touch screen monitors for construction supplier
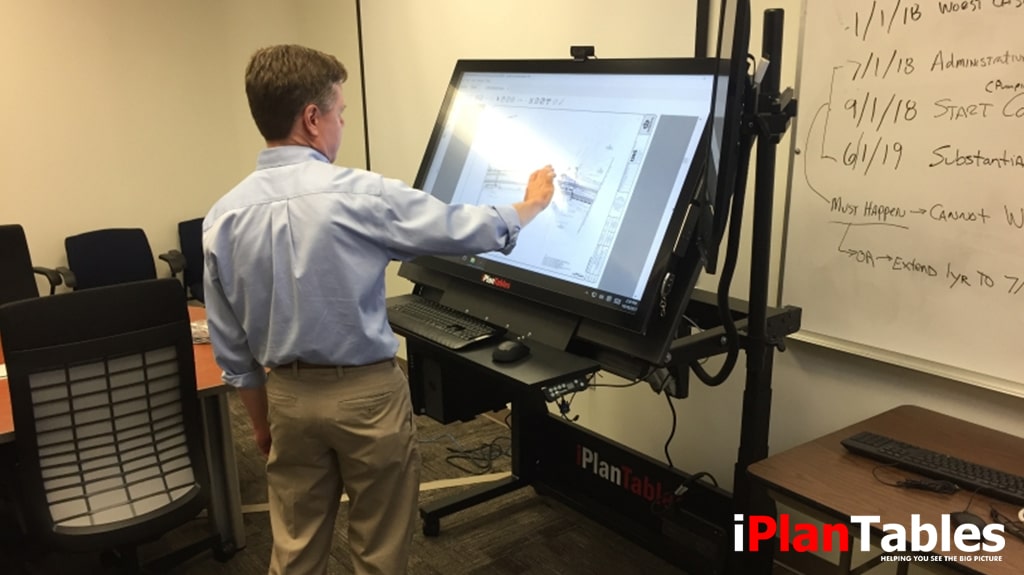

An iPlanTablesworkstation adds a multiple monitor advantage to help discern the information - separating the wide-format document and using smaller monitors for other daily tasks
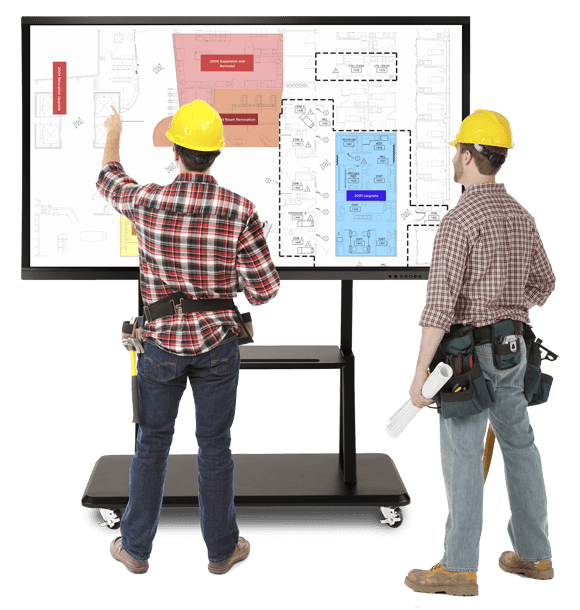
Plan Reviewers and Examiners want to be able to see the drawings. An iPlanTables plan review table allows them to view 30x42 drawings for their profession
An iPlanTablesworkstation adds a multiple monitor advantage to help discern the information - separating the wide-format document and using smaller monitors for other daily tasks
Plan Reviewers and Examiners want to be able to see the drawings. An iPlanTables plan review table allows them to view 30x42 drawings for their profession
A True iPlanTables Command Center for your Complex Information Management Needs – Combining the Power of our Facility Manager with Functionality of Extra Side Monitors for Multiple Active Screens
A True iPlanTables Command Center for your Complex Information Management Needs – Combining the Power of our Facility Manager with Functionality of Extra Side Monitors for Multiple Active Screens
Wire Text block A True iPlanTables Command Center for your Complex Information Management Needs – Combining the Power of our Facility Manager with Functionality of Extra Side Monitors for Multiple Active Screens Space Space s Button Research More Custom Edit contentless keyboard & mous
UFGI plug Text block Smaller, Lighter, and More Compact than its Big Brother iPlanTables Field Commander – Powerful All-in-One Mobile Solution for Job Sites, Factory, and Industrial Floors
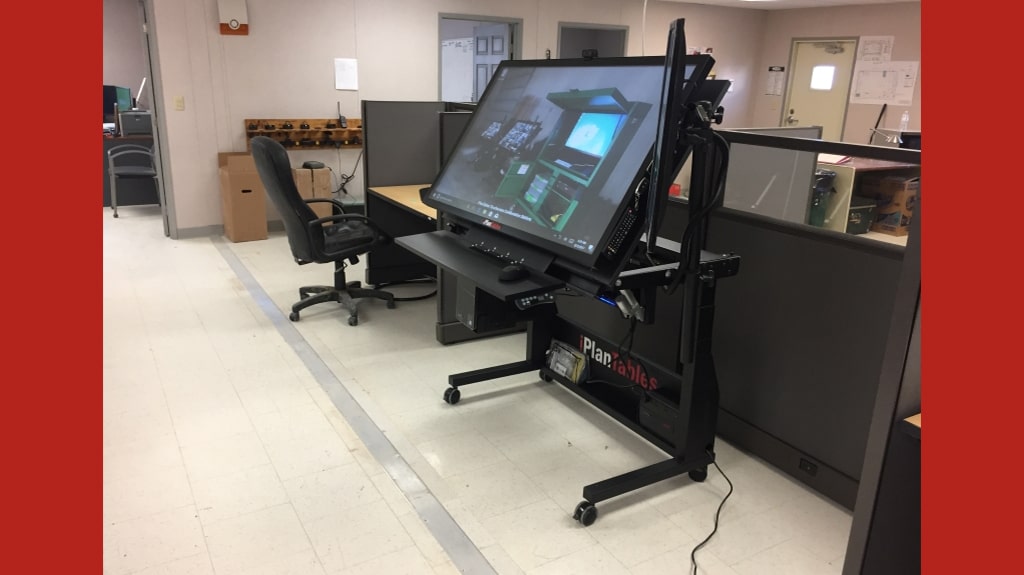

iPlanTables manufactures and brings you the best Custom touch screen monitors workstation with cutting-edge technology, built with the highest quality steel and not flimsy AV stands.
If you are a contractor and have finally decided to go paperless and switch to work on a digital workstation, then iPlanTables has the best solutions for you.
iPlanTables is the United States premier provider of large-format touchscreen display workstations for general contractors, subcontractors, estimators, plan reviewers, examiners, and anyone who uses wide format spreadsheets or documents.
We create several Custom touch screen monitor models for clients who want to transition from a paper-based to a digital workflow to help examine and annotate building plans, specs, spreadsheets, and photos. Good candidates are desktops, sit-stand workstations, conference rooms, and job trailers.
We at iPlanTables have helped hundreds of clients go digital with their plan review and markup process. We challenged the building industry"s attitude of "I"d rather fight than switch”, and demonstrated how an old dog could learn new tricks by using a large-format touch screen monitor that allows you to see your complete drawing without the frequent panning, zooming, and scrolling that small desktop monitors and laptops require.
iPlanTables looks forward to discussing your shift to a "better than paper" solution, whether a Job Commander for your jobsite trailer, or a mobile sit-stand desktop workstation for your estimating team or project managers.
We can help you view your plans and be more productive and effective with your project information. We even have a wall-mounted touch screen model for digital training and conference room collaboration.
Let us help and assist you with your next project as you transition from paper to digital estimating, digital project information management, and digital plan review.
Custom touchscreen monitors workstations from iPlanTables perform for an extended period of time, often longer than computers and conventional input devices such as a keyboard and mouse. Some touch screen gadgets can withstand hundreds of thousands of touches, allowing you to use them for years.
Touchscreen workstations from iPlanTables typically provide more commands than non-touchscreen machines. If a touchscreen device has multi-touch capabilities, contractors can squeeze the screen to zoom in or out of the display. Virtual keyboards, keypads, and other digital, touch-based input are all supported by touchscreen devices.
After implementing a touchscreen workstation in your workplace, you may observe a boost in your company"s productivity. They enable workers to accomplish tasks on a tablet with ease and convenience, increasing productivity. As a business owner, you should consider employing touchscreen devices in your office because enhanced efficiency often leads to higher profitability.
Touchscreen workstations also lead to higher employee satisfaction. Employees prefer touchscreen devices over non-touchscreen devices. They are simple to use, familiar, and natural, as evidenced by the beneficial influence on employee satisfaction.
Touchscreen workstations are highly responsive, activating touch commands even with light pressure inputs. Some touch screen gadgets are more responsive than others. iPlanTables uses projective capacitive touchscreen devices which are the most responsive.
First, however, you must select the appropriate touchscreen device to reap these benefits. Touchscreen devices are distinguished by their touch-based input form, although significant differences exist.
For example, resistive touchscreen devices employ pressure to register touch commands, whereas capacitive touchscreen devices use the conductive qualities of the human body to record touch commands.
iPlanTables Touch Screen Table Top Workstation has an articulating USA-Made Mobile Cart that adjusts from 0 to 90 degrees. It is also adjustable to Sit-to-Conference Room Height for Maximum Flexibility.
By combining the power of our Facility Manager with the functionality of extra side monitors for many active screens, we can create a video wall display of monitors for viewing plans, specs, documents, emails, and spreadsheets all at once.
The iPlanTables wall-mounted 45-Degree Collaboration Workstation with Built-In Wall Mounted PC transforms from the traditional conference room height to an iPlanTables 45-Degree Collaboration Workstation with Built-In Wall Mounted PC.

Six Sigma capable, ISO 9001:2008 & ISO 14000 certified manufacturer of touchscreen displays including flat panel monitors. Types of flat panel monitors include DVI/RGB and hazardous location compatible. Flat panel monitors feature front USB interface, 256K or 16 million color display, analog resistive touch panel, serial/USB touch interfaces, on-screen-display menu for brightness & contrast control, & VESA standard wall mounts. Available with a 2-year warranty. Markets served include industrial, automotive, oil & gas, water/wastewater, semiconductors & agriculture. Modbus-IDA, OMAC & ODVA affiliated. Products are UL® listed, CSA® approved, and ATEX & CE certified. Products are RoHS compliant.
SCADA is an integral part of a business, not just its operations. The flow of data from the control room to the board room must be seamless. In the past, supervisory control and manufacturing information systems have not been integrated. This is changing and companies are realizing both investments only achieve their full potential when they are capable of seamlessly working together.
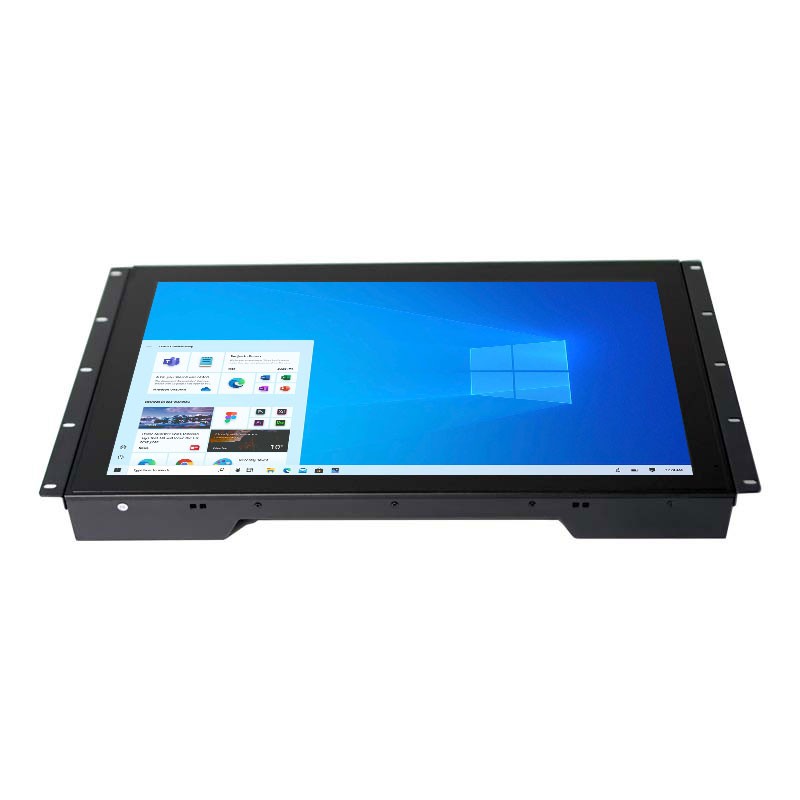

Thanks to the wide range of sizes available and the high-resolution support of those devices (e.g. 768p, 1920~1200 pixels), faytech’s capacitive touch monitors are the perfect choice for a wide range of applications, including but not limited to POS systems, kiosk systems, for office/residence automation and as control panels in industrial fields.
All our Capacitive touch screens are made of an industrial A+ HD LCD capacitive multi-touch panel with energy-saving LED technology and a wide viewing angle. These characteristics make faytech Capacitive touch displays perfect solutions when it comes to fashion shows, industrial 4.0 projects, dealerships, wayfinding, supermarkets, sports arenas, interactive visualizations, and digital signage.
The potential use cases of those units are almost infinite. For residencies, condominiums, or apartment lobbies, the Capacitive Touch Monitors could be used as interfaces or as part of a residential automation system. In hotels, these capacitive touch screen monitors could help enhance communications between staff and residents, as well as being part of a security automation system. Beyond residential and hosteling settings, faytech capacitive touch displays would be a great addition to any educational system, being used to improve interactions between students and professors in classrooms, for personnel management, and as interfaces to plan and communicate about curricular and extracurricular events. Faytech Capacitive Touch Monitors are also a great option to make scheduling and inventory management easier, whether in a private company or a public/educational setting.
In retail environments like mall shops and department stores, the technologies provided by faytech Capacitive Touch Monitors will be a great addition not only for customers, helping them to easily check inventory details without having to ask store personnel, but also for managers, being an easy way to cut back on operating costs. One of the multiple advantages of our capacitive touch screens is that they can be easily integrated with external software applications that, in turn, can allow customers to try demo versions of the products or services they contemplate purchasing. All in all, faytech capacitive touch monitors can serve as a great interactive medium to facilitate the purchasing process and multiply your sales.
While faytech Capacitive Touch Monitors can for sure be used for single-touch applications, these touch devices truly shine in more complex use scenarios. These include for instance directories or maps, when the user may have to use finger-scroll, pinch-zoom, and panning functions. Indeed, one of the main differences between Resistive touch monitors and capacitive touch monitors concerns touch technology. While resistive touch monitors are most of the time equipped with a single touch panel, the capacitive touch monitors are on the other side built to effectively register multi-touch, going as high as ten touches at the same time! It is now even possible to use Capacitive Touch Monitors when wearing heavy gloves, which is a significant upgrade given that this feature was formerly the preserve of Touch Monitors using Resistive-touch technology. Thanks to their patented IP65 front with silicone seal, faytech Capacitive Touch Monitor also work under heavy rain, which makes them adapted to use in semi-outdoor environments.
Worth noting, Capacitive Touch screens can most of the time be divided into two sub-categories: Projected Capacitive Touch Screens (PCAP) and Surface Touch Screens.
Based on projected technology, faytech Capacitive Touch Monitors are suitable for use in some highly specialized industries, including the aerospace (including but not limited to avionic systems), medical, military, and industrial ones (serving for example as an automated equipment control). Particularly, the main advantages of faytech Projected Capacitive Touch Monitors concerning these specific industries are the variety of layers stack-up options available, resulting in unparalleled durability and color perception. The Capacitive Touch Monitors manufactured by faytech respond to all the obligations induced by such demanding industries, thanks to several outstanding features. Those include:
Along with these peculiar applications, faytech Capacitive Touch Screens are also ideally fitted for high usage environments when based on surface technology.
Indeed, this technology stands out thanks to the high environmental robustness and increased resilience it offers. Monitors equipped with such a technology are vandal proof and can be used in areas with high traffic, serving in museums as an interactive display for instance. For example, it is now common to find such devices in electronic voting machines, an application in which security is key. Whether they come with a curved or flat surface, these devices are a perfect fit for any graphic-driven applications, such as ATMs (automated teller machines), game consoles, entertainment (including smartphones, tablets, and personal computers), banking, kitchen appliances, automobiles, and automats.
Technically speaking, on top of the front surface is applied a conductive coating, itself composed of wires connected to every four corners where a small voltage is applied. The system relies on the “capacitance” of the human body, which is to say that when one touches the screen, a small current flows to the touchpoint, generating a voltage drop detected at the corners.
This functioning makes screen surface technology more fitted to use on larger size (i.e. over 12 inches) applications. Besides, the single glass layer structure allows these devices to have excellent optical clarity and high light transmission (from 88 up to 92 percent). Of all the available technologies, it has the fastest touch response time. These monitors can also withstand regular cleaning using harsh chemicals. All in all, these functionalities make the capacitive touch monitors using surface technology especially suitable for commercial uses, such as the ones that we mentioned before.
On top of the potential use cases presented in this section, our Capacitive Touch Monitors can easily be integrated into any conceivable application and setup. Faytech NA is specialized in custom-made solutions and we will be glad to help you find the best Capacitive Touch Monitor for your specific needs and applications. Don’t hesitate to contact us to talk with one of our Capacitive Touch Screen Monitor specialists.
Touch panels have been evolving quickly and touchscreen technologies are becoming ever more sensitive to interactions with something as simple as the human finger.
The following are some important points regarding our touch panel company and some of the ways we are developing surface capacitive touch panel displays and devices.
A capacitive touchscreen can be found in many devices ranging from mobile phones to large touch panels to projected capacitive displays to kiosks with surface capacitance technology.
faytech NA specializes in the design, development, manufacturing, and marketing of specific computing solutions such as Touchscreen Desktops and Displays for Capacitive, Embedded, Industrial, Resistive, Rugged, Sunlight Readable, High Brightness, Open Frame, Kiosks and Accessories.
faytech NA currently manufactures 7–22” Monitors, 8–19” PCs, and the 32–42–55” PC LFT Series. Additionally, we have developed our own proprietary PC motherboard, which is manufactured exclusively by ASUS.
Whether it is finding the ideal product for your business, to the installation of the products or to technical support, our entire team works hard to always provide our customers with the best products and service on the market.
At faytech North America, we guarantee customer satisfaction. Our staff is fully trained and knowledgeable about every product we offer, ready to assist you with whatever information is needed. Feel free to contact us at any time with any questions, or to learn more about a faytech NA high-quality display solutions for your unique company.
Thanks to the accurate touch sensors, capacitive touch screen monitors are implemented as a viable solution for situations where the mouse and keyboard systems cannot be used as suitably accurate. Capacitive touch panel touchscreens offer a rapid, or intuitive means of interaction with the content on the screen.
Touchscreens with controller-based firmware and touch sensor have been made available, historically, by a various after-market system integrators, and not by the motherboard, chip, and display manufacturers.
However, chip and touchscreen manufacturers worldwide have acknowledged in the last few years the trend toward a wide acceptance of touch-friendly interface components as a highly desirable alternative and have begun to integrate this technology into the design of their products.
A capacitive touch screen monitor can be used similar to a keyboard that is invisible since it displays only as many button choices and as much data as users need to complete a particular task.
This is one of the reasons why touch panels are increasing in popularity in various applications from industrial machinery to kiosks and mobile phones.
In selecting the most suitable monitor for your application, the most important decision is in regard to the type of touch screen technology to use. Touch panels and touchscreens come in several types based on a few different technologies, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
A touch screen monitor is made of insulating material covered with transparent conductors. The most common material used as an insulator is glass. As a transparent conductor, indium tin oxide is usually used.
The resulted electric distortion is measured as a change in capacitance. In order to identify the touch display’s locations in a way can be used in various technologies, the location is then sent for processing to the controller of the capacitive touchscreen.
The difference from a resistive touch screen, is that users cannot work with a capacitive touchscreen through gloves and other types of electrically insulating material. In consumer electronics, this is a disadvantage because these smartphone and touch tablet PCs cannot be used in cold weather. However, this disadvantage can be overcome with a special-application glove or a special stylus.
The top manufacturers of capacitance displays continue to develop more accurate and thinner touch screens. For instance, by building the capacitors inside the display itself, mobile devices such as Samsung’s Super AMOLED screens are being produced now with “in-cell” technology that eliminates a layer.
This reduces the visible distance between what the user is touching on the screen and the user’s finger, enabling gestures and taps to be more responsive and creating a more direct contact with the content displayed.
Touch screens based on projected technology deliver interactive solutions for various applications and industries including aerospace, medical, military, and industrial.
Multi-touch projected technology has changed forever the way we interact with machines since the iPhone exploded on the market in the year 2007. Touch monitors with projected technology offer many substrate choices and stack-up options, delivering unmatched durability and outstanding optics.
The more common approach is based now on mutual capacitance. If they are placed close together, the majority of objects with conductive proprieties can hold a charge. When another conductive object bridges the gap (a finger, for example), the interrupted charge field is being detected by the micro-controller.
Surface technology offers environmental robustness and increased durability. These monitors are proven to meet the harsh demands found in vandal prone access sectors, and areas with high traffic.
Curved and flat surface touch screens are suitable for graphic driven applications, such as vending machines, entertaining, gaming, banking, and ATMs. Itcomes with a conductive coating on top of the front surface. The conductive coating features wires connected to each corner. To each of these four corners is applied a small voltage. The operation is based on surface technology relies on the capacitance of the human body. A small current flows to the point when you touch the screen, causing a voltage drop that is then sensed at corners.
This screen surface technology can be used easily on a larger size (over 12 inches) applications. Because the structure is only one glass layer, they provide high light transmission (in the range of 88 to 92 percent) and excellent optical clarity. Of all the available technologies, it has the fastest touch response time. These monitors can also withstand regular cleaning using harsh chemicals.
Because the touch screen display is based on a durable technology, they can be employed in applications that require increased durability. Among their areas of application are included point-of-sale systems, kiosks, and industrial computer machinery. Another advantage is that they have a higher clarity than resistive-type (higher by 88-92 percent).
Interface: Your computer should communicate with the touch screen panels. The most common interface types USB and RS-232. The need for drivers has been eliminated by new HID-compliant touchscreen displays.
Mounting: Among the various mounting options are included free-standing, rack mount, and panel mount. In case that you want to use free-standing, make sure that you use a heavy-duty stand that was specifically designed for touch.
faytech North America’s capacitive touch screen monitor solutions will enhance an organization’s productivity. Contact us today to speak with our capacitive touch screen monitor specialists.

All faytech touch screen monitors are truly industrial grade, with optically bonded touch panels and with minimum operational temperature ranges of -20°C to 70°C.
All faytech touchscreen monitors come with standard display input ports, USB touch output port, and DC power cable. All faytech touchscreen monitor solutions feature LCD displays with LED backlight units.
Technical specifications and drawings are available to download for all of our standard touchscreen monitor modules. Our touch screen monitor lineup is divided into three major categories:
Our touchscreen monitor solutions are perfect for indoor commercial and industrial applications such as point of sale, retail advertising/signage, office, and industrial machine interfaces.
The touchscreen monitor solutions. These touchscreen monitors are excellent alternative options to PCAP for POS systems, control panel interfaces in industrial facilities, kiosk input interfaces, machine interfaces, and in numerous other commercial and industrial applications.
Faytech’s 2 brightness LCDs along with PCAP touch panels. This touchscreen monitor lineup is ideal for outdoor and semi-outdoor applications such as outdoor advertising and information systems, restaurant menus, and outdoor industrial control systems.
Faytech recognizes that many customers need more than just a touchscreen monitor. We also offer a full lineup of industrial touch screen monitors, rugged touch monitors, portable touchscreen monitor along with integrated industrial computers with installed choice of OS. Just add software. If you’re looking to build a touch screen monitor.
Even though we offer a very comprehensive portfolio of touch monitor products, sometime special requirements require special products. If you have a custom need – maybe a specific touchscreen display picked out, a custom form factor, or something larger than our standard line supports, we may still be able to help.
A touch screen monitor is more than just a fad to replace a desktop computer, multi touch displays are changing the way people expect to interact with devices.
Additionally, touch screen monitors are very versatile. They can be used for a variety of purposes, such as customer check-in, product ordering, and employee time tracking.
Another reason why touchscreen monitors are becoming more popular in commercial and industrial settings is that they are very durable. A touch screen monitor can withstand a lot of wear and tear, which is ideal for businesses that have high traffic areas.
Overall, touch screen monitors are becoming more popular in commercial and industrial settings because they are user-friendly, versatile, and durable.
There are many benefits to using touch screen monitors for both customers and employees. First, a touch screen monitor is very user-friendly and easy to use.
This makes touchscreen monitor products with prestine image quality ideal for use in businesses where customers need to be able to quickly and easily navigate through menus or options.
Second, a touchscreen monitors are very durable and can withstand a lot of wear and tear. This makes a touchscreen display ideal for use in retail, governmental or commercial settings where they will be used frequently or in high traffic areas.
Finally, touchscreen monitors offer a great deal of flexibility and can be used in a variety of ways. For example, a touch screen monitor can be used for point-of-sale systems, self-service kiosks, or even as digital signage with optimal image quality.
There are several reasons for this trend of touch screen devices growing in popularity. Touchscreen monitors are interactive and engaging, making them ideal for businesses that want to encourage customer interaction.
A touch screen monitor is also easy to use, which makes them ideal for businesses that want to streamline employee workflow. In addition, touch screen displays are durable and can withstand heavy use, making them ideal for businesses that have high traffic areas.
There are many reasons why commercial and industrial businesses are starting to use touch screen monitors. They’re easy to use, they’re efficient, they have high image quality, and they offer a great user experience.
Touch screen monitors are easy to use because they don’t require any special training or knowledge to operate. They’re also very efficient because they can be used to process transactions quickly and accurately. And finally, they offer a great user experience because they’re interactive and user-friendly.
Many types of organizations are starting to use touch screen monitors for customers and employees because they are versatile and easy to use. A touch screen monitor can help businesses save time and money.
Touch screen monitors are becoming increasingly popular in the business world because they offer a number of advantages over a traditional desktop monitor or 1080p monitor.
A touch monitor with a led backlit display is very versatile and can be used for a variety of purposes, such as customer service, order taking, and inventory management. A touch screen monitor is also very easy to use because of their HD res inputs and tilt angle high screen resolution with image quality that reduces eye strain.
There’s no doubt that touchscreen monitor developments have come a long way in recent years. We’ve seen touchscreen monitor technology become thinner, lighter and more responsive, and now a touch screen monitor is an integral part of many people’s lives.
In light of recent developments in Meta and virtual reality developments, it’s clear that the future of touchscreen monitor technology is looking very exciting.
With Meta, users will be able to interact with their computer and touch screen monitor in a whole new way, and virtual reality will allow them to immerse themselves in their work like never before.
So, what does this all mean for the future of touchscreen monitors? Well, it’s safe to say that we can expect to experience some very exciting touch screen monitor developments in the years to come.
While there are many adaptations in the works regarding NFTs and other Web 3.0 related tech, you’ll want to follow faytech North America to stay up to date with where we take touchscreen monitor devices.
Touchscreen monitor technology has evolved over the years, and the future of touchscreen monitor projects is likely to be even more advanced as image quality technology continues to improve.
Touchscreen monitor technology has been around for decades, but it has only recently become widely used in consumer electronics. Now it is fairly common to see a touch screen monitor with a stylus pen, HD webcam for video conferencing, and convenient software for multi tasking.
The first multi touch screen devices were developed for use in industrial and military applications. These early touchscreens were bulky and expensive, and they were not well suited for use in consumer products.
Touchscreen monitor technology has come a long way in recent years, and the future looks even brighter. With the development of Meta and virtual reality, the potential for touchscreen monitors is even greater.
With these new touch screen monitor technologies, users will be able to interact with a touch screen monitor in ways that were not possible before. This will open up new possibilities for how we use touchscreen monitors in the future.
With the recent developments in meta and virtual reality, it’s difficult to say for sure. However, it’s safe to say that touchscreen technology will only become more advanced and widespread in the years to come.
faytech offers 2 major touch screen monitor technologies in its standard touch monitor catalogue – Projected capacitive (PCAP) touch and Resistive touch.
(PCAP) touch technology was invented in the 1980’s. Devices featuring projected capacitive touch screen monitor first started to appear in the late 1990’s, but none truly gained real popularity during that time. The first device to truly popularize PCAP technology was the iPhone in 2007. The proliferation of the smart phone over the next 5 years made PCAP the consumer touch technology.
Today, PCAP makes up over 97% of all display touch panels worldwide. This scale of adoption has pushed the cost of PCAP technology to be very close to that of 4-wire resistive touch, and much cheaper than other forms of resistive touch.
Nearly all consumer-facing touch screen devices and touch screen monitor devices (phones, laptops, tablets, casino games, automobiles, retail kiosks) have adopted the technology exclusively.
Non-consumer industrial touch screen applications also tend to prefer PCAP due to the strength afforded by its front glass surface and superior optical clarity.
PCAP touch screens are essentially a grid of transparent capacitors typically spaced 5-12mm apart throughout the touch surface. The technology works by detecting changes in the electric field at each capacitor ‘node’ when a conductive object touches the front surface of the device. The touch controller accepts reports of the capacitance at each node every few milliseconds – if any node has a capacitance past a programmed threshold, a touch is registered.
The conductive films do not need force or motion to function, so the front surface can be a strong glass (anywhere from 0.4mm to 6mm thick), or even plastic material. For this reason, PCAP touch devices are the most rugged of all current touch technologies, and do not have the ‘overuse failure’ mechanism of 4-wire resistive touch.
They are extremely popular, in part, due to the multi-touch and gesture controls (drag, flick, pinch) afforded by the technology that open up great interactivity options for end-use applications.
Since there are no moving parts in a PCAP touch, the layers are always optically bonded, which gives PCAP a better overall look than resistive, with significantly better contrast and higher brightness.
However, PCAP touch screens only function when touched by a conductive material, such as a finger or capacitive stylus. Some PCAP touch devices can have issues with liquid spills registering as touches, or heavy gloved fingers failing to trigger a touch (though current-gen industrial devices have mostly solved these problems). faytech industrial PCAP devices have been designed for, and tested with, heavy rain and thick glove environments.
Consumer electronics: Nearly all cell phones, tablets, and laptops use PCAP touch technology. Consumers are used to precise multi-touch gesture controls and not needing to put pressure on the screen to register a touch. Additionally, they are also used to the smooth surface and clean look provided by a front glass.
Gaming: Players at casinos using a touch screen prefer PCAP, since it is what they are generally used to on every other device they own. The front screen is protected by a thick front glass. Units can be protected from spills, and drink glasses on the touch surface won’t inadvertently activate the touch.
Advertising: Public-facing touch screens should be easily accessible by the public. People are used to having PCAP touch screens in their pockets at all times, and using PCAP here provides a consistency of experience. Thick glass surfaces can additionally protect the underlying display from damage.
Outdoor: Since resistive touch always needs to include an air gap, it is not generally good, optically speaking, for usage in high ambient light environments. Optically bonded PCAP units preserve display contrast in outdoor situations, allowing units with lower brightness (and lower power consumption) to still be visible.
Automotive: The look and features of the center information display have become a key selling point for automotive OEMs. Ultimately, this display is a consumer device. Drivers expect the same experiences they have at home on their phones and tablets. For automotive designers, the display systems themselves have requirements similar to rugged industrial uses in order to promote safety, visibility, and reliability of the display. PCAP technology provides the familiarity, optical superiority, and reliability to meet these requirements.
Resistive touch technology was invented in 1970. The technology was popularized through the 1980’s and 90’s in applications such as credit card readers with signature pens, touch interfaces for office printers, and PDAs. While resistive touch is no-longer the most common (now only around 2% of total touch panel market), there are still applications where it is the best option.
Resistive touch screens function by having 2 ITO layers separated by air and spacers. When a force causes the 2 ITO layers to touch, a circuit is completed and the location of the touch is reported. Due to the nature of the technology, just about any object can be used to touch the screen (gloved hands, long fingernails, credit cards, pens).
Resistive touch technology is also great in scenarios where spills or dirt is expected to end up on the touch surface – unless the weight is enough to push the film against the underlying glass, touch functionality will remain. Since it requires some small amount of force for a touch to register, it is less likely than other technologies for a user to inadvertently register a touch on the screen.
However, resistive touch screens are less optically clear than competing technologies due to the 2 layers being separated by air, which increases reflectivity. Lower cost 4-wire resistive touch screens are typically prone to failure after around 200,000 touches, though more rugged 5-wire versions are available which alleviate this issue (faytech offers both).
Typically, the top layer of a resistive touch panel is a thin PET film with ITO rear coating, which limits how rugged these units can be made (though some smaller units can be made with a thin glass front surface). Resistive touch screens do very well with single point touch, but tend to suffer in applications where multi-point and gesture touch controls are required.
POS Systems: Retail employees like being able to use non-conductive objects to tap on-screen buttons – pens, credit cards, long fingernails. These will work with resistive touch screens, but not with capacitive touch. Card readers frequently also come with resistive touch panels for accepting customer signatures.
Cockpit Avionics: Resistive touch panels do not rely on an electric field outside the touch panel surface to operate. Since electromagnetic noise in the cockpit of a certified aircraft must be tightly controlled, resistive touch is still a common technology. Additionally, resistive screens require some small amount of force to register a touch, making pilot errors less likely during turbulent flight.
Gloved Touch: Many applications where thick gloves are worn by operators are still including resistive touch. While capacitive technology has come a long way in allowing heavy glove touch, resistive touch still provides a surety that all gloved touches will register.
What many suppliers view as an upgrade, faytech views as a standard. We believe strongly in the benefits of direct bonding and believe it should be included in all touch products – and so it is in all of our products.
Optically bonded products sold by faytech improve the contrast of the image on the screen. This gives the image on the screen, as well as the display system itself, a crisp, professional look. It is greatly beneficial in outdoor and semi-outdoor environments.
Impact Resistance. Optically bonded displays can survive much greater impacts than unbounded displays. This is truly a must-have for any public-facing display unit.
faytech optically bonded displays have a layer of clear silicone gel between the touch panel and LCD front glass. This layer blocks dirt, dust, and moisture from getting behind the glass. This ensures that your faytech display will be visible in the harshest environments.
Touch screen monitors were initially used in point-of-sale (POS) terminals, kiosk systems, ATM’s and on PDA’s. The ever-expanding popularity of smartphones using Android and iOS operating systems, tablets, GPS systems and gaming consoles are increasing the demand for touch screen technologies.
Early touchscreen displays could only sense a single point of input at a time and only a few of them were capable of detecting the strength of the pressure. This was changed with Apple’s ongoing commercialization of the multi-touch technology with iPhone and iPod touch.
Multi-touch touch screen technology allows the user to interact with the screen with fingers, instead of a stylus. The movement of fingers creates gestures, which are then sent to the software. The initial popularity of the iPhone, has brought touch technology to many smart phones and hand-held devices which paved the way for all-in-one computer systems.
Faytech North America, as a touch screen manufacturer has realized that many companies have upgraded their products, either by adding multi-touch support to the track-pad or by making their tablet PC’s interactable without using a stylus. Both wall mounted and table mounted options have few ergonomic problems. “gorilla arm” was a side effect, that has limited wall-mounted option as a mainstream.
Developers of touch systems, failed to notice, that humans are not designed to hold their arms extended for long periods of time while making small and precise motions.
Table embedded displays do not share this problem, however, users can develop neck pain after using it for a period of time and the view might be obstructed by their arms.
Ever since their development in 1971, touchscreen monitors have been finding their way into more and more commercial applications. They come in any number of configurations, but in the end, they all function on the same principle and that is “see and touch”.
Fast food restaurants were one of the first businesses to implement these screens on a retail level but now more and more business are discovering the benefit of having them available at their point of sale locations.
The resistive touch screen type uses a normal glass panel, that is covered by a resistive and a conductive metallic layer and a protective layer (scratch resistant) on top of all this. When you make contact with the screen, the two metallic layers are joined and the change in electrical field is detected. The circuit on the display then calculates the coordinates and transfer them to the screen software. The driver then transfers the information about the coordinates to the OS, in a form of events similar to mouse clicks and drags.
With the capacitive touch screen type, a layer storing electrical charge, is placed on the glass. When you make contact with the layer, a small amount of the electrical charge is transferred to you, decreasing the charge on the layer. Sensors, located at the corners of the screen, detect a change in electrical charge levels and transfer the information to the software to process.
The biggest advantage of capacitive type over resistive is that it has 90% light throughput. This gives the capacitive touch screen monitors a much clearer picture. Since this type of technology uses electric charge to detect an event, you must use a conductive input, such as a finger.
Since this type has no metallic layers placed on the display surface, they have 100% light throughput, and therefore the most clear picture. Similar to resistive, this type detects events by almost any object, except very small or hard items, such as a pen.
These are just the most commonly used touch screen types and we at faytech North America have our own unique touch solutions. There are many other touchscreen technologies out there, such as strain gauge configuration (from 1960’s) or relatively-modern optical imaging technology. And recently, new touchscreen monitor technologies have been developed such as sunlight readable monitors,rugged monitors and open frame touch screen monitors that can withstand extreme environments.
Touch screen displays are very easy to figure out and most people will learn how to interact with them very quickly. The learning curve is very short. A recently hired employee no longer has to go through lengthy training sessions and can be found effortlessly using an intuitive touch interface within a few hours.
The touch screen technology developed by faytech North America brings significant time savings to point of sale systems in any retail establishment. The touch solutions simplify most transactions. The employee – or the customer – interacts with the screen, reviewing the potential options and makes a selection.
Products that cannot be bar coded, like perishable items, for example, or things that are small or with irregular surfaces that would hinder barcoding can now be easily processed through a point of sale with a touch screen display.
The viability as an interaction tool for the retail establishment has been established for some time now and this is why more and more businesses everywhere are implementing touch screen technologies.
Another factor is that faytech North America touch screen displays have also become more affordable in recent years and they are a technology that isn’t going to become obsolete in this lifetime.

Science fiction has always served as a window into a potential future, namely in the way of technology. But what was once regulated to episodes of Star Trek is quickly becoming the stuff of reality. Many fixtures of these kinds of shows and books have begun to inspire real-life counterparts, including - but not limited to - touchscreen technology.
One only has to look at how far cell phones have come since their inception. Physical keyboards, like those from BlackBerry, gave people about as much of a solution as is possible for those who found themselves doing more on the devices as they became more advanced. Where tactile options came up short, touchscreens graciously stepped up to bat, providing a much fuller experience. This kind of functionality then spread to tablets, which are considered by many to be rivals of laptops and even standard PCs.
While there are still some things that are best done on a desktop computer, that does not change the fact that many users find themselves longing for the same abilities on their PCs afforded by many of their mobile devices. This is what helped breed the touchscreen monitor market, which has many viable options for people seeking the best of both worlds. With stronger computing power and a finer ability to control actions occurring in the screen, users can get more work done in new and exciting ways.
Traditionally, computer mice are what have allowed us to "touch" in a virtual context, but touchscreen monitors are changing all that. It might be said that the reason that mice were used in the first place was because the technology had not evolved to a responsive enough level to enable that natural solution. Now that people have the touchscreen technology, they want it everywhere.
If one thing is for certain, it is that the burgeoning adoption of touchscreen technology is no fad. Proliferation has already come too far to turn back now, and computer manufacturers are taking notice. Everyone is trying to get a piece of the action, including ELO Touch Solutions, Laiputuo Electronics, Planar, HP, 3M, Touch Systems, ViewSonic, Dell and ACER as well. Getting into the touchscreen monitor game is a no-brainer for the companies involved in this generation of computing. With so many different applications made for touchscreen monitors, options exist for all sorts of interested parties.
Touchscreen monitors are becoming the new standard in both private and enterprise settings. Here are some of the ways they can be leveraged effectively for business: touchscreen monitors for workstations, touchscreen monitors for hospitals, and touchscreen monitors for POS systems.
Newegg offers a large selection of touchscreen monitors which vary according to the type from 5-wire Resistive touchscreen monitors, and Accu Touch touchscreen monitors, to Capacitive touchscreen monitors, and more. Newegg’s wide selections will definitely meet your needs.

From cinema content to motion-based digital art, Planar® Luxe MicroLED Displays offer a way to enrich distinctive spaces. HDR support and superior dynamic range create vibrant, high-resolution canvases for creative expression and entertainment. Leading-edge MicroLED technology, design adaptability and the slimmest profiles ensure they seamlessly integrate with architectural elements and complement interior décor.
From cinema content to motion-based digital art, Planar® Luxe Displays offer a way to enrich distinctive spaces. These professional-grade displays provide vibrant, high-resolution canvases for creative expression and entertainment. Leading-edge technology, design adaptability and the slimmest profiles ensure they seamlessly integrate with architectural elements and complement interior decor.
From cinema content to motion-based digital art, Planar® Luxe MicroLED Displays offer a way to enrich distinctive spaces. HDR support and superior dynamic range create vibrant, high-resolution canvases for creative expression and entertainment. Leading-edge MicroLED technology, design adaptability and the slimmest profiles ensure they seamlessly integrate with architectural elements and complement interior décor.
Carbon fiber-framed indoor LED video wall and floor displays with exceptional on-camera visual properties and deployment versatility for various installations including virtual production and extended reality.
a line of extreme and ultra-narrow bezel LCD displays that provides a video wall solution for demanding requirements of 24x7 mission-critical applications and high ambient light environments
Since 1983, Planar display solutions have benefitted countless organizations in every application. Planar displays are usually front and center, dutifully delivering the visual experiences and critical information customers need, with proven technology that is built to withstand the rigors of constant use.

The comprehensive SmartScreen is a full feature touch screen monitor powered by an internal Intel® i7 PC and designed for the unique needs of AEC professionals.
Powered by an Intel® Core™ i7 processor and equipped with both Windows 10 and Android operating systems, SKYSITE SmartScreens offer fast, easy access to presentations, videos, BIM models, hyperlinked drawing sets, spreadsheets, estimating software, and more. Content that was previously stored in your apps or computer becomes truly collaborative when you use a SmartScreen to facilitate meetings and presentations.

A touchscreen or touch screen is the assembly of both an input ("touch panel") and output ("display") device. The touch panel is normally layered on the top of an electronic visual display of an information processing system. The display is often an LCD, AMOLED or OLED display while the system is usually used in a laptop, tablet, or smartphone. A user can give input or control the information processing system through simple or multi-touch gestures by touching the screen with a special stylus or one or more fingers.zooming to increase the text size.
The touchscreen enables the user to interact directly with what is displayed, rather than using a mouse, touchpad, or other such devices (other than a stylus, which is optional for most modern touchscreens).
Touchscreens are common in devices such as game consoles, personal computers, electronic voting machines, and point-of-sale (POS) systems. They can also be attached to computers or, as terminals, to networks. They play a prominent role in the design of digital appliances such as personal digital assistants (PDAs) and some e-readers. Touchscreens are also important in educational settings such as classrooms or on college campuses.
The popularity of smartphones, tablets, and many types of information appliances is driving the demand and acceptance of common touchscreens for portable and functional electronics. Touchscreens are found in the medical field, heavy industry, automated teller machines (ATMs), and kiosks such as museum displays or room automation, where keyboard and mouse systems do not allow a suitably intuitive, rapid, or accurate interaction by the user with the display"s content.
Historically, the touchscreen sensor and its accompanying controller-based firmware have been made available by a wide array of after-market system integrators, and not by display, chip, or motherboard manufacturers. Display manufacturers and chip manufacturers have acknowledged the trend toward acceptance of touchscreens as a user interface component and have begun to integrate touchscreens into the fundamental design of their products.
The prototypeCERNFrank Beck, a British electronics engineer, for the control room of CERN"s accelerator SPS (Super Proton Synchrotron). This was a further development of the self-capacitance screen (right), also developed by Stumpe at CERN
One predecessor of the modern touch screen includes stylus based systems. In 1946, a patent was filed by Philco Company for a stylus designed for sports telecasting which, when placed against an intermediate cathode ray tube display (CRT) would amplify and add to the original signal. Effectively, this was used for temporarily drawing arrows or circles onto a live television broadcast, as described in US 2487641A, Denk, William E, "Electronic pointer for television images", issued 1949-11-08. Later inventions built upon this system to free telewriting styli from their mechanical bindings. By transcribing what a user draws onto a computer, it could be saved for future use. See US 3089918A, Graham, Robert E, "Telewriting apparatus", issued 1963-05-14.
The first version of a touchscreen which operated independently of the light produced from the screen was patented by AT&T Corporation US 3016421A, Harmon, Leon D, "Electrographic transmitter", issued 1962-01-09. This touchscreen utilized a matrix of collimated lights shining orthogonally across the touch surface. When a beam is interrupted by a stylus, the photodetectors which no longer are receiving a signal can be used to determine where the interruption is. Later iterations of matrix based touchscreens built upon this by adding more emitters and detectors to improve resolution, pulsing emitters to improve optical signal to noise ratio, and a nonorthogonal matrix to remove shadow readings when using multi-touch.
The first finger driven touch screen was developed by Eric Johnson, of the Royal Radar Establishment located in Malvern, England, who described his work on capacitive touchscreens in a short article published in 1965Frank Beck and Bent Stumpe, engineers from CERN (European Organization for Nuclear Research), developed a transparent touchscreen in the early 1970s,In the mid-1960s, another precursor of touchscreens, an ultrasonic-curtain-based pointing device in front of a terminal display, had been developed by a team around Rainer Mallebrein[de] at Telefunken Konstanz for an air traffic control system.Einrichtung" ("touch input facility") for the SIG 50 terminal utilizing a conductively coated glass screen in front of the display.
In 1972, a group at the University of Illinois filed for a patent on an optical touchscreenMagnavox Plato IV Student Terminal and thousands were built for this purpose. These touchscreens had a crossed array of 16×16 infrared position sensors, each composed of an LED on one edge of the screen and a matched phototransistor on the other edge, all mounted in front of a monochrome plasma display panel. This arrangement could sense any fingertip-sized opaque object in close proximity to the screen. A similar touchscreen was used on the HP-150 starting in 1983. The HP 150 was one of the world"s earliest commercial touchscreen computers.infrared transmitters and receivers around the bezel of a 9-inch Sony cathode ray tube (CRT).
In 1977, an American company, Elographics – in partnership with Siemens – began work on developing a transparent implementation of an existing opaque touchpad technology, U.S. patent No. 3,911,215, October 7, 1975, which had been developed by Elographics" founder George Samuel Hurst.World"s Fair at Knoxville in 1982.
In 1984, Fujitsu released a touch pad for the Micro 16 to accommodate the complexity of kanji characters, which were stored as tiled graphics.Sega released the Terebi Oekaki, also known as the Sega Graphic Board, for the SG-1000 video game console and SC-3000 home computer. It consisted of a plastic pen and a plastic board with a transparent window where pen presses are detected. It was used primarily with a drawing software application.
Touch-sensitive control-display units (CDUs) were evaluated for commercial aircraft flight decks in the early 1980s. Initial research showed that a touch interface would reduce pilot workload as the crew could then select waypoints, functions and actions, rather than be "head down" typing latitudes, longitudes, and waypoint codes on a keyboard. An effective integration of this technology was aimed at helping flight crews maintain a high level of situational awareness of all major aspects of the vehicle operations including the flight path, the functioning of various aircraft systems, and moment-to-moment human interactions.
In the early 1980s, General Motors tasked its Delco Electronics division with a project aimed at replacing an automobile"s non-essential functions (i.e. other than throttle, transmission, braking, and steering) from mechanical or electro-mechanical systems with solid state alternatives wherever possible. The finished device was dubbed the ECC for "Electronic Control Center", a digital computer and software control system hardwired to various peripheral sensors, servos, solenoids, antenna and a monochrome CRT touchscreen that functioned both as display and sole method of input.stereo, fan, heater and air conditioner controls and displays, and was capable of providing very detailed and specific information about the vehicle"s cumulative and current operating status in real time. The ECC was standard equipment on the 1985–1989 Buick Riviera and later the 1988–1989 Buick Reatta, but was unpopular with consumers—partly due to the technophobia of some traditional Buick customers, but mostly because of costly technical problems suffered by the ECC"s touchscreen which would render climate control or stereo operation impossible.
Multi-touch technology began in 1982, when the University of Toronto"s Input Research Group developed the first human-input multi-touch system, using a frosted-glass panel with a camera placed behind the glass. In 1985, the University of Toronto group, including Bill Buxton, developed a multi-touch tablet that used capacitance rather than bulky camera-based optical sensing systems (see History of multi-touch).
The first commercially available graphical point-of-sale (POS) software was demonstrated on the 16-bit Atari 520ST color computer. It featured a color touchscreen widget-driven interface.COMDEX expo in 1986.
In 1987, Casio launched the Casio PB-1000 pocket computer with a touchscreen consisting of a 4×4 matrix, resulting in 16 touch areas in its small LCD graphic screen.
Touchscreens had a bad reputation of being imprecise until 1988. Most user-interface books would state that touchscreen selections were limited to targets larger than the average finger. At the time, selections were done in such a way that a target was selected as soon as the finger came over it, and the corresponding action was performed immediately. Errors were common, due to parallax or calibration problems, leading to user frustration. "Lift-off strategy"University of Maryland Human–Computer Interaction Lab (HCIL). As users touch the screen, feedback is provided as to what will be selected: users can adjust the position of the finger, and the action takes place only when the finger is lifted off the screen. This allowed the selection of small targets, down to a single pixel on a 640×480 Video Graphics Array (VGA) screen (a standard of that time).
Sears et al. (1990)human–computer interaction of the time, describing gestures such as rotating knobs, adjusting sliders, and swiping the screen to activate a switch (or a U-shaped gesture for a toggle switch). The HCIL team developed and studied small touchscreen keyboards (including a study that showed users could type at 25 wpm on a touchscreen keyboard), aiding their introduction on mobile devices. They also designed and implemented multi-touch gestures such as selecting a range of a line, connecting objects, and a "tap-click" gesture to select while maintaining location with another finger.
In 1990, HCIL demonstrated a touchscreen slider,lock screen patent litigation between Apple and other touchscreen mobile phone vendors (in relation to
An early attempt at a handheld game console with touchscreen controls was Sega"s intended successor to the Game Gear, though the device was ultimately shelved and never released due to the expensive cost of touchscreen technology in the early 1990s.
Touchscreens would not be popularly used for video games until the release of the Nintendo DS in 2004.Apple Watch being released with a force-sensitive display in April 2015.
In 2007, 93% of touchscreens shipped were resistive and only 4% were projected capacitance. In 2013, 3% of touchscreens shipped were resistive and 90% were projected capacitance.
A resistive touchscreen panel comprises several thin layers, the most important of which are two transparent electrically resistive layers facing each other with a thin gap between. The top layer (that which is touched) has a coating on the underside surface; just beneath it is a similar resistive layer on top of its substrate. One layer has conductive connections along its sides, the other along top and bottom. A voltage is applied to one layer and sensed by the other. When an object, such as a fingertip or stylus tip, presses down onto the outer surface, the two layers touch to become connected at that point.voltage dividers, one axis at a time. By rapidly switching between each layer, the position of pressure on the screen can be detected.
Resistive touch is used in restaurants, factories and hospitals due to its high tolerance for liquids and contaminants. A major benefit of resistive-touch technology is its low cost. Additionally, as only sufficient pressure is necessary for the touch to be sensed, they may be used with gloves on, or by using anything rigid as a finger substitute. Disadvantages include the need to press down, and a risk of damage by sharp objects. Resistive touchscreens also suffer from poorer contrast, due to having additional reflections (i.e. glare) from the layers of material placed over the screen.3DS family, and the Wii U GamePad.
Surface acoustic wave (SAW) technology uses ultrasonic waves that pass over the touchscreen panel. When the panel is touched, a portion of the wave is absorbed. The change in ultrasonic waves is processed by the controller to determine the position of the touch event. Surface acoustic wave touchscreen panels can be damaged by outside elements. Contaminants on the surface can also interfere with the functionality of the touchscreen.
The Casio TC500 Capacitive touch sensor watch from 1983, with angled light exposing the touch sensor pads and traces etched onto the top watch glass surface.
A capacitive touchscreen panel consists of an insulator, such as glass, coated with a transparent conductor, such as indium tin oxide (ITO).electrostatic field, measurable as a change in capacitance. Different technologies may be used to determine the location of the touch. The location is then sent to the controller for processing. Touchscreens that use silver instead of ITO exist, as ITO causes several environmental problems due to the use of indium.complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) chip, which in turn usually sends the signals to a CMOS digital signal processor (DSP) for processing.
Unlike a resistive touchscreen, some capacitive touchscreens cannot be used to detect a finger through electrically insulating material, such as gloves. This disadvantage especially affects usability in consumer electronics, such as touch tablet PCs and capacitive smartphones in cold weather when people may be wearing gloves. It can be overcome with a special capacitive stylus, or a special-application glove with an embroidered patch of conductive thread allowing electrical contact with the user"s fingertip.
A low-quality switching-mode power supply unit with an accordingly unstable, noisy voltage may temporarily interfere with the precision, accuracy and sensitivity of capacitive touch screens.
Some capacitive display manufacturers continue to develop thinner and more accurate touchscreens. Those for mobile devices are now being produced with "in-cell" technology, such as in Samsung"s Super AMOLED screens, that eliminates a layer by building the capacitors inside the display itself. This type of touchscreen reduces the visible distance between the user"s finger and what the user is touching on the screen, reducing the thickness and weight of the display, which is desirable in smartphones.
A simple parallel-plate capacitor has two c




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey