raspberry pi tft display code manufacturer

The TFT isn’t ‘plug & play’ with the Raspberry, a patch has to be applied to the kernel to be able to interface via SPI with the ST7735R controller chip on the TFT. Once working, the display will act as a framebuffer device.
As it takes over three hours to compile the kernel on the PI, I will show how to cross compile from another Linux PC. In my case, it is Ubuntu 12.10 running within VMWare on a Windows 7 Quad core PC. Kernel compile time is 15 mins.
-Copy config from the Raspberry Pi to the Ubuntu box using SCP. Replace ‘raspberrypi’ below with the IP address of your Raspberry Pi if hostname lookup fails.
If you are planning on displaying the console on the TFT, then enabling these options in .config will allow you to change the font size and rotate the display later on.
To enable parallel processing for a faster compile. If you have a dual core processor add -j 3 to the end of the command below. If you have quad core, add -j 6
The last step below is to SCP the files from from Ubuntu to the Raspberry Pi. If you have trouble SCPing into your Ubuntu box you may need to install open SSH on Ubuntu with sudo apt-get install openssh-server. This step also copies the files from my home folder ‘mark’… yours would be different.
If you build the st7735 driver pair as built-in, add these options to the end of the line in /boot/cmdline.txt. This will display the console on the TFT.

After execution, the driver will be installed. The system will automatically restart, and the display screen will rotate 90 degrees to display and touch normally.
Raspberry Pi is a Palm Size computer that comes in very handy when prototyping stuff that requires high computational power. It is being extensively used for IOT hardware development and robotics application and much more memory hunger applications. In most of the projects involving the Pi it would be extremely useful if the Pi had a display through which we can monitor the vitals of our project.
The pi itself has a HDMI output which can be directly connected to a Monitor, but in projects where space is a constrain we need smaller displays. So in this tutorial we will learn how we can interface the popular 3.5 inch Touch Screen TFT LCD screen from waveshare with Raspberry pi. At the end of this tutorial you will have a fully functional LCD display with touch screen on top of your Pi ready to be used for your future projects.
It is assumed that your Raspberry Pi is already flashed with an operating system and is able to connect to the internet. If not, follow the Getting started with Raspberry Pi tutorial before proceeding.
It is also assumed that you have access to the terminal window of your raspberry pi. In this tutorial we will be using Putty in SSH mode to connect to the Raspberry Pi. You can use any method but you should somehow be able to have access to your Pi’s terminal window.
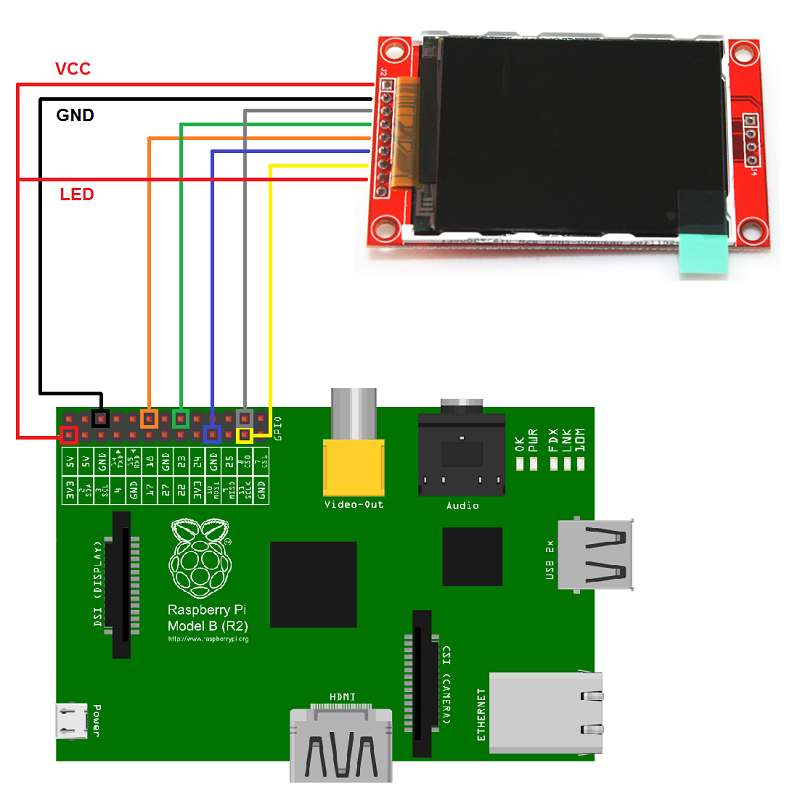
Connecting your 3.5” TFT LCD screen with Raspberry pi is a cake walk. The LCD has a strip of female header pins which will fit snug into the male header pins. You just have to align the pins and press the LCD on top of the Pi to make the connection. Once fixed properly you Pi and LCD will look something like this below. Note that I have used a casing for my Pi so ignore the white box.
For people who are curious to know what these pins are! It is used to establish a SPI communication between the Raspberry Pi and LCD and also to power the LCD from the 5V and 3.3V pin of the raspberry Pi. Apart from that it also has some pins dedicated for the touch screen to work. Totally there are 26 pins, the symbol and description of the pins are shown below
Now, after connecting the LCD to PI, power the PI and you will see a blank white screen on the LCD. This is because there are no drivers installed on our PI to use the connected LCD. So let us open the terminal window of Pi and start making the necessary changes. Again, I am using putty to connect to my Pi you can use your convenient method.
Step 2: Navigate to Boot Options -> Desktop/CLI and select option B4 Desktop Autologin Desktop GUI, automatically logged in as ‘pi’ user as highlighted in below image. This will make the PI to login automatically from next boot without the user entering the password.
Step 3: Now again navigate to interfacing options and enable SPI as show in the image below. We have to enable the SPI interface because as we discussed the LCD and PI communicates through SPI protocol
Step 4: Click on this waveshare driver link to download the driver as a ZIP file. Then move the ZIP file to you PI OS. I used Filezilla to do this, but you can also use a pen drive and simple copy paste work. Mine was placed in the path /home/pi.
Step 7: Now use the below command to restart your Pi. This will automatically end the terminal window. When the PI restarts you should notice the LCD display also showing the boot information and finally the desktop will appear as shown below.
Hope you understood the tutorial and were successful in interfacing your LCD with PI and got it working. If otherwise state your problem in the comment section below or use the forums for more technical quires.

Thanks for bringing this to my attention. It appears that the upgrade package overwrites the FBTFT drivers, in particular, the Raspberry Pi bootloader. This seems to solve the problem:
I just tested this, and it looks like the difference is how SPI is enabled. In the RPi 2 it’s enabled in raspi-config, not commented out in the blacklist file. I just updated the post so it should work now!
Looks like the only difference is in how SPI is enabled. In the new release of Raspbian, SPI is enabled in the raspi-config menu under advanced settings. In older versions of Raspbian, it is enabled by commenting out the line in the blacklist file
dwc_otg.lpm_enable=0 console=ttyAMA0,115200 console=tty1 root=/dev/mmcblk0p6 rootfstype=ext4 elevator=deadline rootwait fbtft_device.custom fbtft_device.name=waveshare32b fbtft_device.gpios=dc:22,reset:27 fbtft_device.bgr=1 fbtft_device.speed=48000000 fbcon=map:10 fbcon=font:ProFont6x11 logo.nologo dma.dmachans=0x7f35 console=tty1 consoleblank=0 fbtft_device.fps=50 fbtft_device.rotate=0
Unfortunately, their “driver” is an SD card image containing a complete installation of Raspbian which has been preconfigured to use their display. Which is fine if you’re setting up a brand new system that doesn’t need to be a specific distro, but if you’re trying to add the display to an existing Raspberry Pi, already configured the way you want it, with software installed and data present, or if you want to use a specific distro such as Octopi, then it’s not terribly helpful.
Hello..I tired to interface this lcd “https://www.crazypi.com/raspberry-pi-products/Raspberry-Pi-Accessories/32-TOUCH-DISPLAY-RASPBERRY-PI” to my Raspberry pi model B+.I got a DVD containing image for LCD in the package.I burned it to the SD card and plugged in the display.But my lcd is completly blank.But green inidcation led (ACT LED) in board is blinking.Why my LCD is Blank ?
Thank you for this great tutorial. I looked everywhere for this information. I have an eleduino 3.5 version A. I was able to get it working on my Pi 2 by following your tutorial and using flexfb as the screen type. I got the other settings from the image that came with the product. I did find that the ts_calibrate didn’t recognize the screen so I installed xinput-calibrator and it worked fine.
Just got my Pi2 running Wheezy, working with the Eleduino 3.5 LCD without running the OEMs image… kinda. I didn’t want to rebuild the application environment again, so was avoiding flashing the SD.
Unzipped it and looked around. From a shell script inside i kinda figured out what it was doing. I didn’t like what I saw, so I manually made changes omitting the parts I didn’t like (it rm -r my /lib/modules directory… omitted that part) and copied 2 files and 1 directory from the OEMs archive to the file system of my Pi2.
[ 0.000000] Kernel command line: dma.dmachans=0x7f35 bcm2708_fb.fbwidth=656 bcm2708_fb.fbheight=416 bcm2709.boardrev=0xa21041 bcm2709.serial=0x631a4eae smsc95xx.macaddr=B8:27:EB:1A:4E:AE bcm2708_fb.fbswap=1 bcm2709.disk_led_gpio=47 bcm2709.disk_led_active_low=0 sdhci-bcm2708.emmc_clock_freq=250000000 vc_mem.mem_base=0x3dc00000 vc_mem.mem_size=0x3f000000 dwc_otg.lpm_enable=0 console=ttyAMA0,115200 console=tty1 root=/dev/mmcblk0p2 rootfstype=ext4 elevator=deadline rootwait fbtft_device.custom fbtft_device.name=flexfb fbtft_device.gpios=dc:22,reset:27 fbtft_device.bgr=1 fbtft_device.speed=48000000 fbcon=map:10 fbcon=font:ProFont6x11 logo.nologo dma.dmachans=0x7f35 console=tty1 consoleblank=0 fbtft_device.fps=50 fbtft_device.rotate=0
i have a watterott display (https://github.com/watterott/RPi-Display) and changed the device-name to “rpi-display”. i use a rsapberrypi 2 and hae the latest raspian image installed.
Did you check to see if your device is supported yet? The device name should be specific for your screen, as listed in the fbtft file linked to in the beginning of the post
I too have a raspberry pi 2, and a waveshare spotpear 3.2 RPi lcd (v3) and I just can’t get it to work! I suspect I have a faulty LCD, but thought I’ll try this forum for help before I sent it back.
Soon as the pi is powered, the LCD lights up all white, with a few vertical pixels coloured at one of the edges, and nothing else. I don’t think that should happen – not at least before the BOIS has started up.
Anyway, point 1, says to change to dev/fb1 – I don’t have fb1. Only fb0 appears to be there. is that a clue what could be wrong? I have enabled SPI (is there a command to tell if its enabled?) I have also ran spidev to troubleshot (though I haven’t a clue what I means)
Any ideas what going wrong? I am using the latest “2015-02-16-raspbian-wheezy_zip”. Enabled SPI. done all the steps. Even changed mmcblk0p2 to mmcblk0p6 as suggested by Dabomber60 (but that freezes for me)
[ 0.000000] Linux version 3.18.5-v7+ (pi@raspi2) (gcc version 4.8.3 20140106 (prerelease) (crosstool-NG linaro-1.13.1-4.8-2014.01 – Linaro GCC 2013.11) ) #1 SMP PREEMPT Fri Feb 6 23:06:57 CET 2015
It seems all appears to be working – just the LCD is still all white with a single line of coloured pixels on edge) and nothing else. Is there a way to output, like jeff G script, of touch points?
I had the same one, I finally found a driver for it here: http://www.waveshare.net/wiki/3.2inch_RPi_LCD_(B) you will need to translate the page, but unpack the driver then run sudo ./LCD-show/LCD32-show. It should reboot and all will be good with the screen :)
Can anyone let me know if the default OS image sent with the screen works with pi2 or just Pi B/B+ as i think my screen maybe broken but can’t confirm it yet as i have not had it working at all
My system: Raspberry Pi 2 Model B with Raspian Wheezy from Febuary 2015. LCD display of Sainsmart 3.2 http://www.conrad.de/ce/de/product/1283498/Raspberry-Pi-Display-Modul-Touch-Display-81-cm-32/?ref=home&rt=home&rb=1
dwc_otg.lpm_enable=0 console=ttyAMA0,115200 console=tty1 root=/dev/mmcblk0p2 rootfstype=ext4 cgroup_enable=memory elevator=deadline rootwait fbtft_device.custom fbtft_device.name=sainsmart32_spi fbtft_device.gpios=dc:24,reset:25 fbtft_device.bgr=1 fbtft_device.speed=48000000 fbcon=map:10 fbcon=font:ProFont6x11 logo.nologo dma.dmachans=0x7f35 console=tty1 consoleblank=0 fbtft_device.fps=50 fbtft_device.rotate=90
sainsmart32_spi width=320 height=240 buswidth=8 init=-1,0xCB,0x39,0x2C,0x00,0x34,0x02,-1,0xCF,0x00,0XC1,0X30,-1,0xE8,0x85,0x00,0x78,-1,0xEA,0x00,0x00,-1,0xED,0x64,0x03,0X12,0X81,-1,0xF7,0x20,-1,0xC0,0x23,-1,0xC1,0x10,-1,0xC5,0x3e,0x28,-1,0xC7,0x86,-1,0×36,0x28,-1,0x3A,0x55,-1,0xB1,0x00,0x18,-1,0xB6,0x08,0x82,0x27,-1,0xF2,0x00,-1,0×26,0x01,-1,0xE0,0x0F,0x31,0x2B,0x0C,0x0E,0x08,0x4E,0xF1,0x37,0x07,0x10,0x03,0x0E,0x09,0x00,-1,0XE1,0x00,0x0E,0x14,0x03,0x11,0x07,0x31,0xC1,0x48,0x08,0x0F,0x0C,0x31,0x36,0x0F,-1,0×11,-2,120,-1,0×29,-1,0x2c,-3
ads7846_device model=7846 cs=1 gpio_pendown=23 speed=2000000 keep_vref_on=1 swap_xy=1 pressure_max=255 x_plate_ohms=60 x_min=300 x_max=3800 y_min=700 y_max=3400
The LCD display shows the raspberry correctly. However, the touch screen input does not work. The mouse pointer can I move correctly with your finger, but I can not select things (function of the left mouse button).
Thank you so much for this great tutorial. I have my WaveShare SpotPear 3.2″ V4 working fine on my Raspberry Pi 2. If you are having problems with this specific hardware, skip step 5.
Can someone upload SD card image that works with RBP2 ? My idea is to use Eleduino TFT as additional screen and play movies via HDMI.. is it possible?
Do not follow this article when you don’t know what kind of LCD module. In my case, I follow all of this and my raspberry pi cannot boot anymore. I will try to recover, but I think I should format my SD card and reinstall OS.
Also can you someone explain what exactly happen when do rpi-update? Want to understand what this step actualy doing and help me to debug any such situation and able to help others.
Does anyone tried splash boot screen with waveshare v4 LCD and Rpi2? I tried to follow some example from https://github.com/notro/fbtft/wiki/Bootsplash but no success.
in the video you say to change the existing line to “snd-bcm2836” for the rasppi2 which isn’t listed in the written part of the instructions (part 4).. this should be added (I believe it caused me to have to re-image the OS again, the Pi wouldn’t boot to anything just using the written steps)
fbtft_device name=waveshare32b gpios=dc:22,reset:27 speed=48000000 width=320 height=240 buswidth=8 init=-1,0xCB,0x39,0x2C,0x00,0x34,0x02,-1,0xCF,0x00,0XC1,0X30,-1,0xE8,0x85,0x00,0x78,-1,0xEA,0x00,0x00,-1,0xED,0x64,0x03,0X12,0X81,-1,0xF7,0x20,-1,0xC0,0x23,-1,0xC1,0x10,-1,0xC5,0x3e,0x28,-1,0xC7,0x86,-1,0×36,0x28,-1,0x3A,0x55,-1,0xB1,0x00,0x18,-1,0xB6,0x08,0x82,0x27,-1,0xF2,0x00,-1,0×26,0x01,-1,0xE0,0x0F,0x31,0x2B,0x0C,0x0E,0x08,0x4E,0xF1,0x37,0x07,0x10,0x03,0x0E,0x09,0x00,-1,0XE1,0x00,0x0E,0x14,0x03,0x11,0x07,0x31,0xC1,0x48,0x08,0x0F,0x0C,0x31,0x36,0x0F,-1,0×11,-2,120,-1,0×29,-1,0x2c,-3
ads7846_device model=7846 cs=1 gpio_pendown=17 speed=1000000 keep_vref_on=1 swap_xy=0 pressure_max=255 x_plate_ohms=60 x_min=200 x_max=3900 y_min=200 y_max=3900
After following this tut to the letter on a brand new image of Raspian, I find that the touch driver does not function. Anyone experience the same? Basically all I did was image a current copy of rasping, did a apt-get upgrade, and then did this tutorial. Then the touch driver does not work, meaning the pointer does not respond.
The reason I did this was because on a production version of my system I added the 3.2 screen and it worked great except for the x-axis. So I wanted to see if there was something in my system that was interfering or if this is another error. Now with a raw rasping the driver does not work at all. I wonder if the touch pin has changed since the kernel is using BCM pins instead of GPIO pin numbers?
I remember that I plugged in the screen wrongly one time, before configuring any of the GPIO pins. Can this have damaged the screen? Still it’s weird that the display part works well and the touch part not at all.
I do not think that has anything to do with it. Other than power pins, the rest are communication. If it still works then you are good. No, there is something else. I do suspect it us related to the BCM pin numbering. The real question is… Why isnt the eeveloper responding? I have since abandoned this TFT because of his lack of response.
Touch actually goes through one of the SPI pins I think. Either the driver is toast with the required kernel update or the driver is using the wrong pin. It is very likely the this works well with previous raspian versions, but not with the new B+ and with the new kernel.
I am trying to use the sainsmart 2.8″ lcd sold through microcenter, using the sainsmart32_spi … seems to have the same pinouts, should I be able to get this to work? I am stuck at the white out screen on the lcd, doesn’t seem to recognize the module either.
Unfortunately I’ve tried that ( a few times actually) but the file still doesn’t exist. Thanks very much for the assistance anyway. I must be doing something wrong. My Raspian came from a Noobs installation, I’m wondering if I should try installing the OS from somewhere else. My LCD screen didn’t come with a CD or any docs so I’m completely in the dark here.
I have just found a way to get this file on my system! Apparently its part of the fbturbo installation. I found it here http://www.raspberrypi.org/forums/viewtopic.php?f=63&t=45746&start=75 (under experimental enhanced x driver (rpifb).. Sorry if this is obvious to everyone but I am SUCH a noob at this!!
Ok, what am I doing wrong. I am using a fresh install of the newest raspbian, on a Pi 2. After doing the first two steps and rebooting I get the rainbow screen, then the boot up process, and then my screen just goes black with a flashing cursor in the top left. I am not able to enter any commands or anything…like the pi is halting just after boot up. Any thoughts/suggestions would be greatly appreciated. Thanks.
Well figured out that step 1 was causing my problems. I’m guessing it is shutting off my hdmi feed and trying to switch it over to the SPI, am I guessing right? If so, not sure how I’m suppose to complete the rest of the steps if my hdmi output gets turned off before the LCD is actually set up to work…that sounds kind of smartass-like, which is not my intention, just looking for some clarification on what is going on in that first step as I am fairly new to this stuff. Thanks.
Here is a link to an updated image from waveshare. Upon install it got the display up and running, but I still do not have touch functionality. I’ve been playing around with it, but it has been to no avail…hopefully someone better at this stuff from me can get the touch working.
I am having an issue with getting the GUI back. Every time I use startx my pi just sits there for about two minutes saying “No protocol specified”, and then it just gives up. I went through this tutorial about four times now and am not certain why it is doing this. I have the exact same LCD as is in the tutotial (WaveShare 3.2b). any help would be great.
Hi I am making a project for school,using the raspberry pi b+ and waveshare spotpare 3.2b. Everything works except the touch input doesn’t work. Any help would be appreciated very much.
I am trying to get this same screen to work with the image of RetroPie 2.6 and it won’t work. I have followed all the steps and nothing, please help I an kinda a noob.
I have a Tontec 7 inch touchscreen with a Raspberry Pi 2 B. After following the instructions the touch screen is functioning but not properly… The only are that works is the upper left (and only a small area of that). I tried changing the width and height in the modules but it didnt change anything. Also the xy seems to be reversed, I changed the swap_xy to 1 but again no change on the screen.
hi i have the same screen with a raspberry pi 2 im trying to run retro pie but it wont show ..however it shows all the commands …but i cant get it to show the gui …if u guys can make an image or something please i have been in this pain for two weeks already thank you
well ,,i follow all instructions and still kernel panic ,,,,may i request from mr. Circuitbasics@Gmail.Com that have a contact with manufacture and just ask for 2-3 links for image files for different versions of pi till all this f discussions are finished,,i cant understand 10 guys said we run it and 40 guys said kernel panic ,,as an expert i did 50 times imaging and follow all changes fro this forum and other forums and still cant run it ,,,so sth is wrong …..just asking the manufacture for simple f image ,,that`s it ,,,,simpleeeeeeeeeeeeeeeee
well i did it at last on pi 2,,after reading 100 pages and reimaging 50 times ,,i finally find the solution ,,,,there is a simple line forgotten to be attached in setup instruction,,,well i give u clue for prodigies ,,there is a step left between step 3 and 4,,,,and a simple change in step 5 according to your pi version ,,,that`s it ,,nothing else,,,,
Damn.. I thought I was kickin ass haha. I am using the SainSmart 3.2″.. the backlight is lit up and the pi was booting and everything just fine but on the final reboot it gets hung and says “nonblocking pool is initialized” ?? No idea what that means. But it’s def just frozen at this point.. on my main screen, and just the backlight is on the SainSmart.
This was an excellent tutorial. I have gotten an output to the screen, but no touchscreen usage . I have the Waveshare SpotPear 3.2 Inch LCD V4 screen, but using Raspberry PI 2 with wheezy. Any ideas?
Thanks a lot for this article. Very clear and easy . I am new in pi’s world and my 3.2″ screen is working fine. I rotate 90 º and works. I can use mouse and so on.Not problems.
I filed the steps to calibrate the screen but it did not work.I think because it did not find the TFT pin, because I think the touch problem is the assigned pin to control it changed.
I actually used the driver from here http://www.waveshare.com/wiki/3.2inch_RPi_LCD_(B) , from a new wheezy build, did nothing except enable SPI in config, install driver, and change mmcblk0p2 to mmcblk0p6 in cmdline.txt and it all worked, no drama.
Hi I managed to set up my touch screen ok but I now have the issue that everything desktop fits fine but the windows I open are all huge and I can’t remember how to change the size and cannot see the option in desktop preferences any idea what I have to do and is it at all possible to install kodi to run through the raspbian is as this would be a lot my useful than having to keep swapping os on every boot up many thanks in advanced hope you can help me
Advice to all who have the drivers from the (touch)screen manufacturer and cannot obtain those otherwise: you can skip everything and go to the update steps skipping the kernel and kernel modules update (as mentioned by the author) so that you don’t override the preinstalled drivers. I have a Waveshare 3.5″ RPi v3 (not the 3.2″ supported by notro’s drivers) and actually managed without any problems to get notro’s drivers make it work. However I am still reading about the xinput and xinput-calibrator to figure out how to include it as a kernel module so that I can compile my own kernel and add it there.
i have raspberry pi 2 with 3.2 inch rpi lcd v4 waveshare spotpear.i have done as per your instructions.the display is working but touch screen not working.error shows waveshare32b module not found as well as touch screen module not found messages.
Hey! i did this and rotated it… It loads console perfectly, but when it goes into startx, i get a black background with only the wastebin/trashcan… how do i get the taskbar(or whatever that bar is called)? and the raspberry background?
Unfortunately I have lost the Touch facility on my Waveshare 3.5″ LCD Touchscreen? Can you offer any reasons as to why? I copied the Raspbian image to my Raspberry Pi from the Waveshare website first of all. The Touchscreen displays but is not reactive with any touch
I have purchased a raspberry pi B+ total kit and waveshare 3.2 TFT display online. In the package i have been given a pre-loaded NOOBS installed SD card. I did not even start anything yet. What should i do what r the things needed and how to connect the display i really want to know. I need help as i don’t know anything. Does the above solution help or will u suggest something………………..
Hi great article thanks. I am trying to get a waveshare 7 inch LCD with capacitive touch running it works with the suppled image but if you upgrade it breaks the capacitive touch. I have a sense-hat and GPS which require the latest kernel and RASPIAN image and the install program for the screen replaces the /lib/modules directory and the kernel with older ones. I need to be able to install the touch drivers into a new clean OS can anyone give me some pointers? Thanks
For anyone who have those unbranded cheap TFT touch modules and cannot get it to work with this guide, I had success on my 3.5″ with the following steps: http://pastebin.com/89qmFbPB
I have the WaveShare 3.5 (A) and cannot get it to work with the Kali Linux with TFT for Raspberry Pi. Have anybody gotten the A to work? (Not the B, theres instructions for the B already and dont work with A)
So I have the original image that came with my screen and it works fine with the LCD but my problem is that I want to use my LCD screen with other distros (at this time I am trying to use it with Kali Linux with TFT support by default https://www.offensive-security.com/kali-linux-vmware-arm-image-download/) What do I have to do to transfer the needed files from the original image that WORKS with the screen and use them with another image?
I originally bought this bundle http://www.amazon.com/gp/product/B013E0IJUK?psc=1&redirect=true&ref_=oh_aui_detailpage_o02_s00 with an RPi LCD V3 and no extra documentation on the specifics on the chipset. I tried with the bftft drivers but since I have no idea what to call this screen I just suppose it isn’t supported.
I’m not sure if the Jessie kernel is compatible – can anyone please confirm or not ?? Adafruit states that their setup for TFT screens are Wheezy only ; is this a different setup ??
Oct 16 17:38:48 spare kernel: [ 12.544859] graphics fb1: fb_ili9340 frame buffer, 320×240, 150 KiB video memory, 4 KiB DMA buffer memory, fps=50, spi0.0 at 48 MHz
After I rebooted in step 3, my raspberry pi won’t boot up again. It goes thru the process of booting and the text scrolls down and every thing says “ok”. Then instead of going to GUI it just guys to a black screen on my monitor with a blinking underscore in the top left corner. Anyway to get around this? or should I start over with a fresh disk image??
That is what happens to mine also.. So long story short —> THIS SITE NEEDS TO BE UPDATED OR SHUT DOWN <— There are a hundred people on here that have all lost everything on the pi drive, and spent all day (or more) working thru this tutorial 4 or 5 (dozen) times and nothing. Just have to reinstall the os over again and again.
Please check out my answer, it may help you if it works. I’m not in that case but I’m assuming that the desktop environment simply doesn’t automatically start running anymore… This can be changed in the raspi-setup
Try typing ‘startx’ if you problem isn’t solved (assuming you’re using Raspbian and LXDE), it should start the desktop environment you’re used to see. What you’re seeing is the Command Line Input interface (CLI), the most basic way to interact with a computer. Hope I helped you a little
I have tried to set up waveshare 32b on my Pi B using the latest Raspian download. I learned a lot in the process using Windows Putty, Nano etc. I have repeated the setup process several times from scratch and included the corrections for possible overwriting. My Waveshare SpotPear 3.2 inch RPi LCD V4 just shows a white screen. Any suggestions?
There was no disk included. I asked for drivers and was given a download link to the image file. After down loading this I tried it and still got just a white screen. The HDMI monitor locks partway though the boot. I can still log in to pi using putty from my PC.
Hi, I am using raspberry pi 2 with raspbian jessie installed. I the waveshare spotpear 3.2 v4. The above instructions are not working. and after completing the steps there was no display from hdmi or lcd. One things to notify is.: the etc/modules files only had i2c-dev and not snd-bcm2835.
I am trying to get this to work with Retro Pie 3.3.1 and the Waveshare3.2″ v4 but I only get the terminal on the lcd and emulation station starts on hdmi. to get it working with retro pie i just replaced startx with emulationstation. how do i get this to work?
Sir, Your post has very useful to me. i am using Tinylcd. but i cant get display. i am performing all the steps in your post. i cant get touch controller information from the product website and also i am using RASPberryPi B+ model. could u please give me best solution to my work. Than you.
what if OS is not Raspbian, any other distro like Yocto project, etc.? Could you please specify process without “rpi-update” that makes driver installation process more generic, not dedicated to Raspbian.
I completed all steps except for the last one (I want it to boot to console). However, when I reboot, it never completes the boot process. I start in recovery mode and check the cmdline.txt file and it is exactly how it appears on this page. I copied the kernel info as well, but I am not sure if it correct as I cannot get to it to check. Any suggestions? I might just reinstall the OS and start over…
i installed android OS in raspberry pi 2. can i use same LCD touch screen set up for android installed raspberry pi 2 which you are used for raspbian.
I have KeDei 3.5 inch TFT version 4.0 by Osoyoo. (released after January 1 2016) how do i get it working with vanilla Raspbian Jessie (do not want to install the image sent by the seller)
I’m trying to use an original Raspberry Pi model B with a cheap 3.5 inch 320×480 LCD which allegedly was manufactured to work with the Pi and has the correct fittings to fit over the GPIO pins. The operating system is the latest, downloaded yesterday and installed with NOOBS. I can’t get past step 2 of this guidance. When I reboot after using raspi-config I can see text generated as the Pi boots, then the HDMI fed screen goes blank apart from a flashing cursor in the top left hand corner. The LCD just remains white with nothing else on it. I have missed out step 1 and rebooted after step 2 and the screen functions as I would expect. Does anyone have any ideas please?
Thanks for the great tutorial. I do have a question. Once you install the drivers for the lcd are you effectively disabiling the hdmi port or is it still available to use and will the pi function with both displays. I have a pi 3
Thanks for the guide, have been doing this with my son but once we leave raspi config and reboot all we get is a black screen with a flashing white horizontal line (dash). Can you help? I have looked in the comments at the end of the article but no one else appears to have this issue.
I have a raspberry pi 2 with waveshare screenn 3.5 inches. Isn’t it the same instructions. But it isnt working, all i get is a white screen, and the red led on the pi is on. The green LED isnot working.
i am sorry, but i am a naive , and i have this question, can we upload any file into it for the display? like have a software in which if i tap it gives back a feedback to the code?
My Rpi3 gets “ERROR: could not insert ‘spi_bcm2708’: No such device” after I enable SPI in the raspi-config.My Rpi3 is freezing on the rainbow screen after I reboot at the end of step 3. I’ve tried adding boot_delay=1 to config.txt.
if any interested, now i have a raspian image working on raspberry 3 with Waveshare 3.5, also with sdr support for dongles and FreqShow working perfectly on touch
ads7846_device model=7846 cs=1 gpio_pendown=17 speed=1000000 keep_vref_on=1 swap_xy=0 pressure_max=255 x_plate_ohms=60 x_min=200 x_max=3900 y_min=200 y_max=3900
No matter what I do, I can’t get this to work. It works perfectly fine on my Pi2, but when I follow and use the guide on my Zero, I always end up with the activity LED blinking 8 times (corrupt SD/filesystem error).
I’d like to find the driver software for my 7″ LCD with touch (official Pi unit) so that I can use it in buildroot. I wanted to make sure this kernel is the one before I started digging further.
I started through your tutorial and completed step 3 and rebooted. After the Raspberry screen and some of the boot text on my HDMI monitor, I now have a black HDMI monitor and a white screen on my LCD. Does this mean that the bootloader was overwritten or something else is wrong? How am I supposed to enter in the proposed fixes to the bootloader, when I can’t get the RPi to boot? Do I have to interrupt the boot process at some point to reinstall the bootloader or what?
Its a script. Download and instead of running sudo ./LCD4-show run cat ./LCD4-show to simply display what it does without actually running it. The commands are fairly simple modifying a few files. I actually saved the LCD-show.tar.gz on my own server for faster future download but also for backup as it saved me tons of hours (if that’s a measuring unit for time :) )
I’m using RasPi Zero with latest (as of last week) Jessie Raspbian. Did you run the script? If it didn’t work and you have modified other files in the process of making it work, I would recommend installing a fresh installed image on a new card and running the script. Can you suspect the screen being faulty or got “burned” in the process?
i bought a 3.5 inch tft lcd screen from banggood. and i have installed raspian jessie, the latest version, in my sd card. but when i power on my Pi, only a white backlit screen comes. there are no images or graphics whatsoever.
The owner of this article should including a WARNING in the header that if someone follows the steps, they will install a deprecated driver (which is only visible as tiny text on its gethub page here https://github.com/notro/rpi-firmware). This driver after install will break Raspberry Pi and the SD card will need to be reimaged, for some less experienced users, this could also mean lost work if they failed to backup their code or resources. On windows, it requires installing Linux reader software and it takes a long time to fix this f**kup which could easily have been avoided if the author had and sense of responsibility.
PLEASE DELETE this article. You have great power with this article showing up for so many people in their search results, and you display ZERO responsibility. This is terrible!
I have done every thing right but the only major problem is that the screen is still white and my raspberrypi freezes after a line of code when booting up and I cant get in with SSH
Will your system work with my SainSmart 2.8″ 2.8 inch TFT LCD 240×320 Arduino DUE MEGA2560 R3 Raspberry Pi ? I would like to know before not be able to back out. Thanks, Lee
I know I will end up regretting this, but how do I change fb0 to fb1? I’m on the screen that has all the info, but no way to change it. Am I looking for a file? I have had my screen for MONTHS and I can’t do anything with my pi or the screen. I am >< close to smashing both. COMPLETE WASTE OF MONEY so far!!
hello. I really appreciate your blog post. I have a raspberry pi 3 B. I have been unable to get my waveshare 3.2 screen to work.I am at a complete loss for what to do. I do step 2 I change fb0 to fb1 and then follow your directions I don’t get the prompt to reboot; however, I do it manually with sudo reboot. that works fine then I complete step three and that works just fine; however once I reboot from getting those drivers and when I attempt to reboot it is unsuccessful and then my whole raspberry pi will not restart. then when I power it back on it will just shut back off. I then have to redo noobs onto a new SD card I would GREATLY appreciate anyones help
I ‘m actually using a LCD Waveshare3.2” , I followed your steps to setup the lcd touchscreen for my rpi and it work but I have a problem with the resolution because if I open a repertory I do not see the whole contents on the screen .
hi! thank you for this post…. I was wondering if all the raspberry pi’s gpio are being held by this screen or do we have any of those availables for use??
it worked. but the resolution is for bigger screens. i got the menubar small, but the rest appears too big , and out of screen. the wastebasket icon is 1/6 of my 3.2″ screen. wich HAS the resolution capability too display the whole desktop. But i’m a PI newby and dunno how to adjust the screen resolution on this display. anybody?
I did a 5inch LCD for my raspberry pi. I dont use the touchscreen so i didnt have to install any drivers. It works out of the box but doesnt cover the whole screen unless you open the terminal and do:
HI I have my RPI running Pi Presents on a view sonic TD2230 Touchscreen. It all works fine, touching the click areas can navigate you thru my presentation, The problem arises when you use multitouch gestures like you would on a iPhone. Pinch or expand etc… and then all touch ability goes away. I can still control the presentation via a mouse, but I don’t get touch control back until I either relaunch Pi Presents, or if I unplug and plug the usb cable going to the touchscreen.
Much of this is outdated on Raspbian Stretch where device tree overlays (see https://www.raspberrypi.org/documentation/configuration/device-tree.md) provide for most of the configuration automatically.
After I did the step that “INSTALL THE FBTFT DRIVERS” and then reboot, my raspberry pi couldn’t boot successfully and the green light is always on, could you help me solve this problem? Thank you.

The LCD in the TFT01 is ILI9341. It"s a 240 * 320 (resolution), 2.2S inch TFT LCD screen.The LCD has a wide viewing angle, the contrast is also very suitable.
Check with "modetest -M vc4 | less" to see if it has brought up DSI as a display. If it is listed, then the Pi side is doing what it has been asked. ("sudo apt install libdrm-tests" if modetest isn"t installed yet).
Check with "modetest -M vc4 | less" to see if it has brought up DSI as a display. If it is listed, then the Pi side is doing what it has been asked. ("sudo apt install libdrm-tests" if modetest isn"t installed yet).
"dmesg |grep vc4" doesn"t give more data (same for "dmesg |grep dsi") for me as well. OP may want to open a VNC connection to this Pi as one will "see" if X is running and DSI brought up (even if the display is pitch black still).
Check with "modetest -M vc4 | less" to see if it has brought up DSI as a display. If it is listed, then the Pi side is doing what it has been asked. ("sudo apt install libdrm-tests" if modetest isn"t installed yet).
[ 0.000000] Linux version 5.15.50-v8+ (root@raspberrypi) (gcc (Debian 10.2.1-6) 10.2.1 20210110, GNU ld (GNU Binutils for Debian) 2.35.2) #1 SMP PREEMPT Fri Jul 1 12:52:50 +07 2022
[ 0.000000] Memory: 3553828K/4050944K available (11776K kernel code, 1956K rwdata, 4120K rodata, 3776K init, 967K bss, 169436K reserved, 327680K cma-reserved)
I can"t see in the pictures, but for constant impedance the same reference plane must be constant under the entire length of diff pair and if you change layers you need vias to join the reference planes or coupling capacitors to join the reference planes.
I can"t see in the pictures, but for constant impedance the same reference plane must be constant under the entire length of diff pair and if you change layers you need vias to join the reference planes or coupling capacitors to join the reference planes.
I can"t see in the pictures, but for constant impedance the same reference plane must be constant under the entire length of diff pair and if you change layers you need vias to join the reference planes or coupling capacitors to join the reference planes.

STONE Technologies is a specialized manufacturer of intelligent TFT LCD modules for HMI. Depending on the application, STONE Technologies offers industrial, advanced and residential smart TFT LCD modules in different sizes.
In this project, I will control LEDs with the help of STONE HMI display and Raspberry Pi GUI design. command data is sent to Raspberry-pi via Display, which is sent in frames, as Display sends data in frames and receives it in frames of HEX code. If you want to understand the data frames and how they work, I am using the STWI056WT-01 model in this project? You can download the datasheet from here.
Once opened, you have to create a new project for this purpose, select “Project” from the top and then select “New”, you will be asked to provide the same details as shown below, now give the project name and select the screen size according to your display size, here I am using 640X480 size display and after filling all the details also select the project path and click “Create”.
Step-6 :-This step is for, to upload the GUI-Designin the display.For this first connect the display with power supply of 9-12 volt through power port. And then connect USB to USB to your PC with Display. It will look like this.
After connected the display now first we have to download the ‘Default’folder through GUI-Tool. For this go to at Debugand click on Downloadthen select the location where you want to download it.
Now we have Defaultfolder in our local machine will upload in the Display memory, for this first connect the display as mentioned above in the image through USB to USB communication with your PC. You will get a storage device in your PC there you have to delete first previous Defaultfolder as mentioned in below image.
After pasted the default folder in display storage, just remove USB from Display and also remove the power supply, and after 2-3 sec just connect the power supply again to the display. Then you will get like this GUI which we have designed.
Now first connect Raspberry-Pi through VNC server or you can connect directly through display as per your convenience. Then there are two codes which are given below. The first one is for testing the all buttons which we have created and second one the Whole code with I/O setup and it has logic.
Here the purpose of testing code is to check all buttons so for this you need to connect first USB-0 of Raspberry-Pi to you Display TTL connector and then copy this code in Thonnyof Raspberry-Pi as given in below image and then click on run button to test it.
By click any button which is on display will get a particular button name which we have assigned in the starting as we discussed it earlier. You can see after pressing Button-1on display we are getting output string as button1because we have done the slicing of whole from which we are getting from display.
Here as in testing code these line of code, here l is variable which is receiving the frame from display size of 20, and then q is storing the sliced value as per our requirement.
And accordingly in complete code we made the logic as per individual button. Below logic is given as button6 will press then it will ON the LED2 high and if button7 will press it will of the LED2 as Off. Similarly all logic are working for others LEDs.
GPIO.setup(red_led,GPIO.OUT) GPIO.setup(green_led,GPIO.OUT) GPIO.setup(blue_led,GPIO.OUT) GPIO.setup(led1,GPIO.OUT) GPIO.setup(led2,GPIO.OUT) GPIO.output(red_led,GPIO.LOW) GPIO.output(green_led,GPIO.LOW) GPIO.output(blue_led,GPIO.LOW) GPIO.output(led1,GPIO.LOW) GPIO.output(led2,GPIO.LOW) ######################
Now that we have understood the logic behind the code, let’s run the second code in Raspberry-Pi, which is the complete code, but before making the circuit connections as shown in the circuit diagram below.

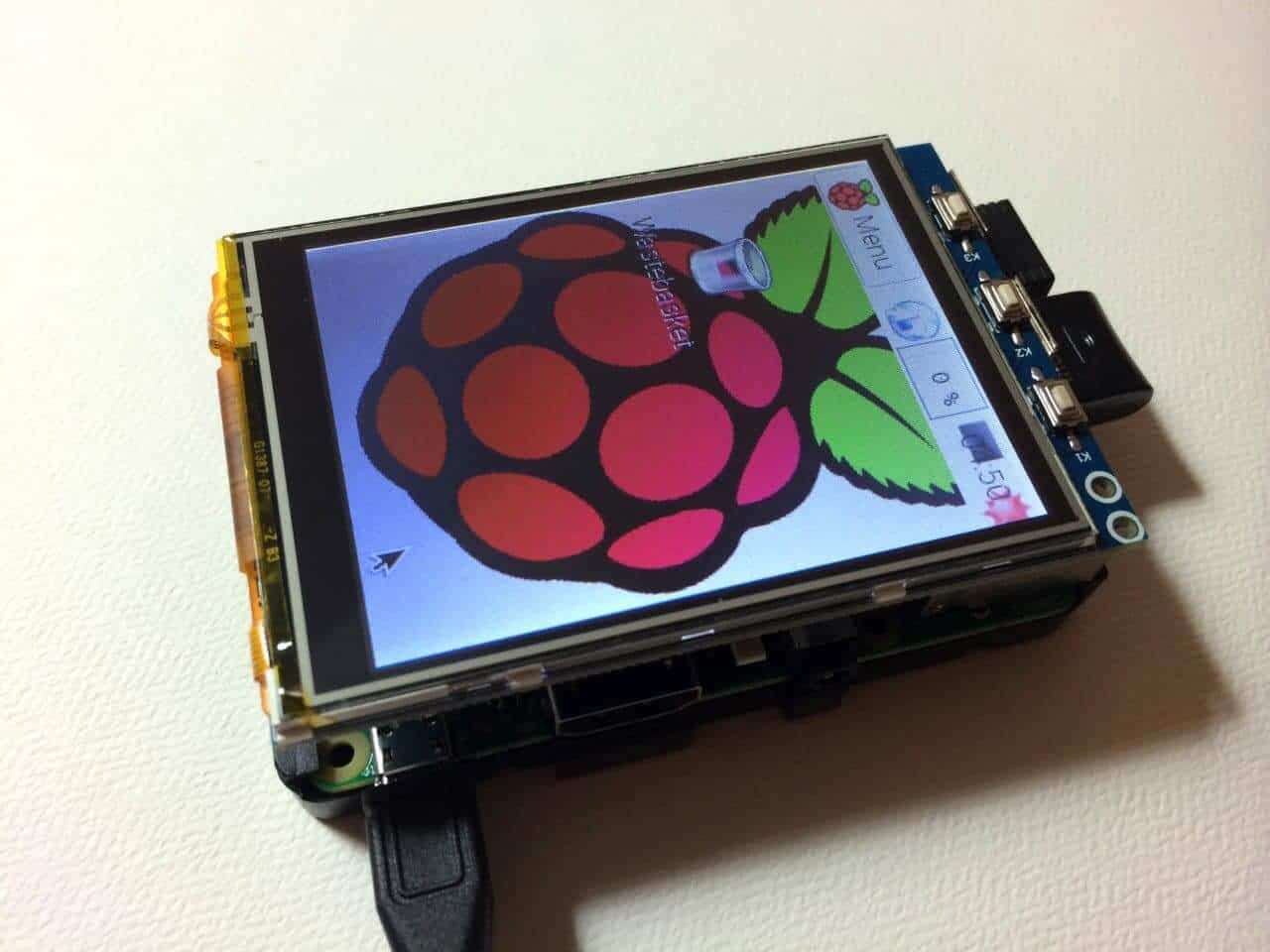
There’s a lot of interest in these little Pi-shaped screens, but there doesn’t seem to be one that is truly “plug n’ play” working straight out of the box.
I may have found something that makes it a little closer to that true plug n’play goal – the 3.5″ TFT screen from NeoSec Solutions. They offer a similar product to the PiTFT however overall I’ve found it a lot easier to set up.
It’s hard to look at any small touch screen for the Pi without comparing it to the ever popular PiTFT – so rather than pretend to not be comparing it – this review will face the boards off against each other and see what’s the best screen in each category. I don’t normally do this, but it just makes sense in this scenario.
The NeoSec 3.5″ TFT is a small touchscreen LCD display that pushes on to your Raspberry Pi (Model A/B) via the GPIO pins. The screen makes use of nearly all available space above the Pi, allowing a decent 480×320 resolution. It comes packaged in a small clip-top box with everything inside.
The GPIO is accessible via the extra PCB tab below the screen, allowing you to connect any kind of header you want (or none at all). It looks as though this could be cut/snapped off if required, as there are a number of droll holes creating the break for you. It’s subtle and out of the way:
The image file is the big winner here for me. I put the image on to a blank SD card (8Gb as it didn’t fit my 4Gb), turned on the Pi, and it was ready to go. No messing around, no code – just a working screen out of the box. Compare that to the hassle of some other TFT screens for the Pi and you’ll see why I’m so impressed with this.
The screen itself is nice and bright, with rich blacks, and that 480×320 resolution keeping the font to a nice size to see as much as possible on screen. I love the size of this screen, and the way it covers the Pi completely. There’s also very little blank space on the screen itself.
I guess it’s hard to keep us happy – we all want the biggest screen on our Pi, but to achieve that you need to remove the PCB area. A tough balance to strike.
Whilst I dont normally compare products when writing a review, theres an obvious competitor that you cant help but compare to when you see other small Raspberry Pi screens…so this review will focus on the pros/cons of the NeoSec 3.5″ TFT compared to the 2.8″ PiTFT from Adafruit.
Although these screens are different in features and size, they’re suitable for comparison in terms of “Pi sized touchscreen vs Pi sized touchscreen”.
The AdaFruit screen rolls up at $34.95 – including the screen only (no buttons). You also have to assemble this screen, including soldering the main GPIO connector and taping down the screen element.
Verdict: NeoSec wins this one. Considering the extras you get with it, I personally think it’s a better deal for a ‘screen on Pi’ solution. (and the basic $25 package is clearly much cheaper)
The PiTFT requires assembly, including GPIO and button soldering, and taping the screen to the PCB. That tape isn’t very sticky at all so you’ll probably need to get your own – I used No Nails tape.
Verdict: I think self-assembly can be a good learning experience, but considering how many people I’ve heard complaining of the difficulty of assembling the PiTFT, NeoSec wins this one.
The NeoSec weighs in at a more comfortable 3.5″ and a clearer 480×320 resolution. The 3.5″ screen covers more of the Pi, which I think looks much smarter. That extra screen space does come at a price, which is the slightly more delicate feel it has, and no mounting holes for support screws like the PiTFT:
The font on the NeoSec screen seems smaller yet clearer, allowing more on screen, but there may be a way to match this on the PiTFT that I haven’t discovered yet:
Verdict: You can’t argue with the bigger screen of the NeoSec, and it does seem to have much better colour and clarity. It seems an easy decision when considering these two as being in the same product market – however the PiTFT certainly feels more sturdy with that PCB surround. I’m going for the NeoSec here – but it is tight.
The PiTFT has holes around it to use nylon screws as a screen support. It also has PCB area around the screen acting as a bit of protection. The PCB covers the entire underside of the screen, ensuring no light comes out of the back.
The NeoSec screen doesnt have any support holes, and has no PCB area around the screen (but its a bigger screen, which is more important in my eyes). I can’t see the NeoSec doing well on a Model A without that Ethernet port holding it up. The NeoSec’s PCB doesn’t cover the rear of the screen either, so light comes out on to your Pi.
Verdict: The PiTFT wins this one, it feels much more secure, and I’m pretty sure light bleed from the back isn’t meant to happen – even if it does look cool.
The PiTFT has an optional upside-down connector to attach a belt to breakout to a breadboard. I don’t like the whole belt thing, it feels a bit too 90’s computing for me, and the upside down back to front thing makes it hard to do something different like add a regular GPIO header.
The NeoSec is a little more traditional with the GPIO, and simply gives you a mirror of the GPIO next to the screen. This is good if you want a simple prototyping access, but perhaps not as ideal if you just want a screen, as it does stick out. It looks as though it can be removed as drill holes indicate an easy option to cut or snap it off.
Verdict: Tie – it all depends on what you want the screen for. The PiTFT may be better for breakout projects, whilst breaking off the GPIO tab on the NeoSec may be better for those looking for a simple screen solution.
The PiTFT comes ready to fit 4 tactile buttons to, however these need to be purchased and fitted separately. The blue PCB of the Adafruit board is attractive when compared to traditional colours.
The other niggle here is that it doesn’t become your default screen output, you have to use a bit of code here and there to push movies, images etc to the screen. All in all – a bit of a hair-pulling experience!
The NeoSec on the other hand, was much easier to get going. I simply installed the image provided on the DVD supplied (no long download required) and it worked straight away. You have to tweak a couple of settings if you’re using a Rev1 board, but with a Model A/B it’s real easy. You also don’t seem to need to push things to the display using code – it picks up everything as default from what I’ve tested.
I thought I’d add a final section on support, as I had a few questions while writing this review, and previously had questions on the PiTFT when I first used it.
The PiTFT benefits from the massive following and fan base that Adafruit command. Their forums are full of information, and generally a lot of people buy their products, so most people have had the issue and written about it on blogs and forums.
The NeoSec screen doesn’t have that massive following that AdaFruit does, so finding information already out there can be difficult. Fortunately NeoSec counteract this by providing excellent personal support by email and also regularly on the Raspberry Pi forum.
It’s important to stress “personal choice” here. Everyone will have different uses for a Pi-sized screen, so a lot of us will probably sway one way or another purely based on the features and functionality we need.
Sure the PiTFT has that sexy blue AdaFruit styling we all love, and the screen feels more secure and has an overall better ‘feel’ to it (plus those optional buttons are very cool), but the setup involved many hours of my life that I’m unlikely to get a refund for.
The extra size and resolution gives a much better picture too – the colour and clarity are beautiful. Add to that the extras such as the pen and the touchpad, and for a extra few dollars the NeoSec feels like the better buy.

» Makerfabs is Open Hardware, Arduino, Raspberry Pi, mbed, BeagleBone, IoT, Smart Home, etc, Related Products& Services Vendor for Makers and new Startups.

» Makerfabs is Open Hardware, Arduino, Raspberry Pi, mbed, BeagleBone, IoT, Smart Home, etc, Related Products& Services Vendor for Makers and new Startups.
Alibaba.com offers 5719 raspberry pi display products. About 30% % of these are lcd modules, 19%% are lcd touch screen, and 4%% are oled/e-paper modules.
A wide variety of raspberry pi display options are available to you, such as call center and on-line technical support, free spare parts and return and replacement.You can also choose from 16:9, raspberry pi display,As well as from new, {2}, and {3}. And whether raspberry pi display is d-sub, usb, or {3}.

This is a 5" Raspberry Pi LCD touchscreen with 800*480 resolution and 108×64.8mm display area. The product supports Raspberry Pi DSI display interface and comes with a capacitive touch panel on its screen and supports 5 touch points.
The special holes design on the back of the screen is convenient to directly install the Raspberry Pi in the product. There is no need to provide external power for the touchscreen as the Raspberry Pi power supply is adopted. In addition, the screen supports hardware backlight adjustment. The function can be realized by turning the potentiometer on the back of the display.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey