1\\AppData\\Local\\Temp\\arduino_build_687817/graphicstest.ino.elf"

As a 2inch IPS display module with a resolution of 240 * 320, it uses an SPI interface for communication. The LCD has an internal controller with basic functions, which can be used to draw points, lines, circles, and rectangles, and display English, Chinese as well as pictures.
The 2inch LCD uses the PH2.0 8PIN interface, which can be connected to the Raspberry Pi according to the above table: (Please connect according to the pin definition table. The color of the wiring in the picture is for reference only, and the actual color shall prevail.)
The LCD supports 12-bit, 16-bit, and 18-bit input color formats per pixel, namely RGB444, RGB565, and RGB666 three color formats, this demo uses RGB565 color format, which is also a commonly used RGB format.
For most LCD controllers, the communication mode of the controller can be configured, usually with an 8080 parallel interface, three-wire SPI, four-wire SPI, and other communication methods. This LCD uses a four-wire SPI communication interface, which can greatly save the GPIO port, and the communication speed will be faster.
The fill color of a certain window in the image buffer: the image buffer part of the window filled with a certain color, usually used to fresh the screen into blank, often used for time display, fresh the last second of the screen.
2. The module_init() function is automatically called in the INIT () initializer on the LCD, but the module_exit() function needs to be called by itself
Python has an image library PIL official library link, it do not need to write code from the logical layer like C, can directly call to the image library for image processing. The following will take 1.54inch LCD as an example, we provide a brief description for the demo.
LCD, or Liquid Crystal Displays, are great choices for many applications. They aren’t that power-hungry, they are available in monochrome or full-color models, and they are available in all shapes and sizes.
Today we will see how to use this display with both an Arduino and an ESP32. We will also use a pair of them to make some rather spooky animated eyeballs!
Waveshare actually has several round LCD modules, I chose the 1.28-inch model as it was readily available on Amazon. You could probably perform the same experiments using a different module, although you may require a different driver.
This display can be used for the experiments we will be doing with the ESP32, as that is a 3.3-volt logic microcontroller. You would need to use a voltage level converter if you wanted to use one of these with an Arduino Uno.
The Arduino Uno is arguably the most common microcontroller on the planet, certainly for experiments it is. However, it is also quite old and compared to more modern devices its 16-MHz clock is pretty slow.
The Waveshare device comes with a cable for use with the display. Unfortunately, it only has female ends, which would be excellent for a Raspberry Pi (which is also supported) but not too handy for an Arduino Uno. I used short breadboard jumper wires to convert the ends into male ones suitable for the Arduino.
Open the Arduino folder. Inside you’ll find quite a few folders, one for each display size that Waveshare supports. As I’m using the 1.28-inch model, I selected theLCD_1inch28folder.
Once you do that, you can open your Arduino IDE and then navigate to that folder. Inside the folder, there is a sketch file namedLCD_1inch28.inowhich you will want to open.
When you open the sketch, you’ll be greeted by an error message in your Arduino IDE. The error is that two of the files included in the sketch contain unrecognized characters. The IDE offers the suggestion of fixing these with the “Fix Encoder & Reload” function (in the Tools menu), but that won’t work.
Unfortunately, Waveshare doesn’t offer documentation for this, but you can gather quite a bit of information by reading theLCD_Driver.cppfile, where the functions are somewhat documented.
The TFT_eSPI library is ideal for this, and several other, displays. You can install it through your Arduino IDE Library Manager, just search for “TFT_eSPI”.
The GC9A01 LCD module is a 1.28-inch round display that is useful for instrumentation and other similar projects. Today we will learn how to use this display with an Arduino Uno and an ESP32.

No! For about the price of a familiar 2x16 LCD, you get a high resolution TFT display. For as low as $4 (shipping included!), it"s possible to buy a small, sharp TFT screen that can be interfaced with an Arduino. Moreover, it can display not just text, but elaborate graphics. These have been manufactured in the tens of millions for cell phones and other gadgets and devices, and that is the reason they are so cheap now. This makes it feasible to reuse them to give our electronic projects colorful graphic displays.
There are quite a number of small cheap TFT displays available on eBay and elsewhere. But, how is it possible to determine which ones will work with an Arduino? And what then? Here is the procedure:ID the display. With luck, it will have identifying information printed on it. Otherwise, it may involve matching its appearance with a picture on Google images. Determine the display"s resolution and the driver chip.
Find out whether there is an Arduino driver available. Google is your friend here. Henning Karlsen"s UTFT library works with many displays. (http://www.rinkydinkelectronics.com/library.php?i...)
Download and install the driver library. On a Linux machine, as root, copy the library archive file to the /usr/share/arduino/libraries directory and untar or unzip it.
Load an example sketch into the Arduino IDE, and then upload it to the attached Arduino board with wired-up TFT display. With luck, you will see text and/or graphics.
We"ll begin with a simple one. The ILI9163 display has a resolution of 128 x 128 pixels. With 8 pins in a single row, it works fine with a standard Arduino UNO or with a Mega. The hardware hookup is simple -- only 8 connections total! The library put together by a smart fella, by the name of sumotoy, makes it possible to display text in multiple colors and to draw lines.
This one is a 2.2" (diagonal) display with 176x220 resolution and parallel interface. It has a standard ("Intel 8080") parallel interface, and works in both 8-bit and 16-bit modes. It uses the S6D0164 driver in Henning Karlsen"s UTFT library, and because of the memory requirements of same, works only with an Arduino Mega or Due. It has an SD card slot on its back
This one is a bit of an oddball. It"s a clone of the more common HY-TFT240, and it has two rows of pins, set at right angles to one another. To enable the display in 8-bit mode, only the row of pins along the narrow edge is used. The other row is for the SD card socket on the back, and for 16-bit mode. To interface with an Arduino ( Mega or Due), it uses Henning Karlsen"s UTFT library, and the driver is ILI9325C. Its resolution is 320x240 (hires!) and it incorporates both a touch screen and an SD card slot.
Having determined that a particular TFT display will work with the Arduino, it"s time to think about a more permanent solution -- constructing hard-wired and soldered plug-in boards. To make things easier, start with a blank protoshield as a base, and add sockets for the TFT displays to plug into. Each socket row will have a corresponding row next to it, with each individual hole "twinned" to the adjacent hole in the adjoining row by solder bridges, making them accessible to jumpers to connect to appropriate Arduino pins. An alternative is hard-wiring the socket pins to the Arduino pins, which is neater but limits the versatility of the board.
In step 5, you mention that the TFT01 display can"t be used with the UTFT library on an Arduino Uno because of its memory requirements. It can - all you have to do is edit memorysaver.h and disable any display models you"re not using.
I think you should add a disclaimer that the code might make the Arduino Uno unprogrammable afterward (due to use up the two 0 and 1 pin) and link to how to fix it: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/5290428/how-to-reset-an-arduino-board/8453576?sfb=2#84535760
Tho I realize this is quickly becoming legacy hardware, these 8,16 bit parallel spi with 4 wire controller 3.2in Taft touch display 240x380. It has become very inexpensive with ally of back stock world wide so incorporating them into any project is easier then ever. Sorry to my question. I’m having difficulty finding wiring solution for this lcd. It is a sd1289 3.3 and 5v ,40 pin parallel 8,16 bit. I do not want to use a extra shield,hat or cape or adapter. But there’s a lot of conflicting info about required lvl shifters for this model any help or links to info would be great .. thank you. I hope I gave enough information to understand what I’m adoing
#1 you need a data sheet for the display and pinout and the i/o board attached to the cable.Than before you buy check for a driver for this chip Raydium/RM69071.if no driver lib are you able to write one and do you have the necessary tools to work on this scale to wire it up ..if you answer no than search for an arduino ready product.WCH0
hooking up and adding a lib is no piece of cake insure the screen you buy is arduino ready and sold by a reputable shop with step by step directions...WCH0
I"m sorry that I can"t help you with this. You"ll have to do your own research. See if you can identify the chipset and find out if there"s an Arduino driver for it.0
Thanks for the wealth of knowledge! It is amazing at what is possible with items the average person can easily acquire. I hope to put some of your tips to use this winter as I would like to build sensors and other items for home automation and monitoring. Being able to have small displays around the house in addition to gathering and controlling things remotely will help the family see room conditions without going to the computer. The idea of a touchscreen control for cheap is mind blowing.
i"m very young in the world of Arduino and i"m having a serious problem with the LCD QC2004A and Arduino Mega because whatever i write in alphanumeric, is translated to chinese language and i really don"t know what to do to change it.

We come across Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) displays everywhere around us. Computers, calculators, television sets, mobile phones, and digital watches use some kind of display to display the time.
An LCD screen is an electronic display module that uses liquid crystal to produce a visible image. The 16×2 LCD display is a very basic module commonly used in DIYs and circuits. The 16×2 translates a display of 16 characters per line in 2 such lines. In this LCD, each character is displayed in a 5×7 pixel matrix.
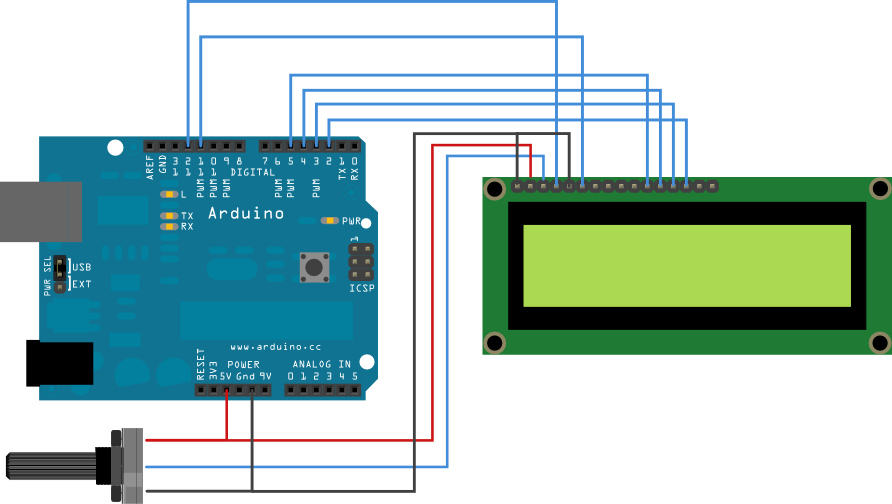
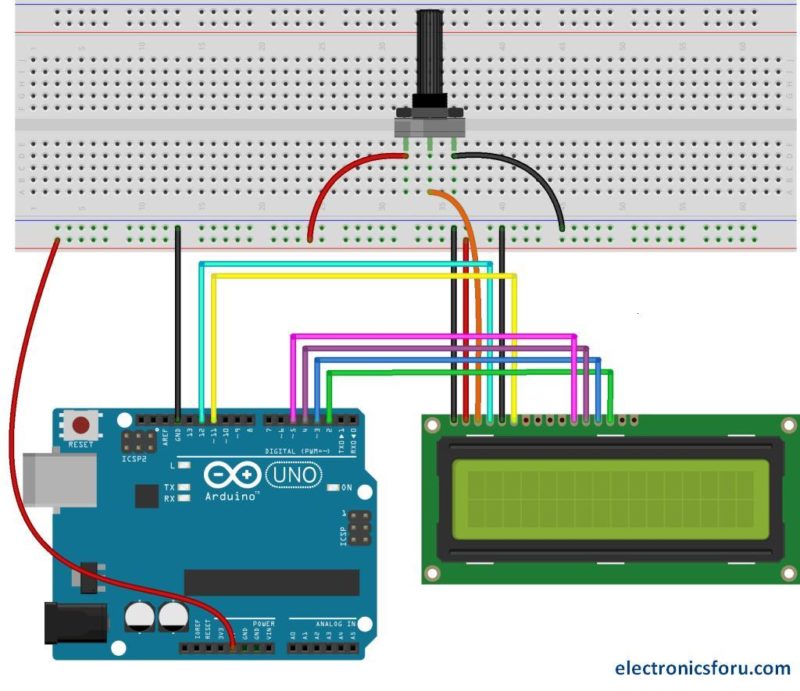
Contrast adjustment; the best way is to use a variable resistor such as a potentiometer. The output of the potentiometer is connected to this pin. Rotate the potentiometer knob forward and backward to adjust the LCD contrast.
A 16X2 LCD has two registers, namely, command and data. The register select is used to switch from one register to other. RS=0 for the command register, whereas RS=1 for the data register.
Command Register: The command register stores the command instructions given to the LCD. A command is an instruction given to an LCD to do a predefined task. Examples like:
Data Register: The data register stores the data to be displayed on the LCD. The data is the ASCII value of the character to be displayed on the LCD. When we send data to LCD, it goes to the data register and is processed there. When RS=1, the data register is selected.
Generating custom characters on LCD is not very hard. It requires knowledge about the custom-generated random access memory (CG-RAM) of the LCD and the LCD chip controller. Most LCDs contain a Hitachi HD4478 controller.
CG-RAM address starts from 0x40 (Hexadecimal) or 64 in decimal. We can generate custom characters at these addresses. Once we generate our characters at these addresses, we can print them by just sending commands to the LCD. Character addresses and printing commands are below.
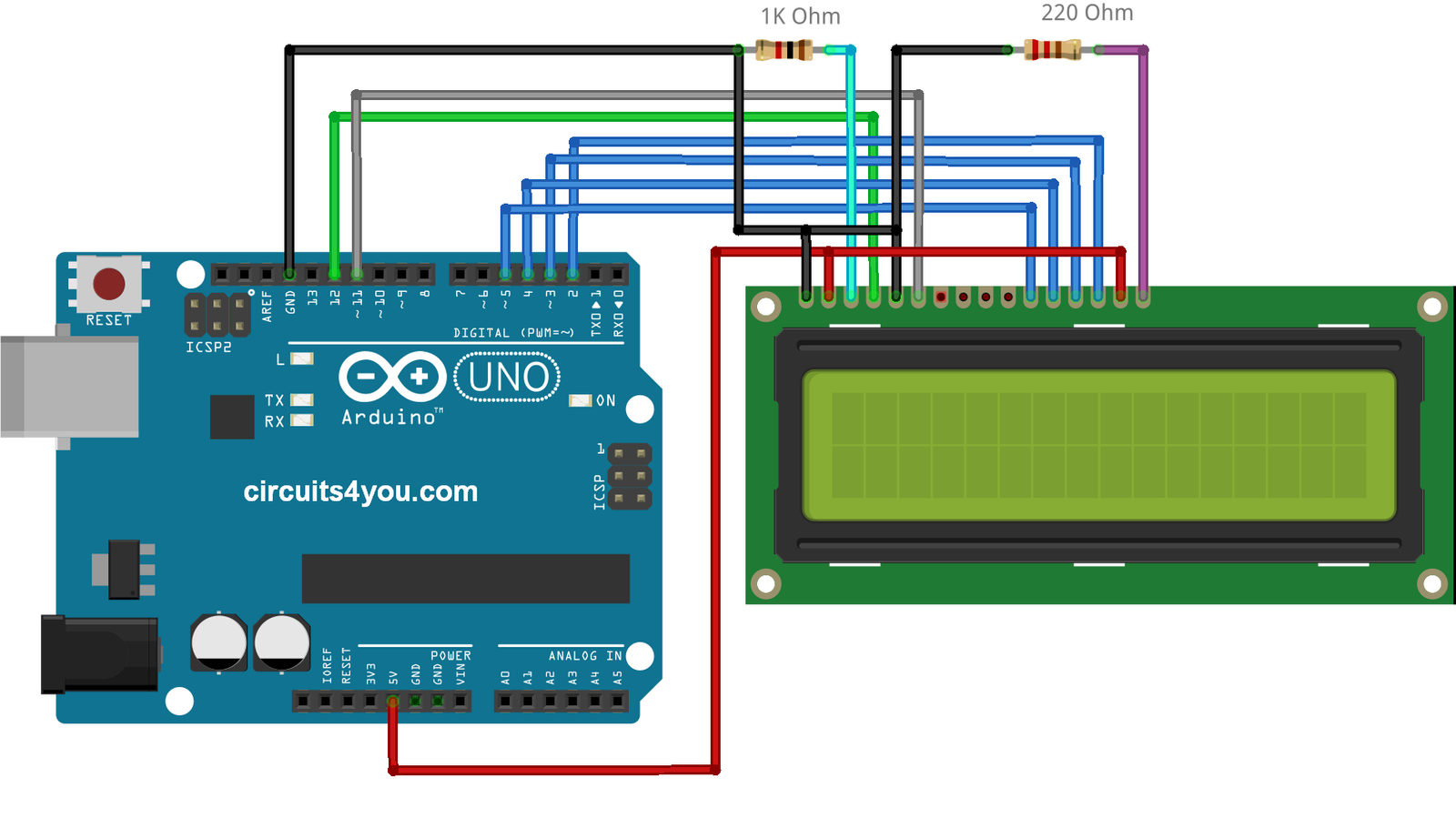
LCD modules are very important in many Arduino-based embedded system designs to improve the user interface of the system. Interfacing with Arduino gives the programmer more freedom to customize the code easily. Any cost-effective Arduino board, a 16X2 character LCD display, jumper wires, and a breadboard are sufficient enough to build the circuit. The interfacing of Arduino to LCD display is below.
The combination of an LCD and Arduino yields several projects, the most simple one being LCD to display the LED brightness. All we need for this circuit is an LCD, Arduino, breadboard, a resistor, potentiometer, LED, and some jumper cables. The circuit connections are below.

This post is an introduction to the Nextion display with the Arduino. We’re going to show you how to configure the display for the first time, download the needed resources, and how to integrate it with the Arduino UNO board. We’ll also make a simple graphical user interface to control the Arduino pins.
Nextion is a Human Machine Interface (HMI) solution. Nextion displays are resistive touchscreens that makes it easy to build a Graphical User Interface (GUI). It is a great solution to monitor and control processes, being mainly applied to IoT applications.
Connecting the Nextion display to the Arduino is very straightforward. You just need to make four connections: GND, RX, TX, and +5V. These pins are labeled at the back of your display, as shown in the figure below.
You can power up the Nextion display directly from the Arduino 5V pin, but it is not recommended. Working with insufficient power supply may damage the display. So, you should use an external power source. You should use a 5V/1A power adaptor with a micro USB cable. Along with your Nextion display, you’ll also receive a USB to 2 pin connector, useful to connect the power adaptor to the display.
The best way to get familiar with a new software and a new device is to make a project example. Here we’re going to create a user interface in the Nextion display to control the Arduino pins, and display data.
The user interface has two pages: one controls two LEDs connected to the Arduino pins, and the other shows data gathered from the DHT11 temperature and humidity sensor;
All components have an attribute called objname. This is the name of the component. Give good names to your components because you’ll need them later for the Arduino code. Also note that each component has one id number that is unique to that component in that page. The figure below shows the objname and id for the slider.
You should trigger an event for the touchable components (the buttons and the slider) so that the Arduino knows that a component was touched. You can trigger events when you press or when you release a component.
Notice that we have labels to hold the units like “ºC”, “ºF” and “%”, and empty labels that will be filled with the readings when we have our Arduino code running.
Once the GUI is ready, you need to write the Arduino code so that the Nextion can interact with the Arduino and vice-versa. Writing code to interact with the Nextion display is not straightforward for beginners, but it also isn’t as complicated as it may seem.
A good way to learn how to write code for the Arduino to interact with the Nextion display is to go to the examples folder in the Nextion library folder and explore. You should be able to copy and paste code to make the Arduino do what you want.
The first thing you should do is to take note of your components in the GUI that will interact with the Arduino and take note of their ID, names and page. Here’s a table of all the components the code will interact to (your components may have a different ID depending on the order you’ve added them to the GUI).
In this post we’ve introduced you to the Nextion display. We’ve also created a simple application user interface in the Nextion display to control the Arduino pins. The application built is just an example for you to understand how to interface different components with the Arduino – we hope you’ve found the instructions as well as the example provided useful.

In this Arduino touch screen tutorial we will learn how to use TFT LCD Touch Screen with Arduino. You can watch the following video or read the written tutorial below.
For this tutorial I composed three examples. The first example is distance measurement using ultrasonic sensor. The output from the sensor, or the distance is printed on the screen and using the touch screen we can select the units, either centimeters or inches.
The third example is a game. Actually it’s a replica of the popular Flappy Bird game for smartphones. We can play the game using the push button or even using the touch screen itself.
As an example I am using a 3.2” TFT Touch Screen in a combination with a TFT LCD Arduino Mega Shield. We need a shield because the TFT Touch screen works at 3.3V and the Arduino Mega outputs are 5 V. For the first example I have the HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor, then for the second example an RGB LED with three resistors and a push button for the game example. Also I had to make a custom made pin header like this, by soldering pin headers and bend on of them so I could insert them in between the Arduino Board and the TFT Shield.
Here’s the circuit schematic. We will use the GND pin, the digital pins from 8 to 13, as well as the pin number 14. As the 5V pins are already used by the TFT Screen I will use the pin number 13 as VCC, by setting it right away high in the setup section of code.
I will use the UTFT and URTouch libraries made by Henning Karlsen. Here I would like to say thanks to him for the incredible work he has done. The libraries enable really easy use of the TFT Screens, and they work with many different TFT screens sizes, shields and controllers. You can download these libraries from his website, RinkyDinkElectronics.com and also find a lot of demo examples and detailed documentation of how to use them.
After we include the libraries we need to create UTFT and URTouch objects. The parameters of these objects depends on the model of the TFT Screen and Shield and these details can be also found in the documentation of the libraries.
Next we need to define the fonts that are coming with the libraries and also define some variables needed for the program. In the setup section we need to initiate the screen and the touch, define the pin modes for the connected sensor, the led and the button, and initially call the drawHomeSreen() custom function, which will draw the home screen of the program.
So now I will explain how we can make the home screen of the program. With the setBackColor() function we need to set the background color of the text, black one in our case. Then we need to set the color to white, set the big font and using the print() function, we will print the string “Arduino TFT Tutorial” at the center of the screen and 10 pixels down the Y – Axis of the screen. Next we will set the color to red and draw the red line below the text. After that we need to set the color back to white, and print the two other strings, “by HowToMechatronics.com” using the small font and “Select Example” using the big font.
Now we need to make the buttons functional so that when we press them they would send us to the appropriate example. In the setup section we set the character ‘0’ to the currentPage variable, which will indicate that we are at the home screen. So if that’s true, and if we press on the screen this if statement would become true and using these lines here we will get the X and Y coordinates where the screen has been pressed. If that’s the area that covers the first button we will call the drawDistanceSensor() custom function which will activate the distance sensor example. Also we will set the character ‘1’ to the variable currentPage which will indicate that we are at the first example. The drawFrame() custom function is used for highlighting the button when it’s pressed. The same procedure goes for the two other buttons.
So the drawDistanceSensor() custom function needs to be called only once when the button is pressed in order to draw all the graphics of this example in similar way as we described for the home screen. However, the getDistance() custom function needs to be called repeatedly in order to print the latest results of the distance measured by the sensor.
Ok next is the RGB LED Control example. If we press the second button, the drawLedControl() custom function will be called only once for drawing the graphic of that example and the setLedColor() custom function will be repeatedly called. In this function we use the touch screen to set the values of the 3 sliders from 0 to 255. With the if statements we confine the area of each slider and get the X value of the slider. So the values of the X coordinate of each slider are from 38 to 310 pixels and we need to map these values into values from 0 to 255 which will be used as a PWM signal for lighting up the LED. If you need more details how the RGB LED works you can check my particular tutorialfor that. The rest of the code in this custom function is for drawing the sliders. Back in the loop section we only have the back button which also turns off the LED when pressed.
In order the code to work and compile you will have to include an addition “.c” file in the same directory with the Arduino sketch. This file is for the third game example and it’s a bitmap of the bird. For more details how this part of the code work you can check my particular tutorial. Here you can download that file:

The Arduino platform is Open Source and extremely popular. It is produced by hundreds of manufacturers around the world and is not always legal and of high quality.
The Arduino board was developed by a company that was founded by Italian Massimo Banzi. Until now, real Arduino boards are only made in Italy (Torino) and in the USA (New York). You can buy the boards either from an Italian store or from official distributors, the list of which is published on this website. Only such boards have the right to be called “Arduino” and are original.
Arduino policy does not prohibit third-party manufacturers from producing their own compatible boards. The only restriction is that such boards must not be called “Arduino,” as it is a registered trademark. However, it is acceptable to use the ending “duino” in their names, so these boards are often referred to as xDuino. Many large official Arduino distributors produce and sell their xDuino boards. For example, RedBoard from Sparkfun, DFRduino from DFRobot, Seeeduino from Seeed Studio, etc.
The Arduino brand’s popularity encourages many people to produce these boards and illegally print the name “Arduino” and “Made in Italy” on them. They claim to be selling authentic boards, but they are only counterfeit.
Such boards’ quality is low, they are made mostly in China, and it is impossible to establish the true manufacturers because they are hiding behind the Arduino name. There are a lot of such manufactures, they open and close, and their main goal is to make the board and sell it, using the low price as a trump card.
Pay attention to the price. The original Arduino Uno costs $20 at the official store. It is not allowed to sell them cheaper under the terms of the contract.
The original Arduino (left) comes in a branded cardboard box. Inside: the board, stickers, an annotation, and a protective plastic backing for the board. The Chinese knockoffs most often come in a simple plastic bag (right).
The price difference between the Chinese Arduino controller and the original is about 80% to 100%. The difference in soldering quality is 20% to 30%. The soldering of the originals is, of course, a bit more careful and beautiful. Well, this is to be expected given the price of the original – in dollars, it is about 20 and above. There are boards and 25-30 dollars, depending on its revision. The price depends on the model – whether it will be Arduino Nano, or Arduino Uno, or Arduino Mega 2560.
The Chinese have learned how to do excellent soldering. Yes, before the first revision, the Arduino boards I ordered from China were poorly made. They weren’t even washed. I mean, they were washed, but there were white marks on the board. There were even traces of oxide. I had to take the board and wash it out with alcohol myself. Now it’s all done great, and it’s all shiny.
The only thing you will ever see on a Chinese Arduino is the Italian originals. Only the original Arduino board will clearly say Arduino on it. As a result, the Chinese, because the rights to the Arduino brand do not belong to them, can call the board Uno, Mega 2560, Nano, or just do not write anything on it call it something else. There are quite a lot of variations of names. The only thing is that the name Arduino is never used. Naturally, all users call these controllers Arduino.
There are many manufacturers of Arduino boards in China, and the boards’ quality is fundamentally different. Most of the differences are in the appearance, but probably also in the components used.

Character display module is an LCD module with a certain number of rows and columns, and has a green or blue backlight and white character. These displays can usually be used to display text, characters and numbers. The contrast can be adjusted by connecting a potentiometer to pin 3. Pin 15 and 16 are for backlight. You can use 6 pins E, RS, DB4, DB5, DB6, DB7 to interface the display with Arduino.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey