arduino tft display library pricelist

Spice up your Arduino project with a beautiful large touchscreen display shield with built in microSD card connection. This TFT display is big (5" diagonal) bright (12 white-LED backlight) and colorfu 480x272 pixels with individual pixel control. As a bonus, this display has a optional resistive touch panel attached on screen by default.
The shield is fully assembled, tested and ready to go. No wiring, no soldering! Simply plug it in and load up our library - you"ll have it running in under 10 minutes! Works best with any classic Arduino (UNO/Due/Mega 2560).
This display shield has a controller built into it with RAM buffering, so that almost no work is done by the microcontroller. You can connect more sensors, buttons and LEDs.
Of course, we wouldn"t just leave you with a datasheet and a "good luck!" - we"ve written a full open source graphics library at the bottom of this page that can draw pixels, lines, rectangles, circles and text. We also have a touch screen library that detects x,y and z (pressure) and example code to demonstrate all of it. The code is written for Arduino but can be easily ported to your favorite microcontroller!
For 5 inch screen,the high current is needed.But the current of arduino uno or arduino mega board is low, an external 5V power supply is needed. Refer to the image shows the external power supply position on shield ER-AS-RA8875.
If you"ve had a lot of Arduino DUEs go through your hands (or if you are just unlucky), chances are you’ve come across at least one that does not start-up properly.The symptom is simple: you power up the Arduino but it doesn’t appear to “boot”. Your code simply doesn"t start running.You might have noticed that resetting the board (by pressing the reset button) causes the board to start-up normally.The fix is simple,here is the solution.

Spice up your Arduino project with a beautiful large touchscreen display shield with built in microSD card connection. This TFT display is big 4"(3.97" diagonal) bright (6 white-LED backlight) and colorful (18-bit 262,000 different shades)! 480x800 pixels with individual pixel control. As a bonus, this display has a optional resistive touch panel with controller XPT2046 and capacitive touch panel with FT6336.
The shield is fully assembled, tested and ready to go. No wiring, no soldering! Simply plug it in and load up our library - you"ll have it running in under 10 minutes! Works best with any classic Arduino (Due/Mega 2560).
This display shield has a controller built into it with RAM buffering, so that almost no work is done by the microcontroller. You can connect more sensors, buttons and LEDs.
Of course, we wouldn"t just leave you with a datasheet and a "good luck!" - we"ve written a full open source graphics library at the bottom of this page that can draw pixels, lines, rectangles, circles and text. We also have a touch screen library that detects x,y and z (pressure) and example code to demonstrate all of it. The code is written for Arduino but can be easily ported to your favorite microcontroller!
If you"ve had a lot of Arduino DUEs go through your hands (or if you are just unlucky), chances are you’ve come across at least one that does not start-up properly.The symptom is simple: you power up the Arduino but it doesn’t appear to “boot”. Your code simply doesn"t start running.You might have noticed that resetting the board (by pressing the reset button) causes the board to start-up normally.The fix is simple,here is the solution.

In this guide we’re going to show you how you can use the 1.8 TFT display with the Arduino. You’ll learn how to wire the display, write text, draw shapes and display images on the screen.
The 1.8 TFT is a colorful display with 128 x 160 color pixels. The display can load images from an SD card – it has an SD card slot at the back. The following figure shows the screen front and back view.
This module uses SPI communication – see the wiring below . To control the display we’ll use the TFT library, which is already included with Arduino IDE 1.0.5 and later.
The TFT display communicates with the Arduino via SPI communication, so you need to include the SPI library on your code. We also use the TFT library to write and draw on the display.
In which “Hello, World!” is the text you want to display and the (x, y) coordinate is the location where you want to start display text on the screen.
The 1.8 TFT display can load images from the SD card. To read from the SD card you use the SD library, already included in the Arduino IDE software. Follow the next steps to display an image on the display:
Note: some people find issues with this display when trying to read from the SD card. We don’t know why that happens. In fact, we tested a couple of times and it worked well, and then, when we were about to record to show you the final result, the display didn’t recognized the SD card anymore – we’re not sure if it’s a problem with the SD card holder that doesn’t establish a proper connection with the SD card. However, we are sure these instructions work, because we’ve tested them.
In this guide we’ve shown you how to use the 1.8 TFT display with the Arduino: display text, draw shapes and display images. You can easily add a nice visual interface to your projects using this display.
Hi guys, welcome to today’s tutorial. Today, we will look on how to use the 1.8″ ST7735 colored TFT display with Arduino. The past few tutorials have been focused on how to use the Nokia 5110 LCD display extensively but there will be a time when we will need to use a colored display or something bigger with additional features, that’s where the 1.8″ ST7735 TFT display comes in.
The ST7735 TFT display is a 1.8″ display with a resolution of 128×160 pixels and can display a wide range of colors ( full 18-bit color, 262,144 shades!). The display uses the SPI protocol for communication and has its own pixel-addressable frame buffer which means it can be used with all kinds of microcontroller and you only need 4 i/o pins. To complement the display, it also comes with an SD card slot on which colored bitmaps can be loaded and easily displayed on the screen.
The schematics for this project is fairly easy as the only thing we will be connecting to the Arduino is the display. Connect the display to the Arduino as shown in the schematics below.
Due to variation in display pin out from different manufacturers and for clarity, the pin connection between the Arduino and the TFT display is mapped out below:
We will use two libraries from Adafruit to help us easily communicate with the LCD. The libraries include the Adafruit GFX library which can be downloaded here and the Adafruit ST7735 Library which can be downloaded here.
We will use two example sketches to demonstrate the use of the ST7735 TFT display. The first example is the lightweight TFT Display text example sketch from the Adafruit TFT examples. It can be accessed by going to examples -> TFT -> Arduino -> TFTDisplaytext. This example displays the analog value of pin A0 on the display. It is one of the easiest examples that can be used to demonstrate the ability of this display.
The second example is the graphics test example from the more capable and heavier Adafruit ST7735 Arduino library. I will explain this particular example as it features the use of the display for diverse purposes including the display of text and “animated” graphics. With the Adafruit ST7735 library installed, this example can be accessed by going to examples -> Adafruit ST7735 library -> graphics test.
The first thing, as usual, is to include the libraries to be used after which we declare the pins on the Arduino to which our LCD pins are connected to. We also make a slight change to the code setting reset pin as pin 8 and DC pin as pin 9 to match our schematics.
Next, we create an object of the library with the pins to which the LCD is connected on the Arduino as parameters. There are two options for this, feel free to choose the most preferred.
Next, we move to the void setup function where we initialize the screen and call different test functions to display certain texts or images. These functions can be edited to display what you want based on your project needs.
The complete code for this is available under the libraries example on the Arduino IDE. Don’t forget to change the DC and the RESET pin configuration in the code to match the schematics.
Uploading the code to the Arduino board brings a flash of different shapes and text with different colors on the display. I captured one and its shown in the image below.
That’s it for this tutorial guys, what interesting thing are you going to build with this display? Let’s get the conversation started. Feel free to reach me via the comment section if you have any questions as regards this project.

Displays are one of the best ways to provide feedback to users of a particular device or project and often the bigger the display, the better. For today’s tutorial, we will look on how to use the relatively big, low cost, ILI9481 based, 3.5″ Color TFT display with Arduino.
This 3.5″ color TFT display as mentioned above, is based on the ILI9481 TFT display driver. The module offers a resolution of 480×320 pixels and comes with an SD card slot through which an SD card loaded with graphics and UI can be attached to the display. The module is also pre-soldered with pins for easy mount (like a shield) on either of the Arduino Mega and Uno, which is nice since there are not many big TFT displays that work with the Arduino Uno.
The module is compatible with either of the Arduino Uno or the Arduino Mega, so feel free to choose between them or test with both. As usual, these components can be bought via the links attached to them.
One of the good things about this module is the ease with which it can be connected to either of the Arduino Mega or Uno. For this tutorial, we will use the Arduino Uno, since the module comes as a shield with pins soldered to match the Uno’s pinout. All we need to do is snap it onto the top of the Arduino Uno as shown in the image below, thus no wiring required.
This ease of using the module mentioned above is, however, one of the few downsides of the display. If we do not use the attached SD card slot, we will be left with 6 digital and one analog pin as the module use the majority of the Arduino pins. When we use the SD card part of the display, we will be left with just 2 digital and one analog pin which at times limits the kind of project in which we can use this display. This is one of the reasons while the compatibility of this display with the Arduino Mega is such a good news, as the “Mega” offers more digital and analog pins to work with, so when you need extra pins, and size is not an issue, use the Mega.
To easily write code to use this display, we will use the GFX and TFT LCD libraries from “Adafruit” which can be downloaded here. With the library installed we can easily navigate through the examples that come with it and upload them to our setup to see the display in action. By studying these examples, one could easily learn how to use this display. However, I have compiled some of the most important functions for the display of text and graphics into an Arduino sketch for the sake of this tutorial. The complete sketch is attached in a zip file under the download section of this tutorial.
As usual, we will do a quick run through of the code and we start by including the libraries which we will use for the project, in this case, the Adafruit GFX and TFT LCD libraries.
With this done, the Void Setup() function is next. We start the function by issuing atft.reset() command to reset the LCD to default configurations. Next, we specify the type of the LCD we are using via the LCD.begin function and set the rotation of the TFT as desired. We proceed to fill the screen with different colors and display different kind of text using diverse color (via the tft.SetTextColor() function) and font size (via the tft.setTextSize() function).
Next is the void loop() function. Here we basically create a UI to display the youtube subscribe button, using some of the same functions we used under the void setup() function.
The Adafruit library helps reduce the amount of work one needs to do while developing the code for this display, leaving the quality of the user interface to the limitations of the creativity and imagination of the person writing the code.

To interface TFT LCD Display with Arduino, for designing custom HMI TFT LCD Display provide rich colours, detailed images, and bright graphics with their full-colour RGB mode it comes in different pixels 128 x 160 pixels, 320×240 pixels and many more.
In this tutorial, we’ll interface the 1.8 TFT LCD display with Arduino Uno. You’ll learn how to interface the TFT LCD with Arduino to write text on this LCD. This tutorial presents the coding, wiring diagram and components list required for the LCD display.
Creating an interface between the user and the system is very important. This interface can be created by displaying useful data, and menus. There are several components to achieving this. LEDs, 7-segments, OLEDs, and full-color TFT LCDs. The right component for your projects depends on the amount of data to be displayed, and the type of user interaction.
TFT LCD is a variant of a liquid-crystal display (LCD) that uses thin-film-transistor (TFT) technology to improve image qualities such as addressability and contrast. In the case of Arduino, the processor frequency is low. So it is not possible to display complex and high-speed motions. Therefore, full-colour TFT LCDs can only be used to display simple data and commands. This TFT has 128 x 160 pixels. 1.8 TFT display can load images from an SD card. It has an SD card slot at the back. You can see the front and back views of the TFT LCD in the figures below.
TFT is an abbreviation of “Thin Film Transistor”. It has transistors made up of thin films of Amorphous silicon. It serves as a control valve to provide an appropriate voltage onto liquid crystals for individual sub-pixels. The working principle is very simple the TFT LCD composes of many pixels that can emit light of any colour. The desired image achieves by controlling each pixel to display the corresponding colour. In TFT LCD, the backlight technology is generally used. In order to accurately control the colour and brightness of each pixel, it is necessary to install a shutter-like switch after each pixel. When the “blinds” are opened, light can pass through them. When the shutters are closed, light cannot pass through them.
Connect your PC to Arduino and open Arduino IDE. For the very first steps, you can refer to Connecting Windows PC with Arduino tutorial. You can get the .ino code and libraries from my download area with the following link:
This is the section before setup which uses for globe variables defining and libraries additions. TFT.h is the library for TFT LCD Display and uses for writing and drawing on the display. The TFT display communicates with the Arduino via SPI communication, so you need to include the SPI library.
This is the setup section in which Serial.begin(9600) initialize. TFTscreen.begin() is use to initialize the library. TFTscreen.background(0, 0, 0) is use to customize the screen background color here TFTscreen.background(0, 0, 0) means the background colour is black. TFTscreen.setTextSize(2) is use to set the font size.
In the loop section first, we will print the “Hi_peppe8o!” in the centre of the LCD and this will be in three different colours (Red, Green, Blue) you can choose any colour using the different colour codes. After 300 milliseconds a straight line will be displayed, after 300 milliseconds a square will be displayed, after 300 milliseconds a circle will be displayed, and after 300 milliseconds screen will be black/ erase and these all shapes and the text will be repeated in the void loop.
The LCD displays the text of “Hi_peppe80” and after that displays the line, square, and circle and then erases everything after completing this sequence. The command used for clearing all the data is TFTscreen.background(0,0,0):

This is a small graphics library, specifically aimed at ATtiny microcontrollers, for the variety of small colour TFT displays available at low cost from suppliers like Adafruit, AliExpress, or Banggood:
It"s an updated version of my Tiny TFT Graphics Library. This latest version of the library supports both the classic ATtiny processors, such as the ATtiny85, and the new 0-series, 1-series, and 2-series ATtiny processors, such as the ATtiny402. Like the original library it allows you to plot points, draw lines, draw filled rectangles, and plot characters and text with an optional scale factor, in 16-bit colour.
This version adds the ability to plot outline rectanges, and outline and filled circles. I"ve included demo curve-plotting and histogram-plotting programs that adjust to fit any display.
This library supports TFT displays that use an SPI interface and require four pins to drive the display. This leaves one pin free on an 8-pin chip such as the ATtiny85 or ATtiny402. If you need more pins choose a larger chip, such as the ATtiny84 or ATtiny404.
Unlike my Compact TFT Graphics Library which uses standard Arduino SPI calls, this library uses direct I/O pin manipulations. This means that you can use any assignment of pins to the four I/O lines needed by the display, and makes it about twice as fast as one using SPI calls. I"ve also added support for some additional displays, so it now supports 16 different TFT displays.
On the classic ATtiny processors, such as the ATtiny85, the library uses the feature that you can toggle one or more bits in a port by writing to the PINB register; for example, to enable or disable the chip-select signal:
So provided you set all the pins to their disabled state at startup, the display routines can simply toggle the appropriate pins to enable or disable them.
The differences between each family of processors are handled by constants to define the pin assignments, and preprocessor macros to define the bit manipulations. If you use the circuits given below you won"t need to change anything, apart from specifying which display you"re using.
The ClearDisplay() routine has been optimised further by realising that we don"t need to keep setting the mosi bit, since to clear the display it is always zero, so the routine only needs to toggle the sck bit the appropriate number of times. I"m grateful to Thomas Scherer for suggesting this.
The library occupies less than 4K bytes, including the character set and demo programs, and so will fit on microcontrollers with 4K flash such as the ATtiny45 and ATtiny402.
This library will work with displays based on the ST7735 which supports a maximum display size of 162x132, or the ST7789 and ILI9340/1 which support a maximum display size of 320x240. It includes parameters for the following colour TFT displays:
* These Adafruit displays conveniently all have the same edge-connector layout, so you can make a prototyping board or PCB that will take any of them, such as my Universal TFT Display Backpack.
Some of the AliExpress displays include a LDO 3.3V regulator, but not logic-level translation, so I recommend only interfacing them to a processor running from 3.3V.
The Adafruit displays all include an LDO 3.3V regulator and logic-level translation, so can be safely interfaced to processors powered from either 5V or 3.3V.
On the AliExpress red 160x128 display you need to connect the backlight pin to Vcc to turn it on. This doesn"t seem to be necessary with the other displays.
The library will probably support other TFT displays that use the same ST7735, ST7789, ILI9340/1 driver chips, but you may need to experiment with the parameters to get the image scaled and centered correctly.
The display needs to be connected to the microcontroller via four I/O lines: MOSI, SCK, CS, and DC. You can use any pins for these, but they should all be in the same port. You need to specify the port pin numbers of the pins you are using at the start of the Tiny TFT Graphics Library listing.
The 33kΩ pullup resistor from the display"s CS pin is optional; it is only needed on the AliExpress displays, and holds the chip select high to prevent the display from flickering while programming the ATtiny85.
The different displays are catered for by seven constants which specify the size of the display, the offsets relative to the area supported by the display driver, whether the display is inverted, the rotation value, and the order of the colours; for example:
By default the parameters give the correct orientation assuming you"re using the display with the header pins along the top, except in the case of the larger displays which have the header pins along the shorter edge, in which case the header pins are assumed to be on the left.
To check or adjust the values for each display you can run the TestChart() program, which draws a one-pixel border around the display area, and plots a red "F" to show the orientation:
The library will probably support other TFT displays that use the same driver chips, but you may need to experiment with the parameters to get the image scaled and centered correctly.
The library includes basic graphics routines for plotting points and drawing lines. These work on a conventional coordinate system with the origin at lower left. For example, on the 80x160 display:

In this Arduino touch screen tutorial we will learn how to use TFT LCD Touch Screen with Arduino. You can watch the following video or read the written tutorial below.
As an example I am using a 3.2” TFT Touch Screen in a combination with a TFT LCD Arduino Mega Shield. We need a shield because the TFT Touch screen works at 3.3V and the Arduino Mega outputs are 5 V. For the first example I have the HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor, then for the second example an RGB LED with three resistors and a push button for the game example. Also I had to make a custom made pin header like this, by soldering pin headers and bend on of them so I could insert them in between the Arduino Board and the TFT Shield.
Here’s the circuit schematic. We will use the GND pin, the digital pins from 8 to 13, as well as the pin number 14. As the 5V pins are already used by the TFT Screen I will use the pin number 13 as VCC, by setting it right away high in the setup section of code.
I will use the UTFT and URTouch libraries made by Henning Karlsen. Here I would like to say thanks to him for the incredible work he has done. The libraries enable really easy use of the TFT Screens, and they work with many different TFT screens sizes, shields and controllers. You can download these libraries from his website, RinkyDinkElectronics.com and also find a lot of demo examples and detailed documentation of how to use them.
After we include the libraries we need to create UTFT and URTouch objects. The parameters of these objects depends on the model of the TFT Screen and Shield and these details can be also found in the documentation of the libraries.
So now I will explain how we can make the home screen of the program. With the setBackColor() function we need to set the background color of the text, black one in our case. Then we need to set the color to white, set the big font and using the print() function, we will print the string “Arduino TFT Tutorial” at the center of the screen and 10 pixels down the Y – Axis of the screen. Next we will set the color to red and draw the red line below the text. After that we need to set the color back to white, and print the two other strings, “by HowToMechatronics.com” using the small font and “Select Example” using the big font.
In order the code to work and compile you will have to include an addition “.c” file in the same directory with the Arduino sketch. This file is for the third game example and it’s a bitmap of the bird. For more details how this part of the code work you can check my particular tutorial. Here you can download that file:
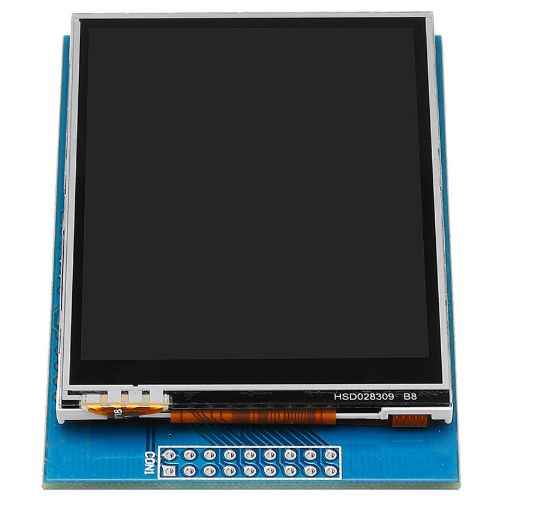

The Arduino TFT screen is a backlit LCD screen with headers. You can draw text, images, and shapes to the screen with the TFT library. There is an onboard micro-SD card slot on the back of the screen that can, among other things, store bitmap images for the screen to display.
The screen"s headers are designed to fit into the socket on the front of the Arduino Esplora, but it is compatible with any AVR-based Arduino (Uno, Leonardo, etc) or with the Arduino Due.
The screen is 1.77" diagonal, with 160 x 128 pixel resolution. The TFT library interfaces with the screen"s controller through SPI when using the TFT library. The TFT library relies on the SPI library, which must be included in any sketch that uses the screen.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey