pls tft display vs super amoled supplier

AMOLED and TFT are two types of display technology used in smartphones. AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode) displays are made up of tiny organic light-emitting diodes, while TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) displays use inorganic thin-film transistors.
AMOLEDs are made from organic materials that emit light when an electric current is passed through them, while TFTs use a matrix of tiny transistors to control the flow of electricity to the display.
Refresh Rate: Another key difference between AMOLED and TFT displays is the refresh rate. The refresh rate is how often the image on the screen is updated. AMOLED screens have a higher refresh rate than TFT screens, which means that they can display images more quickly and smoothly.
Response Time: The response time is how long it takes for the pixels to change from one colour to another. AMOLED screens have a shorter response time than TFT screens..
Colour Accuracy/Display Quality: AMOLED screens are more accurate when it comes to displaying colours. This is because each pixel on an AMOLED screen emits its own light, which means that the colours are more pure and true to life. TFT screens, on the other hand, use a backlight to illuminate the pixels, which can cause the colours to appear washed out or less vibrant.
Viewing Angle: The viewing angle is the angle at which you can see the screen. AMOLED screens have a wider viewing angle than TFT screens, which means that you can see the screen from more angles without the colours looking distorted.
Power Consumption: One of the main advantages of AMOLED displays is that they consume less power than TFT displays. This is because the pixels on an AMOLED screen only light up when they need to, while the pixels on a TFT screen are always illuminated by the backlight.
Production Cost: AMOLED screens are more expensive to produce than TFT screens. This is because the manufacturing process for AMOLED screens is more complex, and the materials used are more expensive.
Availability: TFT screens are more widely available than AMOLED screens and have been around for longer. They are typically used in a variety of devices, ranging from phones to TVs.
Usage: AMOLED screens are typically used in devices where power consumption is a concern, such as phones and wearable devices. TFT screens are more commonly used in devices where image quality is a higher priority, such as TVs and monitors.
AMOLED and TFT are two different types of display technology. AMOLED displays are typically brighter and more vibrant, but they are more expensive to produce. TFT displays are cheaper to produce, but they are not as bright or power efficient as AMOLED displays.
The display technology that is best for you will depend on your needs and preferences. If you need a screen that is bright and vibrant, then an AMOLED display is a good choice. If you need a screen that is cheaper to produce, then a TFT display is a good choice. However, if you’re worried about image retention, then TFT may be a better option.
Nauticomp Inc.provides world-class fully customizable touchscreen displays for commercial and industrial settings. With features like sunlight readability, brightness adjustability, infrared lighting, full backlighting, all-weather capabilities, etc., our displays are second to none. Contact us today to learn more.

Thanks for the display technology development, we have a lot of display choices for our smartphones, media players, TVs, laptops, tablets, digital cameras, and other such gadgets. The most display technologies we hear are LCD, TFT, OLED, LED, QLED, QNED, MicroLED, Mini LED etc. The following, we will focus on two of the most popular display technologies in the market: TFT Displays and Super AMOLED Displays.
TFT means Thin-Film Transistor. TFT is the variant of Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs). There are several types of TFT displays: TN (Twisted Nematic) based TFT display, IPS (In-Plane Switching) displays. As the former can’t compete with Super AMOLED in display quality, we will mainly focus on using IPS TFT displays.
OLED means Organic Light-Emitting Diode. There are also several types of OLED, PMOLED (Passive Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) and AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode). It is the same reason that PMOLED can’t compete with IPS TFT displays. We pick the best in OLED displays: Super AMOLED to compete with the LCD best: IPS TFT Display.
If you have any questions about Orient Display displays and touch panels. Please feel free to contact: Sales Inquiries, Customer Service or Technical Support.

AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode) and TFT (Thin Film Transistor) are the two types of displays that are used in mobile phones. TFT is actually a process of producing the displays and is used even by AMOLED but for most purposes, TFT is used to refer to LCD displays. The difference between them is the material as AMOLED uses organicmaterials, mainly carbon, while TFT does not.
There are differences between the two that are quite tangible. For starters, AMOLED generates its own light rather than relying on a backlight like a TFT-LCD does. This consequently means that AMOLED displays are much thinner than LCD displays; due to the absence of a backlight. It also results in much better colors than a TFT is capable of producing. As each pixel’s color and light intensity can be regulated independently and no light seeps from adjacent pixels. A side by side comparison of the two displays with the same picture should confirm this. Another effect of the lack of a backlight is the much lower power consumption of the device. This is very desirable when it comes to mobile phones where every single feature competes for the limited capacity of the battery. As the screen is on 90% of the time that the device is being used, it is very good that AMOLED displays consume less. Just how much of a difference is not very fixed though as it really depends on the color and intensity of the image. Having a black background with white text consumes much less energy than having black text on a white background.
The biggest disadvantage that AMOLED has is the shorter lifespan of the screen compared to TFT. Each pixel in the display degrades with each second that it is lit and even more so the brighter it is. Â Despite improvements on the lifetime of AMOLED displays, AMOLED still only lasts a fraction of the lifetime of a TFT display. With that said, an AMOLED display is able to outlast the usable lifetime of the device before parts of it start to degrade.
The main hindrance to the massive adaptation of AMOLED is the low production numbers. TFT has been in production for much longer and the infrastructure is already there to meet the demands.

This rise of small, powerful components has also led to significant developments in display technology. The most recent of which, AMOLED, is now the main competitor for the most common display used in quality portable electronics – the TFT–LCD IPS (In-Plane Switching) display. As more factories in the Far East begin to produce AMOLED technology, it seems likely we will enter a battle of TFT IPS versus AMOLED, or LCD vs LED. Where a large percentage of a product’s cost is the display technology it uses, which provides best value for money when you’re designing a new product?
TFT IPSdisplays improved on previous TFT LCD technology, developed to overcome limitations and improve contrast, viewing angles, sunlight readability and response times. Viewing angles were originally very limited – so in-plane switching panels were introduced to improve them.
Modern TFT screens can have custom backlights turned up to whatever brightness that their power limit allows, which means they have no maximum brightness limitation. TFT IPS panels also have the option for OCA bonding, which uses a special adhesive to bond a touchscreen or glass coverlens to the TFT. This improves sunlight readability by preventing light from bouncing around between the layers of the display, and also improves durability without adding excess bulk; some TFT IPS displays now only measure around 2 mm thick.
AMOLED technology is an upgrade to older OLED technology. It uses organic compounds that emit light when exposed to electricity. This means no backlight, which in turn means less power consumption and a reduction in size. AMOLED screens tend to be thinner than TFT equivalents, often produced to be as thin as 1 mm. AMOLED technology also offers greater viewing angles thanks to deeper blacks. Colours tend to be greater, but visibility in daylight is lower than IPS displays.
As manufacturers increasingly focus on smaller devices, such as portable smartphones and wearable technology, the thinness and high colour resolution of AMOLED screens have grown desirable. However, producing AMOLED displays is far more costly as fewer factories offer the technology at a consistent quality and minimum order quantities are high; what capacity there is is often taken up the mobile phone market Full HD TFT IPS displays have the advantage of being offered in industry standard sizes and at a far lower cost, as well as offering superior sunlight visibility.
The competition between displays has benefitted both technologies as it has resulted in improvements in both. For example, Super AMOLED, a marketing brand by Samsung, involves the integration of a touchscreen layer inside the screen, rather than overlaid on it. The backlight in TFT technology means they can never truly replicate the deep blacks in AMOLED, but improvements have been made in resolution to the point where manufacturers like Apple have been happy to use LCD screens in their smartphones, even as they compete with Samsung’s Super AMOLED.
Aside from smartphones, many technologies utilise displays to offer direct interaction with customers. To decide whether TFT LCD will survive the rise of AMOLED technology, we must first recap the advantages of LCD. The backlit quality means that whites are bright and contrast is good, but this will wear down a battery faster than AMOLED. Additionally, cost is a significant factor for LCD screens. They are cheaper, more freely available and are offered in industry standard sizes so can be ordered for new products without difficulty.
It seems hard to deny that AMOLED will someday become the standard for mobile phones, which demand great colour performance and are reliant on battery life. Where size is an issue, AMOLED will also grow to dominance thanks to its superior thinness. But for all other technologies, particularly in industrial applications, TFT-LCD offers bright, affordable display technology that is continually improving as the challenge from AMOLED rises.

Tried and trusted TFT technology works by controlling brightness in red, green and blue sub-pixels through transistors for each pixel on the screen. The pixels themselves do not produce light; instead, the screen uses a backlight for illumination.
By contrast the Active Matrix OLED (AMOLED) display requires no backlight and can light up or turn off each of their pixels independently. As the name suggests, they are made of organic material.
An AMOLED display has many other benefits which make it a superior looking display including exceptional vieiwng angles and a display that looks practically black when it is switched off.
So, why use a TFT display? Well, it is a mature technology meaning the manufacturing processes are efficient, yields high and cost much lower than AMOLED.
TFT displays also have a much longer lifespan than AMOLED displays and are available in a far greater range of standard sizes, which can be cut down to fit a space restricted enclosure for a relatively low cost adder.
Which type of display you choose really depends on your application, environment and users, so why not get in touch with us today to discuss your requirements.
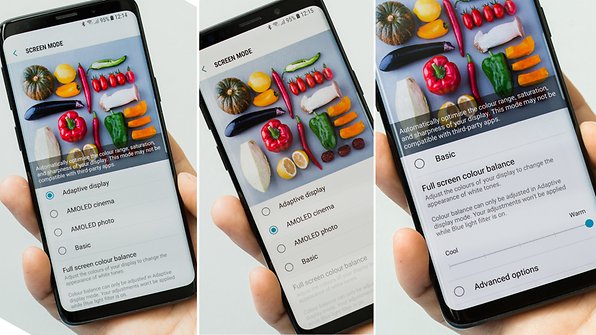
Display technologies are advancing every day. All the major tech giants like Apple, Samsung, One Plus use one among these technologies for building the displays of their Apple phones or Galaxy Notes. Each has its advantages and disadvantages. So which one is better? Is it the AMOLED favored mostly by Samsung? Or is it the IPS LCD favored by Apple for their iPhones? Let us take a detailed look at the features of AMOLED vs IPS display technologies.
AMOLED stands for Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode is a type of display used mainly in mobile phones. You might have seen the AMOLED display mentioned in the specifications for smart devices, especially mobile phones. They are also used in smartwatches, laptops, and even televisions. Let’s see what the terms in AMOLED mean.
The Active Matrix technology came about as an improvement on the existing passive matrix technology that used passive components like wires which were arranged vertically and horizontally to control each pixel. The color and brightness of the pixels and thereby the picture can be altered by varying the electrical charge at the given joint of vertical and horizontal wires. The newer Active Matrix uses active electrical components like transistors and capacitors to carry out the same purpose. Instead of varying current at the intersection of wires to control the pixels, this latest technology uses a grid or matrix of thin-film transistors commonly referred to as TFTs and capacitors.
You might be familiar with the giant LED bulbs used at parties or even as indicators on televisions showing the on/off state. These same LED lights are used in AMOLEDs, but of course in the smallest size possible. The LEDs used are in the primary shades namely Red, Blue, and Green, and are grouped in triangle-shaped pixelated forms.
The Organic Light Emitting Diode is commonly referred to as OLED. It is pronounced as “oh-led”. OLED is a type of display in which each LED lights up one at a time. When you light them up together in different intensities, you will get more colors in the spectrum. So all LEDs switched on at the same time give you white color and similarly switching off all the LEDs together gives black color. An OLED display is comprised of a substrate, an anode, a conductive layer, an emissive layer, a cathode, and the cover. The substrate is either plastic or glass that supports the display panel.
Compared to the LCD and LED displays, the diodes in the OLED display produce light individually meaning they do not need a backlight like their predecessors. OLEDs use lesser electricity and are thinner compared to LEDs. They are also bendable and may even be curved. However, they are much more expensive than LED displays. Hence in the earlier days, it was majorly used for displays for
Now the technologies mentioned above combine to give the AMOLED displays. Here an OLED display is driven with an active matrix control scheme. The TFTs (thin-film transistors) turn on/off each pixel one at a time. The other scheme where the OLEDs are controlled by a passive matrix requires each grid ( rows and lines) to be controlled together. The advanced AMOLED displays allow for higher resolution display with a much bigger physical size.
AMOLEDs have deep black lights. The blacks are darker than LEDs and LCDs because parts of the screen can be switched off altogether. AMOLEDs are also thinner and lighter than LCDs. This feature especially stands out in a dark theater room where OLED displays give a higher contrast ratio compared to LCDs making for an excellent visual experience. This feature of OLED which can work with no backlight makes it better than LCDs whether or not they have an LED backlight.
Since they use Active Matrix technology over the passive matrix version, AMOLEDs have a faster response time. They are up to a millisecond faster and extract less power from your mobile phone’s battery. Extended battery life means major advantages in the portability department. This adding to its high display features leads to them being extensively used. They are preferred over the other versions by major companies like Samsung. Speaking of power, the amount consumed by an OLED display varies according to the brightness and color of the picture displayed.
AMOLEDs have impressive contrast ratios. The contrast ratio is the ratio of the luminance of white color to the black color of a display unit. The high contrast of AMOLEDs is because when the LEDs are off, it gives complete black and since no backlight is used in LEDs, we get deep blacks.
One of the disadvantages the AMOLED had over LCD was the blurriness caused in sunlight which is a result of its lowered peak-brightness values. This issue was corrected in the advanced Super AMOLEDs. In the Super AMOLEDs, the size of gaps between the various layers of the screen namely the cathode layer, anode layer, organic active layer, TFT layer is made narrower than before.
Another problem associated with the AMOLEDs is that the organic materials used in the emissive layer and the conductive layer suffer degradation. This happens comparatively in a short amount of time. As a result, various display problems arise including image persistence, burn-in, etc which are essentially screen burn type problems and color shifts where some colors fade quicker than others. Burn-in is essentially the pixel quality becoming trash after a while because of the degradation of the organic molecules.
Most flagship models of major companies like Samsung, Apple, and One Plus use either super AMOLED or IPS panel premium LCDs. So what exactly is an IPS display? and how does it feature against like the likes of super AMOLEDs?
First, let us understand the basics of a standard LCD. Simply put, when you apply current to some crystals, they may or may not let through the light which comes from a backlight that covers the whole display. In addition to this, there are polarization and color filters present in LCDs which finally give the primary colors Red, Blue, and Green.
Before we get into detailed explanations, you have to keep in mind that for the final end-product that ends up on the market, the quality of the display does not solely depend on whether it is IPS or AMOLED. The companies usually put their tweaks on top of the existing technology before making them available in the market. AMOLEDs are a newer technology than IPS LCD and improve on it in some areas while still lagging in others.
The IPS LCD stands for In-Plane Switching Liquid Crystal Displays. It emerged onto the scene as an improvement on the existing and vulnerable Thin Film Transistor LCD technology commonly referred to as the TFT. Samsung was the leading manufacturer to employ Super AMOLEDs. The IPS display is mainly being used in Apple iPhones. Apple beginning with the iPhone X is switching to AMOLED displays with contrast ratios of 1000000 to 1
As said before, an IPS display is an improved version of the regular TFT LCDs. Here, the difference comes in the way the anode and the cathode are arranged. They are planted as strip electrodes on one of the two glass substrates.
The IPS display scores big time when it comes to offering better viewing angles compared to the other LCD technologies like Twisted Nematic LCD (TN) and Vertical Alignment LCD (VA). The IPS display can be viewed without any color degradation or blurriness at flimsy shallow angles compared to TN and VA displays.
The consistency of colors and clarity of pictures at wider viewing angles is the major advantage of an LCD. IPS displays have higher resolution. They also can display a wide range of colors. These features also make the IPS displays costlier than TN and VA LCDs. Normally IPS monitors allow up to 178 degrees of viewing angles. These displays almost guarantee absolute color accuracy.
For other LCD models, the color and the brightness of an image vary when viewed from different angles. Compared with them, IPS displays are more suited for someone working as a visual/graphic artist. As a regular television, all LCD models are mostly considered equally good. This is because the viewers would mostly be sitting right in front of the screen where these differences between the models do not matter.
IPS displays are capable of displaying a wider spectrum of colors. Considering no monitors can display the entire color spectrum visible to the human eye, IPS LCD panels are the closest things to a perfect display monitor far better than TN and VA LCDs
Image retention is a problem often associated with LCDs. This happens because of the crystal which gets into a particular position for the light to go through stays in that same spot without falling back into its original position. This leads to some parts of the image being left on the screen. This is, however, a temporary problem. The crystal will eventually twist back into the position when the current is applied to it again. When it comes to color accuracy, the previous generation of LCDs was no match for the AMOLED. They had the highest color accuracy among mobile phones. But recent versions of the LCDs have fared much better versus their counterparts.
Large-sized IPS monitors are not affordable for the average customer. They should be avoided since they offer nothing impressive over other LCDs considering the price range. However, if you are a visual artist or a photographer, IPS displays provide the best color accuracy in the market. It would be more beneficial to you compared to an ordinary TN display unit.
AMOLEDs and IPS LCDs are two sides of the same coin in a sense. They both got their advantages and disadvantages. Their disadvantages are mostly overshadowed by the many tweaks installed by the parent companies to ensure customer satisfaction. From high power consumption to ugly blacks, the flaws are minimized in every newer version.

OLED displays are commonplace on all high-end phones, tablets, smartwatches, televisions, and even many of the many budget phones. However, there isn"t one type of OLED technology. Depending on your device, you may have an OLED, AMOLED, or POLED display.
OLED promises inky blacks, high contrast, low response times, and incredible brightness. There are a few downsides (primarily the burn-in phenomenon), but overall it"s the best screen technology you"ll find. We explain the background behind the acronyms, the difference between POLED and AMOLED, and which is better, helping you choose the right phone.
Every OLED screen comprises millions of diodes, hence the name organic light-emitting diode. Viewed under a microscope, each screen consists of a series of red, green, and blue diodes that can be individually turned on and off. Behind this, the light-emitting pixels of an OLED display emit blue and yellow light. The yellow and blue light combine to form white light, passing through the red, green, and blue subpixels to produce a single pixel. Because each pixel handles its light and color, OLED displays do not need a separate backlight.
As an OLED screen doesn"t need a backlight, black is produced by turning off the pixels, resulting in deep, consistent blacks. This allows manufacturers to implement things like an always-on display without quickly burning through battery life.
Another critical advantage of OLED tech is high contrast ratios. Technically, OLED displays offer "infinite contrast," or 1,000,000:1 contrast ratios. This is because OLED displays reproduce black by turning off pixels entirely, and contrast is measured by comparing the brightest part of the screen to the darkest part. Improved contrast makes on-screen content more vivid and makes bright highlights look more impressive. This also means that OLED screens can reach higher brightness than the best IPS LCD screens.
OLED displays can display more colors with greater color accuracy than their LCD peers. This is great for photographers and videographers using their phones to preview, edit, and create content.
OLED displays have near-instantaneous pixel response times. Older LCD screens often have lower response times because to change from one color to another, they must physically change the orientation of a liquid crystal, which takes time. An OLED display turns a subpixel on or off with an electrical charge, giving them a faster pixel response time.
The omission of a separate backlight and the use of fewer components means OLED displays can be thinner than LCDs, making them more versatile in their applications. This means they are more fragile and prone to damage in high-impact or high-stress situations. Engineers combat this by using technologies like Gorilla Glass and robust metal frames. Mitigation strategies like these raise the cost of OLED screens.
OLED displays can also be transparent, depending on the materials used. Transparent displays are helpful for in-display fingerprint readers and under-display cameras, which allow manufacturers to design smartphones with fewer and smaller bezels, notches, and display cutouts. When notches and cutouts are necessary, OLED displays have more even brightness around those cutouts and notches compared with LCDs, where the backlight has to make it around the cutout, and things get a little messy.
Of particular import to smartphones, OLED displays often consume less power, especially when displaying dark images or UI elements, thanks to the pixel-level regulation of brightness. However, at max brightness, an OLED screen usually uses more power than an equivalent LCD.
As with any new technology, OLED tech is not without its flaws.OLED displays are prone to degradation from age and UV exposure, resulting from the organic nature of the molecules that make up the diodes. The organic nature of OLED displays also leads to a phenomenon called screen burn-in, where static UI elements like menus, navigation bars, and status bars (elements that are on-screen for long periods) leave a permanent ghost image, even when they are not displayed. However, burn-in has been somewhat mitigated by pixel shifting and technological advancements in recent years.
Early OLED screens placed all the organic materials on a glass substrate. However, glass is rigid, so a flexible plastic substrate is needed to create foldable display screens, leading to the creation of POLED screens.
POLED (polymer organic light-emitting diode) offers advantages in terms of durability and versatility. The replacement ofglass substrates with plastic ones makes them more shock-resistant. Another unique advantage is in the implementation. Designers can reduce bezel size by folding the electronics underneath an edge of the display instead of having it be on the same plane. POLED displays are also significantly thinner than OLED displays with glass substrates.
Note the difference between P OLED and pOLED. pOLED is the trademark that LG Display uses to brand its plastic OLED displays. It produces these displays for a variety of applications and companies. Google used pOLED displays on the Pixel 2 XL, LG used them on theLG Velvet and several wearables,and Apple reportedly used LG pOLED displays on some Apple Watch models. LG"s pOLED displays seem to suffer from an increased risk of burn-in, as users of the Google Pixel 2 XL complained of burn-in after a few months of use.
To get to the resolution and size of a phone, an AMOLED screen (active matrix organic light emitting diode) is needed. Older, passive matrix OLED displays (PMOLED) require higher voltages for higher pixels/resolutions. The higher the voltage, the lower the screen"s lifetime.
Thin-film transistor (TFT) arrays used in modern active-matrix OLED displays control the charging of the display"s storage capacitors. These TFTs control current flow, resulting in more energy-efficient OLED panels than PMOLED displays. This allows a larger display size without compromising resolution, lifetime, or power consumption.
QLED isn"t related to OLED displays—despite what the name may suggest—but it"s often slated as a competitor to OLED, and it aims to replace the technology by targeting both OLED"s successes and failures. QLED stands for quantum dot light-emitting diode. The core principle of QLED technology is the same as a regular OLED. A backlight is passed through red, green, and blue subpixel layers to generate an image. However, the backlight isn"t one large, uniformly-lit layer. Instead, QLED displays use an array of tiny individually-controlled LEDs to supply the backlight. Using individually-controlled LEDs means the display can produce a more accurate image with a higher contrast.
Generally speaking, QLED displays have similar benefits to OLED displays—high peak brightness, high contrast, perfect blacks, and good saturation. Still, they lack some OLED advantages, like image retention and reduced overall and sustained brightness.
QLED is found in TVs and large computer monitors because that"s where it sees the most benefit. OLED displays in phones are small enough, bright enough, and cheap enough that QLED wouldn"t be able to compete or offer any practical benefit to the end user.
Display type is only one part of the puzzle.What use is exotic technology if it doesn"t make any difference to the end user? Smartphone manufacturers use many approaches to improve their displays. Let"s look at a few things you should look for apart from the display type.
Resolution is the number of pixels a screen has. It is usually written as a ratio: pixels on the long side by pixels on the short side, for example, 1920 x 1080. Most smartphone displays have a resolution between 720p (1280 x 720) on the low-end and 4k (3480 x 2160) on some Sony models. While 4k is excessive and rare for anything under 15 inches, 720p, 1080p, and 1440p are all common smartphone resolutions.
The ideal smartphone screen resolution depends on the screen size. A metric called pixels per inch (PPI) describes the display"s number of pixels in a vertical or horizontal inch. For a 6-inch display, you should aim for at least 1080p or above 350 PPI. This will ensure that the text is crisp.
A subpixel is one of the light-emitting parts of a pixel—in the case of most displays, these are red, blue, and green—that combine in different quantities to display various colors in an image. Although RGB subpixel layouts have been the prevalent option for a long time, some display manufacturers elect to use subpixel arrangements like BGR, PenTile, RGBG, and WRGB. The reason these subpixel layouts exist is to combat the various shortcomings of the display technology.
As with resolution, the subpixel layout can affect perceived image quality. Over the brief course of display history, manufacturers and designers have settled on RGB as a standard, meaning content is generally optimized for that layout. When manufacturers decided to invent new subpixel layouts, the perceived quality took a bit of a hit.
So why do manufacturers use odd-pixel layouts? It depends on the manufacturer and its goals. Samsung uses PenTile displays, which use RGBG instead of RGB subpixels, to combat image retention on its AMOLED displays. WRGB displays add a separate white subpixel to boost brightness on OLED displays—a technology that is otherwise notoriously dim.
Refresh rate is the number of times per second a display refreshes, and higher refresh rates mean motion and animations look smoother. Generally, 60Hz is the lowest commonly-found refresh rate and is perfectly serviceable. Many modern flagship phones and a few mid-range phonesoffer 90Hz, 120Hz, 144Hz, and even 240Hz displays.
Response times on OLED displays are generally lower, meaning displays can reach these high refresh rates and look better at these higher refresh rates thanks to the reduced ghosting.
Smartphones are often used outside in bright sunlight, so display brightness is a huge factor. Display brightness is measured in nits or cd/m². Peak brightness is the momentary maximum brightness of a small portion of a screen, while sustained brightness is a more realistic representation of the brightness of the whole display. Aim for above 600 nits of sustained brightness since anything below may cause legibility issues in bright conditions. On the other hand, brightness is measured logarithmically, not linearly, meaning 1,200 nits is only twice as bright as 300 nits. This is important since many manufacturers lean heavily on high brightness metrics as a marketing point.
Display specifications are no different. While it is true that OLED displays may be the best option for some people, they command a premium, and a lot of people wouldn"t notice the difference.
Brightness, refresh rate, and resolution are all key factors, and performance as a whole should be the determining factor in selecting a display, not the shiny new technology involved. If you"re looking for a phone with an OLED display and a high refresh rate, check out the best Android phones you can buy.

OLED displays are commonplace on all high-end phones, tablets, smartwatches, televisions, and even many of the many budget phones. However, there isn"t one type of OLED technology. Depending on your device, you may have an OLED, AMOLED, or POLED display.
OLED promises inky blacks, high contrast, low response times, and incredible brightness. There are a few downsides (primarily the burn-in phenomenon), but overall it"s the best screen technology you"ll find. We explain the background behind the acronyms, the difference between POLED and AMOLED, and which is better, helping you choose the right phone.
Every OLED screen comprises millions of diodes, hence the name organic light-emitting diode. Viewed under a microscope, each screen consists of a series of red, green, and blue diodes that can be individually turned on and off. Behind this, the light-emitting pixels of an OLED display emit blue and yellow light. The yellow and blue light combine to form white light, passing through the red, green, and blue subpixels to produce a single pixel. Because each pixel handles its light and color, OLED displays do not need a separate backlight.
As an OLED screen doesn"t need a backlight, black is produced by turning off the pixels, resulting in deep, consistent blacks. This allows manufacturers to implement things like an always-on display without quickly burning through battery life.
Another critical advantage of OLED tech is high contrast ratios. Technically, OLED displays offer "infinite contrast," or 1,000,000:1 contrast ratios. This is because OLED displays reproduce black by turning off pixels entirely, and contrast is measured by comparing the brightest part of the screen to the darkest part. Improved contrast makes on-screen content more vivid and makes bright highlights look more impressive. This also means that OLED screens can reach higher brightness than the best IPS LCD screens.
OLED displays can display more colors with greater color accuracy than their LCD peers. This is great for photographers and videographers using their phones to preview, edit, and create content.
OLED displays have near-instantaneous pixel response times. Older LCD screens often have lower response times because to change from one color to another, they must physically change the orientation of a liquid crystal, which takes time. An OLED display turns a subpixel on or off with an electrical charge, giving them a faster pixel response time.
The omission of a separate backlight and the use of fewer components means OLED displays can be thinner than LCDs, making them more versatile in their applications. This means they are more fragile and prone to damage in high-impact or high-stress situations. Engineers combat this by using technologies like Gorilla Glass and robust metal frames. Mitigation strategies like these raise the cost of OLED screens.
OLED displays can also be transparent, depending on the materials used. Transparent displays are helpful for in-display fingerprint readers and under-display cameras, which allow manufacturers to design smartphones with fewer and smaller bezels, notches, and display cutouts. When notches and cutouts are necessary, OLED displays have more even brightness around those cutouts and notches compared with LCDs, where the backlight has to make it around the cutout, and things get a little messy.
Of particular import to smartphones, OLED displays often consume less power, especially when displaying dark images or UI elements, thanks to the pixel-level regulation of brightness. However, at max brightness, an OLED screen usually uses more power than an equivalent LCD.
As with any new technology, OLED tech is not without its flaws.OLED displays are prone to degradation from age and UV exposure, resulting from the organic nature of the molecules that make up the diodes. The organic nature of OLED displays also leads to a phenomenon called screen burn-in, where static UI elements like menus, navigation bars, and status bars (elements that are on-screen for long periods) leave a permanent ghost image, even when they are not displayed. However, burn-in has been somewhat mitigated by pixel shifting and technological advancements in recent years.
Early OLED screens placed all the organic materials on a glass substrate. However, glass is rigid, so a flexible plastic substrate is needed to create foldable display screens, leading to the creation of POLED screens.
POLED (polymer organic light-emitting diode) offers advantages in terms of durability and versatility. The replacement ofglass substrates with plastic ones makes them more shock-resistant. Another unique advantage is in the implementation. Designers can reduce bezel size by folding the electronics underneath an edge of the display instead of having it be on the same plane. POLED displays are also significantly thinner than OLED displays with glass substrates.
Note the difference between P OLED and pOLED. pOLED is the trademark that LG Display uses to brand its plastic OLED displays. It produces these displays for a variety of applications and companies. Google used pOLED displays on the Pixel 2 XL, LG used them on theLG Velvet and several wearables,and Apple reportedly used LG pOLED displays on some Apple Watch models. LG"s pOLED displays seem to suffer from an increased risk of burn-in, as users of the Google Pixel 2 XL complained of burn-in after a few months of use.
To get to the resolution and size of a phone, an AMOLED screen (active matrix organic light emitting diode) is needed. Older, passive matrix OLED displays (PMOLED) require higher voltages for higher pixels/resolutions. The higher the voltage, the lower the screen"s lifetime.
Thin-film transistor (TFT) arrays used in modern active-matrix OLED displays control the charging of the display"s storage capacitors. These TFTs control current flow, resulting in more energy-efficient OLED panels than PMOLED displays. This allows a larger display size without compromising resolution, lifetime, or power consumption.
QLED isn"t related to OLED displays—despite what the name may suggest—but it"s often slated as a competitor to OLED, and it aims to replace the technology by targeting both OLED"s successes and failures. QLED stands for quantum dot light-emitting diode. The core principle of QLED technology is the same as a regular OLED. A backlight is passed through red, green, and blue subpixel layers to generate an image. However, the backlight isn"t one large, uniformly-lit layer. Instead, QLED displays use an array of tiny individually-controlled LEDs to supply the backlight. Using individually-controlled LEDs means the display can produce a more accurate image with a higher contrast.
Generally speaking, QLED displays have similar benefits to OLED displays—high peak brightness, high contrast, perfect blacks, and good saturation. Still, they lack some OLED advantages, like image retention and reduced overall and sustained brightness.
QLED is found in TVs and large computer monitors because that"s where it sees the most benefit. OLED displays in phones are small enough, bright enough, and cheap enough that QLED wouldn"t be able to compete or offer any practical benefit to the end user.
Display type is only one part of the puzzle.What use is exotic technology if it doesn"t make any difference to the end user? Smartphone manufacturers use many approaches to improve their displays. Let"s look at a few things you should look for apart from the display type.
Resolution is the number of pixels a screen has. It is usually written as a ratio: pixels on the long side by pixels on the short side, for example, 1920 x 1080. Most smartphone displays have a resolution between 720p (1280 x 720) on the low-end and 4k (3480 x 2160) on some Sony models. While 4k is excessive and rare for anything under 15 inches, 720p, 1080p, and 1440p are all common smartphone resolutions.
The ideal smartphone screen resolution depends on the screen size. A metric called pixels per inch (PPI) describes the display"s number of pixels in a vertical or horizontal inch. For a 6-inch display, you should aim for at least 1080p or above 350 PPI. This will ensure that the text is crisp.
A subpixel is one of the light-emitting parts of a pixel—in the case of most displays, these are red, blue, and green—that combine in different quantities to display various colors in an image. Although RGB subpixel layouts have been the prevalent option for a long time, some display manufacturers elect to use subpixel arrangements like BGR, PenTile, RGBG, and WRGB. The reason these subpixel layouts exist is to combat the various shortcomings of the display technology.
As with resolution, the subpixel layout can affect perceived image quality. Over the brief course of display history, manufacturers and designers have settled on RGB as a standard, meaning content is generally optimized for that layout. When manufacturers decided to invent new subpixel layouts, the perceived quality took a bit of a hit.
So why do manufacturers use odd-pixel layouts? It depends on the manufacturer and its goals. Samsung uses PenTile displays, which use RGBG instead of RGB subpixels, to combat image retention on its AMOLED displays. WRGB displays add a separate white subpixel to boost brightness on OLED displays—a technology that is otherwise notoriously dim.
Refresh rate is the number of times per second a display refreshes, and higher refresh rates mean motion and animations look smoother. Generally, 60Hz is the lowest commonly-found refresh rate and is perfectly serviceable. Many modern flagship phones and a few mid-range phonesoffer 90Hz, 120Hz, 144Hz, and even 240Hz displays.
Response times on OLED displays are generally lower, meaning displays can reach these high refresh rates and look better at these higher refresh rates thanks to the reduced ghosting.
Smartphones are often used outside in bright sunlight, so display brightness is a huge factor. Display brightness is measured in nits or cd/m². Peak brightness is the momentary maximum brightness of a small portion of a screen, while sustained brightness is a more realistic representation of the brightness of the whole display. Aim for above 600 nits of sustained brightness since anything below may cause legibility issues in bright conditions. On the other hand, brightness is measured logarithmically, not linearly, meaning 1,200 nits is only twice as bright as 300 nits. This is important since many manufacturers lean heavily on high brightness metrics as a marketing point.
Display specifications are no different. While it is true that OLED displays may be the best option for some people, they command a premium, and a lot of people wouldn"t notice the difference.
Brightness, refresh rate, and resolution are all key factors, and performance as a whole should be the determining factor in selecting a display, not the shiny new technology involved. If you"re looking for a phone with an OLED display and a high refresh rate, check out the best Android phones you can buy.

IPS (in-plane switching) is a screen technology for liquid-crystal displays (LCDs). In IPS, a layer of liquid crystals is sandwiched between two glass surfaces. The liquid crystal molecules are aligned parallel to those surfaces in predetermined directions (in-plane). The molecules are reoriented by an applied electric field, whilst remaining essentially parallel to the surfaces to produce an image. It was designed to solve the strong viewing angle dependence and low-quality color reproduction of the twisted nematic field effect (TN) matrix LCDs prevalent in the late 1980s.
The TN method was the only viable technology for active matrix TFT LCDs in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Early panels showed grayscale inversion from up to down,Vertical Alignment (VA)—that could resolve these weaknesses and were applied to large computer monitor panels.
Shortly thereafter, Hitachi of Japan filed patents to improve this technology. A leader in this field was Katsumi Kondo, who worked at the Hitachi Research Center.thin-film transistor array as a matrix and to avoid undesirable stray fields in between pixels.Super IPS). NEC and Hitachi became early manufacturers of active-matrix addressed LCDs based on the IPS technology. This is a milestone for implementing large-screen LCDs having acceptable visual performance for flat-panel computer monitors and television screens. In 1996, Samsung developed the optical patterning technique that enables multi-domain LCD. Multi-domain and in-plane switching subsequently remain the dominant LCD designs through 2006.
IPS technology is widely used in panels for TVs, tablet computers, and smartphones. In particular, most IBM products was marketed as CCFL backlighting, and all Apple Inc. products marketed with the label backlighting since 2010.
IPS has since been superseded by S-IPS (Super-IPS, Hitachi Ltd. in 1998), which has all the benefits of IPS technology with the addition of improved pixel refresh timing.
Toward the end of 2010 Samsung Electronics introduced Super PLS (Plane-to-Line Switching) with the intent of providing an alternative to the popular IPS technology which is primarily manufactured by LG Display. It is an "IPS-type" panel technology, and is very similar in performance features, specs and characteristics to LG Display"s offering. Samsung adopted PLS panels instead of AMOLED panels, because in the past AMOLED panels had difficulties in realizing full HD resolution on mobile devices. PLS technology was Samsung"s wide-viewing angle LCD technology, similar to LG Display"s IPS technology.
In 2012 AU Optronics began investment in their own IPS-type technology, dubbed AHVA. This should not be confused with their long standing AMVA technology (which is a VA-type technology). Performance and specs remained very similar to LG Display"s IPS and Samsung"s PLS offerings. The first 144 Hz compatible IPS-type panels were produced in late 2014 (used first in early 2015) by AUO, beating Samsung and LG Display to providing high refresh rate IPS-type panels.
Cross, Jason (18 March 2012). "Digital Displays Explained". TechHive. PC World. p. 4. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 19 March 2015.
"TFT Technology: Enhancing the viewing angle". Riverdi (TFT Module Manufacturer). Archived from the original on 23 April 2016. Retrieved 5 November 2016. However, [twisted nematic] suffers from the phenomenon called gray scale inversion. This means that the display has one viewing side in which the image colors suddenly change after exceeding the specified viewing angle. (see image Inversion Effect) External link in |quote= (help)
tech2 News Staff (19 May 2011). "LG Announces Super High Resolution AH-IPS Displays". Firstpost.com. Archived from the original on 11 December 2015. Retrieved 10 December 2015.
Baker, Simon (30 April 2011). "Panel Technologies: TN Film, MVA, PVA and IPS Explained". Tftcentral.co.uk. Archived from the original on 29 June 2017. Retrieved 13 January 2012.
"Samsung PLS improves on IPS displays like iPad"s, costs less". electronista.com. Archived from the original on 27 October 2012. Retrieved 30 October 2012.

In recent years, smartphone displays have developed far more acronyms than ever before with each different one featuring a different kind of technology. AMOLED, LCD, LED, IPS, TFT, PLS, LTPS, LTPO...the list continues to grow.
As if the different available technologies weren"t enough, component and smartphone manufacturers adopt more and more glorified names like "Super Retina XDR" and "Dynamic AMOLED", which end up increasing the potential for confusion among consumers. So let"s take a look at some of these terms used in smartphone specification sheets and decipher them.
There are many display types used in smartphones: LCD, OLED, AMOLED, Super AMOLED, TFT, IPS and a few others that are less frequently found on smartphones nowadays, like TFT-LCD. One of the most frequently found on mid-to-high range phones now is IPS-LCD. But what do these all mean?
LCD means Liquid Crystal Display, and its name refers to the array of liquid crystals illuminated by a backlight, and their ubiquity and relatively low cost make them a popular choice for smartphones and many other devices.
LCDs also tend to perform quite well in direct sunlight, as the entire display is illuminated from behind, but does suffer from potentially less accurate colour representation than displays that don"t require a backlight.
Within smartphones, you have both TFT and IPS displays. TFT stands for Thin Film Transistor, an advanced version of LCD that uses an active matrix (like the AM in AMOLED). Active matrix means that each pixel is attached to a transistor and capacitor individually.
The main advantage of TFT is its relatively low production cost and increased contrast when compared to traditional LCDs. The disadvantage of TFT LCDs is higher energy demands than some other LCDs, less impressive viewing angles and colour reproduction. It"s for these reasons, and falling costs of alternative options, that TFTs are not commonly used in smartphones anymore.Affiliate offer
IPS technology (In-Plane Switching) solves the problem that the first generation of LCD displays experience, which adopts the TN (Twisted Nematic) technique: where colour distortion occurs when you view the display from the side - an effect that continues to crop up on cheaper smartphones and tablets.
The PLS (Plane to Line Switching) standard uses an acronym that is very similar to that of IPS, and is it any wonder that its basic operation is also similar in nature? The technology, developed by Samsung Display, has the same characteristics as IPS displays - good colour reproduction and viewing angles, but a lower contrast level compared to OLED and LCD/VA displays.
According to Samsung Display, PLS panels have a lower production cost, higher brightness rates, and even superior viewing angles when compared to their rival, LG Display"s IPS panels. Ultimately, whether a PLS or IPS panel is used, it boils down to the choice of the component supplier.
This is a very common question after "LED" TVs were launched, with the short answer simply being LCD. The technology used in a LED display is liquid crystal, the difference being LEDs generating the backlight.
Despite the improvement in terms of contrast (and potentially brightness) over traditional LCD/LED displays, LCD/mini-LEDs still divide the screen into brightness zones — over 2,500 in the case of the iPad and 2021 "QNED" TVs from LG — compared to dozens or hundreds of zones in previous-generation FALD (full-array local dimming) displays, on which the LEDs are behind the LCD panel instead of the edges.
AMOLED stands for Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode. While this may sound complicated it actually isn"t. We already encountered the active matrix in TFT LCD technology, and OLED is simply a term for another thin-film display technology.
OLED is an organic material that, as the name implies, emits light when a current is passed through it. As opposed to LCD panels, which are back-lit, OLED displays are "always off" unless the individual pixels are electrified.
This means that OLED displays have much purer blacks and consume less energy when black or darker colours are displayed on-screen. However, lighter-coloured themes on AMOLED screens use considerably more power than an LCD using the same theme. OLED screens are also more expensive to produce than LCDs.
Because the black pixels are "off" in an OLED display, the contrast ratios are also higher compared to LCD screens. AMOLED displays have a very fast refresh rate too, but on the downside are not quite as visible in direct sunlight as backlit LCDs. Screen burn-in and diode degradation (because they are organic) are other factors to consider.Affiliate offer
OLED stands for Organic Light Emitting Diode. An OLED display is comprised of thin sheets of electroluminescent material, the main benefit of which is they produce their own light, and so don"t require a backlight, cutting down on energy requirements. OLED displays are more commonly referred to as AMOLED displays when used on smartphones or TVs.
As we"ve already covered, the AM part of AMOLED stands for Active Matrix, which is different from a Passive Matrix OLED (P-OLED), though these are less common in smartphones.
Super AMOLED is the name given by Samsung to its displays that used to only be found in high-end models but have now trickled down to more modestly specced devices. Like IPS LCDs, Super AMOLED improves upon the basic AMOLED premise by integrating the touch response layer into the display itself, rather than as an extra layer on top.
As a result, Super AMOLED displays handle sunlight better than AMOLED displays and also require less power. As the name implies, Super AMOLED is simply a better version of AMOLED. It"s not all just marketing bluster either: Samsung"s displays are regularly reviewed as some of the best around.
The latest evolution of the technology has been christened "Dynamic AMOLED". Samsung didn"t go into detail about what the term means, but highlighted that panels with such identification include HDR10+ certification that supports a wider range of contrast and colours, as well as blue light reduction for improved visual comfort.
In the same vein, the term "Fluid AMOLED" used by OnePlus on its most advanced devices basically highlights the high refresh rates employed, which results in more fluid animations on the screen.Affiliate offer
The technology debuted with the obscure Royole FlexPai, equipped with an OLED panel supplied by China"s BOE, and was then used in the Huawei Mate X (pictured above) and the Motorola Razr (2019), where both also sport BOE"s panel - and the Galaxy Flip and Fold lines, using the component supplied by Samsung Display.Affiliate offer
Resolution describes the number of individual pixels (or points) displayed on the screen and is usually presented for phones by the number of horizontal pixels — vertical when referring to TVs and monitors. More pixels on the same display allow for more detailed images and clearer text.
To make it easier to compare different models, brands usually adopt the same naming scheme made popular by the TV market with terms like HD, FullHD and UltraHD. But with phones adopting a wide range of different screen proportions, just knowing that is not enough to know the total pixels displayed on the screen.Common phone resolutions
But resolution in itself is not a good measure for image clarity, for that we need to consider the display size, resulting in the pixel density by area measured by DPI/PPI (dots/points per inch).Affiliate offer
Speaking of pixel density, this was one of Apple"s highlights back in 2010 during the launch of the iPhone 4. The company christened the LCD screen (LED, TFT, and IPS) used in the smartphone as "Retina Display", thanks to the high resolution of the panel used (960 by 640 pixels back then) in its 3.5-inch display.
The name coined by Apple"s marketing department is applied to screens which, according to the company, the human eye is unable to discern the individual pixels from a normal viewing distance. In the case of iPhones, the term was applied to displays with a pixel density that is greater than 300 ppi (dots per inch).
With the iPhone 11 Pro, another term was introduced to the equation: "Super Retina XDR". Still using an OLED panel (that is supplied by Samsung Display or LG Display), the smartphone brings even higher specs in terms of contrast - with a 2,000,000:1 ratio and brightness level of 1,200 nits, which have been specially optimized for displaying content in HDR format.
As a kind of consolation prize for iPhone XR and iPhone 11 buyers, who continued relying on LCD panels, Apple classified the display used in the smartphones with a new term, "Liquid Retina". This was later applied also to the iPad Pro and iPad Air models, with the name defining screens that boast a high range and colour accuracy, at least based on the company"s standards.
Nit, or candela per square meter in the international system (cd/m²), is a unit of measurement of luminance, i.e. the intensity of light emitted. In the case of smartphone screens and monitors in general, such a value defines just how bright the display is - the higher the value, the more intense the light emitted by the screen.
The result is smoother animations on the phone, both during regular use and in games, compared to screens that have a 60 Hz refresh rate which remains the standard rate in the market when it comes to displays.
Originally touted to be a "gimmick" in 2017, with the launch of the Razer Phone, the feature gained more and more momentum in due time, even with a corresponding decrease in battery life. In order to make the most of this feature, manufacturers began to adopt screens with variable refresh rates, which can be adjusted according to the content displayed - which is 24 fps in most movies, 30 or 60 fps in home video recordings, and so forth.
TFT(Thin Film Transistor) - a type of LCD display that adopts a thin semiconductor layer deposited on the panel, which allows for active control of the colour intensity in each pixel, featuring a similar concept as that of active-matrix (AM) used in AMOLED displays. It is used in TN, IPS/PLS, VA/PVA/MVA panels, etc.
LTPS(Low Temperature PolySilicon) - a variation of the TFT that offers higher resolutions and lower power consumption compared to traditional TFT screens, based on a-Si (amorphous silicon) technology.
IGZO(Indium Gallium Zinc Oxide) - a semiconductor material used in TFT films, which also allows higher resolutions and lower power consumption, and sees action in different types of LCD screens (TN, IPS, VA) and OLED displays
LTPO(Low Temperature Polycrystaline Oxide) - a technology developed by Apple that can be used in both OLED and LCD displays, as it combines LTPS and IGZO techniques. The result? Lower power consumption. It has been used in the Apple Watch 4 and the Galaxy S21 Ultra.
LTPO allows the display to adjust its refresh rate, adapting dynamically to the content shown. Scrolling pages can trigger the fastest mode for a fluid viewing, while displaying a static image allows the phone to use a lower refresh rate, saving the battery.
Among televisions, the long-standing featured technology has always been miniLED - which consists of increasing the number of lighting zones in the backlight while still using an LCD panel. There are whispers going around that smartphones and smartwatches will be looking at incorporating microLED technology in their devices soon, with it being radically different from LCD/LED displays as it sports similar image characteristics to that of OLEDs.
A microLED display has one light-emitting diode for each subpixel of the screen - usually a set of red, green, and blue diodes for each dot. Chances are it will use a kind of inorganic material such as gallium nitride (GaN).
By adopting a self-emitting light technology, microLED displays do not require the use of a backlight, with each pixel being "turned off" individually. The result is impressive: your eyes see the same level of contrast as OLED displays, without suffering from the risk of image retention or burn-in of organic diodes.
Another thing to be wary of is the price - at 170 million Korean won (about US$150,330 after conversion), that is certainly a lot of money to cough up for a 110-inch display.
As previously stated, OLED/AMOLED screens have the advantage of a varied contrast level, resulting from individual brightness control for the pixels. Another result of this is the more realistic reproduction of black, as well as low power consumption when the screen shows off dark images - which has also helped to popularize dark modes on smartphones.
In addition, the organic diodes that give OLED screens their name can lose their ability to change their properties over time, and this happens when the same image is displayed for a long period of time. This problem is known as "burn-in", tends to manifest itself when higher brightness settings are applied for long periods of time.
In the case of LCD displays, the main advantage lies in the low manufacturing cost, with dozens of players in the market offering competitive pricing and a high production volume. Some brands have taken advantage of this feature to prioritize certain features - such as a higher refresh rate - instead of adopting an OLED panel, such as the Xiaomi Mi 10T.

OLED displays have become increasingly common and accessible over the past few years. While they were once reserved for premium smartphones, you’ll now find OLED displays at every smartphone price point. Not every OLED display is equal, though – differences in materials and manufacturing processes can result in varying display qualities. In that vein, let’s explore the differences between POLED vs AMOLED, and what these acronyms mean in the real world.
Before differentiating between POLED and AMOLED, it’s worth understanding the fundamentals of OLED display technology. To that end, let’s ignore the P and AM prefixes for now.
If you look at an OLED display under a microscope, you’ll see these diodes arranged in various red, green, and blue configurations in order to produce a full range of colors. OLED has a key advantage over conventional LCDs – individual light emitters can be switched completely off. This gives OLED deep blacks and an excellent contrast ratio.
Naturally, light emitters in an OLED display need a power source in order to function. Manufacturers can use either a passive wiring matrix or an active wiring matrix. Pass




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey