lcd panel technology explained in stock
Today"s market for monitors is, at a glance, simple. Everyone has settled on LCD displays as the technology of choice, and most displays have roughly the same appearance.
As Tina recently explained, however, things become more complex once you start looking at the details. In fact, even after you"ve considered contrast, connections, display resolutions and other factors you still have one other choice to consider - the display panel technology you"d prefer.
Modern LCD monitors are extremely thin, as if they are made out of a single piece of material. They are, however, made up of multiple components including the display panel. The display panel is a flat sheet of material that contains liquid crystals that react in different ways when electricity is applied.
Your display panel does not work alone. A backlight shines through the panel in order to create a viewable image. Think of it like a kaleidoscope - if you view it in a brightly lit room you"ll see beautiful patterns and colors, but if you try to use it in a dark room you"ll see nothing at all. Today we"re just talking about the kaleidoscope itself and not the light shining through it.
There is a very good chance that you are reading this article on a LCD monitor equipped with a TN display panel. That"s because TN display panels are by far the most popular in the world. They"re found in virtually all laptops and a large majority of desktop monitors.
The term TN stands for Twisted Nematic, the technical name for the liquid crystal technology the panel uses. The crystals in a TN panel like to do the twist when electrical current is applied. The image on a TN panel is controlled by turning up the juice and letting the crystals twist away - or stepping off the juice and letting them calm down.
While popular, TN display panels aren"t the best. They can"t display as wide a range of color as some other technologies and the formation of the crystals causes issues when you attempt to view the display from an off angle - an effect you"d probably noticed on your own monitor before.
TN display panels have low response times, however, which means they can refresh the image displayed quickly. This is a trait that PC gamers often appreciate. Also, TN display panels are the least expensive currently available. You can find TN display panels everywhere - indeed, most brick-and-mortar stores stock nothing but monitors with TN display panels.
Efforts to produce a broader range of colors and better viewing angles resulted in the IPS display, which is the second most popular display panel today. There are two major technical differences that make IPS display panels superior. The crystals in the panel are aligned differently, and each crystal has electricity applied through both ends rather than just one.
These differences give IPS panels the ability to display images in gorgeous detail. IPS panels can reproduce full 8-bit colorand most companies producing IPS panel monitors proudly boast about their monitor"s ability to display a wide color gamut. This is incredibly important to those who digitally edit photos and art. Monitors with IPS display panels also provide wider viewing angles, which means you don"t have to be viewing your monitor dead-on to receive decent image quality.
IPS display panels do have slower response times than TN panels, and some larger monitors with IPS panels aren"t great for gaming due to this trait. The biggest downside, however, is price - these panels are always more expensive, and as a result even a 24" IPS display is usually over $400. Dell"s UltraSharp series is the most well known line of IPS panel monitors in North America. You can also find IPS display panels in the iMac, iPad and the iPhone 4.
If you"re shopping for a monitor you will almost certainly end up choosing between a TN or IPS panel. However, there are a few other panel technologies available. These include MVA and PVA, two related technologies.
You won"t find these technologies frequently, and they"re usually in extremely expensive monitors that are designed for professionals and digital artists. MVA and PVA monitors offer full 8-bit color as well (indeed, a few models claim 10-bit or 16-bit color) and these technologies are generally known to provide the widest viewing angles and deepest black levels of any display technology (although the specifics depend on the individual monitor). The downsides are similar to IPS panels - response times are often a bit high and the prices are very high.
I generally recommend monitors with IPS display panels if you can afford them. Monitors tend to last a long time, so laying down extra cash for a better monitor makes sense. If you have any tips or questions relating to display panel technology feel free to leave them in the comments!
Important technical improvements of LCD, such as LED backlighting and wide viewing Angle, are directly related to LCD. And account for an LCD display 80% of the cost of the LCD panel, enough to show that the LCD panel is the core part of the entire display, the quality of the LCD panel, can be said to directly determine the quality of an LCD display.
The production of civil LCD displays is just an assembly process. The LCD panel, the main control circuit, shell, and other parts of the main assembly, basically will not have too complex technical problems.
Does this mean that LCDS are low-tech products? In fact, it is not. The production and manufacturing process of the LCD panels is very complicated, requiring at least 300 process processes. The whole process needs to be carried out in a dust-free environment and with precise technology.
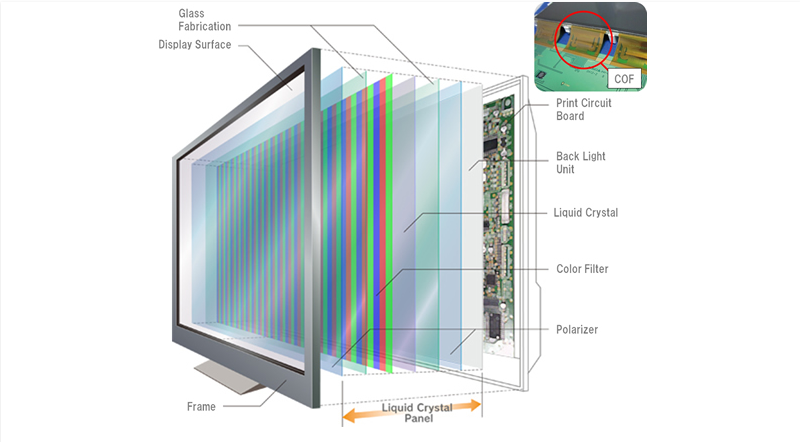
The general structure of the LCD panel is not very complex, now the structure of the LCD panel is divided into two parts: the LCD panel and the backlight system.
Due to the LCD does not shine, so you need to use another light source to illuminate, the function of the backlight system is to this, but currently used CCFL lamp or LED backlight, don’t have the characteristics of the surface light source, so you need to guide plate, spreadsheet components, such as linear or point sources of light evenly across the surface, in order to make the entire LCD panel on the differences of luminous intensity is the same, but it is very difficult, to achieve the ideal state can be to try to reduce brightness non-uniformity, the backlight system has a lot to the test of design and workmanship.
In addition, there is a driving IC and printed circuit board beside the LCD panel, which is mainly used to control the rotation of LCD molecules in the LCD panel and the transmission of display signals. The LCD plate is thin and translucent without electricity. It is roughly shaped like a sandwich, with an LCD sandwiched between a layer of TFT glass and a layer of colored filters.
LCD with light refraction properties of solid crystals, with fluid flow characteristics at the same time, under the drive of the electrode, can be arranged in a way that, in accordance with the master want to control the strength of the light through, and then on the color filter, through the red, green, blue three colors of each pixel toning, eventually get the full-screen image.
According to the functional division, the LCD panel can be divided into the LCD panel and the backlight system. However, to produce an LCD panel, it needs to go through three complicated processes, namely, the manufacturing process of the front segment Array,the manufacturing process of the middle segment Cell, and the assembly of the rear segment module. Today we will be here, for you in detail to introduce the production of the LCD panel manufacturing process.
The manufacturing process of the LCD panel Array is mainly composed of four parts: film, yellow light, etch and peel film. If we just look at it in this way, many netizens do not understand the specific meaning of these four steps and why they do so.
First of all, the motion and arrangement of LCD molecules need electrons to drive them. Therefore, on the TFT glass, the carrier of LCD, there must be conductive parts to control the motion of LCD. In this case, we use ITO (Indium Tin Oxide) to do this.ITO is transparent and also acts as a thin-film conductive crystal so that it doesn’t block the backlight.
The different arrangement of LCD molecules and the rapid motion change can ensure that each pixel displays the corresponding color accurately and the image changes accurately and quickly, which requires the precision of LCD molecule control.ITO film needs special treatment, just like printing the circuit on the PCB board, drawing the conductive circuit on the whole LCD board.
This completes the previous Array process. It is not difficult to see from the whole process that ITO film is deposited, photoresist coated, exposed, developed, and etched on TFT glass, and finally, ITO electrode pattern designed in the early stage is formed on TFT glass to control the movement of LCD molecules on the glass. The general steps of the whole production process are not complicated, but the technical details and precautions are very complicated, so we will not introduce them here. Interested friends can consult relevant materials by themselves.
The glass that the LCD board uses makes a craft also very exquisite. (The manufacturing process flow of the LCD display screen)At present, the world’s largest LCD panel glass, mainly by the United States Corning, Japan Asahi glass manufacturers, located in the upstream of the production of LCD panel, these manufacturers have mastered the glass production technology patents. A few months ago, the earthquake caused a corning glass furnace shutdown incident, which has caused a certain impact on the LCD panel industry, you can see its position in the industry.
As mentioned earlier, the LCD panel is structured like a sandwich, with an LCD sandwiched between the lower TFT glass and the upper color filter. The terminal Cell process in LCD panel manufacturing involves the TFT glass being glued to the top and bottom of a colored filter, but this is not a simple bonding process that requires a lot of technical detail.
As you can see from the figure above, the glass is divided into 6 pieces of the same size. In other words, the LCD made from this glass is finally cut into 6 pieces, and the size of each piece is the final size. When the glass is cast, the specifications and sizes of each glass have been designed in advance.
Directional friction:Flannelette material is used to rub the surface of the layer in a specific direction so that the LCD molecules can be arranged along the friction direction of the aligned layer in the future to ensure the consistency of the arrangement of LCD molecules. After the alignment friction, there will be some contaminants such as flannelette thread, which need to be washed away through a special cleaning process.
After the TFT glass substrate is cleaned, a sealant coating is applied to allow the TFT glass substrate to be bonded to the color filter and to prevent LCD outflow.
Finally, the conductive adhesive is applied to the frame in the bonding direction of the glass of the color filter to ensure that external electrons can flow into the LCD layer. Then, according to the bonding mark on the TFT glass substrate and the color filter, two pieces of glass are bonded together, and the bonding material is solidified at high temperatures to make the upper and lower glasses fit statically.
Color filters are very important components of LCD panels. Manufacturers of color filters, like glass substrate manufacturers, are upstream of LCD panel manufacturers. Their oversupply or undersupply can directly affect the production schedule of LCD panels and indirectly affect the end market.
As can be seen from the above figure, each LCD panel is left with two edges after cutting. What is it used for? You can find the answer in the later module process
Finally, a polarizer is placed on both sides of each LCD substrate, with the horizontal polarizer facing outwards and the vertical polarizer facing inwards.
When making LCD panel, must up and down each use one, and presents the alternating direction, when has the electric field and does not have the electric field, causes the light to produce the phase difference and to present the light and dark state, uses in the display subtitle or the pattern.
The rear Module manufacturing process is mainly the integration of the drive IC pressing of the LCD substrate and the printed circuit board. This part can transmit the display signal received from the main control circuit to the drive IC to drive the LCD molecules to rotate and display the image. In addition, the backlight part will be integrated with the LCD substrate at this stage, and the complete LCD panel is completed.
Firstly, the heteroconductive adhesive is pressed on the two edges, which allows external electrons to enter the LCD substrate layer and acts as a bridge for electronic transmission
Next is the drive IC press. The main function of the drive IC is to output the required voltage to each pixel and control the degree of torsion of the LCD molecules. The drive IC is divided into two types. The source drive IC located in the X-axis is responsible for the input of data. It is characterized by high frequency and has an image function. The gate drive IC located in the Y-axis is responsible for the degree and speed of torsion of LCD molecules, which directly affects the response time of the LCD display. However, there are already many LCD panels that only have driving IC in the X-axis direction, perhaps because the Y-axis drive IC function has been integrated and simplified.
The press of the flexible circuit board can transmit data signals and act as the bridge between the external printed circuit and LCD. It can be bent and thus becomes a flexible or flexible circuit board
The manufacturing process of the LCD substrate still has a lot of details and matters needing attention, for example, rinse with clean, dry, dry, dry, ultrasonic cleaning, exposure, development and so on and so on, all have very strict technical details and requirements, so as to produce qualified eyes panel, interested friends can consult relevant technical information by a search engine.
LCD (LC) is a kind of LCD, which has the properties of light transmission and refraction of solid Crystal, as well as the flow property of Liquid. It is because of this property that it will be applied to the display field.
However, LCD does not emit light autonomously, so the display equipment using LCD as the display medium needs to be equipped with another backlight system.
First, a backplate is needed as the carrier of the light source. The common light source for LCD display equipment is CCFL cold cathode backlight, but it has started to switch to an LED backlight, but either one needs a backplate as the carrier.
CCFL backlight has been with LCD for a long time. Compared with LED backlight, CCFL backlight has many defects. However, it has gradually evolved to save 50% of the lamp and enhance the transmittance of the LCD panel, so as to achieve the purpose of energy-saving.
With the rapid development of LED in the field of lighting, the cost has been greatly reduced.LCD panels have also started to use LED as the backlight on a large scale. Currently, in order to control costs, an LED backlight is placed on the side rather than on the backplate, which can reduce the number of LED grains.
At the top of the diffusion plate, there will be 3~4 diffuser pieces, constantly uniform light to the whole surface, improve the uniformity of light, which is directly related to the LCD panel display effect. Professional LCD in order to better control the brightness uniformity of the screen, panel procurement, the later backlight control circuit, will make great efforts to ensure the quality of the panel.
Since the LCD substrate and the backlight system are not fixed by bonding, a metal or rubber frame is needed to be added to the outer layer to fix the LCD substrate and the backlight system.
After the period of the Module, the process is completed in LCM (LCDModule) factory, the core of this part of the basic does not involve the use of LCD manufacturing technology, mainly is some assembly work, so some machine panel factories such as chi mei, Korea department such as Samsung panel factory, all set with LCM factories in mainland China, Duan Mo group after the LCD panel assembly, so that we can convenient mainland area each big monitor procurement contract with LCD TV manufacturers, can reduce the human in the whole manufacturing and transportation costs.
However, neither Taiwan nor Korea has any intention to set up factories in mainland China for the LCD panel front and middle manufacturing process involving core technologies. Therefore, there is still a long way to go for China to have its own LCD panel industry.

LCD display screens are everywhere. You probably own one or more devices with an LCD display screen at home and at work. This includes your TV, computer monitor, watches, clocks, smartphones, and even calculators.
But have you ever wondered about how your LCD display screen works, its lifespan, components, and how it holds up to other emerging display technologies today?
Knowing all these things about your LCD display lets you appreciate your screen all the more. Caring for your device becomes easier when you’re armed with this knowledge.
LCD display screens make use of Liquid Crystal Display technology. The screen is embedded with liquid crystals, a substance that has properties in between a conventional liquid and a solid crystal. Liquid crystals can flow, but their molecules carry a crystal-like solid orientation.
Liquid crystals are responsible for producing an image flashed onto the LCD screen. They don’t emit light, though. Backlights are used to illuminate these crystals.
Now, in LCD displays, pixels are regulated by using liquid crystals for rotating polarized light. Polarized light denotes light waves with vibrations occurring in a single plane. In LCDs, this is achieved by using polarized layers.
A single LCD contains millions of pixels, nematic liquid crystals, polarizing filters, and transistors. They all work together to create images on the screen.
Most LCD monitors have a lifespan ranging from 30,000 to 60,000 hours. That’s equivalent to 5-7 years using the monitor for 24 hours per day. It could also translate to 10-20 years with running the monitor for 8 hours a day, 5 days a week.
The backlight’s life expectancy is the biggest factor in determining the LCD display lifespan. It’s because liquid crystals do not give off light from themselves. The liquid crystals depend on the backlight for illuminating them. Hence, the LCD screen wears off when the backlights dim as it reaches its maximum lifespan.
The backlight serves as the illuminator of the entire LCD display device. Without a backlight, the LCD device remains darkened and hard to use. Backlights are installed directly behind the LCD panel to lighten up the display.
Simple devices such as pocket calculators don’t use a backlight for their LCD screens. Users rely on natural light to see the numbers displayed on such calculators. However, the majority of modern LCD screens such as televisions, computer monitors, smartphones, aviation screen panels, outdoor signages, and medical monitoring devices use backlights as their internal light source.
This type of backlight is the most popular and widely-used light source for LCDs today. Light-emitting diodes are semiconductors that emit light once electric current flows into it. Particles carrying the electric current are called electrons holes. These combine with electrons in the semiconductor, releasing photons (light particles).
White LED (WLED)– The LCD panel’s rear side is lit up with several white-colored LEDs. A diffuser is set in front of the LEDs to help evenly smooth out the light throughout the screen. Some computer monitors and large-screen LCD TVs use this LED technology.
Red-Green-Blue LED (RGB LED)– This technology works like WLED. The difference is that it uses red, green, and blue LED combination lights instead of white lights. Better picture quality and higher color gamut are its advantages over WLED and EL-WLED.
ELP uses electroluminescent materials such as colored phosphors instead of heat to create light. This material is placed in between two conductor layers. The material emits light as a result of an electric current flowing through it. ELPs are mostly used in small LCD screens.
Computer monitors and TV screens predominantly used CCFLs for backlights. However, modern manufacturers opt for LED technology instead of CCFL for their devices’ backlights.
HCFL backlights have filaments that need to be heated to excite mercury atoms, cause the current to flow, and ultimately emit light. HCFLs are often used in LCD equipment such as medical devices, custom task-oriented lamps, scanners, and outdoor LCD signs.
Liquid crystals are the heart of an LCD display. This unique substance flows like a liquid but retains many characteristics of solid crystals. They have long and cylindrical-shaped molecules that can twist when changes in molecular orientation happen.
Different liquid crystal families are used in LCD displays. One requirement of such liquids is to exhibit mutual attraction. Also, the molecules in the liquid crystal need to be anisotropic. This means that the liquid crystal molecules have that average structural order along a molecular axis.
The nematic phase is characterized by the crystal molecules freely moving around the liquid. However, these molecules point themselves to one direction only, making it unique from pure liquid molecules. Nematic liquid crystals are the most common liquid used in LCD screens.
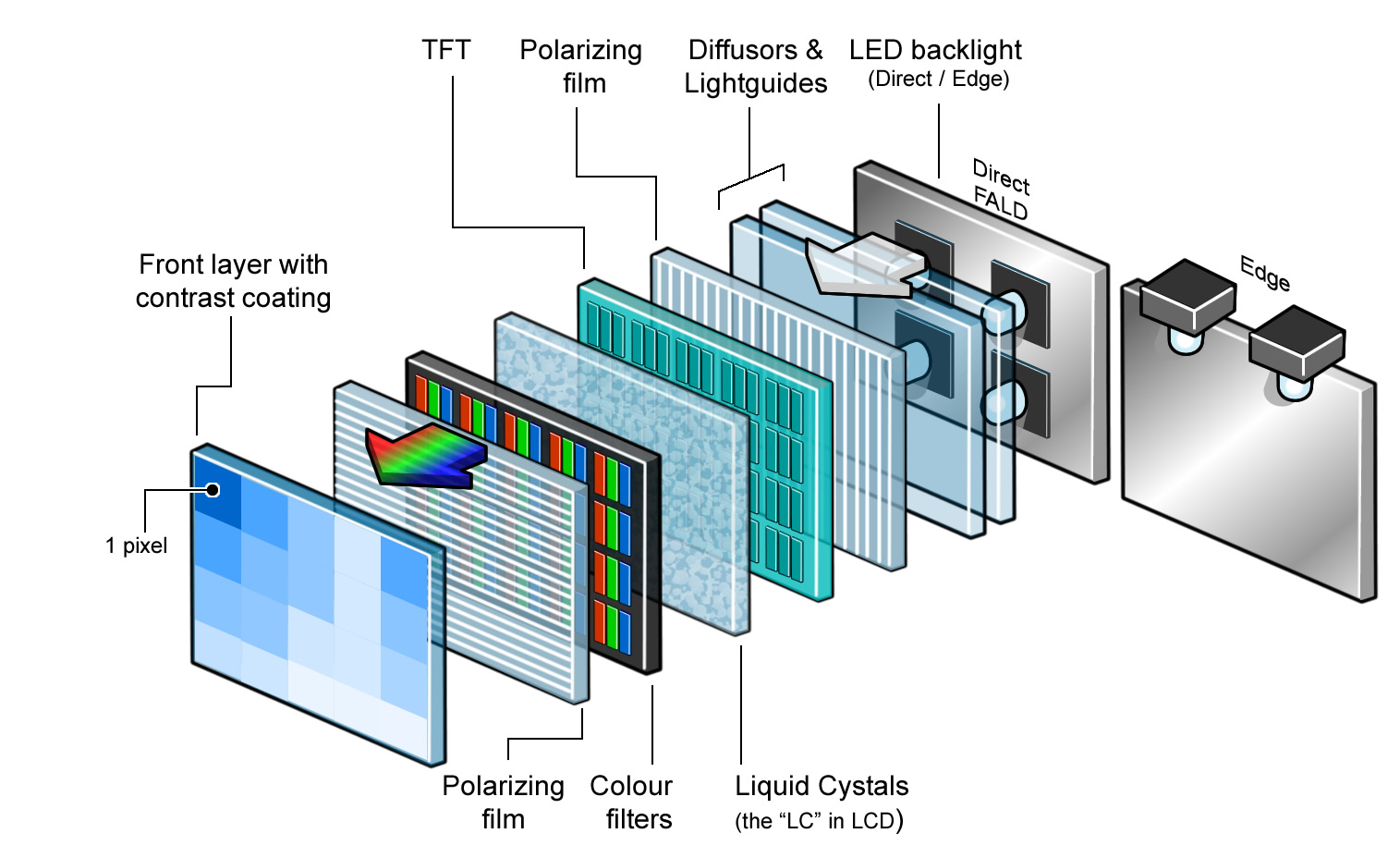
Color filters are found in between the liquid crystals. These filters determine whether the pixel shows red, green, or blue colors when activated. The filters work by independently controlling the pixel’s red, green, and blue sub-pixels. With this, the LCD screen can reproduce all possible colors found in the color space.
An LCD cell is made up of two polarizing filters. They enclose the LCD display and color filters. One polarizing filter is located in front of the backlight and is horizontal in orientation. The other one is found just beneath the pixel in front and is vertical in orientation. Polarizing filters are typically made of transparent crystals or glass substrates.
The role of polarizing filters is to control which light patterns can pass through the LCD screen. Without these filters, visual images generated by the LCD panel will have a poor contrast ratio and an inferior quality image.
Now, light emitted by your panel’s backlight source enters the first horizontal polarizing filter. It then passes through the liquid crystals. The polarized light vibrates vertically if the liquid crystals are in a twisted state. Hence, these light waves can then pass through the second vertical polarizing filter. The pixel on the screen turns on and is illuminated properly.
Meanwhile, if the LCD display is arranged in a straightened way, the horizontal light waves that came from the first polarizing filter will be blocked from entering the vertical polarizing filter. The pixel is then turned off and no light illuminates it.
TFTs are responsible for providing electrical voltage to the LCD display. Each screen pixel has a corresponding transistor, enabling the pixels to easily be controlled in unison through changes in electrical current.
Using TFTs requires less charge and less power to operate the LCD display screen successfully. TFT use also leads to sharper images because each pixel has its own transistor controlling it. The charge given to a certain pixel can be actively maintained even if the screen is refreshed to display another image.
That’s all the basic information you need to know about LCD display screens. Now, you know how an LCD screen works, its possible lifespan, its components, and how it compares to other display technologies.
Armed with this information, you can better appreciate and take care of your LCD display devices. And in case you’re planning to add display devices to your business, the information you’ve learned will help you make educated choices regarding the display technologies you’ll utilize.

Picking a monitor may feel more like art than science, but the technology behind the screen isn"t hard to understand. Learning about those technologies is key to navigating the minefield of marketing buzzwords separating you from your next monitor.
Our guide to the best monitors for PC gaming explains why those monitors are ideal for playing games at high resolutions and high framerates, but it doesn’t dig deep into the details of monitor technology. That’s what this guide is for: it breaks down what you need to know about modern displays: resolutions, aspect ratios, refresh rates, and the differences between panel types like IPS, VA, and TN.
LCD displays have a native resolution, and running games (or the desktop) below that resolution degrades image quality due to the scaling process of enlarging the image. Using lower resolution modes isn"t really a substitute for picking the right number of pixels in the first place.
1440p has become our recommendation as the best overall option. It"s great for office work, professional work, and gaming. You can still get higher refresh rate 144Hz panels (see below), plus G-Sync or FreeSync, and you can run at 100 percent scaling in Windows. For gaming purposes, however, you"ll want at least a GTX 1070/RTX 2060 or RX Vega 56 (or equivalent) graphics card.
The most common and least expensive LCD panels are based on TN, or Twisted Nematic designs. Since TN screens are made on a vast scale and have been around a long time, they are very affordable. Online retailers stock an abundance of attractive 27-inch 1080p monitors(opens in new tab) with reasonable features starting at just $150. The price is nice, but the pixel density isn’t—and neither are the color quality or viewing angles, TN’s greatest weaknesses.
All TFT LCDs work by passing light, such as an LED, through a pair of polarized screens, a color filter, and liquid crystals that twist when current is applied to them. The more current applied, the more the liquid crystals twist and block light. Precise adjustments allow virtually any color or shade to be reproduced, but TN implementations have some limits.
Each pixel in an LCD display is made of red, green and blue subpixels. Colors are made by mixing varying brightness levels for these pixels, resulting in a perceived solid color to the user. The problem with TN is its widespread adoption of a 6-bit per channel model, instead of the 8-bit per channel used in better displays.
TN compensates for this shortcoming via FRC (Frame Rate Control), a pixel trick that uses alternating colors to produce a perceived third, but it"s a poor substitute for proper 24-bit color reproduction. When combined with the inversion and washout that comes from narrow viewing angles, TN"s elderly status in the LCD display world becomes clear.
IPS, short for In-Plane-Switching, was designed to overcome TN"s shortcomings as a display technology. IPS screens also use liquid crystals, polarized filters, and transmitters, but the arrangement is different, with the crystals aligned for better color visibility and less light distortion. Additionally, IPS panels typically use 8-bit depth per color instead of TN"s 6-bit, resulting in a full 256 shades to draw upon for each color.
The differences are pretty dramatic. While TN displays wash out at shallow angles and never truly "pop" with color no matter how well they are calibrated, IPS panels have rich, bright colors that don"t fade or shift when viewed from the sides. Moreover, pressing a finger on an IPS screen doesn"t cause trailing distortions, making them especially useful for touchscreen applications.
While touted as the high end display technology of choice by giants such as Apple, the truth is that IPS screens still have drawbacks. Due to their more complex construction and the additional transmitters and lighting required for each pixel, IPS screens cost more than their TN counterparts. Thankfully, over the past few years, the popularity of no-frills import IPS monitors from Asia has helped drive down prices and force bigger monitor brands to sell more reasonably priced IPS displays.
The complexity introduces additional overhead that reduces panel responsiveness. Most IPS displays clock in a few milliseconds slower than TN panels, with the best models managing 5ms grey-to-grey, and the more common 8ms panels can have noticeable blurring in gaming. Most IPS displays use a 60Hz refresh rate, though the best gaming displays now utilize IPS panels with 144Hz refresh rates, and a price to match.
A lot of research has been done with IPS and many variants exist, including Samsung"s popular PLS panels and AU Optronics AHVA (Advanced Hyper-Viewing Angle). The differences amount to subtle manufacturer variations or generational improvements on the technology, which has been around since 1996.
In between the high speed of TN and the color richness of IPS sits a compromise technology, the VA, or Vertically Aligned, panel. VA and its variants (PVA and MVA, but not AHVA) normally take the IPS approach with 8-bit color depth per channel and a crystal design that reproduces rich colors but retains some of the low latency and high refresh speed of TN. The result is a display that"s theoretically almost as colorful as IPS and almost as fast as TN.
VA panels have a few unique qualities, both positive and negative. They have superior contrast to both IPS and TN screens, often reaching a static 5000:1 ratio, and produce better black levels as a result. Advanced VA variants, such as the MVA panel used by Eizo in the Foris FG2421, support 120Hz officially and offer pixel latencies on par or better than IPS.
The flood of innovation in the display market shows no signs of abating, with TVs on one side and smartphones on the other driving new technologies such as curved screens and desktop-grade OLED panels that promise speeds, contrast and color beyond anything seen so far.
Most standard TFT-LCDs support a refresh rate of 60Hz, which means the screen is redrawn 60 times each second. While 60Hz may be sufficient for many desktop applications, higher refresh rates are desirable since they provide a smoother experience moving windows, watching video, and especially when gaming.
One method popular in gaming monitors is the inclusion of a strobed backlight, which disrupts eye tracking blur by cutting off the backlight for an instant, creating a CRT-like stable image. A strobed 120Hz display is more blur-free than a non-strobed 144Hz panel, but flickering the backlight understandably cuts down on the overall brightness of the image. Users with sensitive eyes can suffer from eyestrain and headaches induced from the flicker as well.

A liquid crystal display (LCD) has liquid crystal material sandwiched between two sheets of glass. Without any voltage applied between transparent electrodes, liquid crystal molecules are aligned in parallel with the glass surface. When voltage is applied, they change their direction and they turn vertical to the glass surface. They vary in optical characteristics, depending on their orientation. Therefore, the quantity of light transmission can be controlled by combining the motion of liquid crystal molecules and the direction of polarization of two polarizing plates attached to the both outer sides of the glass sheets. LCDs utilize these characteristics to display images.
An LCD consists of many pixels. A pixel consists of three sub-pixels (Red/Green/Blue, RGB). In the case of Full-HD resolution, which is widely used for smartphones, there are more than six million (1,080 x 1,920 x 3 = 6,220,800) sub-pixels. To activate these millions of sub-pixels a TFT is required in each sub-pixel. TFT is an abbreviation for "Thin Film Transistor". A TFT is a kind of semiconductor device. It serves as a control valve to provide an appropriate voltage onto liquid crystals for individual sub-pixels. A TFT LCD has a liquid crystal layer between a glass substrate formed with TFTs and transparent pixel electrodes and another glass substrate with a color filter (RGB) and transparent counter electrodes. In addition, polarizers are placed on the outer side of each glass substrate and a backlight source on the back side. A change in voltage applied to liquid crystals changes the transmittance of the panel including the two polarizing plates, and thus changes the quantity of light that passes from the backlight to the front surface of the display. This principle allows the TFT LCD to produce full-color images.

So, why is this important? A monitor’s panel technology is important because it affects what the monitor can do and for which uses it is best suited. Each of the monitor panel types listed above offer their own distinctive benefits and drawbacks.
Choosing which type of monitor panel type to buy will depend largely on your intended usage and personal preference. After all, gamers, graphic designers, and office workers all have different requirements. Specific types of displays are best suited for different usage scenarios.
The reason for this is because none of the different monitor panel types as they are today can be classified as “outstanding” for all of the attributes mentioned above.
Below we’ll take a look at how IPS, TN, and VA monitors affect screen performance and do some handy summaries of strengths, weaknesses, and best-case uses for each type of panel technology.
IPS monitors or “In-Plane Switching” monitors, leverage liquid crystals aligned in parallel to produce rich colors. IPS panels are defined by the shifting patterns of their liquid crystals. These monitors were designed to overcome the limitations of TN panels. The liquid crystal’s ability to shift horizontally creates better viewing angles.
IPS monitors continue to be the display technology of choice for users that want color accuracy and consistency. IPS monitors are really great when it comes to color performance and super-wide viewing angles. The expansive viewing angles provided by IPS monitors help to deliver outstanding color when being viewed from different angles. One major differentiator between IPS monitors and TN monitors is that colors on an IPS monitor won’t shift when being viewed at an angle as drastically as they do on a TN monitor.
IPS monitor variations include S-IPS, H-IPS, e-IPS and P-IPS, and PLS (Plane-to-Line Switching), the latter being the latest iteration. Since these variations are all quite similar, they are all collectively referred to as “IPS-type” panels. They all claim to deliver the major benefits associated with IPS monitors – great color and ultra-wide viewing angles.
In the past, response time and contrast were the initial weakness of IPS technology. Nowadays, however, IPS monitor response times have advanced to the point where they are even capable of satisfying gamers, thus resulting in a rising popularity in IPS monitors for gaming.
With regard to gaming, some criticisms IPS monitors include more visible motion blur coming as a result of slower response times, however the impact of motion blur will vary from user to user. In fact, mixed opinions about the “drawbacks” of IPS monitor for gaming can be found all across the web. Take this excerpt from one gaming technology writer for example: “As for pixel response, opinions vary. I personally think IPS panels are quick enough for almost all gaming. If your gaming life is absolutely and exclusively about hair-trigger shooters, OK, you’ll want the fastest response, lowest latency LCD monitor. And that means TN. For the rest of us, and certainly for those who place even a modicum of importance on the visual spectacle of games, I reckon IPS is clearly the best panel technology.” Read the full article here.
IPS monitors deliver ultra-wide 178-degree vertical and horizontal viewing angles. Graphic designers, CAD engineers, pro photographers, and video editors will benefit from using an IPS monitor. Many value the color benefits of IPS monitors and tech advances have improved IPS panel speed, contrast, and resolution. IPS monitors are more attractive than ever for general desktop work as well as many types of gaming. They’re even versatile enough to be used in different monitor styles, so if you’ve ever compared an ultrawide vs. dual monitor setup or considered the benefits of curved vs. flat monitors, chances are you’ve already come into contact with an IPS panel.
TN monitors, or “Twisted Nematic” monitors, are the oldest LCD panel types around. TN panels cost less than their IPS and VA counterparts and are a popular mainstream display technology for desktop and laptop displays.
Despite their lower perceived value, TN-based displays are the panel type preferred by competitive gamers. The reason for this is because TN panels can achieve a rapid response time and the fastest refresh rates on the market (like this 240Hz eSports monitor). To this effect, TN monitors are able to reduce blurring and screen tearing in fast-paced games when compared to an IPS or VA panel.
On the flip side, however, TN panel technology tends to be ill-suited for applications that benefit from wider viewing angles, higher contrast ratios, and better color accuracy. That being said, LED technology has helped shift the perspective and today’s LED-backlit TN models offer higher brightness along with better blacks and higher contrast ratios.
The greatest constraint of TN panel technology, however, is a narrower viewing angle as TN monitors experience more color shifting than other types of panels when being viewed at an angle.
Today’s maximum possible viewing angles are 178 degrees both horizontally and vertically (178º/178º), yet TN panels are limited to viewing angles of approximately 170 degrees horizontal and 160 degrees vertical (170º /160º).
TN monitors are the least expensive panel technology, making them ideal for cost-conscious businesses and consumers. In addition, TN monitors enjoy unmatched popularity with competitive gamers and other users who seek rapid graphics display.
Vertical alignment (VA) panel technology was developed to improve upon the drawbacks of TN. Current VA-based monitors offer muchhigher contrast, better color reproduction, and wider viewing angles than TN panels. Variations you may see include P-MVA, S-MVA, and AMVA (Advanced MVA).
These high-end VA-type monitors rival IPS monitors as the best panel technology for professional-level color-critical applications. One of the standout features of VA technology is that it is particularly good at blocking light from the backlight when it’s not needed. This enables VA panels to display deeper blacks and static contrast ratios of up to several times higher than the other LCD technologies. The benefit of this is that VA monitors with high contrast ratios can deliver intense blacks and richer colors.
MVA and other recent VA technologies offer the highest static contrast ratios of any panel technology. This allows for an outstanding visual experience for movie enthusiasts and other users seeking depth of detail. Higher-end, feature-rich MVA displays offer the consistent, authentic color representation needed by graphic designers and other pro users.
There is another type of panel technology that differs from the monitor types discussed above and that is OLED or “Organic Light Emitting Diode” technology. OLEDs differ from LCDs because they use positively/negatively charged ions to light up every pixel individually, while LCDs use a backlight, which can create an unwanted glow. OLEDs avoid screen glow (and create darker blacks) by not using a backlight. One of the drawbacks of OLED technology is that it is usually pricier than any of the other types of technology explained.
When it comes to choosing the right LCD panel technology, there is no single right answer. Each of the three primary technologies offers distinct strengths and weaknesses. Looking at different features and specs helps you identify which monitor best fits your needs.
LCD or “Liquid Crystal Display” is a type of monitor panel that embraces thin layers of liquid crystals sandwiched between two layers of filters and electrodes.
While CRT monitors used to fire electrons against glass surfaces, LCD monitors operate using backlights and liquid crystals. The LCD panel is a flat sheet of material that contains layers of filters, glass, electrodes, liquid crystals, and a backlight. Polarized light (meaning only half of it shines through) is directed towards a rectangular grid of liquid crystals and beamed through.
Note: When searching for monitors you can be sure to come across the term “LED Panel” at some point or another. An LED panel is an LCD screen with an LED – (Light Emitting Diode) – backlight. LEDs provide a brighter light source while using much less energy. They also have the ability to produce white color, in addition to traditional RGB color, and are the panel type used in HDR monitors.
Early LCD panels used passive-matrix technology and were criticized for blurry imagery. The reason for this is because quick image changes require liquid crystals to change phase quickly and passive matrix technology was limited in terms of how quickly liquid crystals could change phase.
As a result, active-matrix technology was invented and transistors (TFTs) began being used to help liquid crystals retain their charge and change phase more quickly.
Thanks to active-matrix technology, LCD monitor panels were able to change images very quickly and the technology began being used by newer LCD panels.
Ultimately, budget and feature preferences will determine the best fit for each user. Among the available monitors of each panel type there will also be a range of price points and feature sets. Additionally, overall quality may vary among manufacturers due to factors related to a display’s components, manufacturing, and design.
Alternatively, if you’re into gaming and are in the market for TN panel these gaming monitor options may be along the lines of what you’re looking for.

Photo: Prove to yourself that an LCD display uses polarized light. Simply put on a pair of polarizing sunglasses and rotate your head (or the display). You"ll see the display at its brightest at one angle and at its darkest at exactly 90 degrees to that angle.
Glass substrate with ITO electrodes. The shapes of these electrodes will determine the shapes that will appear when the LCD is switched ON. Vertical ridges etched on the surface are smooth.
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals combined with polarizers. Liquid crystals do not emit light directlybacklight or reflector to produce images in color or monochrome.seven-segment displays, as in a digital clock, are all good examples of devices with these displays. They use the same basic technology, except that arbitrary images are made from a matrix of small pixels, while other displays have larger elements. LCDs can either be normally on (positive) or off (negative), depending on the polarizer arrangement. For example, a character positive LCD with a backlight will have black lettering on a background that is the color of the backlight, and a character negative LCD will have a black background with the letters being of the same color as the backlight. Optical filters are added to white on blue LCDs to give them their characteristic appearance.
LCDs are used in a wide range of applications, including LCD televisions, computer monitors, instrument panels, aircraft cockpit displays, and indoor and outdoor signage. Small LCD screens are common in LCD projectors and portable consumer devices such as digital cameras, watches, digital clocks, calculators, and mobile telephones, including smartphones. LCD screens are also used on consumer electronics products such as DVD players, video game devices and clocks. LCD screens have replaced heavy, bulky cathode-ray tube (CRT) displays in nearly all applications. LCD screens are available in a wider range of screen sizes than CRT and plasma displays, with LCD screens available in sizes ranging from tiny digital watches to very large television receivers. LCDs are slowly being replaced by OLEDs, which can be easily made into different shapes, and have a lower response time, wider color gamut, virtually infinite color contrast and viewing angles, lower weight for a given display size and a slimmer profile (because OLEDs use a single glass or plastic panel whereas LCDs use two glass panels; the thickness of the panels increases with size but the increase is more noticeable on LCDs) and potentially lower power consumption (as the display is only "on" where needed and there is no backlight). OLEDs, however, are more expensive for a given display size due to the very expensive electroluminescent materials or phosphors that they use. Also due to the use of phosphors, OLEDs suffer from screen burn-in and there is currently no way to recycle OLED displays, whereas LCD panels can be recycled, although the technology required to recycle LCDs is not yet widespread. Attempts to maintain the competitiveness of LCDs are quantum dot displays, marketed as SUHD, QLED or Triluminos, which are displays with blue LED backlighting and a Quantum-dot enhancement film (QDEF) that converts part of the blue light into red and green, offering similar performance to an OLED display at a lower price, but the quantum dot layer that gives these displays their characteristics can not yet be recycled.
Since LCD screens do not use phosphors, they rarely suffer image burn-in when a static image is displayed on a screen for a long time, e.g., the table frame for an airline flight schedule on an indoor sign. LCDs are, however, susceptible to image persistence.battery-powered electronic equipment more efficiently than a CRT can be. By 2008, annual sales of televisions with LCD screens exceeded sales of CRT units worldwide, and the CRT became obsolete for most purposes.
Each pixel of an LCD typically consists of a layer of molecules aligned between two transparent electrodes, often made of Indium-Tin oxide (ITO) and two polarizing filters (parallel and perpendicular polarizers), the axes of transmission of which are (in most of the cases) perpendicular to each other. Without the liquid crystal between the polarizing filters, light passing through the first filter would be blocked by the second (crossed) polarizer. Before an electric field is applied, the orientation of the liquid-crystal molecules is determined by the alignment at the surfaces of electrodes. In a twisted nematic (TN) device, the surface alignment directions at the two electrodes are perpendicular to each other, and so the molecules arrange themselves in a helical structure, or twist. This induces the rotation of the polarization of the incident light, and the device appears gray. If the applied voltage is large enough, the liquid crystal molecules in the center of the layer are almost completely untwisted and the polarization of the incident light is not rotated as it passes through the liquid crystal layer. This light will then be mainly polarized perpendicular to the second filter, and thus be blocked and the pixel will appear black. By controlling the voltage applied across the liquid crystal layer in each pixel, light can be allowed to pass through in varying amounts thus constituting different levels of gray.
The chemical formula of the liquid crystals used in LCDs may vary. Formulas may be patented.Sharp Corporation. The patent that covered that specific mixture expired.
Most color LCD systems use the same technique, with color filters used to generate red, green, and blue subpixels. The LCD color filters are made with a photolithography process on large glass sheets that are later glued with other glass sheets containing a TFT array, spacers and liquid crystal, creating several color LCDs that are then cut from one another and laminated with polarizer sheets. Red, green, blue and black photoresists (resists) are used. All resists contain a finely ground powdered pigment, with particles being just 40 nanometers across. The black resist is the first to be applied; this will create a black grid (known in the industry as a black matrix) that will separate red, green and blue subpixels from one another, increasing contrast ratios and preventing light from leaking from one subpixel onto other surrounding subpixels.Super-twisted nematic LCD, where the variable twist between tighter-spaced plates causes a varying double refraction birefringence, thus changing the hue.
LCD in a Texas Instruments calculator with top polarizer removed from device and placed on top, such that the top and bottom polarizers are perpendicular. As a result, the colors are inverted.
The optical effect of a TN device in the voltage-on state is far less dependent on variations in the device thickness than that in the voltage-off state. Because of this, TN displays with low information content and no backlighting are usually operated between crossed polarizers such that they appear bright with no voltage (the eye is much more sensitive to variations in the dark state than the bright state). As most of 2010-era LCDs are used in television sets, monitors and smartphones, they have high-resolution matrix arrays of pixels to display arbitrary images using backlighting with a dark background. When no image is displayed, different arrangements are used. For this purpose, TN LCDs are operated between parallel polarizers, whereas IPS LCDs feature crossed polarizers. In many applications IPS LCDs have replaced TN LCDs, particularly in smartphones. Both the liquid crystal material and the alignment layer material contain ionic compounds. If an electric field of one particular polarity is applied for a long period of time, this ionic material is attracted to the surfaces and degrades the device performance. This is avoided either by applying an alternating current or by reversing the polarity of the electric field as the device is addressed (the response of the liquid crystal layer is identical, regardless of the polarity of the applied field).
Displays for a small number of individual digits or fixed symbols (as in digital watches and pocket calculators) can be implemented with independent electrodes for each segment.alphanumeric or variable graphics displays are usually implemented with pixels arranged as a matrix consisting of electrically connected rows on one side of the LC layer and columns on the other side, which makes it possible to address each pixel at the intersections. The general method of matrix addressing consists of sequentially addressing one side of the matrix, for example by selecting the rows one-by-one and applying the picture information on the other side at the columns row-by-row. For details on the various matrix addressing schemes see passive-matrix and active-matrix addressed LCDs.
LCDs, along with OLED displays, are manufactured in cleanrooms borrowing techniques from semiconductor manufacturing and using large sheets of glass whose size has increased over time. Several displays are manufactured at the same time, and then cut from the sheet of glass, also known as the mother glass or LCD glass substrate. The increase in size allows more displays or larger displays to be made, just like with increasing wafer sizes in semiconductor manufacturing. The glass sizes are as follows:
Until Gen 8, manufacturers would not agree on a single mother glass size and as a result, different manufacturers would use slightly different glass sizes for the same generation. Some manufacturers have adopted Gen 8.6 mother glass sheets which are only slightly larger than Gen 8.5, allowing for more 50 and 58 inch LCDs to be made per mother glass, specially 58 inch LCDs, in which case 6 can be produced on a Gen 8.6 mother glass vs only 3 on a Gen 8.5 mother glass, significantly reducing waste.AGC Inc., Corning Inc., and Nippon Electric Glass.
The origins and the complex history of liquid-crystal displays from the perspective of an insider during the early days were described by Joseph A. Castellano in Liquid Gold: The Story of Liquid Crystal Displays and the Creation of an Industry.IEEE History Center.Peter J. Wild, can be found at the Engineering and Technology History Wiki.
In 1922, Georges Friedel described the structure and properties of liquid crystals and classified them in three types (nematics, smectics and cholesterics). In 1927, Vsevolod Frederiks devised the electrically switched light valve, called the Fréedericksz transition, the essential effect of all LCD technology. In 1936, the Marconi Wireless Telegraph company patented the first practical application of the technology, "The Liquid Crystal Light Valve". In 1962, the first major English language publication Molecular Structure and Properties of Liquid Crystals was published by Dr. George W. Gray.RCA found that liquid crystals had some interesting electro-optic characteristics and he realized an electro-optical effect by generating stripe-patterns in a thin layer of liquid crystal material by the application of a voltage. This effect is based on an electro-hydrodynamic instability forming what are now called "Williams domains" inside the liquid crystal.
In the late 1960s, pioneering work on liquid crystals was undertaken by the UK"s Royal Radar Establishment at Malvern, England. The team at RRE supported ongoing work by George William Gray and his team at the University of Hull who ultimately discovered the cyanobiphenyl liquid crystals, which had correct stability and temperature properties for application in LCDs.
The idea of a TFT-based liquid-crystal display (LCD) was conceived by Bernard Lechner of RCA Laboratories in 1968.dynamic scattering mode (DSM) LCD that used standard discrete MOSFETs.
On December 4, 1970, the twisted nematic field effect (TN) in liquid crystals was filed for patent by Hoffmann-LaRoche in Switzerland, (Swiss patent No. 532 261) with Wolfgang Helfrich and Martin Schadt (then working for the Central Research Laboratories) listed as inventors.Brown, Boveri & Cie, its joint venture partner at that time, which produced TN displays for wristwatches and other applications during the 1970s for the international markets including the Japanese electronics industry, which soon produced the first digital quartz wristwatches with TN-LCDs and numerous other products. James Fergason, while working with Sardari Arora and Alfred Saupe at Kent State University Liquid Crystal Institute, filed an identical patent in the United States on April 22, 1971.ILIXCO (now LXD Incorporated), produced LCDs based on the TN-effect, which soon superseded the poor-quality DSM types due to improvements of lower operating voltages and lower power consumption. Tetsuro Hama and Izuhiko Nishimura of Seiko received a US patent dated February 1971, for an electronic wristwatch incorporating a TN-LCD.
In 1972, the concept of the active-matrix thin-film transistor (TFT) liquid-crystal display panel was prototyped in the United States by T. Peter Brody"s team at Westinghouse, in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania.Westinghouse Research Laboratories demonstrated the first thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display (TFT LCD).high-resolution and high-quality electronic visual display devices use TFT-based active matrix displays.active-matrix liquid-crystal display (AM LCD) in 1974, and then Brody coined the term "active matrix" in 1975.
In 1972 North American Rockwell Microelectronics Corp introduced the use of DSM LCDs for calculators for marketing by Lloyds Electronics Inc, though these required an internal light source for illumination.Sharp Corporation followed with DSM LCDs for pocket-sized calculators in 1973Seiko and its first 6-digit TN-LCD quartz wristwatch, and Casio"s "Casiotron". Color LCDs based on Guest-Host interaction were invented by a team at RCA in 1968.TFT LCDs similar to the prototypes developed by a Westinghouse team in 1972 were patented in 1976 by a team at Sharp consisting of Fumiaki Funada, Masataka Matsuura, and Tomio Wada,
In 1983, researchers at Brown, Boveri & Cie (BBC) Research Center, Switzerland, invented the passive matrix-addressed LCDs. H. Amstutz et al. were listed as inventors in the corresponding patent applications filed in Switzerland on July 7, 1983, and October 28, 1983. Patents were granted in Switzerland CH 665491, Europe EP 0131216,
The first color LCD televisions were developed as handheld televisions in Japan. In 1980, Hattori Seiko"s R&D group began development on color LCD pocket televisions.Seiko Epson released the first LCD television, the Epson TV Watch, a wristwatch equipped with a small active-matrix LCD television.dot matrix TN-LCD in 1983.Citizen Watch,TFT LCD.computer monitors and LCD televisions.3LCD projection technology in the 1980s, and licensed it for use in projectors in 1988.compact, full-color LCD projector.
In 1990, under different titles, inventors conceived electro optical effects as alternatives to twisted nematic field effect LCDs (TN- and STN- LCDs). One approach was to use interdigital electrodes on one glass substrate only to produce an electric field essentially parallel to the glass substrates.Germany by Guenter Baur et al. and patented in various countries.Hitachi work out various practical details of the IPS technology to interconnect the thin-film transistor array as a matrix and to avoid undesirable stray fields in between pixels.
Hitachi also improved the viewing angle dependence further by optimizing the shape of the electrodes (Super IPS). NEC and Hitachi become early manufacturers of active-matrix addressed LCDs based on the IPS technology. This is a milestone for implementing large-screen LCDs having acceptable visual performance for flat-panel computer monitors and television screens. In 1996, Samsung developed the optical patterning technique that enables multi-domain LCD. Multi-domain and In Plane Switching subsequently remain the dominant LCD designs through 2006.South Korea and Taiwan,
In 2007 the image quality of LCD televisions surpassed the image quality of cathode-ray-tube-based (CRT) TVs.LCD TVs were projected to account 50% of the 200 million TVs to be shipped globally in 2006, according to Displaybank.Toshiba announced 2560 × 1600 pixels on a 6.1-inch (155 mm) LCD panel, suitable for use in a tablet computer,transparent and flexible, but they cannot emit light without a backlight like OLED and microLED, which are other technologies that can also be made flexible and transparent.
In 2016, Panasonic developed IPS LCDs with a contrast ratio of 1,000,000:1, rivaling OLEDs. This technology was later put into mass production as dual layer, dual panel or LMCL (Light Modulating Cell Layer) LCDs. The technology uses 2 liquid crystal layers instead of one, and may be used along with a mini-LED backlight and quantum dot sheets.
Since LCDs produce no light of their own, they require external light to produce a visible image.backlight. Active-matrix LCDs are almost always backlit.Transflective LCDs combine the features of a backlit transmissive display and a reflective display.
CCFL: The LCD panel is lit either by two cold cathode fluorescent lamps placed at opposite edges of the display or an array of parallel CCFLs behind larger displays. A diffuser (made of PMMA acrylic plastic, also known as a wave or light guide/guiding plateinverter to convert whatever DC voltage the device uses (usually 5 or 12 V) to ≈1000 V needed to light a CCFL.
EL-WLED: The LCD panel is lit by a row of white LEDs placed at one or more edges of the screen. A light diffuser (light guide plate, LGP) is then used to spread the light evenly across the whole display, similarly to edge-lit CCFL LCD backlights. The diffuser is made out of either PMMA plastic or special glass, PMMA is used in most cases because it is rugged, while special glass is used when the thickness of the LCD is of primary concern, because it doesn"t expand as much when heated or exposed to moisture, which allows LCDs to be just 5mm thick. Quantum dots may be placed on top of the diffuser as a quantum dot enhancement film (QDEF, in which case they need a layer to be protected from heat and humidity) or on the color filter of the LCD, replacing the resists that are normally used.
WLED array: The LCD panel is lit by a full array of white LEDs placed behind a diffuser behind the panel. LCDs that use this implementation will usually have the ability to dim or completely turn off the LEDs in the dark areas of the image being displayed, effectively increasing the contrast ratio of the display. The precision with which this can be done will depend on the number of dimming zones of the display. The more dimming zones, the more precise the dimming, with less obvious blooming artifacts which are visible as dark grey patches surrounded by the unlit areas of the LCD. As of 2012, this design gets most of its use from upscale, larger-screen LCD televisions.
RGB-LED array: Similar to the WLED array, except the panel is lit by a full array of RGB LEDs. While displays lit with white LEDs usually have a poorer color gamut than CCFL lit displays, panels lit with RGB LEDs have very wide color gamuts. This implementation is most popular on professional graphics editing LCDs. As of 2012, LCDs in this category usually cost more than $1000. As of 2016 the cost of this category has drastically reduced and such LCD televisions obtained same price levels as the former 28" (71 cm) CRT based categories.
Monochrome LEDs: such as red, green, yellow or blue LEDs are used in the small passive monochrome LCDs typically used in clocks, watches and small appliances.
Today, most LCD screens are being designed with an LED backlight instead of the traditional CCFL backlight, while that backlight is dynamically controlled with the video information (dynamic backlight control). The combination with the dynamic backlight control, invented by Philips researchers Douglas Stanton, Martinus Stroomer and Adrianus de Vaan, simultaneously increases the dynamic range of the display system (also marketed as HDR, high dynamic range television or FLAD, full-area local area dimming).
The LCD backlight systems are made highly efficient by applying optical films such as prismatic structure (prism s




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey