lcd panel has a line across it quotation
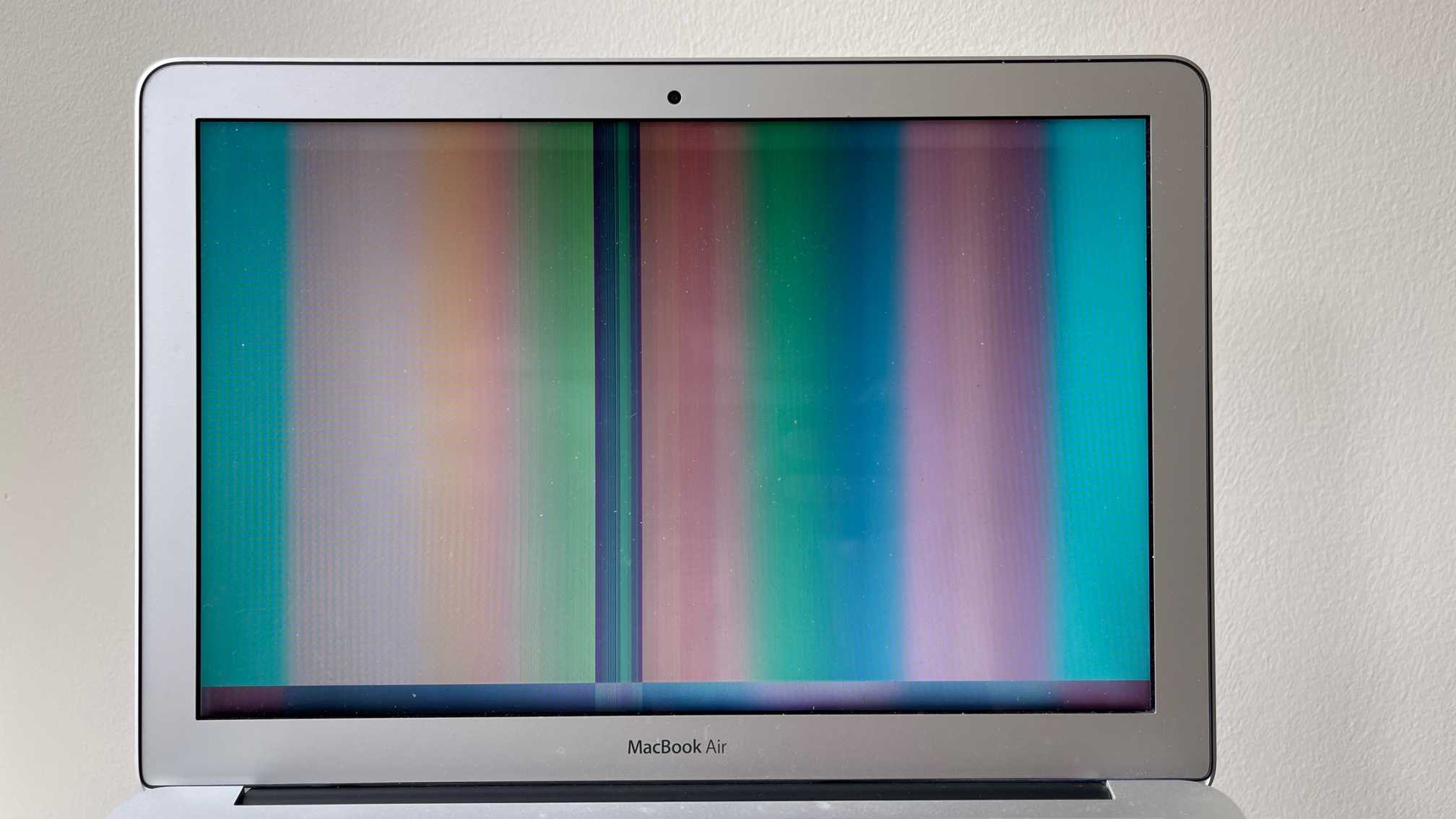
Ours is a Sony Bravia that is now over 10 years old. Several months ago we started noticing lines, especially on the left (our left) side of the screen. They’d go away after the tv warmed up. Then we started noticing it was darker on that side of the screen, but again, after the tv warmed up the screen would be normal. Then about two months ago it started getting worse and didn’t ever get completely better, even after the tv warmed up. So I watched some youtube videos that all talked about the ribbon cables becoming loose over time and to apply pressure along the top and see if that made it better, and if so, it was a loose cable and if you put electrical tape or something that would help keep the pressure, it would fix the problem. Hubby pressed along the top and sure enough, when he pressed in one spot on the left side suddenly the picture cleared up. Stayed good for about a week, then problems again, pressed again, fixed again. A week or so later, same problem, but this time when he pressed on it nothing got better.
So I decided to take the cover off and look at it better. As I was pressing on the tops of the ribbon cables that run down from the top of the frame, for a minute it got better but then suddenly there was a wide white vertical line, with a thin green one down the center of it, running down the front of the screen, and it was perfectly aligned with one of the cables. So now I still have the dark side of the screen, and some ghosting, and some lines, but now this bright white streak/line right down the front. Another weird thing is that if the whole screen is bright (like watching a show set in a snowy place) then the darkness even on the left side is basically gone, but if the scene is dark at all, that side is almost black. I don’t know if it means that particular ribbon cable is bad, or if something is loose, if things need to be replaced or what. It’s very frustrating as it’s been a great tv. Hubby wants to just buy a new one, but even if he does I would still like to try and figure out this one as it could then go in another room.

Responsible for performing installations and repairs (motors, starters, fuses, electrical power to machine etc.) for industrial equipment and machines in order to support the achievement of Nelson-Miller’s business goals and objectives:
• Perform highly diversified duties to install and maintain electrical apparatus on production machines and any other facility equipment (Screen Print, Punch Press, Steel Rule Die, Automated Machines, Turret, Laser Cutting Machines, etc.).
• Provide electrical emergency/unscheduled diagnostics, repairs of production equipment during production and performs scheduled electrical maintenance repairs of production equipment during machine service.
This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.
This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.
when I want to quote a word or use the quotes (either single or the double quotes) I have to either press quote and type, the quote appears and then press quote again, and other times it places 2 dots horizontal above the letter i type. but this time I need to press it twice and then I get 2 quotes and have to back space out one of them - gets to be annoying...
here is what happens, i press quote once änd type - see above my first ""and"" (and see here too) along the line and then so on keep having these issues - annoying i tell yah - i don"t know where to turn it off - anyone???:robotmad:
HP Elite X2 1012 G2, HP ENVY 17-j005tx Notebook, HP ENVY Recline 27-k001a, HP ProLiant MicroServer Gen8 G2020T, HP MediaSmart EX495 Server, HP MediaVault 2020, HP ENVY 120 AiO Printer

By default in a Salesforce org, related list views contain links to both Edit and Delete the records in the list. As a result, if you display the default Quote Line related list on the Quote object record detail page, users will see the option to Edit or Delete those lines from the quote Record detail page. This custom visualforce page and controller extension together can allow you to display the Quote Lines associated with the Quote on the page layout without giving users the ability to edit/delete the lines outside of the line editor.
List
Create the controller extension as an apex class in your org. After creating the controller extension, create the visualforce page. Once both records are created, add the visualforce page to the Quote record detail page layout for the desired profiles.
NOTE: If you wish to display different fields than those listed in this article in your columns, you MUST add those fields to the query in the controller extension in addition to the list of fields in the visualforce page.
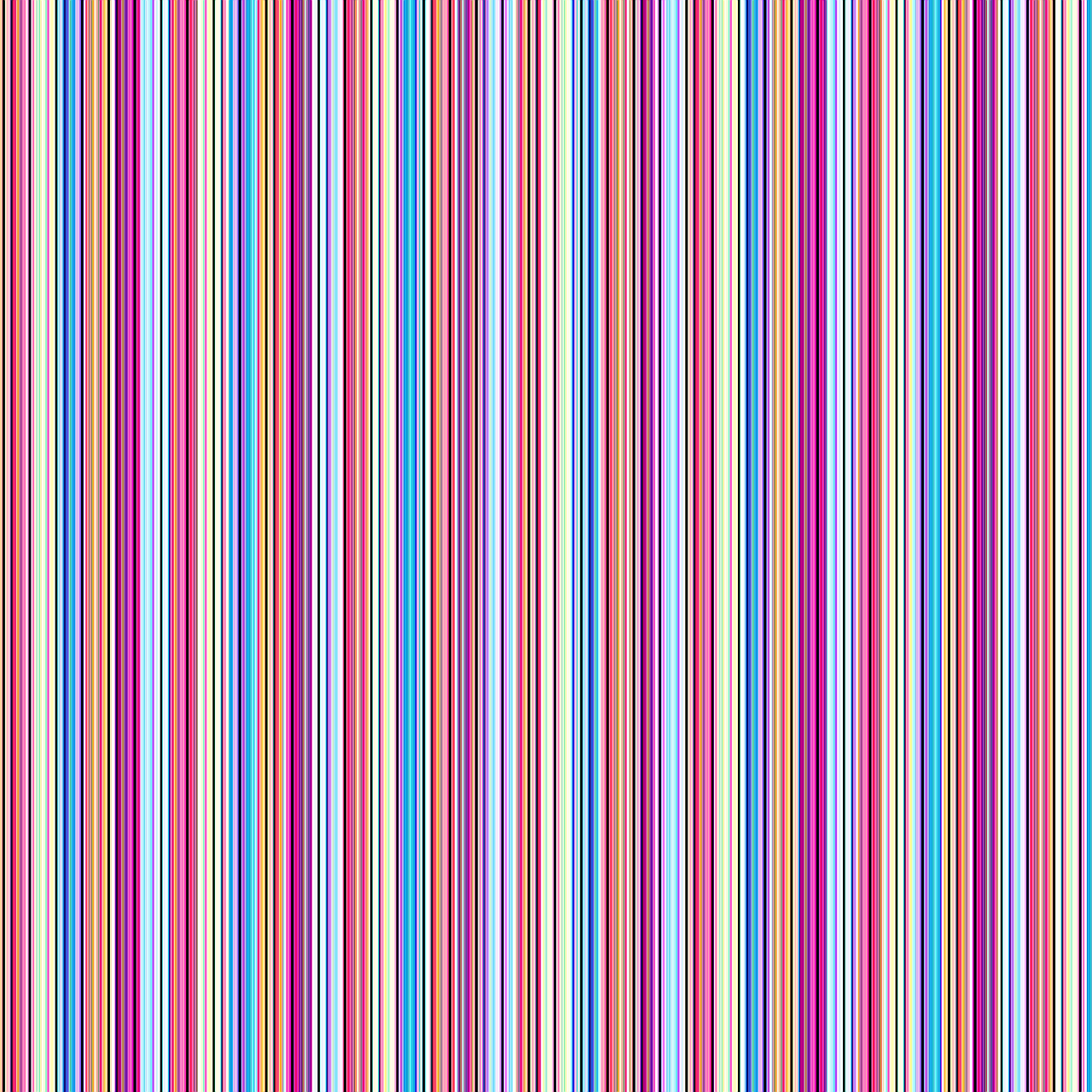
LCD display screens on notebooks, monitors and TVs alike are made up of two thin layers of glass containing liquid crystal material between them. When the glass becomes damaged, debris infiltrates the crystal layer or another issue occurs with the display function, this causes vertical lines of color to appear when the monitor is fully illuminated. These lines are either permanent due to internal failure or temporary due to faulty display connections.
Diagonal, jagged and both horizontal and vertical lines typically indicate panel damage. A single set of horizontal lines could indicate damage, a graphics system failure, or loose internal video cables. Broken signals from cables or graphics hardware creates impurities in reproducing an image on an LCD screen, conditions that often manifest in the form of vertical or horizontal lines of color.
If the lines are infrequent in their appearance, or are not permanently visible, a loose video cable is often the problem. As devices are carried, dropped and bumped, cables become loose even in laptops. Laptops are built with casing to absorb and dissipate small shocks, but even some bumps can cause cables to become loose. Even televisions and monitors, while often stationary, can still have loose cables if not properly seated.
If you"ve ever opened your laptop to clean underneath the keyboard, you might see numerous things like food particles, hair or even dust. On the rear of monitors and televisions, they also contain a series of holes or slits that dust can creep into the inner workings and cause problems. Regularly cleaning out a laptop"s keyboard and dusting off the rear of a monitor or television can greatly extend its useful life. This is a preventative measure and rarely works in removing any existing lines on a screen.
The first step in troubleshooting is determining the extent of the damage. For external monitors or televisions, re-seat any video input cables or consider replacing the cables with new ones. Should the lines continue to display, this indicates an internal failure, something few consumers are able to fix on their own. Instructions exist online for individual products to disassemble a monitor, laptop or television to replace broken parts, but the most suggested course of action is shipping it to the manufacturer for a warranty repair. If no warranty is active for the device, consumers are then advised to replace the device entirely with a new one, as this is usually the cheapest solution. Lines on an LCD panel indicate the LCD screen or screen ribbon cable need to be replaced, parts that can cost several hundred dollars.
Ryan Goodrich has been writing technology and technical articles for a vareity of online and service-based companies since 2008. He"s written content for websites like TopTenREVIEWS and TechNewsDaily, in addition to many other website. He holds a Bachelor of Science in English and a master"s degree in communication and works as a technical writer.
The Full Display page opens when a user selects an area within a record"s brief display that does not contain hypertext links. Selecting on the title or the availability link in the record"s brief display may also take the user to the Full Display page.
The Full Display Page contains various sections, which are called services. If a service is not relevant to a record, it does not appear on the Full Display page. The Full Record Services tab enables you to configure the order of services, the display lines for the Details service, additional links, and whether citation trails and times cited information is displayed.
The Services page looks very similar to the Full Display page, but it does not allow users to perform searches and may not permit access to other pages and functionality (such as My Library Card). You need to configure only a single view in Primo VE to support both types of pages.
Get It, View Online, How to Get It – These sections enable users to request physical items, view electronic materials or get materials from other sources.
The Get It service displays when the library has physical items. For information on how to configure custom sorting of locations, see Configuring the Get It Service.
The How to Get It service displays only general electronic services that are delivery-related (such as an ILL service), and appears only when the record has no holdings. For more information, see Adding a General Electronic Service.
Links – The Links section displays additional links and general electronic services that are not delivery-related. For more information, see the following sections:
Search inside – This section displays on the Full Display page when the journal has an ISSN and a CDI search profile slot has been activated for your view. This service enables users to search for articles within the journal. To enable this functionality, you must define the ISSN field as a search index for advanced searches (see Adding a Search Index, Resource Type, or Language to Advanced Searches).
This type of search uses the view"s first blended search profile slot that includes CDI as its initial scope in Advanced Search. If there are no blended search profile slots (including CDI), it uses the first CDI-only search profile slot. If the view does not have any active search profile slots that include CDI, the Search Inside section will not appear for the journal in its full display.
Details – This service displays information about the record and enables you to display the same information that is displayed in the brief records display, but it is meant to include additional information that can be displayed on more than three rows. For more information, see Configuring the Details Service.
Browse Shelf – This service enables users to visually browse a library shelf in relation to the selected record so that users may find other items that are related to their search. For configuration information, see Configuring the Browse Shelf Service.
Quick Access – This service enables users to visually browse a record"s representation files using Alma"s new digital viewer. For more information, see Configuring the Quick Access Service.
More from the Same Course/Collection – This service expands the search of the current title and enables users to browse items in additional collections and courses that also contain the current title. For more details, see Displaying the More from the Same Service.
May Also Be Held By – This service provides links to this resource at other locations (such as non-Alma institutions). If this service is not enabled and configured for your institution, it does not appear as a service on the Full Record Services tab. For more details, see Displaying the May Also Be Held By Service.
The Get It service displays the physical locations that hold an item. If there are multiple locations, the Get It section lists these locations in the order specified by Alma. If the custom sorting option is enabled in Alma, the Custom Libraries Order mapping table is enabled to enable you to override Alma"s custom settings per view, if needed.
When enabled, the Custom Libraries Order mapping table enables you to assign a library priority for each library (1 = highest priority). For each library priority, Alma further sorts these locations alphabetically by location priority and then by the number of available items. For more details about location priority, see Configuring Physical Locations.
In the following example, the highest priority is given to the Music (Stacks) location since it has the highest library priority (1) and location priority (Display first). The Main (Stacks) location is listed next because it has more available items than the Biology (Stacks) location. The Main (Juvenile) location is listed last in the library priority 1 group because it has the Display last location priority. The Law (Stacks) location is listed last because it has the lowest library priority.
All locations for libraries that are left unassigned are given the lowest library priority and are further sorted alphabetically by location priority and then by the number of available items.
Ensure that the Use Custom Sorting field is set to Yeson Alma"s Locations Ordering Profile page (Configuration Menu > Fulfillment > Discovery Interface Display Logic > Locations Ordering Profile), and decide whether you want to override this custom sort configuration for your view. For more details, see Configuring the Order of Locations in Primo Search Results.
Open the View List page (Configuration Menu > Discovery > Display Configuration > Configure Views) and edit your view to open the View Configuration page.
Add a row for each library and set its library priority (1 = highest priority). All unassigned libraries are grouped together and given the lowest library priority.
The Details service displays the bibliographic information for a record (such as the contributors, description, and so forth). For details on how information is mapped from the source records to the display fields in Primo VE, see the Display sections in Mapping to the Display, Facets, and Search Sections in the Primo VE Record.
Primo VE enables you to configure the display lines for the Details service. The configuration is very similar to the configuration of the display lines in the record"s brief display, but you are not limited to four display lines. Each display line can consist of multiple data fields that are separated by a delimiter (such as a semicolon).
On the Views List page (Configuration Menu > Discovery > Display Configuration > Configure Views), edit your view to open the View Configuration page.
On the Views List page (Configuration Menu > Discovery > Display Configuration > Configure Views), edit your view to open the View Configuration page.
In the Enable Link in Full Display dialog box, select the Display Source Record checkbox if you want users to be able to view the item"s source record.
By default, Browse Shelf displays physical items that appear together on a virtual bookshelf. If you prefer, you can also display electronic material, which is based on call numbers from bibliographic headings, not just the holdings (for physical items).
On the Views List page (Configuration Menu > Discovery > Display Configuration > Configure Views), edit your view to open the View Configuration page.
The Citations service displays the citation trails for the record and also includes a link to the cited by records provided by the Web of Science and Scopus services.
Primo VE enables you to configure whether citation trails and cited by links from the Web of Science and Scopus services appear in the Citations service.
On the Views List page (Configuration Menu > Discovery > Display Configuration > Configure Views), edit your view to open the View Configuration page.
Times Cited – When selected, this option displays the times cited information from the Web of Science and Scopus services in the Citations section. Collections from these services must be activated in Alma to appear.
The Quick Access service embeds Alma"s new digital viewer to enable users to quickly access and view digital representations stored in Alma. From the embedded viewer, users can download the file, open the file in a new tab or window, or select the right/left arrows to view additional representation files.
No configuration in Primo VE is needed to enable this functionality, but you must have the new Alma Viewer enabled. The following table lists other configuration options associated with this service.
On the Viewer Services page (Configuration Menu > Fulfillment > Discovery Interface Display Logic > Viewer Services), edit the Alma Viewer service and select the Use New Viewer checkbox.
On the Discovery Interface Display Logic Rules page (Configuration Menu > Fulfillment > Discovery Interface Display Logic > Display Logic Rules), check the settings of the following out-of-the-box rules:
Hide service Representation Quick Access with Obtrusive Copyrights (Alma representations only) = true - When enabled, the Quick Access section is hidden in Primo VE when obtrusive copyrights are enabled.
The More from the same service is enabled by default. With this configuration, you can hide it from users. for more details, see Configuring the More From the Same Service in Primo VE.
On the Views List page (Configuration Menu > Discovery > Display Configuration > Configure Views), edit your view to open the View Configuration page.
When this service is enabled and configured (see Configuring the "May Also Be Held By" Service in Primo VE), it appears by default on the record"s Full Display page. With this configuration, you can hide this service from users.
On the Views List page (Configuration Menu > Discovery > Display Configuration > Configure Views), edit your view to open the View Configuration page.
On the Views List page (Configuration Menu > Discovery > Display Configuration > Configure Views), edit your view to open the View Configuration page.
Regardless of its setting on this tab, Primo VE displays the Citation section last. For a CSS workaround, see Display order of the full view left menu.

An action you just performed triggered a security alert and blocked your access to this page. This could be because you submitted a SQL command, a certain word or phrase, or invalid data.
Uma ação realizada por você disparou um alerta de segurança e bloqueou seu acesso à página. Isso pode acontecer porque você enviou um comando SQL, uma palavra ou frase específica ou dados inválidos. Se isso continuar acontecendo, crie um arquivo de arquivo morto HTTP (siga essetutorial) com uma reprodução do problema e envie o arquivo para a gente.
Una acción que acaba de realizar activó una alerta de seguridad y bloqueó su acceso a esta página. Podría ser debido a que envió un comando SQL, una cierta palabra o frase, o datos no válidos. Si sigue ocurriendo, cree un archivo de almacenamiento HTTP (siga estetutorial) con el problema reproducido y envíenos el archivo.
Eine Aktion, die Sie soeben ausgeführt haben, hat eine Sicherheitswarnung ausgelöst. Ihr Zugriff auf diese Seite wurde blockiert. Möglicherweise haben Sie einen SQL-Befehl, ein bestimmtes Wort, einen bestimmten Ausdruck oder ungültige Daten eingereicht. Wenn dies andauert, erstellen Sie eine HTTP-Archivdatei (Anweisungen hier), in der das Produkt reproduziert wird, und senden Sie sie dann an uns.
Une action que vous venez d’effectuer a déclenché une alerte de sécurité et a bloqué votre accès à cette page. Vous avez peut-être envoyé une commande SQL, une expression ou un mot donné, ou des données non valides. Si le problème persiste, créez un fichier d’archive HTTP (suivez cedidacticiel) avec le problème reproduit, et envoyez-nous ce fichier.
Een actie die u zojuist hebt uitgevoerd, heeft een beveiligingsmelding geactiveerd. Uw toegang tot deze pagina is geblokkeerd. Een mogelijke oorzaak is dat u een SQL-opdracht, een bepaald woord of een bepaalde woordgroep of ongeldige gegevens hebt verzonden. Als dit probleem zich blijft voordoen, maak dan een HTTP-archiefbestand (volg dezezelfstudie) waarin het probleem is gereproduceerd. Stuur dit bestand vervolgens naar ons.
Una tua azione ha fatto scattare un avviso di sicurezza e ha bloccato il tuo accesso a questa pagina. L’inconveniente potrebbe essere causato da un comando SQL, una determinata parola o frase, oppure dati non validi. Se il problema persiste, crea un file di archivio HTTP (come indicato in questoarticolo) riproducendo l’errore e inviacelo.
The cat function can also be used to print each character string without quotes in a new line of the RStudio console. For this, we have to paste “\n” at the end of each character string:
Another alternative for printing character strings without quotes is provided by the print function. Within the print function we have to specify the quote argument to be equal to the logical value FALSE:
Please accept YouTube cookies to play this video. By accepting you will be accessing content from YouTube, a service provided by an external third party.

Other answers nicely show how to deal with double quotes in your character strings when you create a vector, which was indeed the last thing you asked in your question. But given that you also mentioned display and output, you might want to keep dQuote in mind. It"s useful if you want to surround each element of a character vector with double quotes, particularly if you don"t have a specific need or desire to store the quotes in the actual character vector itself.
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/22422464/image1.jpeg)
In the past decade, LCD monitors have replaced CRT screens for all but the most specialist applications. Although liquid crystal displays boast perfect

Sierra Chart provides a Quote Board feature. A Quote Board provides real-time and current daily quote data for a list of symbols. The symbols can be selected to change the symbol of the associated chart. Open Order and Position data for the symbols is provided on the Quote Board as well.
Theupdate interval of the Quote Board is controlled through a setting and updates at specific time intervals. Global Settings >> General Settings >> Quote Board Update Interval in Milliseconds. The default is 800 ms. We do not recommend making this too low of a value as it will increase CPU usage.
A Quote Board is associated with the active Chartbook at the time it is opened. If a Chartbook is not already open, when you open a new Quote Board, then a Chartbook will be created.
To add a symbol to the end of the list of symbols, select the last row in the list of symbols and type the symbol into the box below the list or press the Find button and select a symbol from the list of available symbols. To add a symbol anywhere else in the list, click at the location in the list where you want to add the symbol and press the Add button. After inserting a blank row into the list, type the symbol into the box below the list or press the Findbutton .
In the case of when using the Sierra Chart Quote Board, you do not need to prefix symbols with a / or # when adding them to the list of symbols, unlike when you enter Quote Request symbols on a Spreadsheet.
To easily save and load a set of symbols to and from a text file respectively, select File >> Save Symbol List or File >> Load Symbol List on the Quote Board menu.
The default file extension is SymbolList. The files are plain text files. If you are loading a list of symbols from other sources, the symbols can be separated with a comma character, a tab character or a new line character.
The Settings >> Set Symbols window also has Import and Export commands for reading and saving a list of symbols from and to a text file, respectively. The symbols in this text file can be separated with a comma character, a tab character or a new line character.
To set the colors for the Quote Board, select Settings >> Graphics Settings on the menu on the Quote Board window. The relevant color settings begin with Quote Board in the list of Colors and Widths.
Quote Board: Price Change Up: This is the color for DailyChange, DailyChange%, TradeDirection, ChangeFromOpen, Non-Sim Position field values which are positive.
Quote Board: Price Change Down: This is the color for DailyChange, DailyChange%, TradeDirection, ChangeFromOpen, Non-Sim Position field values which are negative.
The Quote Board field configuration is specific to each individual Quote Board window. For a new Quote Board window, the initial field configuration will be based upon the global Quote Line field configuration for Quote Spreadsheets which is set through Global Settings >> Quote Spreadsheet Settings.
When a Quote Board is opened, any expired futures symbols will be automatically rolled over to the current contract month if Settings >> Auto Rollover Futures Symbols on the Quote Board menu is enabled which is the default. This occurs when the Quote Board is opened as part of a Chartbook.
The actual rollover date for a particular symbol is controlled by the rollover rules for the symbol in the Global Symbol Settings. There are very specific date based rollover rules for each futures contract symbol which are based upon the exchange rules.
To manually rollover a symbol, right-click anywhere along the Quote Line for the symbol on the Quote Board, and select Roll Forward Futures Symbol. You also have the ability to roll back a symbol by using Roll Back Futures Symbol.
All future symbols in the Quote Board can be rolled over at any time by selecting Settings >> Rollover Futures Symbols Now on the Quote Board menu.
To change the symbol of a chart or Trade DOM to the selected Quote Board symbol, it is first necessary to establish a common link between a Quote Board and the charts and/or Trade DOMs.
To set the same link number on a chart or Trade DOM, select Chart >> Chart Settings >> Linking from the menu. In the Chart Linking >> Link Number list box, select the same Link Number as is set for the Quote Board. Press OK. Any number of charts or Trade DOMs can use the same link number so they are changed to the same selected symbol on the Quote Board.
Simply left click on the symbol in the Symbol column on the Quote Board to change the symbol of the linked charts or Trade DOMs. The selected symbol will be highlighted on the Quote Board. Either the symbol field will be highlighted or the entire Quote Board line for the symbol will be highlighted if Settings >> Highlight All Fields is enabled on the Quote Board menu.
After left clicking on one of the lines on the Quote Board, it is then possible to use the Up Arrow key and Down Arrow key on your keyboard to move up and down through the list of symbols on a Quote Board.
You will not want to link a Quote Board to a chart that uses the Trade and Current Quote Symbol, unless you specify a Trade and Current Quote Symbol in the Global Settings >> Global Symbol Settings for the Symbols you are using in the Quote Board. Otherwise, what you will find is that the Trade and Current Quote Symbol will remain with the chart and only the main symbol of the chart changes.
If you have used one of the Drawing Tools on the chart, make sure that Chart >> Chart Settings >> Chart Drawings >> Show Chart Drawings for Different Symbols is disabled to prevent Chart Drawings for other symbols from displaying on the chart for a different symbol that you have changed to from the Quote Board.
Beginning with version 1338 it is supported for a Quote Board for one Chartbook to be able to link to charts in another Chartbook. Follow these steps.
Set a nonzero Link Number on the Quote board by selecting Settings >> Set Chart Link on the menu on the Quote Board window. Select one of the Link Numbers ( L#).
Select Chart >> Chart Settings >> Linking from the menu. In the Chart Linking >> Link Number list box, select the same Link Number as is set for the Quote Board.
Simply left click on the symbol in the Symbol column on the Quote Board to change the symbol of the linked charts or Trade DOMs. Selecting a symbol on the Quote Board is only going to affect the charts in the active Chartbook with the same Link Number as the Quote Board is set to.
The Sierra Chart Quote Board will highlight a new Daily High or Low on the quote board when the High and/or Low fields are displayed. The High and Low fields are directly highlighted.
The color is controlled by the Quote Board: New High/Low Highlight color setting set through the Global Settings >> Graphics Settings - Global or Chart >> Graphics Settings windows. Refer to Graphics Settings for complete details.
An optional alert sound can also be enabled through Alerts >> Alert Number For New High/Low on the Quote Board menu. Select a particular Alert Number that you want to use for a new Daily High or Low. To configure that particular Alert Number, refer to Alert Sound Settings.
To adjust the width of a column on the Quote Board, move your Pointer to the column header line at the top of the Quote Board window that displays the column names.
After this move the Pointer to the right side of the column that you want to adjust. You will notice that the dividing area between columns will then change to a different color (normally red). Left click with the Pointer to start the adjustment operation and move left or right, then release.
A Quote Board window is a floating window which by default is owned by the main Sierra Chart window and will remain on top of the main window. It can be freely moved around outside of the main window frame.
To detach a Quote Board from the main Sierra Chart window and allow the Quote Board to be completely independent so that it can be moved to other monitors or anywhere on your screen space, select Settings >> Attach/Detach Window on the Quote Board menu. Select that command again to reattach it to the main Sierra Chart window.
If you want the Quote Board to be always on top of other windows on your system, then enable Settings >> Always on Top. This is only supported when a Quote Board is detached. To detach a Quote Board, refer to Attaching and Detaching Quote Board.
The vertical scroll bar on a Quote Board will display when there are more lines in the Quote Board than can be displayed based on the size of the window. The number of quote lines can be adjusted through Setting Symbols.
To remove the scroll bar by adjusting the size of the Quote Board window, use the standard Windows functionality to grab the side or corner of the window and drag it to make the window larger.
Likewise for the horizontal scroll bar, that will display when there are more fields displayed and the width of those fields is greater than can fit in the current window size.
There are several solutions to this. Make the window larger as explained above. Adjust the width of the columns. Or, remove fields. To do this, refer to Setting Fields to Display.
One or more rows in the quote board can be selected and deleted. One row can be selected by clicking on it and multiple rows can be selected by holding Ctrl or Shift Key while clicking on a row. The selected rows can then be deleted in the following ways:
Inserting is not supported when Quote Board column sorting is being used. Sorting can be disabled, by left clicking with your Pointer on the header of any of columns until there is no longer an arrow shown on that header.
One row can be selected by left clicking on it and multiple rows can be selected by holding Control or Shift Key while left clicking on a row. Rows can then be inserted in the following ways:
Keyboard shortcuts can be assigned to move a selected symbol up and down. Keyboard shortcuts Move Symbol Up and Move Symbol Down can be configured by selecting Global Settings >> Customize Keyboard Shortcuts and selecting the QuoteBoard Keyboard Shortcuts. For example, if U is assigned to Move Symbol Up, then pressing the U key in the quote board window will move the selected symbol up.
Note that the assigned keyboard shortcut key is global and cannot be used for any other functionality even if the quote board window is closed. Refer to Keyboard Shortcuts are Global and Affect All Windows for information.
The columns of a Quote Board can be sorted alphabetically or numerically either ascending or descending. Sorting can also be disabled. When sorting is enabled for a particular column, it does increase the CPU usage of the Quote Board. Sorting should only be used when necessary.
Left clicking on a column header, (Symbol, Last, Bid, Ask, ...) on the Quote Board window will either enable sorting ascending, enable sorting descending, or disable sorting.
When an up arrow is displayed on the column header, the sorting is enabled and ascending. When a down arrow is displayed on the column header, the sorting is enabled and descending. When there is no arrow displayed, on any of the Quote Board columns, then sorting is disabled.

Glass substrate with ITO electrodes. The shapes of these electrodes will determine the shapes that will appear when the LCD is switched ON. Vertical ridges etched on the surface are smooth.
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals combined with polarizers. Liquid crystals do not emit light directlybacklight or reflector to produce images in color or monochrome.seven-segment displays, as in a digital clock, are all good examples of devices with these displays. They use the same basic technology, except that arbitrary images are made from a matrix of small pixels, while other displays have larger elements. LCDs can either be normally on (positive) or off (negative), depending on the polarizer arrangement. For example, a character positive LCD with a backlight will have black lettering on a background that is the color of the backlight, and a character negative LCD will have a black background with the letters being of the same color as the backlight. Optical filters are added to white on blue LCDs to give them their characteristic appearance.
LCDs are used in a wide range of applications, including LCD televisions, computer monitors, instrument panels, aircraft cockpit displays, and indoor and outdoor signage. Small LCD screens are common in LCD projectors and portable consumer devices such as digital cameras, watches, digital clocks, calculators, and mobile telephones, including smartphones. LCD screens are also used on consumer electronics products such as DVD players, video game devices and clocks. LCD screens have replaced heavy, bulky cathode-ray tube (CRT) displays in nearly all applications. LCD screens are available in a wider range of screen sizes than CRT and plasma displays, with LCD screens available in sizes ranging from tiny digital watches to very large television receivers. LCDs are slowly being replaced by OLEDs, which can be easily made into different shapes, and have a lower response time, wider color gamut, virtually infinite color contrast and viewing angles, lower weight for a given display size and a slimmer profile (because OLEDs use a single glass or plastic panel whereas LCDs use two glass panels; the thickness of the panels increases with size but the increase is more noticeable on LCDs) and potentially lower power consumption (as the display is only "on" where needed and there is no backlight). OLEDs, however, are more expensive for a given display size due to the very expensive electroluminescent materials or phosphors that they use. Also due to the use of phosphors, OLEDs suffer from screen burn-in and there is currently no way to recycle OLED displays, whereas LCD panels can be recycled, although the technology required to recycle LCDs is not yet widespread. Attempts to maintain the competitiveness of LCDs are quantum dot displays, marketed as SUHD, QLED or Triluminos, which are displays with blue LED backlighting and a Quantum-dot enhancement film (QDEF) that converts part of the blue light into red and green, offering similar performance to an OLED display at a lower price, but the quantum dot layer that gives these displays their characteristics can not yet be recycled.
Since LCD screens do not use phosphors, they rarely suffer image burn-in when a static image is displayed on a screen for a long time, e.g., the table frame for an airline flight schedule on an indoor sign. LCDs are, however, susceptible to image persistence.battery-powered electronic equipment more efficiently than a CRT can be. By 2008, annual sales of televisions with LCD screens exceeded sales of CRT units worldwide, and the CRT became obsolete for most purposes.
Each pixel of an LCD typically consists of a layer of molecules aligned between two transparent electrodes, often made of Indium-Tin oxide (ITO) and two polarizing filters (parallel and perpendicular polarizers), the axes of transmission of which are (in most of the cases) perpendicular to each other. Without the liquid crystal between the polarizing filters, light passing through the first filter would be blocked by the second (crossed) polarizer. Before an electric field is applied, the orientation of the liquid-crystal molecules is determined by the alignment at the surfaces of electrodes. In a twisted nematic (TN) device, the surface alignment directions at the two electrodes are perpendicular to each other, and so the molecules arrange themselves in a helical structure, or twist. This induces the rotation of the polarization of the incident light, and the device appears gray. If the applied voltage is large enough, the liquid crystal molecules in the center of the layer are almost completely untwisted and the polarization of the incident light is not rotated as it passes through the liquid crystal layer. This light will then be mainly polarized perpendicular to the second filter, and thus be blocked and the pixel will appear black. By controlling the voltage applied across the liquid crystal layer in each pixel, light can be allowed to pass through in varying amounts thus constituting different levels of gray.
The chemical formula of the liquid crystals used in LCDs may vary. Formulas may be patented.Sharp Corporation. The patent that covered that specific mixture expired.
Most color LCD systems use the same technique, with color filters used to generate red, green, and blue subpixels. The LCD color filters are made with a photolithography process on large glass sheets that are later glued with other glass sheets containing a TFT array, spacers and liquid crystal, creating several color LCDs that are then cut from one another and laminated with polarizer sheets. Red, green, blue and black photoresists (resists) are used. All resists contain a finely ground powdered pigment, with particles being just 40 nanometers across. The black resist is the first to be applied; this will create a black grid (known in the industry as a black matrix) that will separate red, green and blue subpixels from one another, increasing contrast ratios and preventing light from leaking from one subpixel onto other surrounding subpixels.Super-twisted nematic LCD, where the variable twist between tighter-spaced plates causes a varying double refraction birefringence, thus changing the hue.
LCD in a Texas Instruments calculator with top polarizer removed from device and placed on top, such that the top and bottom polarizers are perpendicular. As a result, the colors are inverted.
The optical effect of a TN device in the voltage-on state is far less dependent on variations in the device thickness than that in the voltage-off state. Because of this, TN displays with low information content and no backlighting are usually operated between crossed polarizers such that they appear bright with no voltage (the eye is much more sensitive to variations in the dark state than the bright state). As most of 2010-era LCDs are used in television sets, monitors and smartphones, they have high-resolution matrix arrays of pixels to display arbitrary images using backlighting with a dark background. When no image is displayed, different arrangements are used. For this purpose, TN LCDs are operated between parallel polarizers, whereas IPS LCDs feature crossed polarizers. In many applications IPS LCDs have replaced TN LCDs, particularly in smartphones. Both the liquid crystal material and the alignment layer material contain ionic compounds. If an electric field of one particular polarity is applied for a long period of time, this ionic material is attracted to the surfaces and degrades the device performance. This is avoided either by applying an alternating current or by reversing the polarity of the electric field as the device is addressed (the response of the liquid crystal layer is identical, regardless of the polarity of the applied field).
Displays for a small number of individual digits or fixed symbols (as in digital watches and pocket calculators) can be implemented with independent electrodes for each segment.alphanumeric or variable graphics displays are usually implemented with pixels arranged as a matrix consisting of electrically connected rows on one side of the LC layer and columns on the other side, which makes it possible to address each pixel at the intersections. The general method of matrix addressing consists of sequentially addressing one side of the matrix, for example by selecting the rows one-by-one and applying the picture information on the other side at the columns row-by-row. For details on the various matrix addressing schemes see passive-matrix and active-matrix addressed LCDs.
LCDs, along with OLED displays, are manufactured in cleanrooms borrowing techniques from semiconductor manufacturing and using large sheets of glass whose size has increased over time. Several displays are manufactured at the same time, and then cut from the sheet of glass, also known as the mother glass or LCD glass substrate. The increase in size allows more displays or larger displays to be made, just like with increasing wafer sizes in semiconductor manufacturing. The glass sizes are as follows:
Until Gen 8, manufacturers would not agree on a single mother glass size and as a result, different manufacturers would use slightly different glass sizes for the same generation. Some manufacturers have adopted Gen 8.6 mother glass sheets which are only slightly larger than Gen 8.5, allowing for more 50 and 58 inch LCDs to be made per mother glass, specially 58 inch LCDs, in which case 6 can be produced on a Gen 8.6 mother glass vs only 3 on a Gen 8.5 mother glass, significantly reducing waste.AGC Inc., Corning Inc., and Nippon Electric Glass.
The origins and the complex history of liquid-crystal displays from the perspective of an insider during the early days were described by Joseph A. Castellano in Liquid Gold: The Story of Liquid Crystal Displays and the Creation of an Industry.IEEE History Center.Peter J. Wild, can be found at the Engineering and Technology History Wiki.
In 1888,Friedrich Reinitzer (1858–1927) discovered the liquid crystalline nature of cholesterol extracted from carrots (that is, two melting points and generation of colors) and published his findings at a meeting of the Vienna Chemical Society on May 3, 1888 (F. Reinitzer: Beiträge zur Kenntniss des Cholesterins, Monatshefte für Chemie (Wien) 9, 421–441 (1888)).Otto Lehmann published his work "Flüssige Kristalle" (Liquid Crystals). In 1911, Charles Mauguin first experimented with liquid crystals confined between plates in thin layers.
In 1922, Georges Friedel described the structure and properties of liquid crystals and classified them in three types (nematics, smectics and cholesterics). In 1927, Vsevolod Frederiks devised the electrically switched light valve, called the Fréedericksz transition, the essential effect of all LCD technology. In 1936, the Marconi Wireless Telegraph company patented the first practical application of the technology, "The Liquid Crystal Light Valve". In 1962, the first major English language publication Molecular Structure and Properties of Liquid Crystals was published by Dr. George W. Gray.RCA found that liquid crystals had some interesting electro-optic characteristics and he realized an electro-optical effect by generating stripe-patterns in a thin layer of liquid crystal material by the application of a voltage. This effect is based on an electro-hydrodynamic instability forming what are now called "Williams domains" inside the liquid crystal.
The MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor) was invented by Mohamed M. Atalla and Dawon Kahng at Bell Labs in 1959, and presented in 1960.Paul K. Weimer at RCA developed the thin-film transistor (TFT) in 1962.
In 1964, George H. Heilmeier, then working at the RCA laboratories on the effect discovered by Williams achieved the switching of colors by field-induced realignment of dichroic dyes in a homeotropically oriented liquid crystal. Practical problems with this new electro-optical effect made Heilmeier continue to work on scattering effects in liquid crystals and finally the achievement of the first operational liquid-crystal display based on what he called the George H. Heilmeier was inducted in the National Inventors Hall of FameIEEE Milestone.
In the late 1960s, pioneering work on liquid crystals was undertaken by the UK"s Royal Radar Establishment at Malvern, England. The team at RRE supported ongoing work by George William Gray and his team at the University of Hull who ultimately discovered the cyanobiphenyl liquid crystals, which had correct stability and temperature properties for application in LCDs.
The idea of a TFT-based liquid-crystal display (LCD) was conceived by Bernard Lechner of RCA Laboratories in 1968.dynamic scattering mode (DSM) LCD that used standard discrete MOSFETs.
On December 4, 1970, the twisted nematic field effect (TN) in liquid crystals was filed for patent by Hoffmann-LaRoche in Switzerland, (Swiss patent No. 532 261) with Wolfgang Helfrich and Martin Schadt (then working for the Central Research Laboratories) listed as inventors.Brown, Boveri & Cie, its joint venture partner at that time, which produced TN displays for wristwatches and other applications during the 1970s for the international markets including the Japanese electronics industry, which soon produced the first digital quartz wristwatches with TN-LCDs and numerous other products. James Fergason, while working with Sardari Arora and Alfred Saupe at Kent State University Liquid Crystal Institute, filed an identical patent in the United States on April 22, 1971.ILIXCO (now LXD Incorporated), produced LCDs based on the TN-effect, which soon superseded the poor-quality DSM types due to improvements of lower operating voltages and lower power consumption. Tetsuro Hama and Izuhiko Nishimura of Seiko received a US patent dated February 1971, for an electronic wristwatch incorporating a TN-LCD.
In 1972, the concept of the active-matrix thin-film transistor (TFT) liquid-crystal display panel was prototyped in the United States by T. Peter Brody"s team at Westinghouse, in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania.Westinghouse Research Laboratories demonstrated the first thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display (TFT LCD).high-resolution and high-quality electronic visual display devices use TFT-based active matrix displays.active-matrix liquid-crystal display (AM LCD) in 1974, and then Brody coined the term "active matrix" in 1975.
In 1972 North American Rockwell Microelectronics Corp introduced the use of DSM LCDs for calculators for marketing by Lloyds Electronics Inc, though these required an internal light source for illumination.Sharp Corporation followed with DSM LCDs for pocket-sized calculators in 1973Seiko and its first 6-digit TN-LCD quartz wristwatch, and Casio"s "Casiotron". Color LCDs based on Guest-Host interaction were invented by a team at RCA in 1968.TFT LCDs similar to the prototypes developed by a Westinghouse team in 1972 were patented in 1976 by a team at Sharp consisting of Fumiaki Funada, Masataka Matsuura, and Tomio Wada,
In 1983, researchers at Brown, Boveri & Cie (BBC) Research Center, Switzerland, invented the passive matrix-addressed LCDs. H. Amstutz et al. were listed as inventors in the corresponding patent applications filed in Switzerland on July 7, 1983, and October 28, 1983. Patents were granted in Switzerland CH 665491, Europe EP 0131216,
The first color LCD televisions were developed as handheld televisions in Japan. In 1980, Hattori Seiko"s R&D group began development on color LCD pocket televisions.Seiko Epson released the first LCD television, the Epson TV Watch, a wristwatch equipped with a small active-matrix LCD television.dot matrix TN-LCD in 1983.Citizen Watch,TFT LCD.computer monitors and LCD televisions.3LCD projection technology in the 1980s, and licensed it for use in projectors in 1988.compact, full-color LCD projector.
In 1990, under different titles, inventors conceived electro optical effects as alternatives to twisted nematic field effect LCDs (TN- and STN- LCDs). One approach was to use interdigital electrodes on one glass substrate only to produce an electric field essentially parallel to the glass substrates.Germany by Guenter Baur et al. and patented in various countries.Hitachi work out various practical details of the IPS technology to interconnect the thin-film transistor array as a matrix and to avoid undesirable stray fields in between pixels.
Hitachi also improved the viewing angle dependence further by optimizing the shape of the electrodes (Super IPS). NEC and Hitachi become early manufacturers of active-matrix addressed LCDs based on the IPS technology. This is a milestone for implementing large-screen LCDs having acceptable visual performance for flat-panel computer monitors and television screens. In 1996, Samsung developed the optical patterning technique that enables multi-domain LCD. Multi-domain and In Plane Switching subsequently remain the dominant LCD designs through 2006.South Korea and Taiwan,
In 2007 the image quality of LCD televisions surpassed the image quality of cathode-ray-tube-based (CRT) TVs.LCD TVs were projected to account 50% of the 200 million TVs to be shipped globally in 2006, according to Displaybank.Toshiba announced 2560 × 1600 pixels on a 6.1-inch (155 mm) LCD panel, suitable for use in a tablet computer,transparent and flexible, but they cannot emit light without a backlight like OLED and microLED, which are other technologies that can also be made flexible and transparent.
In 2016, Panasonic developed IPS LCDs with a contrast ratio of 1,000,000:1, rivaling OLEDs. This technology was later put into mass production as dual layer, dual panel or LMCL (Light Modulating Cell Layer) LCDs. The technology uses 2 liquid crystal layers instead of one, and may be used along with a mini-LED backlight and quantum dot sheets.
Since LCDs produce no light of their own, they require external light to produce a visible image.backlight. Active-matrix LCDs are almost always backlit.Transflective LCDs combine the features of a backlit transmissive display and a reflective display.
CCFL: The LCD panel is lit either by two cold cathode fluorescent lamps placed at opposite edges of the display or an array of parallel CCFLs behind larger displays. A diffuser (made of PMMA acrylic plastic, also known as a wave or light guide/guiding plateinverter to convert whatever DC voltage the device uses (usually 5 or 12 V) to ≈1000 V needed to light a CCFL.
EL-WLED: The LCD panel is lit by a row of white LEDs placed at one or more edges of the screen. A light diffuser (light guide plate, LGP) is then used to spread the light evenly across the whole display, similarly to edge-lit CCFL LCD backlights. The diffuser is made out of either PMMA plastic or special glass, PMMA is used in most cases because it is rugged, while special glass is used when the thickness of the LCD is of primary concern, because it doesn"t expand as much when heated or exposed to moisture, which allows LCDs to be just 5mm thick. Quantum dots may be placed on top of the diffuser as a quantum dot enhancement film (QDEF, in which case they need a layer to be protected from heat and humidity) or on the color filter of the LCD, replacing the resists that are normally used.
WLED array: The LCD panel is lit by a full array of white LEDs placed behind a diffuser behind the panel. LCDs that use this implementation will usually have the ability to dim or completely turn off the LEDs in the dark areas of the image being displayed, effectively increasing the contrast ratio of the display. The precision with which this can be done will depend on the number of dimming zones of the display. The more dimming zones, the more precise the dimming, with less obvious blooming artifacts which are visible as dark grey patches surrounded by the unlit areas of the LCD. As of 2012, this design gets most of its use from upscale, larger-screen LCD televisions.
RGB-LED array: Similar to the WLED array, except the panel is lit by a full array of RGB LEDs. While displays lit with white LEDs usually have a poorer color gamut than CCFL lit displays, panels lit with RGB LEDs have very wide color gamuts. This implementation is most popular on professional graphics editing LCDs. As of 2012, LCDs in this category usually cost more than $1000. As of 2016 the cost of this category has drastically reduced and such LCD televisions obtained same price levels as the former 28" (71 cm) CRT based categories.
Monochrome LEDs: such as red, green, yellow or blue LEDs are used in the small passive monochrome LCDs typically used in clocks, watches and small appliances.
Mini-LED: Backlighting with Mini-LEDs can support over a thousand of Full-area Local Area Dimming (FLAD) zones. This allows deeper blacks and higher contrast ratio.MicroLED.)
Today, most LCD screens are being designed with an LED backlight instead of the traditional CCFL backlight, while that backlight is dynamically controlled with the video information (dynamic backlight control). The combination with the dynamic backlight control, invented by Philips researchers Douglas Stanton, Martinus Stroomer and Adrianus de Vaan, simultaneously increases the dynamic range of the display system (also marketed as HDR, high dynamic range television or FLAD, full-area local area dimming).
The LCD backlight systems are made highly efficient by applying optical films such as prismatic structure (prism sheet) to gain the light into the desired viewer directions and reflective polarizing films that recycle the polarized light that was formerly absorbed by the first polarizer of the LCD (invented by Philips researchers Adrianus de Vaan and Paulus Schaareman),
Due to the LCD layer that generates the desired high resolution images at flashing video speeds using very low power electronics in combination with LED based backlight technologies, LCD technology has become the dominant display technology for products such as televisions, desktop monitors, notebooks, tablets, smartphones and mobile phones. Although competing OLED technology is pushed to the market, such OLED displays do not feature the HDR capabilities like LCDs in combination with 2D LED backlight technologies have, reason why the annual market of such LCD-based products is still growing faster (in volume) than OLED-based products while the efficiency of LCDs (and products like portable computers, mobile phones and televisions) may even be further improved by preventing the light to be absorbed in the colour filters of the LCD.
A pink elastomeric connector mating an LCD panel to circuit board traces, shown next to a centimeter-scale ruler. The conductive and insulating layers in the black stripe are very small.
A standard television receiver screen, a modern LCD panel, has over six million pixels, and they are all individually powered by a wire network embedded in the screen. The fine wires, or pathways, form a grid with vertical wires across the whole screen on one side of the screen and horizontal wires across the whole screen on the other side of the screen. To this grid each pixel has a positive connection on one side and a negative connection on the other side. So the total amount of wires needed for a 1080p display is 3 x 1920 going vertically and 1080 going horizontally for a total of 6840 wires horizontally and vertically. That"s three for red, green and blue and 1920 columns of pixels for each color for a total of 5760 wires going vertically and 1080 rows of wires going horizontally. For a panel that is 28.8 inches (73 centimeters) wide, that means a wire density of 200 wires per inch along the horizontal edge.
The LCD panel is powered by LCD drivers that are carefully matched up with the edge of the LCD panel at the factory level. The drivers may be installed using several methods, the most common of which are COG (Chip-On-Glass) and TAB (Tape-automated bonding) These same principles apply also for smartphone screens that are much smaller than TV screens.anisotropic conductive film or, for lower densities, elastomeric connectors.
Monochrome and later color passive-matrix LCDs were standard in most early laptops (although a few used plasma displaysGame Boyactive-matrix became standard on all laptops. The commercially unsuccessful Macintosh Portable (released in 1989) was one of the first to use an active-matrix display (though still monochrome). Passive-matrix LCDs are still used in the 2010s for applications less demanding than laptop computers and TVs, such as inexpensive calculators. In particular, these are used on portable devices where less information content needs to be displayed, lowest power consumption (no backlight) and low cost are desired or readability in direct sunlight is needed.
A comparison between a blank passive-matrix display (top) and a blank active-matrix display (bottom). A passive-matrix display can be identified when the blank background is more grey in appearance than the crisper active-matrix display, fog appears on all edges of the screen, and while pictures appear to be fading on the screen.
Displays having a passive-matrix structure are employing Crosstalk between activated and non-activated pixels has to be handled properly by keeping the RMS voltage of non-activated pixels below the threshold voltage as discovered by Peter J. Wild in 1972,
STN LCDs have to be continuously refreshed by alternating pulsed voltages of one polarity during one frame and pulses of opposite polarity during the next frame. Individual pixels are addressed by the corresponding row and column circuits. This type of display is called response times and poor contrast are typical of passive-matrix addressed LCDs with too many pixels and driven according to the "Alt & Pleshko" drive scheme. Welzen and de Vaan also invented a non RMS drive scheme enabling to drive STN displays with video rates and enabling to show smooth moving video images on an STN display.
Bistable LCDs do not require continuous refreshing. Rewriting is only required for picture information changes. In 1984 HA van Sprang and AJSM de Vaan invented an STN type display that could be operated in a bistable mode, enabling extremely high resolution images up to 4000 lines or more using only low voltages.
High-resolution color displays, such as modern LCD computer monitors and televisions, use an active-matrix structure. A matrix of thin-film transistors (TFTs) is added to the electrodes in contact with the LC layer. Each pixel has its own dedicated transistor, allowing each column line to access one pixel. When a row line is selected, all of the column lines are connected to a row of pixels and voltages corresponding to the picture information are driven onto all of the column lines. The row line is then deactivated and the next row line is selected. All of the row lines are selected in sequence during a refresh operation. Active-matrix addressed displays look brighter and sharper than passive-matrix addressed displays of the same size, and generally have quicker response times, producing much better images. Sharp produces bistable reflective LCDs with a 1-bit SRAM cell per pixel that only requires small amounts of power to maintain an image.
Segment LCDs can also have color by using Field Sequential Color (FSC LCD). This kind of displays have a high speed passive segment LCD panel with an RGB backlight. The backlight quickly changes color, making it appear white to the naked eye. The LCD panel is synchronized with the backlight. For example, to make a segment appear red, the segment is only turned ON when the backlight is red, and to make a segment appear magenta, the segment is turned ON when the backlight is blue, and it continues to be ON while the backlight becomes red, and it turns OFF when the backlight becomes green. To make a segment appear black, the segment is always turned ON. An FSC LCD divides a color image into 3 images (one Red, one Green and one Blue) and it displays them in order. Due to persistence of vision, the 3 monochromatic images appear as one color image. An FSC LCD needs an LCD panel wi




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey