tft lcd module connector pinout made in china

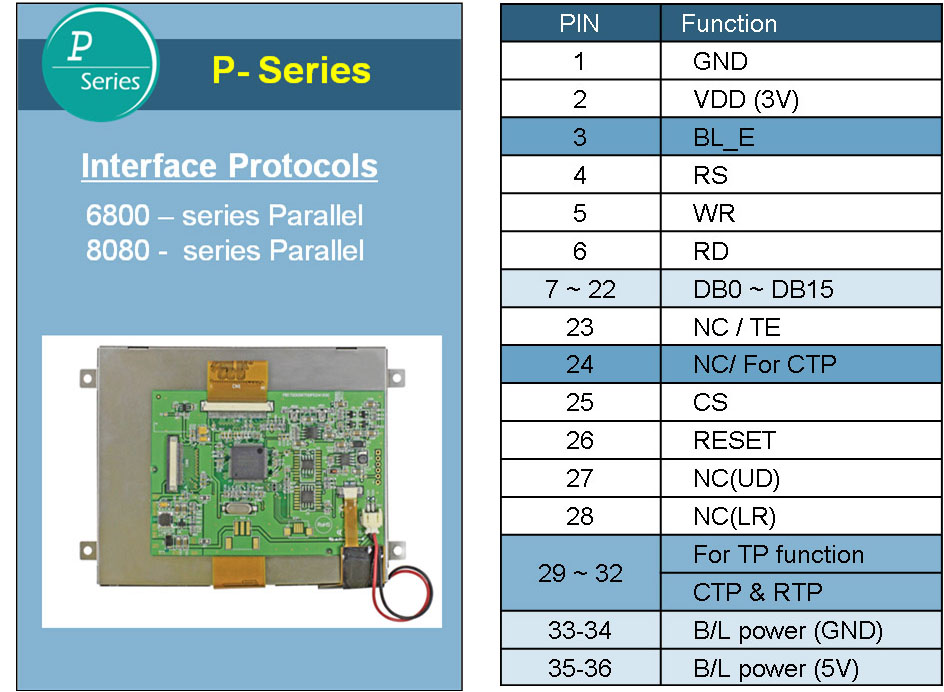
The modules of Winstar TFT P Series are similar to Winstar TFT Q series which are also featured with an integrated 36-pinout connector on controller board. The P Series modules are derivative products from the Winstar existing standard TFT modules which uniform the pin assignment into 36 pins on a RA8875 controller board.
Winstar P Series is a TFT module Family which is including 3.5 inch, 4.3 inch, 5.7 inch, 7.0 inch, 8.0 inch and 10.2 inch TFT modules. The modules of Winstar TFT P Series which are all have an integrated 36-pinout connector on the RA8875 controller board. The P Series is featured with 8 bit or 16 bit options and already defined pin no. 33 ~ 36 as backlight supply; therefore, the customers no need to design extra backlight circuit. If the customers require different function controller for applications, you can consider choosing Winstar TFT P Series. It supports many import functions such as Chinese character display, backlight brightness adjustment, Flash Memory and touch panel driver.
The 1.8inch LCD uses the PH2.0 8PIN interface, which can be connected to the Raspberry Pi according to the above table: (Please connect according to the pin definition table. The color of the wiring in the picture is for reference only, and the actual color shall prevail.)
ST7735S is a 132*162 pixel LCD, and this product is a 128*160 pixel LCD, so some processing has been done on the display: the display starts from the second pixel in the horizontal direction, and the first pixel in the vertical direction. Start to display, so as to ensure that the position corresponding to the RAM in the LCD is consistent with the actual position when displayed.
The LCD supports 12-bit, 16-bit and 18-bit input color formats per pixel, namely RGB444, RGB565, RGB666 three color formats, this routine uses RGB565 color format, which is also a commonly used RGB format
2. The module_init() function is automatically called in the INIT () initializer on the LCD, but the module_exit() function needs to be called by itself
Python has an image library PIL official library link, it do not need to write code from the logical layer like C, can directly call to the image library for image processing. The following will take 1.54inch LCD as an example, we provide a brief description for the demo.
The demo is developed based on the HAL library. Download the demo, find the STM32 program file directory, and open the LCD_demo.uvprojx in the STM32\STM32F103RBT6\MDK-ARM directory to check the program.
image.cpp(.h): is the image data, which can convert any BMP image into a 16-bit true color image array through Img2Lcd (downloadable in the development data).

LCD, or Liquid Crystal Displays, are great choices for many applications. They aren’t that power-hungry, they are available in monochrome or full-color models, and they are available in all shapes and sizes.
Waveshare actually has several round LCD modules, I chose the 1.28-inch model as it was readily available on Amazon. You could probably perform the same experiments using a different module, although you may require a different driver.
Open the Arduino folder. Inside you’ll find quite a few folders, one for each display size that Waveshare supports. As I’m using the 1.28-inch model, I selected theLCD_1inch28folder.
Once you do that, you can open your Arduino IDE and then navigate to that folder. Inside the folder, there is a sketch file namedLCD_1inch28.inowhich you will want to open.
Unfortunately, Waveshare doesn’t offer documentation for this, but you can gather quite a bit of information by reading theLCD_Driver.cppfile, where the functions are somewhat documented.
Here is the hookup for the ESP32 and the GC9A01 display. As with most ESP32 hookup diagrams, it is important to use the correct GPIO numbers instead of physical pins. The diagram shows the WROVER, so if you are using a different module you’ll need to consult its documentation to ensure that you hook it up properly.
The TFT_eSPI library is ideal for this, and several other, displays. You can install it through your Arduino IDE Library Manager, just search for “TFT_eSPI”.
The Animated Eyes sketch can be found within the sample files for the TFT_eSPI library, under the “generic” folder. Assuming that you have wired up the second GC9A01 display, you’ll want to use theAnimated_Eyes_2sketch.
The GC9A01 LCD module is a 1.28-inch round display that is useful for instrumentation and other similar projects. Today we will learn how to use this display with an Arduino Uno and an ESP32.

In this Arduino touch screen tutorial we will learn how to use TFT LCD Touch Screen with Arduino. You can watch the following video or read the written tutorial below.
As an example I am using a 3.2” TFT Touch Screen in a combination with a TFT LCD Arduino Mega Shield. We need a shield because the TFT Touch screen works at 3.3V and the Arduino Mega outputs are 5 V. For the first example I have the HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor, then for the second example an RGB LED with three resistors and a push button for the game example. Also I had to make a custom made pin header like this, by soldering pin headers and bend on of them so I could insert them in between the Arduino Board and the TFT Shield.
Here’s the circuit schematic. We will use the GND pin, the digital pins from 8 to 13, as well as the pin number 14. As the 5V pins are already used by the TFT Screen I will use the pin number 13 as VCC, by setting it right away high in the setup section of code.
I will use the UTFT and URTouch libraries made by Henning Karlsen. Here I would like to say thanks to him for the incredible work he has done. The libraries enable really easy use of the TFT Screens, and they work with many different TFT screens sizes, shields and controllers. You can download these libraries from his website, RinkyDinkElectronics.com and also find a lot of demo examples and detailed documentation of how to use them.
After we include the libraries we need to create UTFT and URTouch objects. The parameters of these objects depends on the model of the TFT Screen and Shield and these details can be also found in the documentation of the libraries.
So now I will explain how we can make the home screen of the program. With the setBackColor() function we need to set the background color of the text, black one in our case. Then we need to set the color to white, set the big font and using the print() function, we will print the string “Arduino TFT Tutorial” at the center of the screen and 10 pixels down the Y – Axis of the screen. Next we will set the color to red and draw the red line below the text. After that we need to set the color back to white, and print the two other strings, “by HowToMechatronics.com” using the small font and “Select Example” using the big font.

The TFT display is a kind of LCD that is connected to each pixel using a transistor and it features low current consumption, high-quality, high-resolution and backlight. This 2.8-inch full color LCD has a narrow PCB display. The resolution is 320×280 pixels and it has a four-wire SPI interface and white backlight.

Checking a TFT lcd driver is very messy thing especially if its a Chinese manufactured TFT. TFT’s that are supplied by Chinese manufactures are cheap and every body loves to purchase them since they are cheap,but people are unaware of the problems that comes in future when finding the datasheet or specs of the particular TFT they purchased. Chinese manufactures did not supply datasheet of TFT or its driver. The only thing they do is writes about the TFT driver their lcd’s are using on their websites. I also get in trouble when i started with TFT’s because i also purchased a cheap one from aliexpress.com. After so many trials i succeeded in identifying the driver and initializing it. Now i though to write a routine that can identify the driver.
I wrote a simple Arduino Sketch that can easily and correctly identify the TFT Lcd driver. I checked it on 2.4, 3.2 and 3.8 inch 8-bit TFT lcd and it is identifying the drivers correctly. The drivers which i successfully recognized are ILI9325, ILI9328, ILI9341, ILI9335, ST7783, ST7781 and ST7787. It can also recognize other drivers such as ML9863A, ML9480 and ML9445 but i don’t have tft’s that are using this drivers.
The basic idea behind reading the driver is reading the device ID. Since all the drivers have their ID’s present in their register no 0x00, so what i do is read this register and identify which driver tft is using. Reading the register is also a complex task, but i have gone through it many times and i am well aware of how to read register. A simple timing diagram from ST7781 driver explains all. I am using tft in 8-bit interface so i uploaded timing diagram of 8-bit parallel interface. The diagram below is taken from datasheet of ST7781 tft lcd driver.
The most complex tft i came across is from a Chinese manufacturer “mcufriend”. mcufriend website says that they use ILI9341 and ILI9325 drivers for their tft’s. But what i found is strange their tft’s are using ST7781 driver(Device ID=7783). This is really a mesh. I have their 2.4 inch tft which according to their website is using ILI9341 driver but i found ST7783 driver(Device ID=7783). The tft i have is shown below.
I am using Arduino uno to read driver. I inserted my lcd on arduino uno and read the driver. After reading driver i am printing its number on Serial Monitor.
Note:On serial monitor driver number will be displayed like if your lcd is using ST7783 controller than on serial monitor 7783 will be displayed or if tft is using ILI9341 than on 9341 will be displayed.
The code works on Arduino uno perfectly but if you are using any other board, than just change the pin numbers according to the board that you are using also check out for the Ports D and B. TFT Data Pin D0 is connected to Port-B Pin#0 and D1 is connected to Port-B Pin#1. TFT Data Pins D2 to D7 are connected to Port-D Pins 2,3,4,5,6,7. So if you are using Arduino mega than check for the Ports D and B and Make connections according to them. Arduino mega is working on ATmega2560 or ATmega1280 Microcontroller and Arduino uno is working on ATmega328p Microcontroller so both platforms have ports on different locations on arduino board so first check them and then make connections. The same process applies to all Arduino boards.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey