tft display vs super amoled display hindi made in china
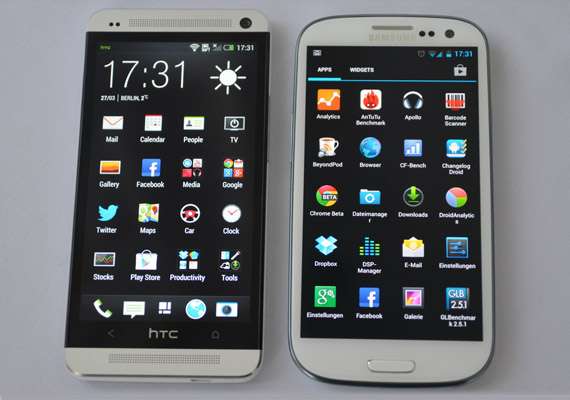
New Delhi: The technology used in mobile displays in the modern day smartphones has progressed significantly. In the era of touchscreen smartphones, the display technology has become one of its primary selling points, and certainly its most unique feature. Not only we want the touch screens to offer crisp text, vibrant images, blur-free video and enough brightness, we want them at low cost too.
For instance, HTC One uses Super LCD3 tech, in its 4.7in screen which gives a resolution of 1920 x 1080 pixels, with pixel density of 469 pixels per inch (ppi). This results in super display in terms of crispness and colour reproduction. HTC says the SLCD technology gives the phone better power management, improved viewing angles and is easier to produce.
The Thin film transistor liquid crystal display (TFT LCD) technology is the most common display technology used in mobile phones. A variant of liquid crystal display (LCD), the technology uses TFT technology to enhance image quality. It offers better image quality and higher resolutions as compared to earlier generation LCD displays.
IPS LCD Stands for In Plane Switching liquid Crystal Display. This technology offers better display quality as compared to the TFT-LCD display. The good part about IPS LCD is that it offers better viewing angles and consumes less power. Due to higher costs, it is found only on high-end smartphones. Apple uses a high resolution (640x960 pixels) version of IPS LCD in its iPhone 4, which is also called Retina Display.
Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED) display technology is much better as compared to the LCD display technology because of its excellent colour reproduction, faster response times, wider viewing angles, higher brightness and extremely light weight designs.
Since these display forms are easier to produce, they can be made to larger sizes. Because OLEDs are essentially plastics, they can be made into large, thin sheets.
AMOLED stands for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode. A step ahead of OLED screens, the AMOLED screens can control each pixel individuality while maintaining the properties of an OLED panel. AMOLED screens use a different subpixel arrangement which can reduce the image quality a bit.
AMOLED screens have all the attributes of an OLED display like excellent colour reproduction, faster response times, wider viewing angles, higher brightness and extremely light weight designs.
Super AMOLED display technology is an advanced version of AMOLED display. Samsung uses this term for the AMOLED panels that they develop. Super AMOLED screens are built with capacitive touch sensors on the display itself. Super AMOLED display is much more responsive than an AMOLED display. Samsung top-of-the-line Galaxy SII comes engineered with Super AMOLED display technology. Samsung has already took it"s SMOLED screen to next levels by developing Super AMOLED+, HD Super AMOLED+ and FHD Super AMOLED+ screens.
It is a name given by Apple to the high-resolution screen technology introduced on the iPhone 4 in June 2010. Something is a Retina Display when it offers a density of pixels above 163 pixels per inch. The company calls it the Retina display because its pixels cannot be individually identified by a human eye, thus rendering a super sharp display, more crisp text and more clear pictures.
Retina Display is designed to smooth the jagged edges of pixels are provide a higher-quality image than previously available on mobile devices. Apple claims that its resolution is so good that it makes it impossible for the human eye to distinguish individual pixels. Its effects shows up in text, images and videos.
Color boost is simply Moto"s marketing term for their new display. Although it now uses LCD displays, the company fine-tuned its panels to match the saturation of OLED displays while maintaining the higher performance of LCD. It"s somewhere in the middle ground.
The demand for the best visual experience has grown higher over recent years. Everyone wants the best in the class display to their smartphones to view the high-definition magic their phone provides. This demand for better display has risen recently as big brands like iPhone and Samsung have added some absolutely gorgeous displays to their smartphones.
The major battle begins here. The two competitors of the game are LTPS LCD and AMOLED. These are state of the art displays and people often find themselves comparing these two displays. People are wondering about the result for LTPS vs AMOLED.
LTPS and AMOLED comparison has always been an interesting debate. Potential buyers of smartphones keep comparing the difference between LTPS and AMOLED. There is a complete LTPS and AMOLED comparison below which outlines the difference between these two types:
LTPS stands for Low-Temperature PolySilicon. This type of display provides a faster and more integrated display compared to a standard LCD. The LTPS display provides a better picture quality for the user and some people consider it to be more true to life. It provides larger picture densities and is also lower on power consumption as it does not light up every pixel individually. People can expect a higher picture resolution in their displays.
AMOLED stands for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode. AMOLED displays are completely different. They use an array of LEDs that help light up every pixel individually, so the only area of the display that is in use, only those pixels light up and the others stay shut. This helps provide a higher contrast to the image with very deep blacks. The display also helps in power consumption as every pixel draws power individually.
There is no actual winner to this debate, just like the console war or the Android vs Apple debate. The choice depends completely on the user and their tastes and preferences. If the users want a better picture resolution in their display, they can go with LTPS LCD and if the user wants a higher contrast picture to their display then they can go with AMOLED. Both displays deteriorate faster than standard LCD screens. Apple is known to use LCD panels in their smartphones and Samsung is known to use AMOLED ones. These are the points that can help the user make an informed decision about which display they would want to go with.
Over time, the purpose of using mobile phones or Smartphones has changed. Comparatively, it has now become a basic necessity of every individual. Smartphone has dramatically transformed the lives of individuals. It has now become a mini-computer that everyone carries in their pocket. Instead, you can have multiple things at your fingertips in a few seconds. While there are plenty of things to look for, AMOLED vs OLED is also a part of it.
Before purchasing any Smartphone, everyone goes through a list of specifications. This list includes display type, screen size, battery backup, supported operating system, total internal memory, and many others. Today, we have brought a comprehensive study of the significant display technologies available nowadays.
This article will introduce you to AMOLED vs OLED display technologies. Then, we will discuss the properties of both display technologies, followed by the difference between AMOLED vs OLED.
It stands for Natural Light-Emitting Diode, a type of LED technique that utilises LEDs wherein the light is of organic molecules that cause the LEDs to shine brighter. These organic LEDs are in use to make what are thought to be the best display panels in the world.
When you make an OLED display, you put organic films among two conductors to make them. As a result, a bright light comes out when electricity is used—a simple design with many advantages over other ways to show things.
OLEDs can be used to make emissive displays, which implies that each pixel can be controlled and emits its very own light. As a result, OLED displays have excellent picture quality. They have bright colours, fast motion, and most importantly, very high contrast. Most of all, “real” blacks are the most important. The simple design of OLEDs also makes it easy to create flexible displays that can bend and move.
PMOLED stands for Passive Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode. The PMOLEDs are easy to find and much cheaper than other LEDs, but they cannot work for a long duration as their lifespan is very short. Therefore, this type of display is generally for small devices up to 3 inches.
AMOLED stands for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode. This type of display is generally for large platforms. It contains TFT, which further consists of a storage capacitor. It also works on the same principle as OLED displays.
AMOLED offers no restriction on the size of the display. The power consumption of AMOLED is much less than other display technologies. The AMOLED provides incredible performance. It is thinner, lighter, and more flexible than any other display technology like LED, or LCD technology.
The AMOLED display is widely used in mobiles, laptops, and televisions as it offers excellent performance. Therefore, SAMSUNG has introduced AMOLED displays in almost every product. For example, Full HD Super AMOLED in Samsung Galaxy S4 and Samsung Galaxy Note 3, Super AMOLED in Samsung Galaxy S3, HD Super AMOLED in Samsung Galaxy Note, and HD Super AMOLED Plus in Samsung Galaxy S3. Apart from this, it is also used in AMOLED vs OLED creating the following:
So far, we have discussed OLED and AMOLED display technologies. Now, we will look at some of the differences between OLED and AMOLED display technology:

Thanks for the display technology development, we have a lot of display choices for our smartphones, media players, TVs, laptops, tablets, digital cameras, and other such gadgets. The most display technologies we hear are LCD, TFT, OLED, LED, QLED, QNED, MicroLED, Mini LED etc. The following, we will focus on two of the most popular display technologies in the market: TFT Displays and Super AMOLED Displays.
TFT means Thin-Film Transistor. TFT is the variant of Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs). There are several types of TFT displays: TN (Twisted Nematic) based TFT display, IPS (In-Plane Switching) displays. As the former can’t compete with Super AMOLED in display quality, we will mainly focus on using IPS TFT displays.
OLED means Organic Light-Emitting Diode. There are also several types of OLED, PMOLED (Passive Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) and AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode). It is the same reason that PMOLED can’t compete with IPS TFT displays. We pick the best in OLED displays: Super AMOLED to compete with the LCD best: IPS TFT Display.
If you have any questions about Orient Display displays and touch panels. Please feel free to contact: Sales Inquiries, Customer Service or Technical Support.

The demand for the best visual experience has grown higher over recent years. Everyone wants the best in the class display to their smartphones to view the high-definition magic their phone provides. This demand for better display has risen recently as big brands like iPhone and Samsung have added some absolutely gorgeous displays to their smartphones.
The major battle begins here. The two competitors of the game are LTPS LCD and AMOLED. These are state of the art displays and people often find themselves comparing these two displays. People are wondering about the result for LTPS vs AMOLED.
LTPS and AMOLED comparison has always been an interesting debate. Potential buyers of smartphones keep comparing the difference between LTPS and AMOLED. There is a complete LTPS and AMOLED comparison below which outlines the difference between these two types:
LTPS stands for Low-Temperature PolySilicon. This type of display provides a faster and more integrated display compared to a standard LCD. The LTPS display provides a better picture quality for the user and some people consider it to be more true to life. It provides larger picture densities and is also lower on power consumption as it does not light up every pixel individually. People can expect a higher picture resolution in their displays.
AMOLED stands for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode. AMOLED displays are completely different. They use an array of LEDs that help light up every pixel individually, so the only area of the display that is in use, only those pixels light up and the others stay shut. This helps provide a higher contrast to the image with very deep blacks. The display also helps in power consumption as every pixel draws power individually.
There is no actual winner to this debate, just like the console war or the Android vs Apple debate. The choice depends completely on the user and their tastes and preferences. If the users want a better picture resolution in their display, they can go with LTPS LCD and if the user wants a higher contrast picture to their display then they can go with AMOLED. Both displays deteriorate faster than standard LCD screens. Apple is known to use LCD panels in their smartphones and Samsung is known to use AMOLED ones. These are the points that can help the user make an informed decision about which display they would want to go with.

New Delhi: The technology used in mobile displays in the modern day smartphones has progressed significantly. In the era of touchscreen smartphones, the display technology has become one of its primary selling points, and certainly its most unique feature. Not only we want the touch screens to offer crisp text, vibrant images, blur-free video and enough brightness, we want them at low cost too.
For instance, HTC One uses Super LCD3 tech, in its 4.7in screen which gives a resolution of 1920 x 1080 pixels, with pixel density of 469 pixels per inch (ppi). This results in super display in terms of crispness and colour reproduction. HTC says the SLCD technology gives the phone better power management, improved viewing angles and is easier to produce.
The Thin film transistor liquid crystal display (TFT LCD) technology is the most common display technology used in mobile phones. A variant of liquid crystal display (LCD), the technology uses TFT technology to enhance image quality. It offers better image quality and higher resolutions as compared to earlier generation LCD displays.
IPS LCD Stands for In Plane Switching liquid Crystal Display. This technology offers better display quality as compared to the TFT-LCD display. The good part about IPS LCD is that it offers better viewing angles and consumes less power. Due to higher costs, it is found only on high-end smartphones. Apple uses a high resolution (640x960 pixels) version of IPS LCD in its iPhone 4, which is also called Retina Display.
Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED) display technology is much better as compared to the LCD display technology because of its excellent colour reproduction, faster response times, wider viewing angles, higher brightness and extremely light weight designs.
Since these display forms are easier to produce, they can be made to larger sizes. Because OLEDs are essentially plastics, they can be made into large, thin sheets.
AMOLED stands for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode. A step ahead of OLED screens, the AMOLED screens can control each pixel individuality while maintaining the properties of an OLED panel. AMOLED screens use a different subpixel arrangement which can reduce the image quality a bit.
AMOLED screens have all the attributes of an OLED display like excellent colour reproduction, faster response times, wider viewing angles, higher brightness and extremely light weight designs.
Super AMOLED display technology is an advanced version of AMOLED display. Samsung uses this term for the AMOLED panels that they develop. Super AMOLED screens are built with capacitive touch sensors on the display itself. Super AMOLED display is much more responsive than an AMOLED display. Samsung top-of-the-line Galaxy SII comes engineered with Super AMOLED display technology. Samsung has already took it"s SMOLED screen to next levels by developing Super AMOLED+, HD Super AMOLED+ and FHD Super AMOLED+ screens.
It is a name given by Apple to the high-resolution screen technology introduced on the iPhone 4 in June 2010. Something is a Retina Display when it offers a density of pixels above 163 pixels per inch. The company calls it the Retina display because its pixels cannot be individually identified by a human eye, thus rendering a super sharp display, more crisp text and more clear pictures.
Retina Display is designed to smooth the jagged edges of pixels are provide a higher-quality image than previously available on mobile devices. Apple claims that its resolution is so good that it makes it impossible for the human eye to distinguish individual pixels. Its effects shows up in text, images and videos.
Color boost is simply Moto"s marketing term for their new display. Although it now uses LCD displays, the company fine-tuned its panels to match the saturation of OLED displays while maintaining the higher performance of LCD. It"s somewhere in the middle ground.

Over time, the purpose of using mobile phones or Smartphones has changed. Comparatively, it has now become a basic necessity of every individual. Smartphone has dramatically transformed the lives of individuals. It has now become a mini-computer that everyone carries in their pocket. Instead, you can have multiple things at your fingertips in a few seconds. While there are plenty of things to look for, AMOLED vs OLED is also a part of it.
Before purchasing any Smartphone, everyone goes through a list of specifications. This list includes display type, screen size, battery backup, supported operating system, total internal memory, and many others. Today, we have brought a comprehensive study of the significant display technologies available nowadays.
This article will introduce you to AMOLED vs OLED display technologies. Then, we will discuss the properties of both display technologies, followed by the difference between AMOLED vs OLED.
It stands for Natural Light-Emitting Diode, a type of LED technique that utilises LEDs wherein the light is of organic molecules that cause the LEDs to shine brighter. These organic LEDs are in use to make what are thought to be the best display panels in the world.
When you make an OLED display, you put organic films among two conductors to make them. As a result, a bright light comes out when electricity is used—a simple design with many advantages over other ways to show things.
OLEDs can be used to make emissive displays, which implies that each pixel can be controlled and emits its very own light. As a result, OLED displays have excellent picture quality. They have bright colours, fast motion, and most importantly, very high contrast. Most of all, “real” blacks are the most important. The simple design of OLEDs also makes it easy to create flexible displays that can bend and move.
PMOLED stands for Passive Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode. The PMOLEDs are easy to find and much cheaper than other LEDs, but they cannot work for a long duration as their lifespan is very short. Therefore, this type of display is generally for small devices up to 3 inches.
AMOLED stands for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode. This type of display is generally for large platforms. It contains TFT, which further consists of a storage capacitor. It also works on the same principle as OLED displays.
AMOLED offers no restriction on the size of the display. The power consumption of AMOLED is much less than other display technologies. The AMOLED provides incredible performance. It is thinner, lighter, and more flexible than any other display technology like LED, or LCD technology.
The AMOLED display is widely used in mobiles, laptops, and televisions as it offers excellent performance. Therefore, SAMSUNG has introduced AMOLED displays in almost every product. For example, Full HD Super AMOLED in Samsung Galaxy S4 and Samsung Galaxy Note 3, Super AMOLED in Samsung Galaxy S3, HD Super AMOLED in Samsung Galaxy Note, and HD Super AMOLED Plus in Samsung Galaxy S3. Apart from this, it is also used in AMOLED vs OLED creating the following:
So far, we have discussed OLED and AMOLED display technologies. Now, we will look at some of the differences between OLED and AMOLED display technology:
OLED comprises thin layers of the organic component, which emits light when the current passes through it. In this technology, each pixel transmits its own light. On the other side, AMOLED consists of an additional layer of thin-film transistors (TFTs). In AMOLED, the storage capacitors are used to maintain the pixel states.
While the technology is different among various manufacturers, Samsung’s edge AMOLED displays use plastic substrates with poly-Si TFT technology similar to how LG uses it in their POLED technology. This technology is what makes the possibility to build curved displays using an active-matrix OLED panel.
OLED display much deeper blacks as compared to the AMOLED displays. You cannot see the screen in AMOLED display under direct sunlight. The AMOLED display quality is much better than the OLEDs as it contains an additional layer of TFTs and follows backplane technologies.
These organic compounds are present between the protective layers of glass or plastic. Comparatively, AMOLED comprises an active matrix of OLED pixels along with an additional layer of TFTs. This extra layer is responsible for controlling the current flow in each pixel.
The OLED display offers a high level of control over pixels. Hence, it can be turned off completely, resulting in an excellent contrast ratio compared to the AMOLED displays and less power consumption. On the other side, AMOLED has faster refresh rates than OLEDs. Also, they offer a tremendous artificial contrast ratio as each pixel transmits light but consumes more power than OLEDs.
OLED displays are comparatively much thinner compared to the LCDs. Hence, it provides more efficient and bright presentations. In addition, OLED offers support for large display sizes compared to the traditional LCDs. AMOLEDs remove the limitation of display sizes. one can fit it into any display size.
Putting all the points mentioned above in view, the key difference to understand appropriately is that POLED is an OLED display with a plastic substrate. On the other hand, AMOLED is Samsung’s word for its display technology which is mainly for marketing. Therefore, most phone manufacturers having AMOLED displays mean that they are using Samsung displays. It is as simple as that. To add to that, all the curved display technology is made possible because of the usage of plastic substrate.
So, based on the points mentioned above, the difference between OLED and AMOLED displays, you can choose any of the two display technology at your convenience. Both are good, offer excellent performance, and are customised according to your requirements.
The AMOLED display has a higher quality than OLEDs since it has an additional layer of TTs and uses backplane technologies. When compared to OLED screens, AMOLED displays are far more flexible. As a result, they are substantially more expensive than an OLED display.
Window to the digital world, the display is one of the first seen features when selecting a smartphone, so a show must be good, and an AMOLED display offers the same. Offering a great viewing experience, here are the top 3 AMOLED screen smartphones available in the market right now:
Realme 8 Pro features a 6.4-inch Super AMOLED display with 411 PPI and a 2.5D curved display. It runs on Snapdragon 720G, bundled with Adreno 618 and 6GB of RAM. On the rear, the Realme 8 Pro has a quad-camera setup with 108-megapixels primary sensor, 8-megapixel ultra-wide angle sensor, 2-megapixel macro sensor, and a 2-megapixel monochrome sensor.
Coming to the front, it has a 16-megapixel selfie camera housed in the punch-hole display. It comes with a 4,500 mAh battery that supports Super Dart fast charging, with 100 per cent coming in just 47 min. The Realme 8 Pro is one of the best segments with a Super AMOLED FHD+ display. Media lovers will enjoy this phone with its deep blacks and vibrant colours.
The Xiaomi Mi 11 Lite runs on Snapdragon 732G chipset bundled with Adreno 618 GPU and up to 8GB RAM. The display front comes with a 6.55-inch AMOLED display with HDR 10+ support and 402 PPI.
The cameras have a triple rear camera setup with a 64-megapixel primary sensor, 8-megapixel ultra-wide angle sensor, and a 5-megapixel macro sensor. In addition, it has a 16-megapixel selfie camera housed in the punch-hole display on the front. It has a 4,250 mAh battery with 33W fast charging with USB Type-C. With the support for HDR 10+, the AMOLED display on the Mi 11 Lite is a treat for all media enthusiasts.
OPPO has recently launched the Oppo Reno 6 Pro with MediaTek’s Density 1200 chipset coupled with Mali-G77 MC9 GPU and up to 12GB of RAM. In addition, it comes with a 6.55-inch curved AMOLED FHD+ display with support for HDR 10+ and an Oleophobic coating.
On the rear, it comes with a quad-camera setup with a 64-megapixel primary sensor, an 8MP ultra-wide angle sensor, a 2-megapixel macro sensor, and a 2-megapixel depth sensor. In addition, it has a 32-megapixel selfie camera integrated inside the punch-hole on display on the front. It comes with a 4,500 mAh battery that supports 65W Super VOOC fast charging and can charge the phone 100 per cent in just 31 minutes. Since it comes with an FHD+ curved AMOLED display on the display front, it is a treat for gamers and media consumption lovers.
Smartphone displays have advanced significantly in recent years, more so than most people realise in this technological age. Display screens are similar to windows in the mobile world, which has seen a tremendous transformation in innovative products in the last several years. People have gotten more selective when buying a phone in recent years, and although all of the functions are important, the display is always the most noticeable.
Major smartphone manufacturers attempt to provide their consumers with the most delicate devices possible that incorporate the most up-to-date technologies. In AMOLED vs OLED, AMOLED is a type of OLED and a more prominent example of both OLED and POLED, so there’s no debate about which is superior.

AMOLED and TFT are two types of display technology used in smartphones. AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode) displays are made up of tiny organic light-emitting diodes, while TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) displays use inorganic thin-film transistors.
AMOLEDs are made from organic materials that emit light when an electric current is passed through them, while TFTs use a matrix of tiny transistors to control the flow of electricity to the display.
Refresh Rate: Another key difference between AMOLED and TFT displays is the refresh rate. The refresh rate is how often the image on the screen is updated. AMOLED screens have a higher refresh rate than TFT screens, which means that they can display images more quickly and smoothly.
Response Time: The response time is how long it takes for the pixels to change from one colour to another. AMOLED screens have a shorter response time than TFT screens..
Colour Accuracy/Display Quality: AMOLED screens are more accurate when it comes to displaying colours. This is because each pixel on an AMOLED screen emits its own light, which means that the colours are more pure and true to life. TFT screens, on the other hand, use a backlight to illuminate the pixels, which can cause the colours to appear washed out or less vibrant.
Viewing Angle: The viewing angle is the angle at which you can see the screen. AMOLED screens have a wider viewing angle than TFT screens, which means that you can see the screen from more angles without the colours looking distorted.
Power Consumption: One of the main advantages of AMOLED displays is that they consume less power than TFT displays. This is because the pixels on an AMOLED screen only light up when they need to, while the pixels on a TFT screen are always illuminated by the backlight.
Production Cost: AMOLED screens are more expensive to produce than TFT screens. This is because the manufacturing process for AMOLED screens is more complex, and the materials used are more expensive.
Availability: TFT screens are more widely available than AMOLED screens and have been around for longer. They are typically used in a variety of devices, ranging from phones to TVs.
Usage: AMOLED screens are typically used in devices where power consumption is a concern, such as phones and wearable devices. TFT screens are more commonly used in devices where image quality is a higher priority, such as TVs and monitors.
AMOLED and TFT are two different types of display technology. AMOLED displays are typically brighter and more vibrant, but they are more expensive to produce. TFT displays are cheaper to produce, but they are not as bright or power efficient as AMOLED displays.
The display technology that is best for you will depend on your needs and preferences. If you need a screen that is bright and vibrant, then an AMOLED display is a good choice. If you need a screen that is cheaper to produce, then a TFT display is a good choice. However, if you’re worried about image retention, then TFT may be a better option.
Nauticomp Inc.provides world-class fully customizable touchscreen displays for commercial and industrial settings. With features like sunlight readability, brightness adjustability, infrared lighting, full backlighting, all-weather capabilities, etc., our displays are second to none. Contact us today to learn more.

A thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display (TFT LCD) is a variant of a liquid-crystal display that uses thin-film-transistor technologyactive matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven (i.e. with segments directly connected to electronics outside the LCD) LCDs with a few segments.
In February 1957, John Wallmark of RCA filed a patent for a thin film MOSFET. Paul K. Weimer, also of RCA implemented Wallmark"s ideas and developed the thin-film transistor (TFT) in 1962, a type of MOSFET distinct from the standard bulk MOSFET. It was made with thin films of cadmium selenide and cadmium sulfide. The idea of a TFT-based liquid-crystal display (LCD) was conceived by Bernard Lechner of RCA Laboratories in 1968. In 1971, Lechner, F. J. Marlowe, E. O. Nester and J. Tults demonstrated a 2-by-18 matrix display driven by a hybrid circuit using the dynamic scattering mode of LCDs.T. Peter Brody, J. A. Asars and G. D. Dixon at Westinghouse Research Laboratories developed a CdSe (cadmium selenide) TFT, which they used to demonstrate the first CdSe thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display (TFT LCD).active-matrix liquid-crystal display (AM LCD) using CdSe TFTs in 1974, and then Brody coined the term "active matrix" in 1975.high-resolution and high-quality electronic visual display devices use TFT-based active matrix displays.
The liquid crystal displays used in calculators and other devices with similarly simple displays have direct-driven image elements, and therefore a voltage can be easily applied across just one segment of these types of displays without interfering with the other segments. This would be impractical for a large display, because it would have a large number of (color) picture elements (pixels), and thus it would require millions of connections, both top and bottom for each one of the three colors (red, green and blue) of every pixel. To avoid this issue, the pixels are addressed in rows and columns, reducing the connection count from millions down to thousands. The column and row wires attach to transistor switches, one for each pixel. The one-way current passing characteristic of the transistor prevents the charge that is being applied to each pixel from being drained between refreshes to a display"s image. Each pixel is a small capacitor with a layer of insulating liquid crystal sandwiched between transparent conductive ITO layers.
The circuit layout process of a TFT-LCD is very similar to that of semiconductor products. However, rather than fabricating the transistors from silicon, that is formed into a crystalline silicon wafer, they are made from a thin film of amorphous silicon that is deposited on a glass panel. The silicon layer for TFT-LCDs is typically deposited using the PECVD process.
Polycrystalline silicon is sometimes used in displays requiring higher TFT performance. Examples include small high-resolution displays such as those found in projectors or viewfinders. Amorphous silicon-based TFTs are by far the most common, due to their lower production cost, whereas polycrystalline silicon TFTs are more costly and much more difficult to produce.
The twisted nematic display is one of the oldest and frequently cheapest kind of LCD display technologies available. TN displays benefit from fast pixel response times and less smearing than other LCD display technology, but suffer from poor color reproduction and limited viewing angles, especially in the vertical direction. Colors will shift, potentially to the point of completely inverting, when viewed at an angle that is not perpendicular to the display. Modern, high end consumer products have developed methods to overcome the technology"s shortcomings, such as RTC (Response Time Compensation / Overdrive) technologies. Modern TN displays can look significantly better than older TN displays from decades earlier, but overall TN has inferior viewing angles and poor color in comparison to other technology.
Most TN panels can represent colors using only six bits per RGB channel, or 18 bit in total, and are unable to display the 16.7 million color shades (24-bit truecolor) that are available using 24-bit color. Instead, these panels display interpolated 24-bit color using a dithering method that combines adjacent pixels to simulate the desired shade. They can also use a form of temporal dithering called Frame Rate Control (FRC), which cycles between different shades with each new frame to simulate an intermediate shade. Such 18 bit panels with dithering are sometimes advertised as having "16.2 million colors". These color simulation methods are noticeable to many people and highly bothersome to some.gamut (often referred to as a percentage of the NTSC 1953 color gamut) are also due to backlighting technology. It is not uncommon for older displays to range from 10% to 26% of the NTSC color gamut, whereas other kind of displays, utilizing more complicated CCFL or LED phosphor formulations or RGB LED backlights, may extend past 100% of the NTSC color gamut, a difference quite perceivable by the human eye.
IPS has since been superseded by S-IPS (Super-IPS, Hitachi Ltd. in 1998), which has all the benefits of IPS technology with the addition of improved pixel refresh timing.
In 2004, Hydis Technologies Co., Ltd licensed its AFFS patent to Japan"s Hitachi Displays. Hitachi is using AFFS to manufacture high end panels in their product line. In 2006, Hydis also licensed its AFFS to Sanyo Epson Imaging Devices Corporation.
Less expensive PVA panels often use dithering and FRC, whereas super-PVA (S-PVA) panels all use at least 8 bits per color component and do not use color simulation methods.BRAVIA LCD TVs offer 10-bit and xvYCC color support, for example, the Bravia X4500 series. S-PVA also offers fast response times using modern RTC technologies.
A technology developed by Samsung is Super PLS, which bears similarities to IPS panels, has wider viewing angles, better image quality, increased brightness, and lower production costs. PLS technology debuted in the PC display market with the release of the Samsung S27A850 and S24A850 monitors in September 2011.
TFT dual-transistor pixel or cell technology is a reflective-display technology for use in very-low-power-consumption applications such as electronic shelf labels (ESL), digital watches, or metering. DTP involves adding a secondary transistor gate in the single TFT cell to maintain the display of a pixel during a period of 1s without loss of image or without degrading the TFT transistors over time. By slowing the refresh rate of the standard frequency from 60 Hz to 1 Hz, DTP claims to increase the power efficiency by multiple orders of magnitude.
Due to the very high cost of building TFT factories, there are few major OEM panel vendors for large display panels. The glass panel suppliers are as follows:
External consumer display devices like a TFT LCD feature one or more analog VGA, DVI, HDMI, or DisplayPort interface, with many featuring a selection of these interfaces. Inside external display devices there is a controller board that will convert the video signal using color mapping and image scaling usually employing the discrete cosine transform (DCT) in order to convert any video source like CVBS, VGA, DVI, HDMI, etc. into digital RGB at the native resolution of the display panel. In a laptop the graphics chip will directly produce a signal suitable for connection to the built-in TFT display. A control mechanism for the backlight is usually included on the same controller board.
The low level interface of STN, DSTN, or TFT display panels use either single ended TTL 5 V signal for older displays or TTL 3.3 V for slightly newer displays that transmits the pixel clock, horizontal sync, vertical sync, digital red, digital green, digital blue in parallel. Some models (for example the AT070TN92) also feature input/display enable, horizontal scan direction and vertical scan direction signals.
New and large (>15") TFT displays often use LVDS signaling that transmits the same contents as the parallel interface (Hsync, Vsync, RGB) but will put control and RGB bits into a number of serial transmission lines synchronized to a clock whose rate is equal to the pixel rate. LVDS transmits seven bits per clock per data line, with six bits being data and one bit used to signal if the other six bits need to be inverted in order to maintain DC balance. Low-cost TFT displays often have three data lines and therefore only directly support 18 bits per pixel. Upscale displays have four or five data lines to support 24 bits per pixel (truecolor) or 30 bits per pixel respectively. Panel manufacturers are slowly replacing LVDS with Internal DisplayPort and Embedded DisplayPort, which allow sixfold reduction of the number of differential pairs.
The bare display panel will only accept a digital video signal at the resolution determined by the panel pixel matrix designed at manufacture. Some screen panels will ignore the LSB bits of the color information to present a consistent interface (8 bit -> 6 bit/color x3).
With analogue signals like VGA, the display controller also needs to perform a high speed analog to digital conversion. With digital input signals like DVI or HDMI some simple reordering of the bits is needed before feeding it to the rescaler if the input resolution doesn"t match the display panel resolution.
Kawamoto, H. (2012). "The Inventors of TFT Active-Matrix LCD Receive the 2011 IEEE Nishizawa Medal". Journal of Display Technology. 8 (1): 3–4. Bibcode:2012JDisT...8....3K. doi:10.1109/JDT.2011.2177740. ISSN 1551-319X.
Brody, T. Peter; Asars, J. A.; Dixon, G. D. (November 1973). "A 6 × 6 inch 20 lines-per-inch liquid-crystal display panel". 20 (11): 995–1001. Bibcode:1973ITED...20..995B. doi:10.1109/T-ED.1973.17780. ISSN 0018-9383.
K. H. Lee; H. Y. Kim; K. H. Park; S. J. Jang; I. C. Park & J. Y. Lee (June 2006). "A Novel Outdoor Readability of Portable TFT-LCD with AFFS Technology". SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers. AIP. 37 (1): 1079–82. doi:10.1889/1.2433159. S2CID 129569963.
Kim, Sae-Bom; Kim, Woong-Ki; Chounlamany, Vanseng; Seo, Jaehwan; Yoo, Jisu; Jo, Hun-Je; Jung, Jinho (15 August 2012). "Identification of multi-level toxicity of liquid crystal display wastewater toward Daphnia magna and Moina macrocopa". Journal of Hazardous Materials. Seoul, Korea; Laos, Lao. 227–228: 327–333. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.05.059. PMID 22677053.

This rise of small, powerful components has also led to significant developments in display technology. The most recent of which, AMOLED, is now the main competitor for the most common display used in quality portable electronics – the TFT–LCD IPS (In-Plane Switching) display. As more factories in the Far East begin to produce AMOLED technology, it seems likely we will enter a battle of TFT IPS versus AMOLED, or LCD vs LED. Where a large percentage of a product’s cost is the display technology it uses, which provides best value for money when you’re designing a new product?
TFT IPSdisplays improved on previous TFT LCD technology, developed to overcome limitations and improve contrast, viewing angles, sunlight readability and response times. Viewing angles were originally very limited – so in-plane switching panels were introduced to improve them.
Modern TFT screens can have custom backlights turned up to whatever brightness that their power limit allows, which means they have no maximum brightness limitation. TFT IPS panels also have the option for OCA bonding, which uses a special adhesive to bond a touchscreen or glass coverlens to the TFT. This improves sunlight readability by preventing light from bouncing around between the layers of the display, and also improves durability without adding excess bulk; some TFT IPS displays now only measure around 2 mm thick.
AMOLED technology is an upgrade to older OLED technology. It uses organic compounds that emit light when exposed to electricity. This means no backlight, which in turn means less power consumption and a reduction in size. AMOLED screens tend to be thinner than TFT equivalents, often produced to be as thin as 1 mm. AMOLED technology also offers greater viewing angles thanks to deeper blacks. Colours tend to be greater, but visibility in daylight is lower than IPS displays.
As manufacturers increasingly focus on smaller devices, such as portable smartphones and wearable technology, the thinness and high colour resolution of AMOLED screens have grown desirable. However, producing AMOLED displays is far more costly as fewer factories offer the technology at a consistent quality and minimum order quantities are high; what capacity there is is often taken up the mobile phone market Full HD TFT IPS displays have the advantage of being offered in industry standard sizes and at a far lower cost, as well as offering superior sunlight visibility.
The competition between displays has benefitted both technologies as it has resulted in improvements in both. For example, Super AMOLED, a marketing brand by Samsung, involves the integration of a touchscreen layer inside the screen, rather than overlaid on it. The backlight in TFT technology means they can never truly replicate the deep blacks in AMOLED, but improvements have been made in resolution to the point where manufacturers like Apple have been happy to use LCD screens in their smartphones, even as they compete with Samsung’s Super AMOLED.
Aside from smartphones, many technologies utilise displays to offer direct interaction with customers. To decide whether TFT LCD will survive the rise of AMOLED technology, we must first recap the advantages of LCD. The backlit quality means that whites are bright and contrast is good, but this will wear down a battery faster than AMOLED. Additionally, cost is a significant factor for LCD screens. They are cheaper, more freely available and are offered in industry standard sizes so can be ordered for new products without difficulty.
It seems hard to deny that AMOLED will someday become the standard for mobile phones, which demand great colour performance and are reliant on battery life. Where size is an issue, AMOLED will also grow to dominance thanks to its superior thinness. But for all other technologies, particularly in industrial applications, TFT-LCD offers bright, affordable display technology that is continually improving as the challenge from AMOLED rises.

I should add that it"s likely that Nokia decided to use IPS LCD for the 701"s display because of cost and supply reasons, rather than technical ones. After all, Samsung make most of the AMOLED screens found in Nokia phones and it must be galling to be dependent on the company"s biggest competitor.
In other words, the switch was almost certainly not primarily to make the phone more useable, per se. However, with one caveat, the IPS display does have a couple of big advantages:
it"s more power efficient for typical use. AMOLED seemed a great idea back in 2009/2010, with potentially big power savings, but the number of web pages and applications which use white backgrounds (for which AMOLED is a staggering ten times - or more - hungrier) has perhaps forced a rethink. IPS and other LCD displays do use a bit more power when showing all white, but the difference is far smaller than for AMOLED.
when combined with a ClearBlack Display screen arrangement, as on the 701, screen contrast outdoors is much improved. As you"ll see in the photo examples below, when the sun is really shining, the CBD-less AMOLED on the Nokia C7 struggles to be seen, while the reduction of reflection by the use of CBD means that the Nokia 701"s screen is genuinely visible in all light conditions.
The caveat - of course - is that once you go AMOLED it"s quite hard to go back to more traditional screen technologies (like LCD). The richness of AMOLED colours, the blacker-than-black blacks, all are quite addictive. Yes, I got used to the Nokia 701 screen for the reasons stated on this page, but if I was offered the choice I think I"d still go for the AMOLED screen - it"s something you come to love....!
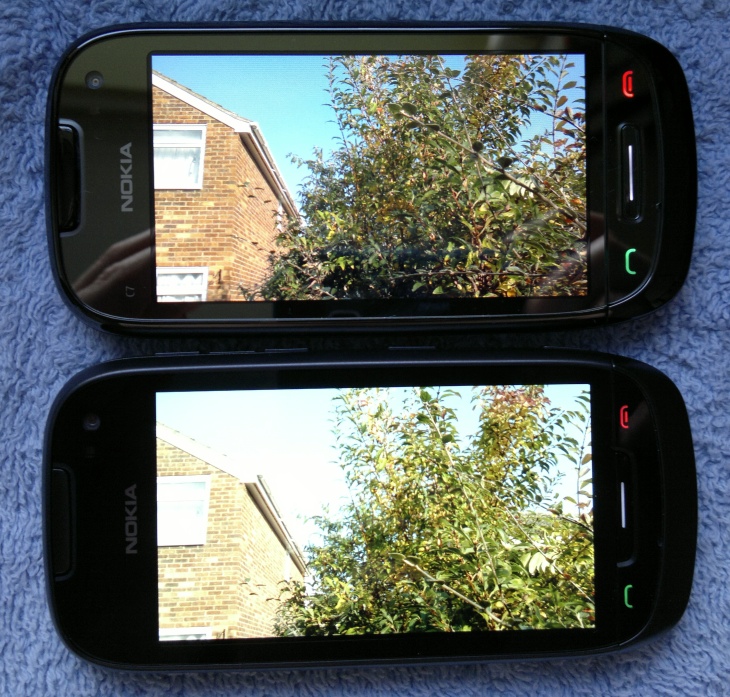
All of which means that you"ll be wanting to see how the two screen technologies fare in different light conditions, in photo evidence form, everything else being equal. I took a bright, colourful photo and loaded it in Photos/Gallery on the Nokia 701 and C7, in each case making sure the screen was at full brightness and also splaying the 4:3 photo to fill the screen. One variable I could do nothing about was the phones" own internal display auto-brightness, which is set by Nokia.
The photo above was taken in average light, indoors, near a window. Typical office or home conditions, perhaps even equal to a cloudy day outdoors. You can see that the 701"s IPS/CBD display is noticeably brighter than the C7"s. But let"s look at the displays head on, in case viewing angles are to blame here:
Don"t get too hung up on the 701"s display looking overblown - that"s simply my N8"s camera not being able to handle the brightness being displayed - the screen looked fine in practice. Having said that, the slightly dimmer AMOLED display on the C7 did show richer colours, as you"d expect, and the sky was definitely bluer and more attractive.
Interestingly, the auto-brightness in the 701 is tuned slightly differently to the C7 and they both end up at about the same brightness level. And, indeed, you can see for yourself how the AMOLED screen (top) wins out in terms of colours - I"m not entirely sure that the sky was that shade of blue in real life, but it certainly looks great. AMOLED for the win in the dark then.
Here you can see that the C7"s AMOLED display is dominated by the reflection of my hands holding the N8 taking the photo, whereas the 701"s IPS/CBD display remains surprisingly clear, with only a hint of sunny reflection.
The six million dollar question is either how would the C7 have coped if its AMOLED display had also had CBD, or how would the 701 have coped if its IPS display wasn"t helped by CBD? I suspect that the sun test would have shown both to be on a par with each other. In other words, AMOLED trumps IPS (because of the richer colours) given an equal amount of CBD polariser help.
But I really wouldn"t worry too much if you"re thinking of buying the Nokia 701 - the difference in colour renditions isn"t that large and indeed Rafe is on record as saying he didn"t really notice it didn"t have AMOLED at first. And you can console yourself with the knowledge that many "white" apps will now run using far less power drain and that the CBD will mean you"re still communicating and navigating even when the sun"s at its zenith.

OLED displays offer the best quality images and the freedom of flexible design. OLEDs have become very popular in high-end smartphones in recent years, with companies such as Samsung, Apple, Huawei, Xiaomi and others all releasing OLED smartphones.
For many years, Samsung branded its smartphone OLEDs as Super AMOLED displays. These AMOLED displays have an integrated touch layer, offer an extremely high image quality and are generally considered to be the world"s best mobile displays.
In short, a Dynamic AMOLED display is a Super AMOLED display with an added HDR10+ support. Samsung says that these next-generation OLED display panels includes "HDR10+ certification for cinema-grade color and contrast" - Mobile Color Volume 100% of DCI-P3 (Digital Cinema Initiatives) coverage with a contrast ratio of 2,000,000:1, certified by VDE Germany.
Dynamic AMOLED displays have also received eye comfort certification from TUV Rheinland. Based on the lower blue light emission of the OLED displays, they are safer to use compared to other displays (LCDs) on the market.
Many people wonder what is the actual difference between a Dynamic AMOLED and a Super AMOLED. Samsung is not very clear about this, and it continues to use both brands for its display products. It is most likely that a Dynamic AMOLED is a Super AMOLED with HDR10+ certification.
Samsung Galaxy S10 smartphones also use what Samsung calls Infinity-O Display. This term is used by Samsung to note that the display covers the entire from of the device, with a hole cut for the camera. This is to distinguish Samsung designs from notch-type OLEDs such as these used by Apple in its latest iPhones.

IPS (In-Plane Switching) lcd is still a type of TFT LCD, IPS TFT is also called SFT LCD (supper fine tft ),different to regular tft in TN (Twisted Nematic) mode, theIPS LCD liquid crystal elements inside the tft lcd cell, they are arrayed in plane inside the lcd cell when power off, so the light can not transmit it via theIPS lcdwhen power off, When power on, the liquid crystal elements inside the IPS tft would switch in a small angle, then the light would go through the IPS lcd display, then the display on since light go through the IPS display, the switching angle is related to the input power, the switch angle is related to the input power value of IPS LCD, the more switch angle, the more light would transmit the IPS LCD, we call it negative display mode.
The regular tft lcd, it is a-si TN (Twisted Nematic) tft lcd, its liquid crystal elements are arrayed in vertical type, the light could transmit the regularTFT LCDwhen power off. When power on, the liquid crystal twist in some angle, then it block the light transmit the tft lcd, then make the display elements display on by this way, the liquid crystal twist angle is also related to the input power, the more twist angle, the more light would be blocked by the tft lcd, it is tft lcd working mode.
A TFT lcd display is vivid and colorful than a common monochrome lcd display. TFT refreshes more quickly response than a monochrome LCD display and shows motion more smoothly. TFT displays use more electricity in driving than monochrome LCD screens, so they not only cost more in the first place, but they are also more expensive to drive tft lcd screen.The two most common types of TFT LCDs are IPS and TN displays.

The Samsung Galaxy A20e is an undertoned version of the Galaxy A20. To make the Galaxy A20e more affordable, it has watered down the two segments including display and battery. The Galaxy A20e settles for a TFT LCD screen while the Galaxy A20 gets Super AMOLED display. Both the smartphones do have a similar Infinity-V display design, i.e. waterdrop notch on top of the screen. In terms of disparity in the battery capacity, the Galaxy A20e ends up with a smaller 3,000mAh battery due to its size but thankfully retains 15W fast charging support as the Galaxy A20. Being bigger, the Galaxy A20 has a massive 4,000mAh battery. Other than the difference in screen and battery, both the Galaxy A20 and Galaxy A20e are similar smartphones. They share the same chipset, camera setup, RAM and storage capacity. Samsung has positioned the Galaxy A20e in the market as a compact alternative to the Galaxy A20. It would be an ideal pick for the buyers who want a small phone to carry around with decent specs.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey