28 pin lcd display free sample

From Figure 3 above we can see that the DDRAM controller should have a memory map of 104 bytes (00H to 67H = 68H = 104D), but the location that can be used is only 80 bytes 00H-27H (40 bytes) and 40H-67H (40 bytes); Note that the 28H-3FH address (24 location) is not visible.
LCD connected to this controller will adjust itself to the memory map of this DDRAM controller; each location on the LCD will take 1 DDRAM address on the controller. Because we use 2 × 16 type LCD, the first line of the LCD will take the location of the 00H-0FH addresses and the second line will take the 40H-4FH addresses of the controller DDRAM; so neither the addresses of the 10H-27H on the first line or the addresses of the 50H-67H on the second line on DDRAM is used.
To be able to display a character on the first line of the LCD, we must provide written instructions (80h + DDRAM address where our character is to be displayed on the first line) in the Instruction Register-IR and then followed by writing the ASCII code of the character or address of the character stored on the CGROM or CGRAM on the LCD controller data register, as well as to display characters in the second row we must provide written instructions (C0H + DDRAM address where our character to be displayed on the second line) in the Instructions Register-IR and then followed by writing the ASCII code or address of the character on CGROM or CGRAM on the LCD controller data register.
As mentioned above, to display a character (ASCII) you want to show on the LCD, you need to send the ASCII code to the LCD controller data register-DR. For characters from CGROM and CGRAM we only need to send the address of the character where the character is stored; unlike the character of the ASCII code, we must write the ASCII code of the character we want to display on the LCD controller data register to display it. For special characters stored on CGRAM, one must first save the special character at the CGRAM address (prepared 64 addresses, namely addresses 0–63); A special character with a size of 5 × 8 (5 columns × 8 lines) requires eight consecutive addresses to store it, so the total special characters that can be saved or stored on the CGRAM addresses are only eight (8) characters. To be able to save a special character at the first CGRAM address we must send or write 40H instruction to the Instruction Register-IR followed by writing eight consecutive bytes of the data in the Data Register-DR to save the pattern/image of a special character that you want to display on the LCD [9, 10].
We can easily connect this LCD module (LCD + controller) with MCS51, and we do not need any additional electronic equipment as the interface between MCS51 and it; This is because this LCD works with the TTL logic level voltage—Transistor-Transistor Logic.
The voltage source of this display is +5 V connected to Pin 2 (VCC) and GND power supply connected to Pin 1 (VSS) and Pin 16 (GND); Pin 1 (VSS) and Pin 16 (GND) are combined together and connected to the GND of the power supply.
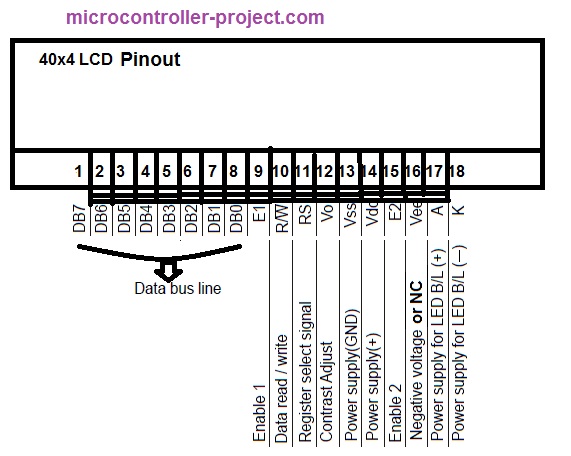
Pins 7–14 (8 Pins) of the display function as a channel to transmit either data or instruction with a channel width of 1 byte (D0-D7) between the display and MCS51. In Figure 6, it can be seen that each Pin connected to the data bus (D0-D7) of MCS51 in this case P0 (80h); P0.0-P0.7 MCS-51 connected to D0-D7 of the LCD.
Pins 4–6 are used to control the performance of the display. Pin 4 (Register Select-RS) is in charge of selecting one of the 2 display registers. If RS is given logic 0 then the selected register is the Instruction Register-IR, otherwise, if RS is given logic 1 then the selected register is the Data Register-DR. The implication of this selection is the meaning of the signal sent down through the data bus (D0-D7), if RS = 0, then the signal sent from the MCS-51 to the LCD is an instruction; usually used to configure the LCD, otherwise if RS = 1 then the data sent from the MCS-51 to the LCD (D0-D7) is the data (object or character) you want to display on the LCD. From Figure 6 Pin 4 (RS) is connected to Pin 16 (P3.6/W¯) of MCS-51 with the address (B6H).
Pin 5 (R/W¯)) of the LCD does not appear in Figure 6 is used for read/write operations. If Pin 5 is given logic 1, the operation is a read operation; reading the data from the LCD. Data will be copied from the LCD data register to MCS-51 via the data bus (D0-D7), namely Pins 7–14 of the LCD. Conversely, if Pin 5 is given a voltage with logical 0 then the operation is a write operation; the signal will be sent from the MCS51 to LCD through the LCD Pins (Pins 7–14); The signal sent can be in the form of data or instructions depending on the logic level input to the Register Select-RS Pin, as described above before if RS = 0 then the signal sent is an instruction, vice versa if the RS = 1 then the signal sent/written is the data you want to display. Usually, Pin 5 of the LCD is connected with the power supply GND, because we will never read data from the LCD data register, but only send instructions for the LCD work configuration or the data you want to display on the LCD.
Pin 6 of the LCD (EN¯) is a Pin used to enable the LCD. The LCD will be enabled with the entry of changes in the signal level from high (1) to low (0) on Pin 6. If Pin 6 gets the voltage of logic level either 1 or 0 then the LCD will be disabled; it will only be enabled when there is a change of the voltage level in Pin 6 from high logic level to low logic level for more than 1000 microseconds (1 millisecond), and we can send either instruction or data to processed during that enable time of Pin 6.
Pin 3 and Pin 15 are used to regulate the brightness of the BPL (Back Plane Light). As mentioned above before the LCD operates on the principle of continuing or inhibiting the light passing through it; instead of producing light by itself. The light source comes from LED behind this LCD called BPL. Light brightness from BPL can be set by using a potentiometer or a trimpot. From Figure 6 Pin 3 (VEE) is used to regulate the brightness of BPL (by changing the current that enters BPL by using a potentiometers/a trimpot). While Pin 15 (BPL) is a Pin used for the sink of BPL LED.
4RSRegister selector on the LCD, if RS = 0 then the selected register is an instruction register (the operation to be performed is a write operation/LCD configuration if Pin 5 (R/W¯) is given a logic 0), if RS = 1 then the selected register is a data register; if (R/W¯) = 0 then the operation performed is a data write operation to the LCD, otherwise if (R/W¯) = 1 then the operation performed is a read operation (data will be sent from the LCD to μC (microcontroller); it is usually used to read the busy bit/Busy Flag- BF of the LCD (bit 7/D7).
5(R/W¯)Sets the operating mode, logic 1 for reading operations and logic 0 for write operations, the information read from the LCD to μC is data, while information written to the LCD from μC can be data to be displayed or instructions used to configure the LCD. Usually, this Pin is connected to the GND of the power supply because we will never read data from the LCD but only write instructions to configure it or write data to the LCD register to be displayed.
6Enable¯The LCD is not active when Enable Pin is either 1 or 0 logic. The LCD will be active if there is a change from logic 1 to logic 0; information can be read or written at the time the change occurs.
The 64128N uses our 64128K LCD module which has a viewing area of 50 x 25 mm and the ST7565R COG IC. The backlight uses a single LED for low power consumption.The PCB allows for easy mounting and assembly.
The ST7565R is a single-chip dot matrix LCD driver that can be connected directly to a microprocessor bus. 8-bit parallel or 4-line SPI display data sent from the microprocessor is stored in the internal display data RAM and the chip generates a LCD drive signal independent of the microprocessor. Because the chips in the ST7565R contain 65x132 bits of display data RAM and there is a 1-to-1 correspondence between the LCD panel pixels and the internal RAM bits, these chips enable displays with a high degree of freedom. The ST7565R chips contain 65 common output circuits and 132 segment output circuits, so that a single chip can drive a 65x132 dot display (capable of displaying 8 columns x4 rows of a 16x16 dot kanji font).

If you only use 4bit data then with the Register Select and enable pins you only need 6 gpio. You will have to connect read/write to ground rather a gpio pin.
Hello and thank you very much for your feedback: unfortunately I"m a total newbye about GPIO and LCD screens, so I could not understand the first part of your answer.
So that is a HDD44780 compatible LCD which is what I assumed you were talking about it clearly states only 6 digital lines required, so that"s 6 gpio the pi gpio being digital.
Now there are lots and lots of examples on line https://www.google.com/search?q=16x2+lc ... =firefox-b of how to use this type of lcd with the pi you are just going to have to modify which ever example you choose to follow to use the free gpio you have.
it also works with python2 and 3 as long as you install it for which ever version of python you intend to use, it also has the option for you to choose which gpio pins you want to use for which functions ( remember I said 4bit data then with the Register Select and enable pins you only need 6 gpio ).
I"ve seen some LCD2USB boards that, of course, are supported by LCDproc and should make everything easier, nevertheless I"d really like to find a (solderless) solution to exploit that unused pins on the VGA hat.
So, aside from LCD2USB boards, I wonder which connection board (I2C?) is OK to connect the LCD display to the pins of the VGA hat (I prefer a solderless solution so I"d like to buy display + connection board yet assembled).
If you intend to use specific software then I suggest you contact the writer of the software to see if it can be configured to drive the LCD using only the gpio pins you have free.
As the software seems to be written to use usb, serial and parallel ports for connecting to the LCD you may find you will not be able to use it with the limited gpio you have free.

This tutorial shows how to use the I2C LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) with the ESP32 using Arduino IDE. We’ll show you how to wire the display, install the library and try sample code to write text on the LCD: static text, and scroll long messages. You can also use this guide with the ESP8266.
Additionally, it comes with a built-in potentiometer you can use to adjust the contrast between the background and the characters on the LCD. On a “regular” LCD you need to add a potentiometer to the circuit to adjust the contrast.
Before displaying text on the LCD, you need to find the LCD I2C address. With the LCD properly wired to the ESP32, upload the following I2C Scanner sketch.
After uploading the code, open the Serial Monitor at a baud rate of 115200. Press the ESP32 EN button. The I2C address should be displayed in the Serial Monitor.
Displaying static text on the LCD is very simple. All you have to do is select where you want the characters to be displayed on the screen, and then send the message to the display.
The next two lines set the number of columns and rows of your LCD display. If you’re using a display with another size, you should modify those variables.
Then, you need to set the display address, the number of columns and number of rows. You should use the display address you’ve found in the previous step.
To display a message on the screen, first you need to set the cursor to where you want your message to be written. The following line sets the cursor to the first column, first row.
Scrolling text on the LCD is specially useful when you want to display messages longer than 16 characters. The library comes with built-in functions that allows you to scroll text. However, many people experience problems with those functions because:
The messageToScroll variable is displayed in the second row (1 corresponds to the second row), with a delay time of 250 ms (the GIF image is speed up 1.5x).
In a 16×2 LCD there are 32 blocks where you can display characters. Each block is made out of 5×8 tiny pixels. You can display custom characters by defining the state of each tiny pixel. For that, you can create a byte variable to hold the state of each pixel.
In summary, in this tutorial we’ve shown you how to use an I2C LCD display with the ESP32/ESP8266 with Arduino IDE: how to display static text, scrolling text and custom characters. This tutorial also works with the Arduino board, you just need to change the pin assignment to use the Arduino I2C pins.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey