burned lcd module free sample
Have you ever left your TV or monitor on for days, stuck on the same image? You return to your screen, only to find an image burned into the display. No matter what you do, it won"t go away. It is a permanent image burn.
Why do monitors and TVs get image burn? Why can"t manufacturers prevent LCDs and plasma screens from a burnt image imprint? Moreover, what can you do to fix an image burn?
LCD and LED do not work in the same way as CRTs, either. LCD and LED screens use backlit liquid crystals to display colors. Although manufacturers market screens using LED and LCD, an LED screen is still a type of LCD. The white backlight filters through the liquid crystals, which extract particular colors per pixel.
LCD and LED displays don"t suffer from the same type of image burn as CRTs and plasma screens. They"re not completely clear, though. LCD and LED screens suffer from image persistence. Read on to find out more about image persistence.
Before you can fix screen burn-in, take a second to understand why these images burn in the first place. LCDs and LEDs don"t suffer from burn-in as seriously as plasma screens. But static images can leave an imprint on both display types if left alone for too long. So, why does image burn happen?
LCD and LED screens can also experience image burn, though the image burn process can take longer to develop into a permanent issue. In addition, LCD and LED screens suffer from another issue, known as image retention (also known as image persistence or an LCD shadow).
Image retention is a temporary issue that you are more likely to notice before it becomes a permanent issue. However, proper image burn can still affect LCD, LED, and OLED screens.
Image burn-in fixes exist for LCD and plasma screens. How effective an image burn-in fix is depends on the screen damage. Depending on the length and severity of the image burn, some displays may have permanent damage.
If your plasma or LCD screen already has image burn-in, you can try turning on white static for 12 to 24 hours. The constant moving of white-and-black across your screen in random patterns can help remove the ghost image from your screen.
Pixel-shift constantly slightly adjusts the image on your screen, which varies the pixel usage to counteract image burn. You might have to enable a pixel or screen shift option in your screen settings. Pixel-shift is a handy feature for LED and OLED screens that cannot recover from image burn and should help counteract an LCD shadow.
While the Deluxe version uses advanced algorithms to repair burned screens and prolong plasma and LCD longevity, the official site is no longer up and running, and there is no way to download the full version officially.

TFT LCD image retention we also call it "Burn-in". In CRT displays, this caused the phosphorus to be worn and the patterns to be burnt in to the display. But the term "burn in" is a bit misleading in LCD screen. There is no actual burning or heat involved. When you meet TFT LCD burn in problem, how do you solve it?
When driving the TFT LCD display pixels Continously, the slightly unbalanced AC will attract free ions to the pixels internal surface. Those ions act like an addition DC with the AC driving voltage.
For normal white TFT LCD, white area presenting minimal drive, black area presenting maximum drive. Free ions inside the TFT may are attracted towards the black area (maximum drive area)
Screen burn can also become a problem on LCD mobile screens. While this may be a rare occurrence, it’s not impossible either. When it does, fixing it is a lot more of a challenge, since LCD pixels work differently from OLED screens. Therefore, you might have to accept that screen burns on your LCD screen are most likely there to stay. But before you give upall hope, you should still tryusing LCD Burn-In Wiper, whichcycles colors similar to its OLED counterpart to try to repair pixels.

Screen burn, also called screen burn-in, ghost image, or display burns are images or icons that are displayed on a screen when they should not be there. Screen burn comes on gradually and gets worse over time and is most common on OLED screens. The navigation bar, the top status bar, or home screen apps are frequent images that get “burned” into the display.
The display is a major factor that affects our decision to purchase a particular smartphone. The difficult part is choosing between AMOLED (or OLED) and LCD. Although in recent times most of the flagship brands have made the shift to AMOLED, it does not mean that it is flawless. One point of concern with AMOLED display is that of screen burn-in or ghost images. AMOLED displays are much more likely to face the problem of screen burn-in, image retention, or ghost images when compared to LCD. Thus, in the debate between LCD and AMOLED, the latter has a clear disadvantage in this field.
The color black is the least harmful to your display. It requires minimum illumination and thus increases the lifespan of the pixels of an AMOLED screen. Using a black screen as your wallpaper greatly reduces the chances of burn-in on AMOLED or LCD display. Check your wallpaper gallery, if the solid color black is available as an option then set it as your wallpaper. If you are using Android 8.0 or higher then you will probably be able to do this.
As mentioned above it is unlikely that screen burn-in will take place on an LCD screen but it is not impossible. Also, if a screen burn-in does happen on an LCD screen then the damage is mostly permanent. However, there is an app called LCD Burn-in Wiper that you can download and install on your device. The app only works for devices having an LCD screen. It cycles the LCD pixels through various colors at different intensities to reset the effect of burn-in. If it does not work then you need to visit a service center and consider changing the LCD display panel.
I hope the above tutorial was helpful and you were able to fix screen burn-in on the AMOLED or LCD display of your Android phone. But if you still have any queries then feel free to ask them in the comment section.

At the outset, it is important to know what this problem actually is. A screen burn-in is the phenomenon observed on displays where a part of the display suffers from permanent discoloration—often caused by prolonged use of a static image. It is also important to note that OLED displays are much more susceptible to screen burn-in than their LCD counterparts. In fact, what people think of as screen burn-in on an LCD panel might usually another issue.
For LCD screens, there"s a dedicated app, LCD Burn-in Wiper that could possibly fix minor cases. However, this tool is not suitable for OLED or AMOLED displays, such as those found on most modern flagship smartphones. For that, you"ll need a different app.
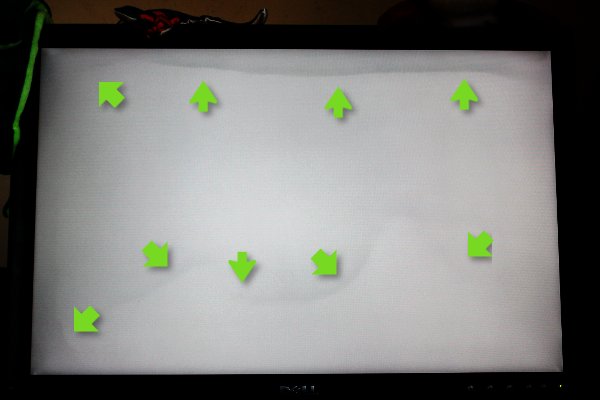
Screen burn on an amber CRT computer monitor. Note that there are two separate burned-in images: one of a spreadsheet program, and another of an ASCII-art welcome screen.
A nearly two-year-old LCD television showing extreme burn-in of CNN"s circa 2008 digital on-screen graphic; this television is in a McDonald"s restaurant where CNN is permanently turned on and displayed throughout the business day.
In the case of LCDs, the physics of burn-in are different than plasma and OLED, which develop burn-in from luminance degradation of the light-emitting pixels. For LCDs, burn-in develops in some cases because pixels permanently lose their ability to return to their relaxed state after a continued static use profile. In most typical usage profiles, this image persistence in LCD is only transient.
Both plasma-type and LCD-type displays exhibit a similar phenomenon called transient image persistence, which is similar to screen burn but is not permanent. In the case of plasma-type displays, transient image persistence is caused by charge build-up in the pixel cells (not cumulative luminance degradation as with burn-in), which can be seen sometimes when a bright image that was set against a dark background is replaced by a dark background only; this image retention is usually released once a typical-brightness image is displayed and does not inhibit the display"s typical viewing image quality.
Other examples: Apple"s iPhone X and Samsung"s Galaxy series both mitigate or delay the onset of burn-in by shifting the pixels every minute or so for the battery, Wi-Fi, location, and service bars. Also, parallax scrolling may be enabled for the home screen to give icons a 3D-like effect, a setting Apple refers to as "perspective zoom". AG Neovo patented Anti-burn-in technology is also using pixel shifting to activate the pixels to move by the designed time interval to prevent burn in effect on LCD monitors.
Google requests that when these techniques are enabled, watch face developers do not use large blocks of pixels so that different pixels are burned in with each shift, reducing the overall wear of the pixels.
Depending on the type of screen, it is sometimes possible to remedy screen burn-in through the use of remedial software and remedial devices. In the case of OLED screens on Android phones, burn-in reduction apps can display an inverted image of the navigation and status bars (which are constantly displayed and therefore the most likely elements to be burned in) to burn in opposite pattern, resulting in a screen whose sub-pixels have more even luminosity and therefore less visible burn-in artifacts.

So if the fear of the mere possibility of burn-in is your primary concern, the decision is simple: Buy an LCD-based display instead. But know that you"re sacrificing the best picture quality that money can buy. Here are some points to keep in mind:
To repeat, you can watch those channels, play games or whatever else to use your TV as a TV, your phone as a phone, etc. You just shouldn"t watch only those channels, all day every day. And if that sounds extreme, know that emails I"ve gotten from readers about burn-in always have some variation on "well I only watched that channel for 5 hours a day." If that sounds like you, get an LCD.
When CNET reached out to Samsung for details, the representative defined "normal consumer use" as "use of the product by consumers in a home environment for viewing content and/or gaming in a typical manner. It doesn"t cover business use." In other words, those ESPN logos you see burned into the screens at your local sports bar would not be covered.
With TVs, beyond the methods outlined above, there"s not much you can do to reverse burn-in. In theory, I suppose, you could create an inverse image using Photoshop and run that on your screen for a while. This could age the rest of the panel to more evenly match the "burned in" area. Figuring out how to do this is well beyond the scope of this article, and you"d need to be pretty well versed in Photoshop to even attempt it.
The most comprehensive independent tests for burn-in on TVs was run by the aforementioned review site RTings. In August 2017 they began a burn-in torture test with LCD and OLED TVs, followed by a "real life" torture test in 2018. They stopped regularly updating the test in 2020, but that was after the equivalent of 5 years of normal use on multiple TVs, and still they felt that most people will never have an issue with burn-in.
Before you check it out, keep in mind what they"re doing is not normal use. You"d have to be trying to wreck a TV to make it look that bad, which is literally what they"re trying to do. That said, the information is still valuable, and the main takeaway is that OLED is indeed more susceptible to burn-in than LCD.
With OLED TVs, it"s something to keep in mind if you"re a TV news junkie, or only ever play one video game. Keep an eye out for image retention or uneven wear. If you spot it, perhaps switch up your viewing habits, adjust the TV"s settings, or run the pixel refresher a few times. And if you watch content with hours of the same static image each day, or just keep CNN, Fox or CNBC on in the background all day, you should probably get an LCD TV.

Update 11/05/2018: After more than 5000 hours, there has been no appreciable change to the brightness or color gamut of these TVs. Long periods of static content have resulted in some permanent burn-in (see the CNN TVs); however, the other TVs with more varied content don"t yet have noticeable uniformity issues on normal content. As a result, we don"t expect most people who watch varied content without static areas to experience burn-in issues with an OLED TV. Those who display the same static content over long periods should consider the risk of burn-in, though (like those who watch lots of news, use the TV as a PC monitor, or play the same game with a bright static HUD). Those concerned about the risk of burn-in should go with an LCD TV for peace of mind.

Most of the time, these guides explain how image retention works and how you can speed up its recovery process. We want to clear up any confusion you might have about image burn-in and image retention on LCD and OLED displays.
Image retention, also known as ghosting or image persistence, is the temporary effect of images remaining visible on LCDs or OLEDs for a short period, usually a few seconds.
Image burn-in is caused by screen pixels that stay activated in a static position for long periods of time.Think of a TV in a lobby or waiting area that"s always playing the same news channel. The news channel footer and logo get burned into the screen permanently, even when you change the channel.
When LCD or OLED pixels stay activated in a static position, they"ll eventually become "stuck" in that position. When this happens, you"ll notice a faded, stubborn image that persists on the screen.
When pixels fail to activate or deactivate entirely, it results in faded images that won"t clear from the screen. This is common in applications using character LCDs where the alphanumeric characters are updated less frequently.
Get those pixels moving! The longer a pixel stays activated in a static position, the closer it gets to being burned in. You can exercise your screen"s pixels with scrolling text, moving images, or changing colors.
For a LCD display, lowering the contrast will put less stress on the liquid crystals and will help to reduce the rate of pixels becoming weak, or sticking.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey