2.8 inch tft lcd shield touch display module datasheet free sample
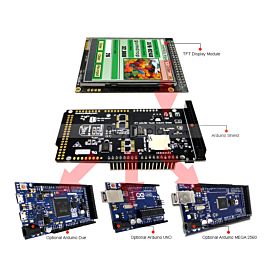
Spice up your Arduino project with a beautiful large touchscreen display shield with built in microSD card connection. This TFT display is big (2.8" diagonal) bright (4 white-LED backlight) and colorful (18-bit 262,000 different shades)! 240x320 pixels with individual pixel control. As a bonus, this display has a optional resistive touch panel with controller XPT2046 attached by default and a optional capacitive touch panel with controller FT6206 attached by default, so you can detect finger presses anywhere on the screen and doesn"t require pressing down on the screen with a stylus and has nice glossy glass cover.
The shield is fully assembled, tested and ready to go. No wiring, no soldering! Simply plug it in and load up our library - you"ll have it running in under 10 minutes! Works best with any classic Arduino (UNO/Due/Mega 2560).
This display shield has a controller built into it with RAM buffering, so that almost no work is done by the microcontroller. You can connect more sensors, buttons and LEDs.
Of course, we wouldn"t just leave you with a datasheet and a "good luck!" - we"ve written a full open source graphics library at the bottom of this page that can draw pixels, lines, rectangles, circles and text. We also have a touch screen library that detects x,y and z (pressure) and example code to demonstrate all of it. The code is written for Arduino but can be easily ported to your favorite microcontroller!

ER-TFTM028-4 is 240x320 dots 2.8" color tft lcd module display with ILI9341 controller board,superior display quality,super wide viewing angle and easily controlled by MCU such as 8051, PIC, AVR, ARDUINO,ARM and Raspberry PI.It can be used in any embedded systems,industrial device,security and hand-held equipment which requires display in high quality and colorful image.
It supports 8080 8-bit /9-bit/16-bit /18-bit parallel ,3-wire,4-wire serial spi interface.Built-in optional microSD card slot, 2.8" 4-wire resistive touch panel with controller XPT2046 and 2.8" capacitive touch panel with controller FT6206. It"s optional for font chip, flash chip and microsd card. We offer two types connection,one is pin header and the another is ZIF connector with flat cable mounting on board by default and suggested. Lanscape mode is also available.
Of course, we wouldn"t just leave you with a datasheet and a "good luck!".Here is the link for 2.8"TFT Touch Shield with Libraries, EXxamples.Schematic Diagram for Arduino Due,Mega 2560 and Uno . For 8051 microcontroller user,we prepared the detailed tutorial such as interfacing, demo code and development kit at the bottom of this page.
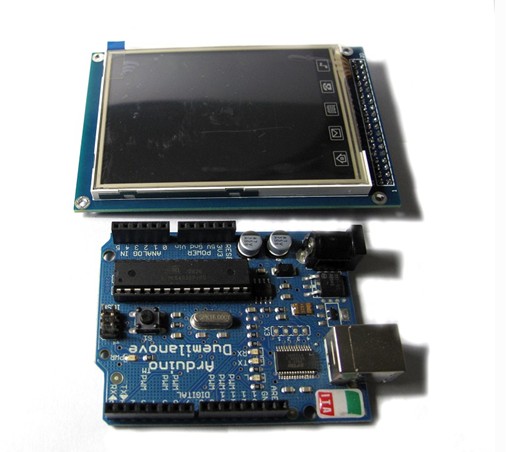

HY-TFT280 is a 2.8 inch TFT LCD Screen module, 320*240 (resolution), 65K color, 40pins interface , not just a LCD breakout, but include the Touch screen, SD card. So it’s a powerful extension module for your project.
This Screen includes a controller ILI9331, it’s 16bit data interface, easy to drive by many MCU like STM32 ,AVR and 8051.HY-TFT280 is designed with a touch controller in it . The touch IC is XPT2046 , and touch interface is included in the 40 pins breakout. Another useful extension in this module is the SD Card socket . It use the SPI mode to operate the SD card, the SPI interface include in the 40pins breakout.
The TFT library is required to be installed to get this screen model display. This library is especially designed for TFT LCD screen using 16 bit mode. The library require the following connections.
Note: The TFT controller model needs to be declared in the initializing statement. ITDB02 myGLCD(38,39,40,41) needs to be modified as myGLCD(GEEE28,38,39,40,41) when using Arduino Mega2560.ITDB02 myGLCD(GEEE28,19,18,17,16) needs to be commented when using Aduino UNO. Otherwise it just show a blank screen. In practice, RS, WR, CS, RSET can be connected to any free pin. But the pin number must be in accord with myGLCD(RS,WR,CS,RST).
The LCD has a 2.8" 4-wire resistive touch screen lying over it. The Touch library needs to be installed to get it works. This library is designed for 2.4’’ TFT, 2.8” TFT LCD screen module.
Note:TCLK, TCS, TDIN, TDOUT, IRQ also can be connected to any free pin. But the pin number must be in accord with the touch screen initializing statement myTouch(DCLK,CS,IN,OUT,IRQ).
The default setting is accurate for 2.4” TFT module, but you need to calibrate when using 2.8” TFT module. A program to calibrate the touch screen is included in the example. If you touch screen is inaccurate, you need to run touch_calibration. Follow the on-screen instruction to calibrate the touch screen. Better not use your finger to calibrate it, use your accessory touch pen to pressure the frontsight with stength. Then record the calibration parameters and apply them in ITDB02_Touch.cpp in your touch screen library.
There is built-in SD card slot in the shield, so we can use it to upload images. But the images need to be converted RAW format first. SD libraries tinyFAT and tinyFAT_16 need to be preinstalled for displaying the image.

The four sample codes: DisplayString, DrawGraphic, ShowBMP, and TouchPanel are used to display strings, graphics, pictures in BMP format, and touch pen functions.
Before performing the ShowImage display picture experiment, first, copy the pictures in the PIC folder in the data to the root directory of the SD card
Before experimenting with the TouchPanel, the touchscreen must be calibrated according to the displayed prompts. Open the corresponding project, burn the program, and you will be prompted when running:
The demos are developed based on the HAL library. Download the program, find the STM32 program file directory, and open the STM32 with four project folders: DisplayString, DrawGraphic, ShowImage, and Touchscreen.
The four sample codes: DisplayString, DrawGraphic, ShowBMP, and TouchPanel are used to display strings, graphics, pictures in BMP format, and touch pen functions.
Before performing the ShowImage display picture experiment, first, copy the pictures in the PIC folder in the data to the root directory of the SD card
Before experimenting with the TouchPanel, the touchscreen must be calibrated according to the displayed prompts. Open the corresponding project, burn the program, and you will be prompted when running:

In this Arduino touch screen tutorial we will learn how to use TFT LCD Touch Screen with Arduino. You can watch the following video or read the written tutorial below.
For this tutorial I composed three examples. The first example is distance measurement using ultrasonic sensor. The output from the sensor, or the distance is printed on the screen and using the touch screen we can select the units, either centimeters or inches.
The third example is a game. Actually it’s a replica of the popular Flappy Bird game for smartphones. We can play the game using the push button or even using the touch screen itself.
As an example I am using a 3.2” TFT Touch Screen in a combination with a TFT LCD Arduino Mega Shield. We need a shield because the TFT Touch screen works at 3.3V and the Arduino Mega outputs are 5 V. For the first example I have the HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor, then for the second example an RGB LED with three resistors and a push button for the game example. Also I had to make a custom made pin header like this, by soldering pin headers and bend on of them so I could insert them in between the Arduino Board and the TFT Shield.
Here’s the circuit schematic. We will use the GND pin, the digital pins from 8 to 13, as well as the pin number 14. As the 5V pins are already used by the TFT Screen I will use the pin number 13 as VCC, by setting it right away high in the setup section of code.
I will use the UTFT and URTouch libraries made by Henning Karlsen. Here I would like to say thanks to him for the incredible work he has done. The libraries enable really easy use of the TFT Screens, and they work with many different TFT screens sizes, shields and controllers. You can download these libraries from his website, RinkyDinkElectronics.com and also find a lot of demo examples and detailed documentation of how to use them.
After we include the libraries we need to create UTFT and URTouch objects. The parameters of these objects depends on the model of the TFT Screen and Shield and these details can be also found in the documentation of the libraries.
Next we need to define the fonts that are coming with the libraries and also define some variables needed for the program. In the setup section we need to initiate the screen and the touch, define the pin modes for the connected sensor, the led and the button, and initially call the drawHomeSreen() custom function, which will draw the home screen of the program.
So now I will explain how we can make the home screen of the program. With the setBackColor() function we need to set the background color of the text, black one in our case. Then we need to set the color to white, set the big font and using the print() function, we will print the string “Arduino TFT Tutorial” at the center of the screen and 10 pixels down the Y – Axis of the screen. Next we will set the color to red and draw the red line below the text. After that we need to set the color back to white, and print the two other strings, “by HowToMechatronics.com” using the small font and “Select Example” using the big font.
Here’s that function which uses the ultrasonic sensor to calculate the distance and print the values with SevenSegNum font in green color, either in centimeters or inches. If you need more details how the ultrasonic sensor works you can check my particular tutorialfor that. Back in the loop section we can see what happens when we press the select unit buttons as well as the back button.
Ok next is the RGB LED Control example. If we press the second button, the drawLedControl() custom function will be called only once for drawing the graphic of that example and the setLedColor() custom function will be repeatedly called. In this function we use the touch screen to set the values of the 3 sliders from 0 to 255. With the if statements we confine the area of each slider and get the X value of the slider. So the values of the X coordinate of each slider are from 38 to 310 pixels and we need to map these values into values from 0 to 255 which will be used as a PWM signal for lighting up the LED. If you need more details how the RGB LED works you can check my particular tutorialfor that. The rest of the code in this custom function is for drawing the sliders. Back in the loop section we only have the back button which also turns off the LED when pressed.
Module Size:67mm(length)*40mm(width)*4mm(thickness), Active Area: 47.5mm(Length)x36.5mm(Width)Package Included:1*2.2" 2.2 inch 4-Wire SPI TFT LCD Display ModuleHow to use it?1. use 5v to led pin, 3.3v to vcc and 1k / 1.5k resistor voltage dividers to get it to work. 1k resistor in series from Arduino to tft logic pin, 1.5k from tft pin to ground.

Spice up your Arduino project with a beautiful large touchscreen display shield with built in microSD card connection. This TFT display is big (2.8" diagonal) bright (4 white-LED backlight) and colorful (18-bit 262,000 different shades)! 240x320 pixels with individual pixel control. It has way more resolution than a black and white 128x64 display. As a bonus, this display has a resistive touchscreen attached to it already, so you can detect finger presses anywhere on the screen.
The shield is fully assembled, tested and ready to go. No wiring, no soldering! Simply plug it in and load up our library - you"ll have it running in under 10 minutes!
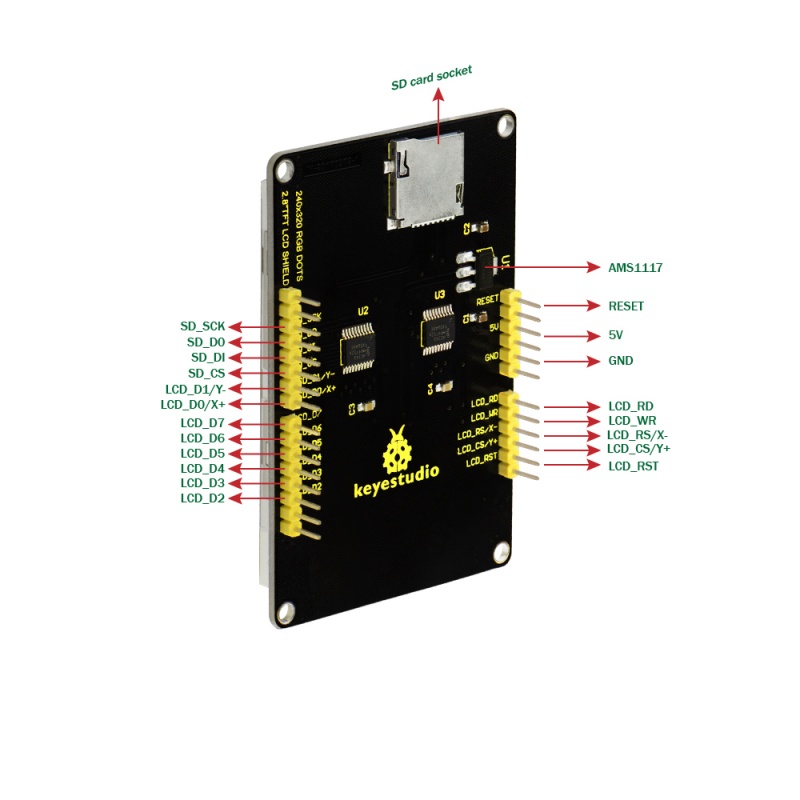
This display shield has a controller built into it with RAM buffering, so that almost no work is done by the microcontroller. The shield does require a lot of pins: 12 lines total for the display, 13 total if you use the microSD card
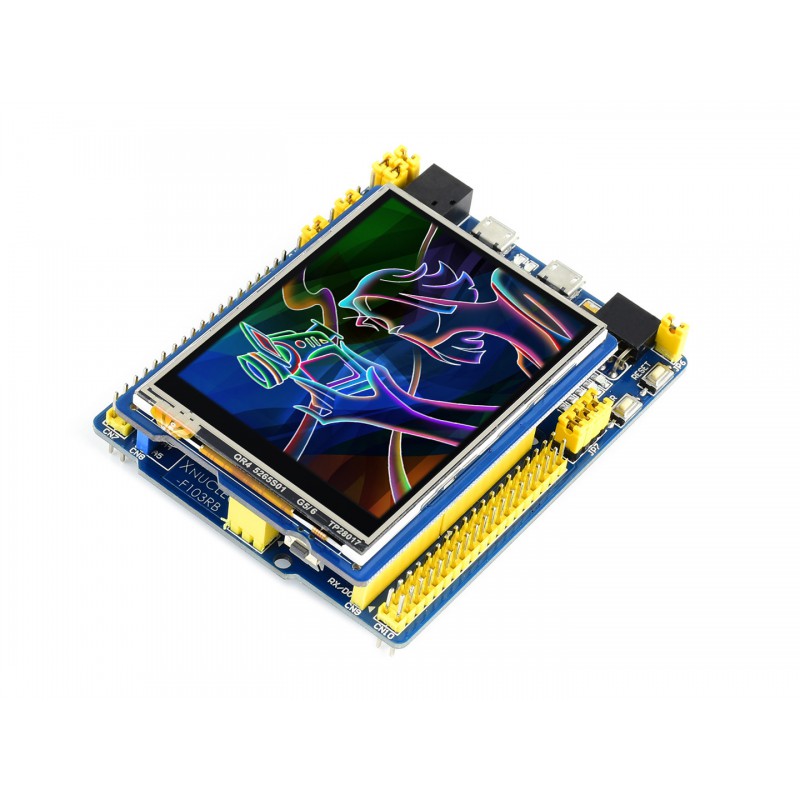

(The following is the touch screen signal line wiring, if you do not need to touch function or the module itself does not have touch function, you can not connect them)

You can build a Timer project where the user can set the time right on the LCD. Other examples include interactive games, controlling thermostats, etc.
This article is part of our series on the different types of displaysthat you can use with Arduino, so if you’re weighing up the options, then do check out our guide to the best displays to use with Arduino.
The TFT displays come in two variants: With touch and without touch. The modules with touch come with an additional layer of transparent touch screen.
The pinouts for the display and the SD card remain the same. Only pinouts related to the touch sensor will change depending on whether the module has a resistive or capacitive type touch sensor.
The electric field gets coupled through your hand when you touch the screen. This change is the electric field reflected as the change in the capacitance.
Some dedicated controllers can help Arduino detect the screen’s finger touch easily. One example is an FT6206 which can support small to medium-sized screens with up to 28 sensors.
I am confident that the article was easy to follow. I have used TFT display with touch for an HMI project which controls the thermostat in my hobby projects to learn more about the OT system (open Therm)




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey