arduino tft lcd connection free sample
![]()
The Arduino TFT screen is a backlit TFT LCD screen with a micro SD card slot in the back. You can draw text, images, and shapes to the screen with the TFT library.
The Arduino TFT library extends the Adafruit GFX, and Adafruit ST7735 libraries that it is based on. The GFX library is responsible for the drawing routines, while the ST7735 library is specific to the screen on the Arduino screen. The Arduino specific additions were designed to work as similarly to the Processing API as possible.
The TFT library relies on the SPI library, which must be included in any sketch that uses the scree. If you wish to use the SD card, you need to include the SD library as well.
The screen can be configured for use in two ways. One is to use an Arduino"s hardware SPI interface. The other is to declare all the pins manually. There is no difference in the functionality of the screen between the two methods, but using hardware SPI is significantly faster when drawing.
If you are using an Esplora, the structure of the program is the exact same. As the Esplora has a socket designed for the screen, and the pins for using the screen are fixed, an Esplora only object is created when targeting sketches for that board. You can reference the screen attached to an Esplora throughEsploraTFT.
To give the illusion of motion, you need to quickly erase and draw images on the screen. When using Processing on a powerful computer, you can callbackground() every time through your draw() function to erase the window contests and dra objects in their new positions. The Arduino is not as fast, is it takes a little time to clear the screen when calling background() with the TFT library.
The TFT library includes a basic font for drawing text on screen. By default, characters are 5 pixels wide and 8 pixels tall. It is possible to change the font size to 10x16, 15x24, or 20x32. For additional information on the underlying font capabilities, see the Adafruit page on graphic primitives.
The TFT library has the ability to read .bmp files off a SD card and display them on the screen. Images can be smaller or larger than the screen resolution (160x128), but there is no method on the Arduino for image manipulation. The images should be sized before you put them on the SD card.
In the following example, a bitmap that is 160x128 pixels named "arduino.bmp" is in the root directory of a SD card. When read by the library and drawn, the image will fill the screen.
Even if the screen"s headers are designed to fit into the socket on the front of the Arduino Esplora or the Arduino Robot but, this module is compatible with any AVR-based Arduino (UNO, Leonardo, etc...) or with the Arduino Due. If you want to use one these other boards, some slight changes on connections are required.
Connecting the pins in the proper way, you can see the lcd screen working with your Uno (or Duemilanove) just uploading the simple "TFTBitmapLogo" sketch.
The Arduino Leonardo & Arduino Yún use different pins to be compatible with the lcd screen. To set the pins MISO, MOSI and SCK, you have to use the ICSP terminals.+5V:+5V
The screen will show this message: "Arduino TFT Bitmap Example. Open serial monitor to run the sketch". Open the serial monitor to view the Arduino Logo.
To connect the lcd screen to an Arduino Due, use this pin configuration and don"t forget to set the right value for the variable "sd_cs" (#definesd_cs7) in the sketch:+5V:+3.3V
Now that you have tested the basic functionality of the screen, see the TFT library pages for information about the library"s API and additional examples. It"s also recommended to visit the Adafruit graphics library page for additional information on functions not covered.

In this article, you will learn how to use TFT LCDs by Arduino boards. From basic commands to professional designs and technics are all explained here. At the end of this article, you can :Write texts and numbers with your desired font.
There are several components to achieve this. LEDs, 7-segments, Character and Graphic displays, and full-color TFT LCDs. The right component for your projects depends on the amount of data to be displayed, type of user interaction, and processor capacity.
TFT LCD is a variant of a liquid-crystal display (LCD) that uses thin-film-transistor (TFT) technology to improve image qualities such as addressability and contrast. A TFT LCD is an active matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven LCDs with a few segments.
In Arduino-based projects, the processor frequency is low. So it is not possible to display complex, high definition images and high-speed motions. Therefore, full-color TFT LCDs can only be used to display simple data and commands.
After choosing the right display, It’s time to choose the right controller. If you want to display characters, tests, numbers and static images and the speed of display is not important, the Atmega328 Arduino boards (such as Arduino UNO) are a proper choice. If the size of your code is big, The UNO board may not be enough. You can use Arduino Mega2560 instead. And if you want to show high resolution images and motions with high speed, you should use the ARM core Arduino boards such as Arduino DUE.
In electronics/computer hardware a display driver is usually a semiconductor integrated circuit (but may alternatively comprise a state machine made of discrete logic and other components) which provides an interface function between a microprocessor, microcontroller, ASIC or general-purpose peripheral interface and a particular type of display device, e.g. LCD, LED, OLED, ePaper, CRT, Vacuum fluorescent or Nixie.
The LCDs manufacturers use different drivers in their products. Some of them are more popular and some of them are very unknown. To run your display easily, you should use Arduino LCDs libraries and add them to your code. Otherwise running the display may be very difficult. There are many free libraries you can find on the internet but the important point about the libraries is their compatibility with the LCD’s driver. The driver of your LCD must be known by your library. In this article, we use the Adafruit GFX library and MCUFRIEND KBV library and example codes. You can download them from the following links.
You must add the library and then upload the code. If it is the first time you run an Arduino board, don’t worry. Just follow these steps:Go to www.arduino.cc/en/Main/Software and download the software of your OS. Install the IDE software as instructed.
The second adds a library that supports drivers of MCUFRIEND Arduino display shields.#include "TouchScreen.h" // only when you want to use touch screen#include "bitmap_mono.h" // when you want to display a bitmap image from library#include "bitmap_RGB.h" // when you want to display a bitmap image from library#include "Fonts/FreeSans9pt7b.h" // when you want other fonts#include "Fonts/FreeSans12pt7b.h" // when you want other fonts#include "Fonts/FreeSerif12pt7b.h" // when you want other fonts#include "FreeDefaultFonts.h" // when you want other fonts#include "SPI.h" // using sdcard for display bitmap image#include "SD.h"
fillScreen function change the color of screen to t color. The t should be a 16bit variable containing UTFT color code.#define BLACK 0x0000#define NAVY 0x000F#define DARKGREEN 0x03E0#define DARKCYAN 0x03EF#define MAROON 0x7800#define PURPLE 0x780F#define OLIVE 0x7BE0#define LIGHTGREY 0xC618#define DARKGREY 0x7BEF#define BLUE 0x001F#define GREEN 0x07E0#define CYAN 0x07FF#define RED 0xF800#define MAGENTA 0xF81F#define YELLOW 0xFFE0#define WHITE 0xFFFF#define ORANGE 0xFD20#define GREENYELLOW 0xAFE5#define PINK 0xF81F
Drawing Linestft.drawFastVLine(x,y,h,t);//drawFastVLine(int16_t x, int16_t y, int16_t h, uint16_t t)tft.drawFastHLine(x,y,w,t);//drawFastHLine(int16_t x, int16_t y, int16_t w, uint16_t t)tft.drawLine(xi,yi,xj,yj,t);//drawLine(int16_t x0, int16_t y0, int16_t x1, int16_t y1, uint16_t t)
drawLinefunction draws a line that starts in xi and yi locationends is in xj and yj and the color is t.for (uint16_t a=0; a<5; a++){ tft.drawFastVLine(x+a, y, h, t);}for (uint16_t a=0; a<5; a++){ tft.drawFastHLine(x, y+a, w, t);}for (uint16_t a=0; a<5; a++){ tft.drawLine(xi+a, yi, xj+a, yj, t);}for (uint16_t a=0; a<5; a++){ tft.drawLine(xi, yi+a, xj, yj+a, t);}
These three blocks of code draw lines like the previous code with 5-pixel thickness.tft.fillRect(x,y,w,h,t);//fillRect(int16_t x, int16_t y, int16_t w, int16_t h, uint16_t t)tft.drawRect(x,y,w,h,t);//drawRect(int16_t x, int16_t y, int16_t w, int16_t h, uint16_t t)tft.fillRoundRect(x,y,w,h,r,t);//fillRoundRect (int16_t x, int16_t y, int16_t w, int16_t h, uint8_t R , uint16_t t)tft.drawRoundRect(x,y,w,h,r,t);//drawRoundRect(int16_t x, int16_t y, int16_t w, int16_t h, uint8_t R , uint16_t t)
Drawing Circlestft.drawCircle(x,y,r,t); //drawCircle(int16_t x, int16_t y, int16_t r, uint16_t t)tft.fillCircle(x,y,r,t); //fillCircle(int16_t x, int16_t y, int16_t r, uint16_t t)
fillCirclefunction draws a filled circle in x and y location and r radius and t color.for (int p = 0; p < 4000; p++){ j = 120 * (sin(PI * p / 2000));i = 120 * (cos(PI * p / 2000));j2 = 60 * (sin(PI * p / 2000));i2 = 60 * (cos(PI * p / 2000));tft.drawLine(i2 + 160, j2 + 160, i + 160, j + 160, col[n]);}
Drawing Trianglestft.drawTriangle(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3,t);//drawTriangle(int16_t x1, int16_t y1, int16_t x2, int16_t y2, int16_t x3, int16_t y3,// uint16_t t)tft.fillTriangle(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3,t);//fillTriangle(int16_t x1, int16_t y1, int16_t x2, int16_t y2, int16_t x3, int16_t y3,// uint16_t t)
This code sets the cursor position to of x and ytft.setTextColor(t); //setTextColor(uint16_t t)tft.setTextColor(t,b); //setTextColor(uint16_t t, uint16_t b)
The second function just displays the string.showmsgXY(x,y,sz,&FreeSans9pt7b,"www.Electropeak.com");//void showmsgXY(int x, int y, int sz, const GFXfont *f, const char *msg)void showmsgXY(int x, int y, int sz, const GFXfont *f, const char *msg){ uint16_t x1, y1;uint16_t wid, ht;tft.setFont(f);tft.setCursor(x, y);tft.setTextColor(0x0000);tft.setTextSize(sz);tft.print(msg);}
This function changes the font of the text. You should add this function and font libraries.for (int j = 0; j < 20; j++) {tft.setCursor(145, 290);int color = tft.color565(r -= 12, g -= 12, b -= 12);tft.setTextColor(color);tft.print("www.Electropeak.com");delay(30);}
First you should convert your image to hex code. Download the software from the following link. if you don’t want to change the settings of the software, you must invert the color of the image and make the image horizontally mirrored and rotate it 90 degrees counterclockwise. Now add it to the software and convert it. Open the exported file and copy the hex code to Arduino IDE. x and y are locations of the image. sx and sy are sizes of image. you can change the color of the image in the last input.
Upload your image and download the converted file that the UTFT libraries can process. Now copy the hex code to Arduino IDE. x and y are locations of the image. sx and sy are size of the image.
In this template, We just used a string and 8 filled circles that change their colors in order. To draw circles around a static point, You can use sin(); and cos(); functions. you should define the PI number. To change colors, you can use color565(); function and replace your RGB code.#include "Adafruit_GFX.h"#include "MCUFRIEND_kbv.h"MCUFRIEND_kbv tft;#include "Fonts/FreeSans9pt7b.h"#include "Fonts/FreeSans12pt7b.h"#include "Fonts/FreeSerif12pt7b.h"#include "FreeDefaultFonts.h"#define PI 3.1415926535897932384626433832795int col[8];void showmsgXY(int x, int y, int sz, const GFXfont *f, const char *msg){int16_t x1, y1;uint16_t wid, ht;tft.setFont(f);tft.setCursor(x, y);tft.setTextColor(0x0000);tft.setTextSize(sz);tft.print(msg);}void setup() {tft.reset();Serial.begin(9600);uint16_t ID = tft.readID();tft.begin(ID);tft.setRotation(1);tft.invertDisplay(true);tft.fillScreen(0xffff);showmsgXY(170, 250, 2, &FreeSans9pt7b, "Loading...");col[0] = tft.color565(155, 0, 50);col[1] = tft.color565(170, 30, 80);col[2] = tft.color565(195, 60, 110);col[3] = tft.color565(215, 90, 140);col[4] = tft.color565(230, 120, 170);col[5] = tft.color565(250, 150, 200);col[6] = tft.color565(255, 180, 220);col[7] = tft.color565(255, 210, 240);}void loop() {for (int i = 8; i > 0; i--) {tft.fillCircle(240 + 40 * (cos(-i * PI / 4)), 120 + 40 * (sin(-i * PI / 4)), 10, col[0]); delay(15);tft.fillCircle(240 + 40 * (cos(-(i + 1)*PI / 4)), 120 + 40 * (sin(-(i + 1)*PI / 4)), 10, col[1]); delay(15);tft.fillCircle(240 + 40 * (cos(-(i + 2)*PI / 4)), 120 + 40 * (sin(-(i + 2)*PI / 4)), 10, col[2]); delay(15);tft.fillCircle(240 + 40 * (cos(-(i + 3)*PI / 4)), 120 + 40 * (sin(-(i + 3)*PI / 4)), 10, col[3]); delay(15);tft.fillCircle(240 + 40 * (cos(-(i + 4)*PI / 4)), 120 + 40 * (sin(-(i + 4)*PI / 4)), 10, col[4]); delay(15);tft.fillCircle(240 + 40 * (cos(-(i + 5)*PI / 4)), 120 + 40 * (sin(-(i + 5)*PI / 4)), 10, col[5]); delay(15);tft.fillCircle(240 + 40 * (cos(-(i + 6)*PI / 4)), 120 + 40 * (sin(-(i + 6)*PI / 4)), 10, col[6]); delay(15);tft.fillCircle(240 + 40 * (cos(-(i + 7)*PI / 4)), 120 + 40 * (sin(-(i + 7)*PI / 4)), 10, col[7]); delay(15);}}
In this template, We converted a.jpg image to.c file and added to the code, wrote a string and used the fade code to display. Then we used scroll code to move the screen left. Download the.h file and add it to the folder of the Arduino sketch.#include "Adafruit_GFX.h" // Core graphics library#include "MCUFRIEND_kbv.h" // Hardware-specific libraryMCUFRIEND_kbv tft;#include "Ard_Logo.h"#define BLACK 0x0000#define RED 0xF800#define GREEN 0x07E0#define WHITE 0xFFFF#define GREY 0x8410#include "Fonts/FreeSans9pt7b.h"#include "Fonts/FreeSans12pt7b.h"#include "Fonts/FreeSerif12pt7b.h"#include "FreeDefaultFonts.h"void showmsgXY(int x, int y, int sz, const GFXfont *f, const char *msg){int16_t x1, y1;uint16_t wid, ht;tft.setFont(f);tft.setCursor(x, y);tft.setTextSize(sz);tft.println(msg);}uint8_t r = 255, g = 255, b = 255;uint16_t color;void setup(){Serial.begin(9600);uint16_t ID = tft.readID();tft.begin(ID);tft.invertDisplay(true);tft.setRotation(1);}void loop(void){tft.invertDisplay(true);tft.fillScreen(WHITE);tft.drawRGBBitmap(100, 50, Logo, 350, 200);delay(1000);tft.setTextSize(2);for (int j = 0; j < 20; j++) {color = tft.color565(r -= 12, g -= 12, b -= 12);tft.setTextColor(color);showmsgXY(95, 280, 1, &FreeSans12pt7b, "ELECTROPEAK PRESENTS");delay(20);}delay(1000);for (int i = 0; i < 480; i++) {tft.vertScroll(0, 480, i);tft.drawFastVLine(i, 0, 320, 0xffff); // vertical linedelay(5);}while (1);}
In this template, We used draw lines, filled circles, and string display functions.#include "Adafruit_GFX.h"#include "MCUFRIEND_kbv.h"MCUFRIEND_kbv tft;uint16_t ox=0,oy=0;int ave=0, avec=0, avet=0;////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////void aveg(void){int z=0;Serial.println(ave);Serial.println(avec);avet=ave/avec;Serial.println(avet);avet=avet*32;for (int i=0; i<24; i++){for (uint16_t a=0; a<3; a++){tft.drawLine(avet+a, z, avet+a, z+10, 0xFB21);} // thickfor (uint16_t a=0; a<2; a++){ tft.drawLine(avet-a, z, avet-a, z+10, 0xFB21);} delay(100); z=z+20; } } ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// void dchart_10x10(uint16_t nx,uint16_t ny) { ave+=nx; avec++; nx=nx*32; ny=ny*48; tft.drawCircle(nx, ny, 10, 0x0517); tft.drawCircle(nx, ny, 9, 0x0517); tft.fillCircle(nx, ny, 7, 0x0517); delay (100); ox=nx; oy=ny; } /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// void dotchart_10x10(uint16_t nx,uint16_t ny) { ave+=nx; avec++; nx=nx*32; ny=ny*48; int plus=0; float fplus=0; int sign=0; int y=0,x=0; y=oy; x=ox; float xmines, ymines; xmines=nx-ox; ymines=ny-oy; if (ox>nx){xmines=ox-nx;sign=1;}elsesign=0;for (int a=0; a<(ny-oy); a++){fplus+=xmines/ymines;plus=fplus;if (sign==1)tft.drawFastHLine(0, y, x-plus, 0xBFDF);elsetft.drawFastHLine(0, y, x+plus, 0xBFDF);y++;delay(5);}for (uint16_t a=0; a<2; a++){tft.drawLine(ox+a, oy, nx+a, ny, 0x01E8);} // thickfor (uint16_t a=0; a<2; a++){tft.drawLine(ox, oy+a, nx, ny+a, 0x01E8);}ox=nx;oy=ny;}////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////void setup() {tft.reset();Serial.begin(9600);uint16_t ID = tft.readID();tft.begin(ID);}void loop() {tft.invertDisplay(true);tft.fillScreen(0xffff);dotchart_10x10(3, 0);dotchart_10x10(2, 1);dotchart_10x10(4, 2);dotchart_10x10(4, 3);dotchart_10x10(5, 4);dotchart_10x10(3, 5);dotchart_10x10(6, 6);dotchart_10x10(7, 7);dotchart_10x10(9, 8);dotchart_10x10(8, 9);dotchart_10x10(10, 10);dchart_10x10(3, 0);dchart_10x10(2, 1);dchart_10x10(4, 2);dchart_10x10(4, 3);dchart_10x10(5, 4);dchart_10x10(3, 5);dchart_10x10(6, 6);dchart_10x10(7, 7);dchart_10x10(9, 8);dchart_10x10(8, 9);dchart_10x10(10, 10);tft.setRotation(1);tft.setTextSize(2);tft.setTextColor(0x01E8);tft.setCursor(20, 20);tft.print("Average");int dl=20;for (int i=0;i<6;i++){for (uint16_t a=0; a<3; a++){tft.drawLine(dl, 40+a, dl+10, 40+a, 0xFB21);}dl+=16;}tft.setRotation(0);aveg();while(1);}
In this template, We added a converted image to code and then used two black and white arcs to create the pointer of volumes. Download the.h file and add it to the folder of the Arduino sketch.#include "Adafruit_GFX.h"#include "MCUFRIEND_kbv.h"MCUFRIEND_kbv tft;#include "Volume.h"#define BLACK 0x0000int a = 0,b = 4000,c = 1000,d = 3000;int s=2000;int j, j2;int i, i2;int White;void setup(){Serial.begin(9600);uint16_t ID = tft.readID();tft.begin(ID);tft.invertDisplay(true);tft.setRotation(1);}void loop(void){tft.invertDisplay(true);tft.fillScreen(BLACK);tft.drawRGBBitmap(0, 0, test, 480, 320);White = tft.color565(255, 255, 255);while(1){if (a < s) {j = 14 * (sin(PI * a / 2000));i = 14 * (cos(PI * a / 2000));j2 = 1 * (sin(PI * a / 2000));i2 = 1 * (cos(PI * a / 2000));tft.drawLine(i2 + 62, j2 + 240, i + 62, j + 240, White);j = 14 * (sin(PI * (a-300) / 2000));i = 14 * (cos(PI * (a-300) / 2000));j2 = 1 * (sin(PI * (a-300) / 2000));i2 = 1 * (cos(PI * (a-300) / 2000));tft.drawLine(i2 + 62, j2 + 240, i + 62, j + 240, 0x0000);tft.fillRect(50, 285, 30, 30, 0x0000);tft.setTextSize(2);tft.setTextColor(0xffff);tft.setCursor(50, 285);tft.print(a / 40); tft.print("%");a++;}if (b < s) {j = 14 * (sin(PI * b / 2000));i = 14 * (cos(PI * b / 2000));j2 = 1 * (sin(PI * b / 2000));i2 = 1 * (cos(PI * b / 2000));tft.drawLine(i2 + 180, j2 + 240, i + 180, j + 240, White);j = 14 * (sin(PI * (b-300) / 2000));i = 14 * (cos(PI * (b-300) / 2000));j2 = 1 * (sin(PI * (b-300) / 2000));i2 = 1 * (cos(PI * (b-300) / 2000));tft.drawLine(i2 + 180, j2 + 240, i + 180, j + 240, 0x0000);tft.fillRect(168, 285, 30, 30, 0x0000);tft.setTextSize(2);tft.setTextColor(0xffff);tft.setCursor(168, 285);tft.print(b / 40); tft.print("%");b++;}if (c < s) {j = 14 * (sin(PI * c / 2000));i = 14 * (cos(PI * c / 2000));j2 = 1 * (sin(PI * c / 2000));i2 = 1 * (cos(PI * c / 2000));tft.drawLine(i2 + 297, j2 + 240, i + 297, j + 240, White);j = 14 * (sin(PI * (c-300) / 2000));i = 14 * (cos(PI * (c-300) / 2000));j2 = 1 * (sin(PI * (c-300) / 2000));i2 = 1 * (cos(PI * (c-300) / 2000));tft.drawLine(i2 + 297, j2 + 240, i + 297, j + 240, 0x0000);tft.fillRect(286, 285, 30, 30, 0x0000);tft.setTextSize(2);tft.setTextColor(0xffff);tft.setCursor(286, 285);tft.print(c / 40); tft.print("%");c++;}if (d < s) { j = 14 * (sin(PI * d / 2000)); i = 14 * (cos(PI * d / 2000)); j2 = 1 * (sin(PI * d / 2000)); i2 = 1 * (cos(PI * d / 2000)); tft.drawLine(i2 + 414, j2 + 240, i + 414, j + 240, White); j = 14 * (sin(PI * (d-300) / 2000)); i = 14 * (cos(PI * (d-300) / 2000)); j2 = 1 * (sin(PI * (d-300) / 2000)); i2 = 1 * (cos(PI * (d-300) / 2000)); tft.drawLine(i2 + 414, j2 + 240, i + 414, j + 240, 0x0000); tft.fillRect(402, 285, 30, 30, 0x0000); tft.setTextSize(2); tft.setTextColor(0xffff); tft.setCursor(402, 285); tft.print(d / 40); tft.print("%"); d++;} if (a > s) {j = 14 * (sin(PI * a / 2000));i = 14 * (cos(PI * a / 2000));j2 = 1 * (sin(PI * a / 2000));i2 = 1 * (cos(PI * a / 2000));tft.drawLine(i2 + 62, j2 + 240, i + 62, j + 240, White);j = 14 * (sin(PI * (a+300) / 2000));i = 14 * (cos(PI * (a+300) / 2000));j2 = 1 * (sin(PI * (a+300) / 2000));i2 = 1 * (cos(PI * (a+300) / 2000));tft.drawLine(i2 + 62, j2 + 240, i + 62, j + 240, 0x0000);tft.fillRect(50, 285, 30, 30, 0x0000);tft.setTextSize(2);tft.setTextColor(0xffff);tft.setCursor(50, 285);tft.print(a / 40); tft.print("%");a--;}if (b > s) {j = 14 * (sin(PI * b / 2000));i = 14 * (cos(PI * b / 2000));j2 = 1 * (sin(PI * b / 2000));i2 = 1 * (cos(PI * b / 2000));tft.drawLine(i2 + 180, j2 + 240, i + 180, j + 240, White);j = 14 * (sin(PI * (b+300) / 2000));i = 14 * (cos(PI * (b+300) / 2000));j2 = 1 * (sin(PI * (b+300) / 2000));i2 = 1 * (cos(PI * (b+300) / 2000));tft.drawLine(i2 + 180, j2 + 240, i + 180, j + 240, 0x0000);tft.fillRect(168, 285, 30, 30, 0x0000);tft.setTextSize(2);tft.setTextColor(0xffff);tft.setCursor(168, 285);tft.print(b / 40); tft.print("%");b--;}if (c > s) {j = 14 * (sin(PI * c / 2000));i = 14 * (cos(PI * c / 2000));j2 = 1 * (sin(PI * c / 2000));i2 = 1 * (cos(PI * c / 2000));tft.drawLine(i2 + 297, j2 + 240, i + 297, j + 240, White);j = 14 * (sin(PI * (c+300) / 2000));i = 14 * (cos(PI * (c+300) / 2000));j2 = 1 * (sin(PI * (c+300) / 2000));i2 = 1 * (cos(PI * (c+300) / 2000));tft.drawLine(i2 + 297, j2 + 240, i + 297, j + 240, 0x0000);tft.fillRect(286, 285, 30, 30, 0x0000);tft.setTextSize(2);tft.setTextColor(0xffff);tft.setCursor(286, 285);tft.print(c / 40); tft.print("%");c--;}if (d > s) {j = 14 * (sin(PI * d / 2000));i = 14 * (cos(PI * d / 2000));j2 = 1 * (sin(PI * d / 2000));i2 = 1 * (cos(PI * d / 2000));tft.drawLine(i2 + 414, j2 + 240, i + 414, j + 240, White);j = 14 * (sin(PI * (d+300) / 2000));i = 14 * (cos(PI * (d+300) / 2000));j2 = 1 * (sin(PI * (d+300) / 2000));i2 = 1 * (cos(PI * (d+300) / 2000));tft.drawLine(i2 + 414, j2 + 240, i + 414, j + 240, 0x0000);tft.fillRect(402, 285, 30, 30, 0x0000);tft.setTextSize(2);tft.setTextColor(0xffff);tft.setCursor(402, 285);tft.print(d / 40); tft.print("%");d--;}}}
In this template, We just display some images by RGBbitmap and bitmap functions. Just make a code for touchscreen and use this template. Download the.h file and add it to folder of the Arduino sketch.#include "Adafruit_GFX.h" // Core graphics library#include "MCUFRIEND_kbv.h" // Hardware-specific libraryMCUFRIEND_kbv tft;#define BLACK 0x0000#define RED 0xF800#define GREEN 0x07E0#define WHITE 0xFFFF#define GREY 0x8410#include "images.h"#include "Fonts/FreeSans9pt7b.h"#include "Fonts/FreeSans12pt7b.h"#include "Fonts/FreeSerif12pt7b.h"#include "FreeDefaultFonts.h"int a = 3000;int b = 4000;int j, j2;int i, i2;void showmsgXY(int x, int y, int sz, const GFXfont *f, const char *msg){int16_t x1, y1;uint16_t wid, ht;// tft.drawFastHLine(0, y, tft.width(), 0xffff);tft.setFont(f);tft.setCursor(x, y);tft.setTextColor(WHITE);tft.setTextSize(sz);tft.print(msg);delay(1000);}void setup(){Serial.begin(9600);uint16_t ID = tft.readID();tft.begin(ID);tft.invertDisplay(true);tft.setRotation(1);}void loop(void){tft.invertDisplay(true);tft.fillScreen(BLACK);tft.drawRGBBitmap(0, 0, test, 480, 320);tft.drawBitmap(20, 20, Line1, 45, 45, 0xffff);//batterytft.drawBitmap(65, 20, Line2, 45, 45, 0xffff);//wifitft.drawBitmap(125, 25, Line3, 45, 45, 0xffff);//mailtft.drawBitmap(185, 25, Line4, 45, 45, 0xffff);//instagramtft.drawBitmap(245, 25, Line6, 45, 45, 0xffff);//powertft.drawBitmap(20, 260, Line5, 45, 45, 0xffff);//twittertft.drawBitmap(410, 140, Line7, 45, 45, 0xffff);//raintft.setTextSize(6);tft.setTextColor(0xffff);tft.setCursor(280, 210);tft.print("20:45");tft.setTextSize(2);tft.setTextColor(0xffff);showmsgXY(330, 280, 1, &FreeSans12pt7b, "Saturday");showmsgXY(300, 305, 1, &FreeSans12pt7b, "6 October 2018");while (1);}
×SPECIAL OFFER (VALID UNTIL NOVEMBER 1ST 2018): If you order the 3.5″ LCD from ElectroPeak, our technical staff will design your desired template for free! Just send an email to info@electropeak.Com containing your order number and requirements ;)

There are many tutorials on Arduino shields for 2.4 inch TFT LCD displays. In this road test I apply different tutorials to check the performance and issues of this specific shield: AZ-Delivery 2.4 inch TFT LCD display with resistive 4-wire touchscreen and an integrated SD card reader.AZ-Delivery 2.4 inch TFT LCD display.
TFT LCD is a variant of a liquid-crystal display (LCD) that uses thin-film-transistor (TFT) technology. That improves image quality, better contrast and addressability.
Depends on the needs of your project. Arduino UNO processor frequency is low. With the Arduino UNO full-color TFT LCDs are suitable to display simple data and commands. The TFT controller used cannot switch internal display RAM, so you can"t use the double buffer technique for animations but still you can only re-draw small sections of screen.
Given the limitations of the Arduino UNO the bigger the display the worse the performance. The size of this display is adequate to meet that compromise between number of pixels, display area and capabilities of the Arduino UNO.
This module consumes most of the resources available in Arduino UNO. This is not a limitation of the module itself. In return, using a parallel interface allows you to quickly update the image. If you want to take advantage of all its functionality (LCD + touch screen + SD card), only pins 0 and 1 (RX and TX, respectively) and pin 19 (A5) remain unused. If the SD card is not used, pins 10, 11, 12 and 13 are additionally available. With a suitable layout, some SPI devices could be connected even if the SD card is used.
The PCB silkscreen indicates the main function of each pin, the labels are easy to read, although it does not show labels for the touch screen pins:Pin 9 - Touch X+ / LCD_D1
The SD card reader is very well located between the USB connector and the power connector, it does not touch either of them as it happens in other lcd tft shield modules and it is easily accessible to insert and remove the SD cards.
You can directly use the shield with any arduino uno. In this case we are using an Arduino UNO that exposes all the pins both on the header and on the board. In such a way that you do not need another shield to access the pins not used by the screen
ShieldCompatible with Arduino. 5V compatible, can be used with 3.3V or 5V logic. On-board 3.3 V (300mA LDO controller). The design is very well thought out and fits Arduino UNO perfectly.
2x74LVC245A Octal Bus Transceiver With 3-State outputs. This octal bus transceiver is designed for 1.65-V to 3.6-V VCC operation. The LVC245A is designed for asynchronous communication between data buses. The device transmits data from the A bus to the B bus or from the B bus to the A bus, depending on the logic level at the direction-control (DIR) input. The output-enable (OE) input can be used to disable the device so the buses effectively are isolated. Inputs can be driven from either 3.3-V or 5-V devices. This feature allows the use of this device as a translator in a mixed 3.3-V/5-V system environment. This chip solves the problem of how to interface 3.3V logic devices to a 5.0V logic chip such as the Arduino. Most 3.3V devices do not like being run with 5V signals and can be damaged or flaky. The 74LVC245 is designed so that even when it runs at 1.8V, it still happily accepts 5V signals in one pin and converts it to a lower logic level on the opposite pin. It has 8 pipes it can convert but it won"t work with bi-directional/pull-up based devices such as I2C or 1-Wire. It does work great for SPI, Serial, Parallel bus, and other logic interfaces.
If you want to take advantage of all its functionality (LCD + touch screen + SD card), only pins 0 and 1 (RX and TX, respectively) and pin 19 (A5) remain unused. If the SD card is not used, pins 10, 11, 12 and 13 are additionally available. With a suitable layout, some SPI devices could be connected even if the SD card is used.
The ILI9341 which can control each pixel with a small number of pins. The shield connects ILI9341"s data pins 0-7 to Arduino digital pins 2-8 (allowing parallel communication, not SPI). ILI"s RESET goes to pin to Arduino analog pin A4.CS (chip select) to A3. RS (CD command/data) to A2. WR and RD to A1 and A0.
Includes a resistive 4-wire touchscreen (touchpad). The touch screen is attached on the surface of the display. Touch screen needs two analog inputs and two digital outputs. It connects through 4 wires, which share arduino pins 8, 9, A2, A3 with the ILI9341 driver. So you can"t write to LCD display and read the touch screen in the same time. I. Driver chip is XPT2046.
The resistive touch screen does not appear to appreciably affect the optical characteristics. Works properly, It takes a little pressure with the stylus for it to respond like in old mobile phones. You notice how it sinks into the screen when you press with the stylus. The stylus that comes with the module makes it easy to use if your interface design uses small controls. Some touch screen libraries offer better accuracy by specifying the resistance of the touch screen in the X direction. Resistance can be easily measured with a multimeter by connecting the test leads to the LCD_D1 - X + and LCD_DS X- terminals. Touch is sensitive to pressure.

This project involves yet another Arduino-compatible display which can be used as an output to display any information in the form of graphics, text or animations. Since this is a 1.3" 240x240 IPS (In-Plane Switching) TFT display module, it does offer a high-resolution colour display with fine graphics, and that is one of the things which I really enjoy about this display. It is also very easy to program, as it runs on the STT789 display, which is helpful to know, as the Adafruit ST7789 library supports this display, and is what we will be using today. The code used below is a fairly complex code at first, which showcases this display"s capabilities and what it can do, in terms of functionality. For the wiring, a 6-pin wiring configuration is used with the SPI interface to the Arduino, which will be shown below. Finally, for this project, here are the components which you will need:1 1.3" 240x240 IPS TFT Display Module
This project is fairly straightforward to set up so make sure you start by unplugging any power source feeding into your Arduino to prevent any shorts while wiring. Firstly, take a jumper wire and connect the GND pin on the display to any of your Arduino"s GND pins and follow that up by connecting the VCC pin from the display to the 3v3 pin of your Arduino to supply a +3.3 volt power supply to the module. +5v will have a possibility to damage the display. Now, for the i2c connections, hook up the SCL (Serial Clock) pin of the display to A13 (analog pin 13) on the Arduino and the SDA (Serial Data) pin to A11 (analog pin 11). For the RES (Reset) pin, connect it up to A8 (analog pin 8) as well as the DC (Data/Command) pin to A9 (analog pin 9). The hardware part is finally done!
This code may seem slightly intimidating at first, due to its length and much newer functions, but once it is broken down, it isn"t so hard anymore. In the first three lines, we declare libraries for running this display, the graphics used, and for the interface used, which is the SPI interface. In the next three lines, the RST (Reset) and DC (Data/Command) pins are defined, which are connected to A8 (analog pin 8) and A9 (analog pin 9). In the next line, we initialize the Adafruit ST7789 library for use with this display and we follow that by defining the value of pi as a float variable in that next line. We will be using this float variable later on for graphics and calculations needed. Thevoid setupsection is now here where we first start by begining serial communication with a baud rate of 9600 bauds and printing a test message which is "Hello! ST7789 TFT Test!". In regards to the display, we address that our display module is of 240x240 resolution and we set the rotation of our display in the next line. If your display is flipped, removetft.setRotation(2). From there, we print the text "Initialized" as our display is now correctly set up. After that, we count up the seconds from the startup with themillis()function and store it in an unsigned 16-bit integer, namedtime, for use later. We then fill up the TFT screen with a black colour. Since we already started the stopwatch which counts up, we can always reset the stopwatch back to zero by using subtracting thetimefunction with themillis().To end off this section, we set a delay for 500 milliseconds before moving on. This section onwards will only be for the animations, graphics and images displayed on the screen, and we start off by filling the screen with a black background and writing some text with a white colour before a 1-second delay. Proceeding that, we execute a print test which basically is already programmed to print out a set of text in different font colours and sizes. We end this test by setting a delay for 4 seconds. From this point, the rest of the code is responsible for printing out the different graphics, which can be composed of shapes, pixels and text. All the different graphics and its individual code are mentioned at the end of the code so I recommend really going through this program to learn all the commands, which can help you build your own demo code, even with your own personal images being displayed. This project is now done!
![]()
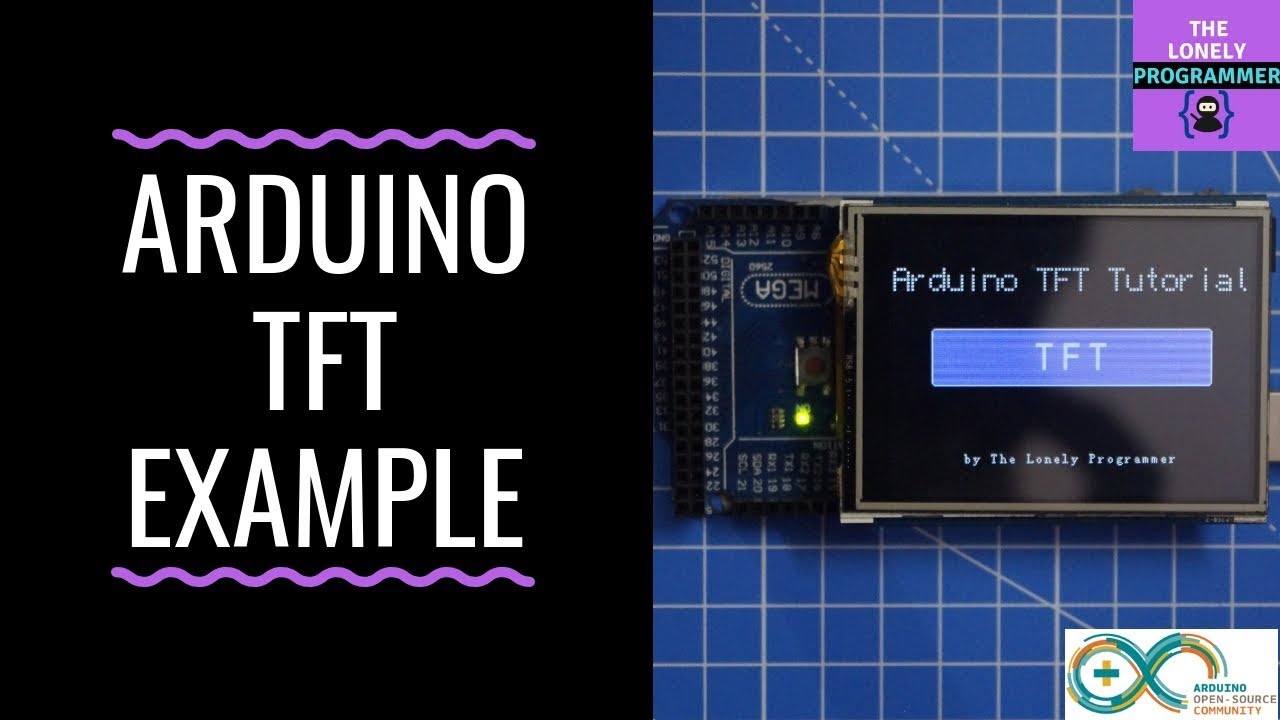
In this Arduino touch screen tutorial we will learn how to use TFT LCD Touch Screen with Arduino. You can watch the following video or read the written tutorial below.
As an example I am using a 3.2” TFT Touch Screen in a combination with a TFT LCD Arduino Mega Shield. We need a shield because the TFT Touch screen works at 3.3V and the Arduino Mega outputs are 5 V. For the first example I have the HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor, then for the second example an RGB LED with three resistors and a push button for the game example. Also I had to make a custom made pin header like this, by soldering pin headers and bend on of them so I could insert them in between the Arduino Board and the TFT Shield.
Here’s the circuit schematic. We will use the GND pin, the digital pins from 8 to 13, as well as the pin number 14. As the 5V pins are already used by the TFT Screen I will use the pin number 13 as VCC, by setting it right away high in the setup section of code.
I will use the UTFT and URTouch libraries made by Henning Karlsen. Here I would like to say thanks to him for the incredible work he has done. The libraries enable really easy use of the TFT Screens, and they work with many different TFT screens sizes, shields and controllers. You can download these libraries from his website, RinkyDinkElectronics.com and also find a lot of demo examples and detailed documentation of how to use them.
After we include the libraries we need to create UTFT and URTouch objects. The parameters of these objects depends on the model of the TFT Screen and Shield and these details can be also found in the documentation of the libraries.
So now I will explain how we can make the home screen of the program. With the setBackColor() function we need to set the background color of the text, black one in our case. Then we need to set the color to white, set the big font and using the print() function, we will print the string “Arduino TFT Tutorial” at the center of the screen and 10 pixels down the Y – Axis of the screen. Next we will set the color to red and draw the red line below the text. After that we need to set the color back to white, and print the two other strings, “by HowToMechatronics.com” using the small font and “Select Example” using the big font.
In order the code to work and compile you will have to include an addition “.c” file in the same directory with the Arduino sketch. This file is for the third game example and it’s a bitmap of the bird. For more details how this part of the code work you can check my particular tutorial. Here you can download that file:
The ST7789 TFT module contains a display controller with the same name: ST7789. It’s a color display that uses SPI interface protocol and requires 3, 4 or 5 control pins, it’s low cost and easy to use. This display is an IPS display, it comes in different sizes (1.3″, 1.54″ …) but all of them should have the same resolution of 240×240 pixel, this means it has 57600 pixels. This module works with 3.3V only and it doesn’t support 5V (not 5V tolerant).
As mentioned above, the ST7789 TFT display controller works with 3.3V only (power supply and control lines). The display module is supplied with 3.3V (between VCC and GND) which comes from the Arduino board.
To connect the Arduino to the display module, I used voltage divider for each line which means there are 4 voltage dividers. Each voltage divider consists of 2.2k and 3.3k resistors, this drops the 5V into 3V which is sufficient.
The first library is a driver for the ST7789 TFT display which can be installed from Arduino IDE library manager (Sketch —> Include Library —> Manage Libraries …, in the search box write “st7789” and install the one from Adafruit).

In this guide we’re going to show you how you can use the 1.8 TFT display with the Arduino. You’ll learn how to wire the display, write text, draw shapes and display images on the screen.
The 1.8 TFT is a colorful display with 128 x 160 color pixels. The display can load images from an SD card – it has an SD card slot at the back. The following figure shows the screen front and back view.
This module uses SPI communication – see the wiring below . To control the display we’ll use the TFT library, which is already included with Arduino IDE 1.0.5 and later.
The TFT display communicates with the Arduino via SPI communication, so you need to include the SPI library on your code. We also use the TFT library to write and draw on the display.
The 1.8 TFT display can load images from the SD card. To read from the SD card you use the SD library, already included in the Arduino IDE software. Follow the next steps to display an image on the display:
Note: some people find issues with this display when trying to read from the SD card. We don’t know why that happens. In fact, we tested a couple of times and it worked well, and then, when we were about to record to show you the final result, the display didn’t recognized the SD card anymore – we’re not sure if it’s a problem with the SD card holder that doesn’t establish a proper connection with the SD card. However, we are sure these instructions work, because we’ve tested them.
In this guide we’ve shown you how to use the 1.8 TFT display with the Arduino: display text, draw shapes and display images. You can easily add a nice visual interface to your projects using this display.

No! For about the price of a familiar 2x16 LCD, you get a high resolution TFT display. For as low as $4 (shipping included!), it"s possible to buy a small, sharp TFT screen that can be interfaced with an Arduino. Moreover, it can display not just text, but elaborate graphics. These have been manufactured in the tens of millions for cell phones and other gadgets and devices, and that is the reason they are so cheap now. This makes it feasible to reuse them to give our electronic projects colorful graphic displays.
There are quite a number of small cheap TFT displays available on eBay and elsewhere. But, how is it possible to determine which ones will work with an Arduino? And what then? Here is the procedure:ID the display. With luck, it will have identifying information printed on it. Otherwise, it may involve matching its appearance with a picture on Google images. Determine the display"s resolution and the driver chip.
Find out whether there is an Arduino driver available. Google is your friend here. Henning Karlsen"s UTFT library works with many displays. (http://www.rinkydinkelectronics.com/library.php?i...)
Download and install the driver library. On a Linux machine, as root, copy the library archive file to the /usr/share/arduino/libraries directory and untar or unzip it.
Load an example sketch into the Arduino IDE, and then upload it to the attached Arduino board with wired-up TFT display. With luck, you will see text and/or graphics.
We"ll begin with a simple one. The ILI9163 display has a resolution of 128 x 128 pixels. With 8 pins in a single row, it works fine with a standard Arduino UNO or with a Mega. The hardware hookup is simple -- only 8 connections total! The library put together by a smart fella, by the name of sumotoy, makes it possible to display text in multiple colors and to draw lines.
Note that these come in two varieties, red and black. The red ones may need a bit of tweaking to format the display correctly -- see the comments in the README.md file. The TFT_ILI9163C.h file might need to be edited.
It is 5-volt friendly, since there is a 74HC450 IC on the circuit board that functions as a level shifter. These can be obtained for just a few bucks on eBay and elsewhere, for example -- $3.56 delivered from China. It uses Henning Karlsen"s UTFT library, and it does a fine job with text and graphics. Note that due to the memory requirement of UTFT, this display will work with a standard UNO only with extensive tweaking -- it would be necessary to delete pretty much all the graphics in the sketch, and just stay with text.
This one is a 2.2" (diagonal) display with 176x220 resolution and parallel interface. It has a standard ("Intel 8080") parallel interface, and works in both 8-bit and 16-bit modes. It uses the S6D0164 driver in Henning Karlsen"s UTFT library, and because of the memory requirements of same, works only with an Arduino Mega or Due. It has an SD card slot on its back
This one is a bit of an oddball. It"s a clone of the more common HY-TFT240, and it has two rows of pins, set at right angles to one another. To enable the display in 8-bit mode, only the row of pins along the narrow edge is used. The other row is for the SD card socket on the back, and for 16-bit mode. To interface with an Arduino ( Mega or Due), it uses Henning Karlsen"s UTFT library, and the driver is ILI9325C. Its resolution is 320x240 (hires!) and it incorporates both a touch screen and an SD card slot.
Having determined that a particular TFT display will work with the Arduino, it"s time to think about a more permanent solution -- constructing hard-wired and soldered plug-in boards. To make things easier, start with a blank protoshield as a base, and add sockets for the TFT displays to plug into. Each socket row will have a corresponding row next to it, with each individual hole "twinned" to the adjacent hole in the adjoining row by solder bridges, making them accessible to jumpers to connect to appropriate Arduino pins. An alternative is hard-wiring the socket pins to the Arduino pins, which is neater but limits the versatility of the board.
In step 5, you mention that the TFT01 display can"t be used with the UTFT library on an Arduino Uno because of its memory requirements. It can - all you have to do is edit memorysaver.h and disable any display models you"re not using.
I think you should add a disclaimer that the code might make the Arduino Uno unprogrammable afterward (due to use up the two 0 and 1 pin) and link to how to fix it: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/5290428/how-to-reset-an-arduino-board/8453576?sfb=2#84535760
Tho I realize this is quickly becoming legacy hardware, these 8,16 bit parallel spi with 4 wire controller 3.2in Taft touch display 240x380. It has become very inexpensive with ally of back stock world wide so incorporating them into any project is easier then ever. Sorry to my question. I’m having difficulty finding wiring solution for this lcd. It is a sd1289 3.3 and 5v ,40 pin parallel 8,16 bit. I do not want to use a extra shield,hat or cape or adapter. But there’s a lot of conflicting info about required lvl shifters for this model any help or links to info would be great .. thank you. I hope I gave enough information to understand what I’m adoing
#1 you need a data sheet for the display and pinout and the i/o board attached to the cable.Than before you buy check for a driver for this chip Raydium/RM69071.if no driver lib are you able to write one and do you have the necessary tools to work on this scale to wire it up ..if you answer no than search for an arduino ready product.WCH0
hooking up and adding a lib is no piece of cake insure the screen you buy is arduino ready and sold by a reputable shop with step by step directions...WCH0
I"m sorry that I can"t help you with this. You"ll have to do your own research. See if you can identify the chipset and find out if there"s an Arduino driver for it.0

In this article, you will learn how to use TFT LCDs by Arduino boards. From basic commands to professional designs and technics are all explained here.
There are several components to achieve this. LEDs, 7-segments, Character and Graphic displays, and full-color TFT LCDs. The right component for your projects depends on the amount of data to be displayed, type of user interaction, and processor capacity.
TFT LCD is a variant of a liquid-crystal display (LCD) that uses thin-film-transistor (TFT) technology to improve image qualities such as addressability and contrast. A TFT LCD is an active matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven LCDs with a few segments.
In Arduino-based projects, the processor frequency is low. So it is not possible to display complex, high definition images and high-speed motions. Therefore, full-color TFT LCDs can only be used to display simple data and commands.
There are several components to achieve this. LEDs, 7-segments, Character and Graphic displays, and full-color TFT LCDs. The right component for your projects depends on the amount of data to be displayed, type of user interaction, and processor capacity.
TFT LCD is a variant of a liquid-crystal display (LCD) that uses thin-film-transistor (TFT) technology to improve image qualities such as addressability and contrast. A TFT LCD is an active matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven LCDs with a few segments.
In Arduino-based projects, the processor frequency is low. So it is not possible to display complex, high definition images and high-speed motions. Therefore, full-color TFT LCDs can only be used to display simple data and commands.
After choosing the right display, It’s time to choose the right controller. If you want to display characters, tests, numbers and static images and the speed of display is not important, the Atmega328 Arduino boards (such as Arduino UNO) are a proper choice. If the size of your code is big, The UNO board may not be enough. You can use Arduino Mega2560 instead. And if you want to show high resolution images and motions with high speed, you should use the ARM core Arduino boards such as Arduino DUE.
In electronics/computer hardware a display driver is usually a semiconductor integrated circuit (but may alternatively comprise a state machine made of discrete logic and other components) which provides an interface function between a microprocessor, microcontroller, ASIC or general-purpose peripheral interface and a particular type of display device, e.g. LCD, LED, OLED, ePaper, CRT, Vacuum fluorescent or Nixie.
The LCDs manufacturers use different drivers in their products. Some of them are more popular and some of them are very unknown. To run your display easily, you should use Arduino LCDs libraries and add them to your code. Otherwise running the display may be very difficult. There are many free libraries you can find on the internet but the important point about the libraries is their compatibility with the LCD’s driver. The driver of your LCD must be known by your library. In this article, we use the Adafruit GFX library and MCUFRIEND KBV library and example codes. You can download them from the following links.
You must add the library and then upload the code. If it is the first time you run an Arduino board, don’t worry. Just follow these steps:Go to www.arduino.cc/en/Main/Software and download the software of your OS. Install the IDE software as instructed.
First you should convert your image to hex code. Download the software from the following link. if you don’t want to change the settings of the software, you must invert the color of the image and make the image horizontally mirrored and rotate it 90 degrees counterclockwise. Now add it to the software and convert it. Open the exported file and copy the hex code to Arduino IDE. x and y are locations of the image. sx and sy are sizes of image. you can change the color of the image in the last input.
Upload your image and download the converted file that the UTFT libraries can process. Now copy the hex code to Arduino IDE. x and y are locations of the image. sx and sy are size of the image.
In this template, We converted a .jpg image to .c file and added to the code, wrote a string and used the fade code to display. Then we used scroll code to move the screen left. Download the .h file and add it to the folder of the Arduino sketch.
In this template, We used sin(); and cos(); functions to draw Arcs with our desired thickness and displayed number by text printing function. Then we converted an image to hex code and added them to the code and displayed the image by bitmap function. Then we used draw lines function to change the style of the image. Download the .h file and add it to the folder of the Arduino sketch.
In this template, We added a converted image to code and then used two black and white arcs to create the pointer of volumes. Download the .h file and add it to the folder of the Arduino sketch.
In this template, We added a converted image and use the arc and print function to create this gauge. Download the .h file and add it to folder of the Arduino sketch.
while (a < b) { Serial.println(a); j = 80 * (sin(PI * a / 2000)); i = 80 * (cos(PI * a / 2000)); j2 = 50 * (sin(PI * a / 2000)); i2 = 50 * (cos(PI * a / 2000)); tft.drawLine(i2 + 235, j2 + 169, i + 235, j + 169, tft.color565(0, 255, 255)); tft.fillRect(200, 153, 75, 33, 0x0000); tft.setTextSize(3); tft.setTextColor(0xffff); if ((a/20)>99)
while (b < a) { j = 80 * (sin(PI * a / 2000)); i = 80 * (cos(PI * a / 2000)); j2 = 50 * (sin(PI * a / 2000)); i2 = 50 * (cos(PI * a / 2000)); tft.drawLine(i2 + 235, j2 + 169, i + 235, j + 169, tft.color565(0, 0, 0)); tft.fillRect(200, 153, 75, 33, 0x0000); tft.setTextSize(3); tft.setTextColor(0xffff); if ((a/20)>99)
In this template, We display simple images one after each other very fast by bitmap function. So you can make your animation by this trick. Download the .h file and add it to folder of the Arduino sketch.
In this template, We just display some images by RGBbitmap and bitmap functions. Just make a code for touchscreen and use this template. Download the .h file and add it to folder of the Arduino sketch.

Hi guys, welcome to today’s tutorial. Today, we will look on how to use the 1.8″ ST7735 colored TFT display with Arduino. The past few tutorials have been focused on how to use the Nokia 5110 LCD display extensively but there will be a time when we will need to use a colored display or something bigger with additional features, that’s where the 1.8″ ST7735 TFT display comes in.
The ST7735 TFT display is a 1.8″ display with a resolution of 128×160 pixels and can display a wide range of colors ( full 18-bit color, 262,144 shades!). The display uses the SPI protocol for communication and has its own pixel-addressable frame buffer which means it can be used with all kinds of microcontroller and you only need 4 i/o pins. To complement the display, it also comes with an SD card slot on which colored bitmaps can be loaded and easily displayed on the screen.
The schematics for this project is fairly easy as the only thing we will be connecting to the Arduino is the display. Connect the display to the Arduino as shown in the schematics below.
Due to variation in display pin out from different manufacturers and for clarity, the pin connection between the Arduino and the TFT display is mapped out below:
We will use two libraries from Adafruit to help us easily communicate with the LCD. The libraries include the Adafruit GFX library which can be downloaded here and the Adafruit ST7735 Library which can be downloaded here.
We will use two example sketches to demonstrate the use of the ST7735 TFT display. The first example is the lightweight TFT Display text example sketch from the Adafruit TFT examples. It can be accessed by going to examples -> TFT -> Arduino -> TFTDisplaytext. This example displays the analog value of pin A0 on the display. It is one of the easiest examples that can be used to demonstrate the ability of this display.
The second example is the graphics test example from the more capable and heavier Adafruit ST7735 Arduino library. I will explain this particular example as it features the use of the display for diverse purposes including the display of text and “animated” graphics. With the Adafruit ST7735 library installed, this example can be accessed by going to examples -> Adafruit ST7735 library -> graphics test.
The first thing, as usual, is to include the libraries to be used after which we declare the pins on the Arduino to which our LCD pins are connected to. We also make a slight change to the code setting reset pin as pin 8 and DC pin as pin 9 to match our schematics.
Next, we create an object of the library with the pins to which the LCD is connected on the Arduino as parameters. There are two options for this, feel free to choose the most preferred.
The complete code for this is available under the libraries example on the Arduino IDE. Don’t forget to change the DC and the RESET pin configuration in the code to match the schematics.
Uploading the code to the Arduino board brings a flash of different shapes and text with different colors on the display. I captured one and its shown in the image below.

The TFT configuration (user setup) can now be included inside an Arduino IDE sketch providing the instructions in the example Generic->Sketch_with_tft_setup are followed. See ReadMe tab in that sketch for the instructions. If the setup is not in the sketch then the library settings will be used. This means that "per project" configurations are possible without modifying the library setup files. Please note that ALL the other examples in the library will use the library settings unless they are adapted and the "tft_setup.h" header file included. Note: there are issues with this approach, #2007 proposes an alternative method.
Smooth fonts can now be rendered direct to the TFT with very little flicker for quickly changing values. This is achieved by a line-by-line and block-by-block update of the glyph area without drawing pixels twice. This is a "breaking" change for some sketches because a new true/false parameter is needed to render the background. The default is false if the parameter is missing, Examples:
Frank Boesing has created an extension library for TFT_eSPI that allows a large range of ready-built fonts to be used. Frank"s library (adapted to permit rendering in sprites as well as TFT) can be downloaded here. More than 3300 additional Fonts are available here. The TFT_eSPI_ext library contains examples that demonstrate the use of the fonts.
Users of PowerPoint experienced with running macros may be interested in the pptm sketch generator here, this converts graphics and tables drawn in PowerPoint slides into an Arduino sketch that renders the graphics on a 480x320 TFT. This is based on VB macros created by Kris Kasprzak here.
The library now supports the Raspberry Pi Pico with both the official Arduino board package and the one provided by Earle Philhower. The setup file "Setup60_RP2040_ILI9341.h" has been used for tests with an ILI9341 display. At the moment only SPI interface displays have been tested. SPI port 0 is the default but SPI port 1 can be specifed in the setup file if those SPI pins are used.
The library now provides a "viewport" capability. See "Viewport_Demo" and "Viewport_graphicstest" examples. When a viewport is defined graphics will only appear within that window. The coordinate datum by default moves to the top left corner of the viewport, but can optionally remain at top left corner of TFT. The GUIslice library will make use of this feature to speed up the rendering of GUI objects (see #769).
An Arduino IDE compatible graphics and fonts library for 32 bit processors. The library is targeted at 32 bit processors, it has been performance optimised for STM32, ESP8266 and ESP32 types. The library can be loaded using the Arduino IDE"s Library Manager. Direct Memory Access (DMA) can be used with the ESP32, RP2040 and STM32 processors with SPI interface displays to improve rendering performance. DMA with a parallel interface is only supported with the RP2040.
"Four wire" SPI and 8 bit parallel interfaces are supported. Due to lack of GPIO pins the 8 bit parallel interface is NOT supported on the ESP8266. 8 bit parallel interface TFTs (e.g. UNO format mcufriend shields) can used with the STM32 Nucleo 64/144 range or the UNO format ESP32 (see below for ESP32).
The library supports some TFT displays designed for the Raspberry Pi (RPi) that are based on a ILI9486 or ST7796 driver chip with a 480 x 320 pixel screen. The ILI9486 RPi display must be of the Waveshare design and use a 16 bit serial interface based on the 74HC04, 74HC4040 and 2 x 74HC4094 logic chips. Note that due to design variations between these displays not all RPi displays will work with this library, so purchasing a RPi display of these types solely for use with this library is not recommended.
Some displays permit the internal TFT screen RAM to be read, a few of the examples use this feature. The TFT_Screen_Capture example allows full screens to be captured and sent to a PC, this is handy to create program documentation.
The library includes a "Sprite" class, this enables flicker free updates of complex graphics. Direct writes to the TFT with graphics functions are still available, so existing sketches do not need to be changed.
The "Animated_dial" example shows how dials can be created using a rotated Sprite for the needle. To run this example the TFT interface must support reading from the screen RAM (not all do). The dial rim and scale is a jpeg image, created using a paint program.
The XPT2046 touch screen controller is supported for SPI based displays only. The SPI bus for the touch controller is shared with the TFT and only an additional chip select line is needed. This support will eventually be deprecated when a suitable touch screen library is available.
The library supports SPI overlap on the ESP8266 so the TFT screen can share MOSI, MISO and SCLK pins with the program FLASH, this frees up GPIO pins for other uses. Only one SPI device can be connected to the FLASH pins and the chips select for the TFT must be on pin D3 (GPIO0).
Configuration of the library font selections, pins used to interface with the TFT and other features is made by editing the User_Setup.h file in the library folder, or by selecting your own configuration in the "User_Setup_Selet,h" file. Fonts and features can easily be enabled/disabled by commenting out lines.
It would be possible to compress the vlw font files but the rendering performance to a TFT is still good when storing the font file(s) in SPIFFS, LittleFS or FLASH arrays.
Anti-aliased fonts can also be drawn over a gradient background with a callback to fetch the background colour of each pixel. This pixel colour can be set by the gradient algorithm or by reading back the TFT screen memory (if reading the display is supported).
Unfortunately the typical UNO/mcufriend TFT display board maps LCD_RD, LCD_CS and LCD_RST signals to the ESP32 analogue pins 35, 34 and 36 which are input only. To solve this I linked in the 3 spare pins IO15, IO33 and IO32 by adding wires to the bottom of the board as follows:
If you load a new copy of TFT_eSPI then it will overwrite your setups if they are kept within the TFT_eSPI folder. One way around this is to create a new folder in your Arduino library folder called "TFT_eSPI_Setups". You then place your custom setup.h files in there. After an upgrade simply edit the User_Setup_Select.h file to point to your custom setup file e.g.:
The library was intended to support only TFT displays but using a Sprite as a 1 bit per pixel screen buffer permits support for the Waveshare 2 and 3 colour SPI ePaper displays. This addition to the library is experimental and only one example is provided. Further examples will be added.

Spice up your Arduino project with a beautiful large touchscreen display shield with built in microSD card connection. This TFT display is big (3.5" diagonal) bright (6 white-LED backlight) and colorful (18-bit 262,000 different shades)! 320x480 pixels with individual pixel control. As a bonus, this display has a optional resistive touch panel with controller XPT2046 attached by default and a optional capacitive touch panel with controller FT6236 attached by default, so you can detect finger presses anywhere on the screen and doesn"t require pressing down on the screen with a stylus and has nice glossy glass cover.
The shield is fully assembled, tested and ready to go. No wiring, no soldering! Simply plug it in and load up our library - you"ll have it running in under 10 minutes! Works best with any classic Arduino (Due/Mega 2560).
Of course, we wouldn"t just leave you with a datasheet and a "good luck!" - we"ve written a full open source graphics library at the bottom of this page that can draw pixels, lines, rectangles, circles and text. We also have a touch screen library that detects x,y and z (pressure) and example code to demonstrate all of it. The code is written for Arduino but can be easily ported to your favorite microcontroller!
If you"ve had a lot of Arduino DUEs go through your hands (or if you are just unlucky), chances are you’ve come across at least one that does not start-up properly.The symptom is simple: you




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey