difference between tft lcd led displays free sample

Confused about LED vs. LCD vs. TFT? Here"s everything you need to know. Creating or upgrading a device display or screen can involve a lot of different things, but it often comes down to one major question - what kind of display should you get?
So, there are 3 common displays LED, LCD and TFT available in the market. All terms refer to the flat-panel display, or screen, of a computer monitor or television set. In this article, we are going to differentiate between them. It will help you to choose a better one.
LCD stands for liquid crystal display. Works by adjusting the amount of light blocked. Usually has a backlight but might not (clocks, calculators, Nintendo Gameboy). The green-black ones can be very cheap and are a mature technology. Response time can be slow. An LCD display uses the light balancing qualities of crystals. Today LCDs are used in a great number of products and applications. Your TV, computer screen, calculator, cell phone and the dreaded alarm clock are all made of an LCD flat panel. Color LCDs produce the color based on two techniques: Passive matrix and active matrix. Passive matrix is the cheapest technology of the two. The other technology is called an active matrix or TFT. Active matrix displays produce really sharp and clear images.
This is a type of LCD with a thin film transistor attached to each pixel. All computer LCD screens are TFT since the early 2000s; older ones had slower response times and poorer color. Cost is now very good; power consumption is fairly good but dominated by the backlight. Has to be manufactured out of glass. The TFT layer is embedded in the screen itself, it reduces crosstalk between pixels. Crosstalk happens when a signal sends to a pixel also affects the pixel next to it. This makes the TFT technology the technology offering the best resolution and image quality. It also makes it a bit more expensive. Today TFTs have become the standard when producing LCD screens.
LED stands for a light emitting diode. As the name suggests, emits light rather than blocking it like LCD. Used for red/green/blue/white indicator lights everywhere. Some manufacturers advertise "LED" displays that are TFT screens with a white LED backlight, which is just confusing. Ones that are real LED screens are usually OLED.
Some devices actually have backlights made from Red, Green and Blue LEDs, normally referred to as RGB LED, which tend to have better color reproduction than any other display.
LED screen is just like saying that it is a plastic screen. You still have the WHOLE screen illuminated all the time and LED is "good" only for being more eco-friendly and probably more bright at max setting if you ever need this.
An LCD panel is, in fact, 2 layers of glass with some volume of Liquid Crystal in between. These two form the panel itself. The 2 layers are usually called Color Filter Glass (above) and TFT glass (below).
LCDs can’t completely prevent light from passing through, though, even during dark scenes, so dimming the light source itself aids in creating deeper blacks and more impressive contrast in the picture.
A standard TFT has a whole "lamp" behind it, illuminating the whole screen all the time. This way, you cannot have a true black, as it is still illuminated and stay grayish.
TFTs are a type of active matrix display that controls individual pixel updates several times per second on the screen to update the image relative to the content source.
TFT displays use more electricity than regular LCD screens, so they not only cost more in the first place, but they are also more expensive to operate.
LCDs use fluorescent lights while LEDs use those light emitting diodes. The fluorescent lights in an LCD are always behind the screen. On an LED, the light emitting diodes can be placed either behind the screen or around its edges.
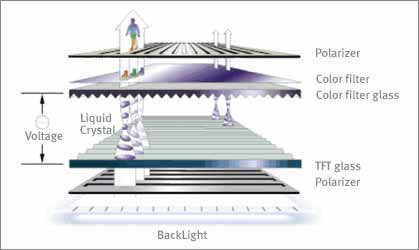
TFT displays are also known as an “Active Matrix TFT LCD module” and have an array of thin film transistors fabricated on the glass that makes the LCD. There is one of these transistors for each pixel on the LCD.
LCDs use voltage applied to a field of microscopic liquid crystals to change the crystal’s orientation, which in turn changes the polarization of the liquid crystal which creates light or dark pixels on the display.
Beautiful, complex images: All of our TFT modules are full-color graphic displays. Unlike standard monochrome character displays, you can create complex images for an imaginative user experience.
Thin and light: These are ideal display modules for handheld devices, communications equipment, information displays, and test and measurement equipment.
Single Supply: Most of the TFTs use an integrated controller with built-in voltage generation so only a single 3.3v supply is needed for both the panel power and logic voltage.
Many of our character LCD modules use a standard HD44780 controller, so they can be quickly integrated into a new product or used as a replacement in your existing products.
Many of the LCD controllers on board our graphic LCD display modules also include a CGROM (character generator ROM) which allows for easy character information as well as full bit-mapped graphic information to be shown.
Some of the graphic LCD displays have the ability to render graphics in grayscale, enabling you to show images and elements of your UI (user interface) with more depth and definition.
Because OLEDs are emissive, these displays can always be used in dark environments. There is usually a software command or hardware setting that will allow OLEDs to be dimmed.
Some OLED displays are bright enough to be sunlight readable–these models will typically take more current and may have a shorter rated lifetime. Additionally, OLEDs have extremely wide viewing angles.
What makes OLEDs useful for display construction is that they can be fabricated in bulk. Using OLED fabrication techniques, all the diodes can be made at the same time, at a much lower cost. OLEDs also come in a wide variety of colors.

Let us start with the basics first; refresh the knowledge about TN and LCD displays in general, later we will talk about TFTs (Thin Film Transistors), how they differ from regular monochrome LCD displays. Then we will go on to the ghosting effect, so we will not only discuss the technology behind the construction of the TFT, but also some phenomena, like the ghosting effect, or grayscale inversion, that are important to understand when using an LCD TFT display.
Next, we will look at different technologies of the TFT LCD displays like TN, IPS, VA, and of course about transmissive and transflective LCD displays, because TFT displays also can be transmissive and transflective. In the last part we will talk about backlight.
Let us start with a short review of the most basic liquid crystal cell, which is the TN (twisted nematic) display. On the picture above, we can see that the light can be transmit through the cell or blocked by the liquid crystal cell using voltage. If you want to learn more about monochrome LCD displays and the basics of LCD displays, follow this link.
What is a TFT LCD display and how it is different from a monochrome LCD display? TFT is called an active display. Active, means we have one or more transistors in every cell, in every pixel and in every subpixel. TFT stands for Thin Film Transistor, transistors that are very small and very thin and are built into the pixel, so they are not somewhere outside in a controller, but they are in the pixel itself. For example, in a 55-inch TV set, the TFT display contains millions of transistors in the pixels. We do not see them, because they are very small and hidden, if we zoom in, however, we can see them in every corner of each pixel, like on the picture below.
On the picture above we can see subpixels, that are basic RGB (Red, Green, Blue) colors and a black part, with the transistors and electronic circuits. We just need to know that we have pixels, and subpixels, and each subpixel has transistors. This makes the display active, and thus is called the TFT display. TFT displays are usually color displays, but there are also monochrome TFT displays, that are active, and have transistors, but have no colors. The colors in the TFT LCD display are typically added by color filters on each subpixel. Usually the filters are RGB, but we also have RGBW (Red, Green, Blue, White) LCD displays with added subpixels without the filter (White) to make the display brighter.
Going a little bit deeper, into the TFT cell, there is a part inside well known to us from the monochrome LCD display Riverdi University lecture. We have a cell, liquid crystal, polarizers, an ITO (Indium Tin Oxide) layer for the electrodes, and additionally an electronic circuit. Usually, the electronic circuit consists of one transistor and some capacitors to sustain the pixel state when we switch the pixel OFF and ON. In a TFT LCD display the pixels are much more complicated because apart from building the liquid crystal part, we also need to build an electronic part.
That is why TFT LCD display technologies are very expensive to manufacture. If you are familiar with electronics, you know that the transistor is a kind of switch, and it allows us to switch the pixel ON and OFF. Because it is built into the pixel itself, it can be done very quickly and be very well controlled. We can control the exact state of every pixel not only the ON and OFF states, but also all the states in between. We can switch the light of the cells ON and OFF in several steps. Usually for TFT LCD displays it will be 8-bit steps per color, so we have 256 steps of brightness for every color, and every subpixel. Because we have three subpixels, we have a 24-bit color range, that means over 16 million combinations, we can, at least theoretically, show on our TFT LCD display over 16 million distinct colors using RGB pixels.
Now that we know how the TFT LCD display works, we can now learn some practical things one of which is LCD TFT ghosting. We know how the image is created, but what happens when we have the image on the screen for a prolonged time, and how to prevent it. In LCD displays we have something called LCD ghosting. We do not see it very often, but in some displays this phenomenon still exists.
You may have seen this phenomenon already as it is common in every display technology, and even companies like Apple put information on their websites, that users may encounter this phenomenon and how to fix it. It is called image ghosting or image persistence, and even Retina displays are not free of it.
Another issue present in TFT displays, especially TN LCD displays, is grayscale inversion. This is a phenomenon that changes the colors of the screen according to the viewing angle, and it is only one-sided. When buying a TFT LCD display, first we need to check what kind of technology it is. If it is an IPS display, like the Riverdi IPS display line, then we do not need to worry about the grayscale inversion because all the viewing angles will be the same and all of them will be very high, like 80, 85, or 89 degrees. But if you buy a more common or older display technology type, like the TN (twisted nematic) display, you need to think where it will be used, because one viewing angle will be out. It may be sometimes confusing, and you need to be careful as most factories define viewing direction of the screen and mistake this with the greyscale inversion side.
On the picture above, you can see further explanation of the grayscale inversion from Wikipedia. It says that some early panels and also nowadays TN displays, have grayscale inversion not necessary up-down, but it can be any angle, you need to check in the datasheet. The reason technologies like IPS (In-Plane Switching), used in the latest Riverdi displays, or VA, were developed, was to avoid this phenomenon. Also, we do not want to brag, but the Wikipedia definition references our website.
We know already that TN (twisted nematic) displays, suffer from grayscale inversion, which means the display has one viewing side, where the image color suddenly changes. It is tricky, and you need to be careful. On the picture above there is a part of the LCD TFT specification of a TN (twisted nematic) display, that has grayscale inversion, and if we go to this table, we can see the viewing angles. They are defined at 70, 70, 60 and 70 degrees, that is the maximum viewing angle, at which the user can see the image. Normally we may think that 70 degrees is better, so we will choose left and right side to be 70 degrees, and then up and down, and if we do not know the grayscale inversion phenomena, we may put our user on the bottom side which is also 70 degrees. The viewing direction will be then like a 6 o’clock direction, so we call it a 6 o’clock display. But you need to be careful! Looking at the specification, we can see that this display was defined as a 12 o’clock display, so it is best for it to be seen from a 12 o’clock direction. But we can find that the 12 o’clock has a lower viewing angle – 60 degrees. What does it mean? It means that on this side there will be no grayscale inversion. If we go to 40, 50, 60 degrees and even a little bit more, probably we will still see the image properly. Maybe with lower contrast, but the colors will not change. If we go from the bottom, from a 6 o’clock direction where we have the grayscale inversion, after 70 degrees or lower we will see a sudden color change, and of course this is something we want to avoid.
To summarize, when you buy older technology like TN and displays, which are still very popular, and Riverdi is selling them as well, you need to be careful where you put your display. If it is a handheld device, you will see the display from the bottom, but if you put it on a wall, you will see the display from the top, so you need to define it during the design phase, because later it is usually impossible or expensive to change the direction.
We will talk now about the other TFT technologies, that allow us to have wider viewing angles and more vivid colors. The most basic technology for monochrome and TFT LCD displays is twisted nematic (TN). As we already know, this kind of displays have a problem with grayscale inversion. On one side we have a higher retardation and will not get a clear image. That is why we have other technologies like VA (Vertical Alignment), where the liquid crystal is differently organized, and another variation of the TFT technology – IPS which is In-Plane Switching. The VA and IPS LCD displays do not have a problem with the viewing angles, you can see a clear image from all sides.
Apart from the different organization of the liquid crystals, we also organize subpixels a little bit differently in a VA and IPS LCD displays. When we look closer at the TN display, we will just see the subpixels with color filters. If we look at the VA or IPS display they will have subpixels of subpixels. The subpixels are divided into smaller parts. In this way we can achieve even wider viewing angles and better colors for the user, but of course, it is more complicated and more expensive to do.
The picture above presents the TN display and grayscale inversion. For IPS or VA technology there is no such effect. The picture will be the same from all the sides we look so these technologies are popular where we need wide viewing angles, and TN is popular where we don’t need that, like in monitors. Other advantages of IPS LCD displays are they give accurate colors, and wide viewing angles. What is also important in practice, in our projects, is that the IPS LCD displays are less susceptible to mechanical force. When we apply mechanical force to the screen, and have an optically bonded touch screen, we push the display as well as squeeze the cells. When we have a TN display, every push on the cell changes the image suddenly, with the IPS LCD displays with in-plane switching, different liquid crystals organization, this effect is lesser. It is not completely removed but it is much less distinct. That is another reason IPS displays are very popular for smartphones, tablets, when we have the touchscreens usually optically bonded.
If we wanted to talk about disadvantages, there is a question mark over it, as some of them may be true, some of them do not rely on real cases, what kind of display, what kind of technology is it. Sometimes the IPS displays can have higher power consumption than others, in many cases however, not. They can be more expensive, but not necessarily. The new IPS panels can cost like TN panels, but IPS panels definitely have a longer response time. Again, it is not a rule, you can make IPS panels that are very fast, faster than TN panels, but if you want the fastest possible display, probably the TN panel will be the fastest. That is why the TN technology is still popular on the gaming market. Of course, you can find a lot of discussions on the internet, which technology is better, but it really depends on what you want to achieve.
Now, let us look at the backlight types. As we see here, on the picture above, we have four distinct types of backlight possible. The most common, 95 or 99 per cent of the TFT LCD displays on the market are the transmissive LCD display type, where we need the backlight from the back. If you remember from our Monochrome LCD Displays lecture, for transmissive LCD displays you need the backlight to be always on. If you switch the backlight off, you will not see anything. The same as for monochrome LCD displays, but less popular for TFT displays, we have the transflective LCD display type. They are not popular because usually for transflective TFT displays, the colors lack in brightness, and the displays are not very practical to use. You can see the screen, but the application is limited. Some transflective LCD displays are used by military, in applications where power consumption is paramount; where you can switch the backlight off and you agree to have lower image quality but still see the image. Power consumption and saving energy is most important in some kind of applications and you can use transflective LCD displays there. The reflective type of LCD displays are almost never used in TFT. There is one technology called Low Power Reflective Displays (LPRD) that is used in TFT but it is not popular. Lastly, we have a variation of reflective displays with frontlight, where we add frontlight to the reflective display and have the image even without external light.
Just a few words about Low Power Reflective Displays (LPRD). This kind of display uses environmental light, ambient light to reflect, and produce some colors. The colors are not perfect, not perfectly clear, but this technology is becoming increasingly popular because it allows to have color displays in battery powered applications. For example, a smartwatch would be a case for that technology, or an electrical bike or scooter, where we can not only have a standard monochrome LCD display but also a TFT LCD color display without the backlight; we can see the image even in
strong sunlight and not need backlight at all. So, this kind of TFL LCD display technology is getting more and more popular when we have outdoor LCD displays and need a low power consumption.
On the picture above, we have some examples of how transmissive and reflective LCD displays work in the sunlight. If we have a simple image, like a black and white pattern, then on a transmissive LCD display, even with 1000 candela brightness, the image probably will be lower quality than for a reflective LCD display; if we have sunlight, we have very strong light reflections on the surface of the screen. We have talked about contrast in more detail in the lecture Sunlight Readable Displays. So, reflective LCD displays are a better solution for outdoor applications than transmissive LCD displays, where you need a really strong backlight, 1000 candela or more, to be really seen outdoors.
To show you how the backlight of LCD displays is built, we took the picture above. You can see the edge backlight there, where we have LEDs here on the small PCB on the edge, and we have a diffuser that distributes the light to the whole surface of LCD screen.
In addition to the backlight, we have something that is called a frontlight. It is similar to backlight, it also uses the LEDs to put the light into it, but the frontlight needs to be transparent as we have the display behind. On the example on the picture above we can see an e-paper display. The e-paper display is also a TFT display variation, but it is not LCD (liquid crystal), it is a different technology, but the back of the display is the same and it is reflective. The example you see is the Kindle 4 eBook reader. It uses an e-paper display and a frontlight as well, so you can read eBooks even during the night.
In market, LCD means passive matrix LCDs which increase TN (Twisted Nematic), STN (Super Twisted Nematic), or FSTN (Film Compensated STN) LCD Displays. It is a kind of earliest and lowest cost display technology.
LCD screens are still found in the market of low cost watches, calculators, clocks, utility meters etc. because of its advantages of low cost, fast response time (speed), wide temperature range, low power consumption, sunlight readable with transflective or reflective polarizers etc. Most of them are monochrome LCD display and belong to passive-matrix LCDs.
TFT LCDs have capacitors and transistors. These are the two elements that play a key part in ensuring that the TFT display monitor functions by using a very small amount of energy without running out of operation.
Normally, we say TFT LCD panels or TFT screens, we mean they are TN (Twisted Nematic) Type TFT displays or TN panels, or TN screen technology. TFT is active-matrix LCDs, it is a kind of LCD technologies.
TFT has wider viewing angles, better contrast ratio than TN displays. TFT display technologies have been widely used for computer monitors, laptops, medical monitors, industrial monitors, ATM, point of sales etc.
Actually, IPS technology is a kind of TFT display with thin film transistors for individual pixels. But IPS displays have superior high contrast, wide viewing angle, color reproduction, image quality etc. IPS screens have been found in high-end applications, like Apple iPhones, iPads, Samsung mobile phones, more expensive LCD monitors etc.
Both TFT LCD displays and IPS LCD displays are active matrix displays, neither of them can produce color, there is a layer of RGB (red, green, blue) color filter in each LCD pixels to make LCD showing colors. If you use a magnifier to see your monitor, you will see RGB color. With switch on/off and different level of brightness RGB, we can get many colors.
Neither of them can’t release color themselves, they have relied on extra light source in order to display. LED backlights are usually be together with them in the display modules as the light sources. Besides, both TFT screens and IPS screens are transmissive, it will need more power or more expensive than passive matrix LCD screens to be seen under sunlight. IPS screens transmittance is lower than TFT screens, more power is needed for IPS LCD display.
LCD: liquid crystal display. Works by adjusting the amount of light blocked. Usually has a backlight but might not (clocks, calculators, Nintendo Gameboy). The green-black ones can be very cheap and are a mature technology. Response time can be slow.
TFT: is a type of LCD with a thin film transistor attached to each pixel. All computer LCD screens are TFT since early 2000s; older ones had slower response times and poorer colour. Cost is now very good; power consumption is fairly good but dominated by the backlight. Has to be manufactured out of glass.
LED: light emitting diode. As the name suggests, emits light rather than blocking it like LCD. Used for red/green/blue/white indicator lights everywhere.
Some manufacturers advertise "LED" displays that are TFT screens with a white LED backlight, which is just confusing. Ones that are real LED screens are usually OLED.
OLED: organic LED (rather than silicon or germanium based like regular LEDs). Comparatively recent technology, so cost still quite variable and not available in really large sizes. In theory can be printed on plastic, resulting in lighter flexible displays with good brightness, good power consumption and good response time.

TFT is an abbreviation for Thin Film Transistor, a flat panel display used to improve the operation and utility of LCD screens. In order to portray an appearance to the audience, a liquid crystal display (LCD) utilizes a crystalline-filled fluid to modify rear lighting polarized origin through the use of an electromagnetic force among two relatively thin metal wires such as indium oxide (ITO). However, color TFT displays are associated with this method, which can be employed in both divided and pixelated display systems.
With motion pictures displayed on an LCD, the intrinsic sluggish rate of increase between liquid phases over a significant number of pixel components can be an issue due to capacitance impacts, which can create a blurring of the visuals. Placing a high-velocity LCD control device inside the formation of a thin-film transistor immediately next to the cell component just on a glass screen, the issue of LCD picture speed may be substantially improved, and image blur can be eliminated for all useful purposes entirely.
Organic light-emitting diodes (AMOLEDs) are a type of flat light-emitting advanced technologies that are created by interspersing a succession of organic thin sheets over two conducting conductors. An electrical charge causes a brilliant light to be produced when the current flows. AMOLED displays are light-emitting screens that do not require a backlight, making them thinner and more energy-efficient than liquid crystal displays (LCDs) (which will need a white backlight).
AMOLED displays are not only thin and fuel-intensive, but they also deliver the highest image quality available, so they can be made translucent, elastic, bendable, or even rollable and stretchy in the future, allowing for a variety of applications. AMOLEDs are a revolutionary technology in terms of display devices! It is possible to create an AMOLED by sandwiching a sequence of thin films across phase conductors. Electric charge causes a brilliant light to be emitted when the current flows through the coil.
Half-Life has been expanded. TFT displays have a far longer half-life than its LED equivalents, and they are available in a number of sizes, which might have an effect on the device"s half-life based on the phone"s usage as well as other variables. Touch panels for TFT screens can be either resistant or capacitance in nature.
They rely on backlight to give illumination rather than generating their own light. Hence they require constructed light-creating diodes (LEDs) in their backlit display framework to ensure enough brightness.
Backlighting is unnecessary for AMOLEDs. LCDs produce images by selectively blocking parts of the illumination, whereas AMOLEDs produce light. AMOLEDs utilize less energy than LCDs since they don"t need backlighting. This is critical for battery-powered devices such as phones.
While AMOLED light-emitting sheets are lightweight, the substrate can also be elastic rather than stiff. AMOLED films are not limited to glass-like LEDs and LCDs.
AMOLEDs offer 170-degree ranges of vision. LCDs operate by obscuring the light. Hence they have intrinsic viewing obstacles. In addition, AMOLEDs have a substantially wider viewing spectrum.
AMOLEDs outperform LEDs. Since AMOLED organic coatings are less than LED inorganic crystal levels, AMOLED conducting and particle emitters layers can just be multi-layered. Also, LEDs and LCDs need glass backing, which absorbs light. AMOLEDs don"t need it.
AMOLEDs seem to be simpler to implement and larger. AMOLEDs are constructed of polymers and may be produced into big sheets. It takes a lot of extra liquid crystals to build and set down.
While red and green AMOLED sheets have a greater lifespan (46,000 to 230,000 hours), azure compounds have significantly shorter longevity (up to roughly 14,000 hours).
Due to the fact that AMOLED displays inherently emit illumination, they do not need a backlight when used on a monitor screen. Conversely, LCDs require backlights since the liquid crystals themselves are incapable of producing light under their own. Direct light emission from AMOLED displays also allows for the developing of lightweight display devices than others using TFT LCDs.
LCD displays have a higher brightness than AMOLED panels. This is owing to the LCD"s usage of led backlight, which may provide a brilliant illumination of the entire display. Despite the fact that AMOLEDs produce high levels of brilliance from their illumination, they will never be able to match the intensity of LCD lighting.
LCD screens use less power than AMOLED displays, which provides a slight advantage. The amount of energy consumed by AMOLED displays is dependent on the intensity of the screen. Lowered luminance results in lower energy usage, however, it might not be the best solution because the contrast would suffer as a result of the decreased brightness. In some situations, such as when to use an AMOLED device in direct sunlight, it is not an optimal situation.
However, the backlit keys of TFT displays account for the majority of their power usage. TFT screens" efficiency is considerably improved when the backlight is set to a lesser brightness level than the default setting. For example, replacing the light of an LCD TV with just an Led flash will have no effect on the image quality, but will result in lower power usage than replacing the light of an AMOLED TV.
With the exception of phones, numerous other technologies make use of displays to allow customers to engage in direct communication with them. To determine whether or not TFT LCD will be able to withstand the development of AMOLED innovation, we should first review the benefits of LCD technology. The backlighting quality ensures that whites are strong and brightness is superb but will deplete a battery much more quickly than just an AMOLED display. Furthermore, the cost of LCD screens is a considerable consideration. In addition to being less expensive and more easily accessible, they are produced in standard industry sizes, allowing them to be purchased for innovative products with relative ease.

For years, TFT displays have been the dominating technology in visualization. TFT LCD displays are everywhere in our daily lives; in consumer electronics, health care, communication devices and industry applications. While there are many LCD products in the market, they are not always suitable for every application. This is especially true for industrial TFT LCD. Understanding different requirements between industrial display and consumer TFT LCD, will help determine the best TFT LCD for your application.
Consumer grade TFT LCD like cell phone screen and computer monitor occupy big chunk of LCD market. Due to the nature of consumer market, competitive pricing and quick production cycles, these TFT LCDs are lack of the durability that industrial LCD has. Not like our cell phone screen and computer monitor, industrial LCD displays are used in much challenging environments. For example, an TFT LCD display on production line will face constant vibration, high working temperature. Its endurance to outside condition is a must.
Industrial TFT LCD has very good visibility. Which includes wide viewing angle, so that staff on production line can easily read information from different angles.
Sunlight readable is another important aspect that industrial TFT LCD persists. Many industrial applications are used outdoor, under direct sunlight. And user needs to be able to read what is on LCD screen easily. Topway has years experience on producing sunlight readable TFT LCD by using high brightness LED backlight and low reflectance technologies.
Industrial TFT LCD is made with high quality industrial grade components and material. Only then we could produce high quality TFT display that survives rigid tests like ESD, EMI and aging test, etc. All LCD product from Topway went through strict testings before reaching customers" warehouses.
Industrial TFT LCD has way longer supply commitment than consumer LCD. Ever try to fix a 2~3 years old cell phone"s crack screen? It is very difficult and expensive. Because replacement LCD screen is no longer being made. On the other hand, industrial LCD screen usually is in production for 10 plus years. And most of the time, for Topway anyway, there will be an upgrade model to replace end-of-life product. Thus, our customers won"t need to do much change on their product.
Industrial TFT LCD is a lot better in many areas than consumer one, even they look similar in normal situation. Topway as an industrial TFT LCD manufacturer, has been designing and producing industry grade LCD for more than twenty years. Our commitment on quality and customer service wins Topway friendship and orders. Please feel free to leave us message on your next industry project.

What are the key differences between leading electronic visual displays available in the market? Such are the times that we live in that today most of us cannot possibly imagine a life without an electronic device. In fact, we have managed to surround ourselves and depend on a growing number of electronic appliances. Several of these devices - as it happens - also have an electronic visual display; be it a mobile phone, a tablet, a desktop monitor or the television set. Without a doubt, these electronic screen devices have revolutionised the way we lead our lives now as all of the four devices have become increasingly commonplace to the point of becoming basic necessities. Which brings to our blog topic: what exactly is an electronic screen and which are the leading screen technologies available today? Read on to know more…
An electronic screen or an electronic visual display, informally called a screen, is basically a device used to display / present images, text, or video transmitted electronically, without creating a permanent record. As mentioned earlier, electronic visual displays include television sets, computer monitors, and digital signage in information appliances. As per the definition, an overhead projector (along with screen onto which the text, images, or video is projected) can also be called an electronic visual display.
1. Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) display:A vacuum tube containing one or more electron guns and a phosphorescent screen, the cathode-ray tube (CRT) is used to display images. It modulates, accelerates, and deflects electron beams onto the screen to make the images. The images could be electrical waveforms (oscilloscope), pictures (television, computer monitor) or radar targets. CRTs have also been used as memory devices, wherein the visible light from the fluorescent material (if any) does not really have any significant meaning to a visual observer, but the visible pattern on the tube face could cryptically represent the stored data. In television sets and computer monitors, the front area of the tube is scanned systematically and repetitively in a pattern called a raster. Thanks to the intensity of each of the three electron beams - one for each additive primary color (red, green, and blue) - being controlled with a video signal as a reference, an image is produced. In modern CRT monitors and TVs, magnetic deflection bends the beams; magnetic deflection is essentially a varying magnetic field generated by coils and driven by electronic circuits around the neck of the tube, although electrostatic deflection is often used in oscilloscopes, a type of electronic test instrument. CRT is one of the older screen/ display technologies.
2. Flat-Panel display: Flat-panel displays are electronic viewing technologies that are used to allow people to see content (still images, moving images, text, or other visual material) in a range of entertainment, consumer electronics, personal computer, and mobile devices, and several kinds of medical, transportation and industrial equipment. They are much lighter and thinner than traditional cathode ray tube (CRT) television sets and video displays and are typically less than 10 centimetres (3.9 in) thick. Flat-panel displays can be classified under two display device categories: volatile and static. Volatile displays need pixels to be periodically electronically refreshed to retain their state (say, liquid-crystal displays). A volatile display only shows an image when it has battery or AC mains power. Static flat-panel displays rely on materials whose color states are bistable (say, e-book reader tablets from Sony), and they retain the text or images on the screen even when the power is off. In recent times, flat-panel displays have almost completely replaced old CRT displays. Most flat-panel displays from the 2010s use LCD and/or LED technologies. Majority of the LCD screens are back-lit as color filters are used to display colors. Being thin and lightweight, flat-panel displays offer better linearity and have higher resolution than the average consumer-grade TV from the earlier decades. The highest resolution for consumer-grade CRT TVs was 1080i, whereas many flat-panels can display 1080p or even 4K resolution.
3. Plasma (P) display: A plasma display panel (PDP) is a type of flat panel display that uses small cells containing plasma; ionized gas that responds to electric fields. Earlier, plasma displays were commonly used in larger televisions (30 inches and larger). But since more than a decade now, they have lost almost all market share due to competition from low-cost LCDs and more expensive but high-contrast OLED flat-panel displays. Companies stopped manufacturing plasma displays for the United States retail market in 2014, and for the Chinese market in 2016.
4. Electroluminescent display (ELD):Electroluminescent Displays (ELDs) are screens that make use of electroluminescence. Electroluminescence (EL) is an optical and electrical phenomenon where a material emits light in response to an electric current passed through it, or to a strong electric field.
So ELD then is a kind of flat panel display produced by sandwiching a layer of electroluminescent material between two layers of conductors. When the current flows, the layer of material emits radiation in the form of visible light. Basically, electroluminescence works by exciting atoms by passing an electric current through them, leading them to emit photons. By varying the material being excited, the color of the light being emitted is changed. The actual ELD is built using flat, opaque electrode strips running parallel to each other, covered by a layer of electroluminescent material, followed by another layer of electrodes, running perpendicular to the bottom layer. This top layer has to be transparent so as to allow light to escape. At each intersection, the material lights, creating a pixel.
5. Liquid Crystal Display (LCD): A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other electronically modulated optical device that makes use of the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals. Liquid crystals do not give out light directly; they use a backlight or reflector to create images in color or monochrome. LCDs display arbitrary images like in a general-purpose computer display or fixed images with low information content, that can be displayed or hidden, such as preset words, digits, and seven-segment displays, like in a digital clock. They use the same core technology, apart from the fact that arbitrary images are made up of a large number of small pixels, while other displays have larger elements. LCDs could be on (positive) or off (negative), as per the polarizer arrangement. For instance, a character positive LCD with a backlight has black lettering on a background the same color as the backlight, and a character negative LCD has a black background with the letters matching the backlight color. Blue LCDs typically get their characteristic appearance from optical filters being added to white.
LCD screens are being used in several applications such as LCD televisions, computer monitors, instrument panels, aircraft cockpit displays, and indoor and outdoor signage. Small LCD screens are seen in portable consumer devices such as digital cameras, watches, calculators and mobile telephones, including smartphones. LCDs are also found in consumer electronics products such as DVD players, video game devices and clocks. It is interesting to note that these displays are available in a wide range of screen sizes as compared to CRT and plasma displays. Also, while LCD screens have replaced heavy, bulky cathode ray tube (CRT) displays in almost all applications, they are slowly being replaced by OLEDs, which can be easily made into different shapes, and boast other advantages such as having a lower response time, wider color gamut, virtually infinite color contrast and viewing angles, lower weight for a given display size and a slimmer profile and potentially lower power consumption. OLEDs, however, are more expensive for a given display size and they can suffer from screen burn-in when a static image is displayed on a screen for a long time (for instance, the table frame for an airline flight schedule on an indoor sign), not to mention that there is currently no way to recycle OLED displays. LCD panels, on the other hand, are susceptible to image persistence but they rarely suffer image burn-in as they do not use phosphors, plus they can be recycled, although this technology is not exactly common as yet. Not surprisingly, attempts have been made to increase the lifespan of LCDs in the form of quantum dot displays, which provide performance to that of an OLED display, but the Quantum dot sheet that gives these displays their characteristics can not yet be recycled. LCDs are also more energy-efficient and can be disposed of more safely than a CRT display.
6. Light-Emitting Diode (LED) display:An LED display is a flat panel display that uses an array of light-emitting diodes as pixels for a video display. Their brightness lets them be used outdoors where they are visible in the sun for store signs and billboards. It was in 1962 that LED diodes first came into being; this was when the first practical LED was invented by General Electric’s Nick Holonyak Jr. This was also when they were mainly red in color. While the early models had a monochromatic design, the efficient Blue LED completing the color triad became available in the market only in the late 1980s. Today, large displays use high-brightness diodes to generate a wide spectrum of colors. In fact, recently, LEDs have also become a popular choice among destination signs on public transport vehicles and variable-message signs on highways. LED displays can offer general illumination in addition to visual display, as when used for stage lighting or other decorative (as opposed to informational) purposes. Several big corporations such as Apple, Samsung and LG are currently looking to develop MicroLED displays. These displays are easily scalable, and help with making the production process more streamlined. That said, production costs continue to be quite high and thus remain a limiting factor.
7. Organic Light-Emitting Diode OLED display: An organic light-emitting diode (OLED), also called an organic EL (organic electroluminescent) diode, is a light-emitting diode (LED), where the emissive electroluminescent layer is a film of organic compound that gives out light in response to an electric current. The organic layer is located between two electrodes, at least one of which is transparent. OLEDs are used to build digital displays in devices such as television screens, computer monitors, portable systems such as smartphones, handheld game consoles and digital assistants. Typically, an OLED display works without a backlight because it emits visible light. This means that it can display deep black levels and can be thinner and lighter than a liquid crystal display (LCD). In low ambient light conditions, say in a dark room, an OLED screen can achieve a higher contrast ratio than an LCD, irrespective of whether the LCD uses an LED backlight or cold cathode fluorescent lamps.
Also important to note an OLED display can be driven with a passive-matrix (PMOLED) or active-matrix (AMOLED) control scheme. In the former, each row (and line) in the display is controlled sequentially, one by one, as opposed to in the AMOLED where a thin-film transistor backplane is used to directly control and switch each individual pixel on or off, thus offering higher resolution and larger display sizes.
Lastly, there are two main families of OLED: those based on small molecules and those making use of polymers. A big area of research is the development of white OLED devices for use in solid-state lighting applications.
8. Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode (AMOLED) display: AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) is a display device technology being used in smartwatches, mobile devices, laptops, televisions, media players and digital cameras. As mentioned earlier, it is a type of OLED; rather a specific type of thin-film-display technology where organic compounds form the electroluminescent material. What distinguishes it from PMOLED is the active matrix technology behind the addressing of pixels. An AMOLED display basically comprises an active matrix of OLED pixels generating light (luminescence) upon electrical activation that have been positioned or integrated onto a thin-film transistor (TFT) array, which in turn operates as a series of switches to control the current flowing to each individual pixel. AMOLED technology has continued to work towards consuming low power, becoming low-cost and offering scalability (mainly by offering larger sizes.
9. Super AMOLED display: Super AMOLED is essentially an AMOLED display but it is a term coined for marketing purposes by leading device manufacturers. It is used to denote AMOLED displays that come with an integrated digitizer, i.e. the layer that detects touch is integrated into the screen, instead of overlaid on top of it. The display technology however is not an improvement on the AMOLED. For instance, Samsung claims that Super AMOLED displays reflect one-fifth as much sunlight as the first generation AMOLED. In fact, Super AMOLED displays that are part of the Pentile matrix family, are also at times known as SAMOLED. Other variations of this term include Super AMOLED Advanced, Super AMOLED Plus, HD Super AMOLED, HD Super AMOLED Plus and Full HD Super AMOLED.
10. Quantum Dot (QD) display:A quantum dot display is a display device that uses quantum dots (QD), basically semiconductor nanocrystals that can generate pure monochromatic red, green, and blue light. Photo-emissive quantum dot particles are used in a QD layer which converts the backlight to give out pure basic colors that in turn enhance display brightness and color gamut by decreasing light loss and color crosstalk in RGB color filters. This technology is used in LED-backlit LCDs, though it applies to other display technologies as well (such as white or blue/UV OLED).
Among devices employing QD screens, one can find electro-emissive or electroluminescent quantum dot displays, which are currently an experimental type of display based on quantum-dot light-emitting diodes (QD-LED). These displays are similar to active-matrix organic light-emitting diode (AMOLED) and MicroLED displays, as in light is produced directly in each pixel by applying an electric current to inorganic nano-particles. QD-LED displays are supposed to support large, flexible displays and not degrade as readily as OLEDs, making them good bets for flat-panel TV screens, digital cameras, mobile phones and handheld game consoles. As of 2018, all commercial products like LCD TVs that use quantum dots and are called QLED, use photo-emissive particles, whereas electro-emissive QD-LED TVs are only to be found in laboratories today.

It seems as if modern displays have all kinds of different labels: high definition, 3D, smart, 4K, 4K Ultra, the list goes on. The two most common labels are LCD and LED. What’s the difference between the two? Is there a difference? And does this difference make one or the other preferable for certain types of activities like gaming or graphic design?
All LED monitors are LCD monitors. But not all LCD monitors are LEDs. Kind of like all eagles are birds, but not all birds are eagles. While the names might be confusing to those wading through specs to find the best monitor, once you break it down it’s easier to understand than you think.
We’ll explain the tech and the naming conventions, and then highlight some HP monitors that might be the perfect fit for your needs. Let’s figure out exactly what LCD and LED monitors are and how to pick the right one for you.
Both types of displays use liquid crystals to help create an image. The difference is in the backlights. While a standard LCD monitor uses fluorescent backlights, an LED monitor uses light-emitting diodes for backlights. LED monitors usually have superior picture quality, but they come in varying backlight configurations. And some backlight configurations create better images than others.
Until 2014, plasma displays were the most commonly manufactured displays. But then the LCD took over. LCD stands for liquid crystal display. We’ll go over what that means in a minute. But first, it’s important to note that an LED also uses liquid crystals, so the name is somewhat misleading. Technically, an “LED monitor” should really go by the name, “LED LCD monitor.”
First, let’s go over how LCD and LED monitors utilize liquid crystals. The science behind this stuff features an incredibly complicated mix of optics, electrical engineering, and chemistry. But we’ll explain it in layman’s terms.
LCD monitors have backlights behind the screen that emit white light, and the light can’t pass through the liquid crystals while they’re in their liquid arrangement. But when the pixel is in use, the monitor applies an electric current to the liquid crystals, which then straighten out and allow light to pass through them[2].
Standard LCD monitors employ “cold cathode fluorescent lamps,” also known as CCFLs as backlights. These fluorescent lights are evenly placed behind the screen so that they deliver consistent lighting across the display. All regions of the picture will have similar brightness levels.
LED monitors don’t use fluorescent lamps. Instead, they use “light-emitting diodes,” which are extremely small lights. There are two methods of LED backlighting: full-array backlighting and edge lighting.
With full-array backlighting, the LEDs are placed evenly across the entire screen, similar to an LCD setup. But what’s different is that the LEDs are arranged in zones. Each zone of LED lights can be dimmed (also known as local dimming).
When there’s an area of the picture that needs to be darker (a night sky, for instance), the LEDs in that region of the picture can be dimmed to create a truer black. This is not possible on standard LCD monitors, where the entire picture is lit evenly throughout.
There are no local dimming capabilities in edge-lighted displays, so they can’t create pictures that are as high-quality as those created by full-array LEDs. However, edge lighting enables manufacturers to create extremely thin displays that don’t cost as much to produce - and which are better for a tight budget.
When it comes to picture quality, full-array LED monitors are almost always superior to LCD monitors. But bear in mind that only full-array LEDs are superior. Edge-lit LEDs may actually be inferior to LCD monitors.
A full-array LED monitor should be your number one choice for gaming. Steer clear if its edge lighting. The problem with edge lighting is that you’ll have fewer optimal viewing angles with which to play games. That’s not an issue if you prefer to sit directly in front of the screen while you’re gaming. But if you like to kick back in your chair or view from different angles, you’ll find that an edge-lit LED loses visibility as you move away from the center viewing angle.
But even if you play while you’re directly in front of the monitor, edge-lit LEDs have more issues with glare than full-array LEDs do. That’s because of the uneven lighting (very bright around the edges, darker as you approach the center of the display). Because the pixels are evenly lit, LCD monitors tend to have better viewing angles and anti-glare than edge-lit LEDs.
Edge-lit LEDs do have two big advantages. If you have a very tight space in which to fit your monitor, you’ll like having an edge-lit LED because they’re usually thinner than the other types. They’re also less expensive to manufacture, which make them easier on the wallet.
Because LED monitors create better pictures than LCD monitors, nearly all of HP’s displays are built with LED backlights. When you’re browsing through the HP LED monitors, you might notice that some of them are equipped with either “IPS” or “AHVA” technology. These refer to the types of liquid crystal panels that are used. Both are fantastic, although they have some minor differences:
You’ll also see that some monitors have “TN” LED backlights. This is the oldest form of liquid crystal technology. It’s still very effective, but TN panels are typically used in small, work-oriented monitors that are made to be mounted or used in the field.
HP OMEN gaming monitors are built for the power PC gamer. One of the best gaming monitors for your rig is the HP OMEN 32 32-inch display. This LED monitor has VA-type panels, which help give it a fast refresh rate that’s perfect for high-performance gaming.
If you’re a business person, try one our HP EliteDisplay monitors, like the HP EliteDisplay E243 23.8-inch monitor. The IPS LED display is gorgeous and will give you a crisp and clear picture no matter what software you’re using. The micro edges make it perfect for a dual monitor setup, and the 23.8-inch size is wide, but not too large to accommodate a second monitor or to fit into tighter workstations.
There are some up-and-coming technologies that are making LED displays even better. OLED and QLED displays are bound to become more commonplace in the future.
“OLED” stands for “organic light-emitting diode.” What makes an OLED unique is that each pixel has a light source that can be individually shut off. On an LED monitor, the only way to keep a pixel from emitting light is to keep the liquid crystal closed. It’s effective, but not perfect - a small portion of light will always seep through. On an OLED monitor, each pixel’s light can be entirely shut off so no light at all will emanate through the liquid crystal. These means you can get truer blacks, which means deeper contrast ratios and better image quality.
There are two additional advantages. First, OLED monitors can be made even thinner than LED monitors because there’s not a separate layer of LEDs behind the pixels. Second, these monitors are more energy efficient because the pixels will only draw power when their light is turned on. One of the downsides, though, is that pixel burn-in will be more noticeable since some pixels will inevitably be used more than others[4].
“QLED” stands for “quantum light-emitting diode.” In a QLED monitor, each pixel has a “quantum dot.” Quantum dots are tiny phosphor particles that glow when you shine a light upon them[5].
Why would you need a glowing particle over each pixel? Because LEDs aren’t very good at emitting bright light. The brightest color is white. But an LED doesn’t emit white light – it emits blue light. Each LED is given a yellow phosphor coating to make it appear less blue and more white, but it’s still not true white. The “blueness” of LEDs negatively impacts the red, blue, and green colors on LED displays. LED monitors have automatic features that adjust the RGB colors to compensate for the blue light, but it can’t compensate for the weaker light intensity.
That’s where the quantum dots come in. The pixels are overlayed by a sheet of red and green quantum dots (there is no blue because blue light is already being emitted by the LED). When the light shines through the liquid crystals, the quantum dots glow, and you’re given a bright, vivid, and lovely spectrum of RGB colors.
Displays are a complicated science, right? But next time you’re shopping for monitors at the store or on our HP Store site, you’ll be a true expert and will be able to pick out exactly the right display for you.
In this article, you will learn how to use TFT LCDs by Arduino boards. From basic commands to professional designs and technics are all explained here.
In electronic’s projects, creating an interface between user and system is very important. This interface could be created by displaying useful data, a menu, and ease of access. A beautiful design is also very important.
There are several components to achieve this. LEDs, 7-segments, Character and Graphic displays, and full-color TFT LCDs. The right component for your projects depends on the amount of data to be displayed, type of user interaction, and processor capacity.
TFT LCD is a variant of a liquid-crystal display (LCD) that uses thin-film-transistor (TFT) technology to improve image qualities such as addressability and contrast. A TFT LCD is an active matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven LCDs with a few segments.
In Arduino-based projects, the processor frequency is low. So it is not possible to display complex, high definition images and high-speed motions. Therefore, full-color TFT LCDs can only be used to display simple data and commands.
In electronic’s projects, creating an interface between user and system is very important. This interface could be created by displaying useful data, a menu, and ease of access. A beautiful design is also very important.
There are several components to achieve this. LEDs, 7-segments, Character and Graphic displays, and full-color TFT LCDs. The right component for your projects depends on the amount of data to be displayed, type of user interaction, and processor capacity.
TFT LCD is a variant of a liquid-crystal display (LCD) that uses thin-film-transistor (TFT) technology to improve image qualities such as addressability and contrast. A TFT LCD is an active matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven LCDs with a few segments.
In Arduino-based projects, the processor frequency is low. So it is not possible to display complex, high definition images and high-speed motions. Therefore, full-color TFT LCDs can only be used to display simple data and commands.
Size of displays affects your project parameters. Bigger Display is not always better. if you want to display high-resolution images and signs, you should choose a big size display with higher resolution. But it decreases the speed of your processing, needs more space and also needs more current to run.
In electronics/computer hardware a display driver is usually a semiconductor integrated circuit (but may alternatively comprise a state machine made of discrete logic and other components) which provides an interface function between a microprocessor, microcontroller, ASIC or general-purpose peripheral interface and a particular type of display device, e.g. LCD, LED, OLED, ePaper, CRT, Vacuum fluorescent or Nixie.
The LCDs manufacturers use different drivers in their products. Some of them are more popular and some of them are very unknown. To run your display easily, you should use Arduino LCDs libraries and add them to your code. Otherwise running the display may be very difficult. There are many free libraries you can find on the internet but the important point about the libraries is their compatibility with the LCD’s driver. The driver of your LCD must be known by your library. In this article, we use the Adafruit GFX library and MCUFRIEND KBV library and example codes. You can download them from the following links.
Upload your image and download the converted file that the UTFT libraries can process. Now copy the hex code to Arduino IDE. x and y are locations of the image. sx and sy are size of the image.
In this template, We just used a string and 8 filled circles that change their colors in order. To draw circles around a static point ,You can use sin(); and cos(); functions. you should define the PI number . To change colors, you can use color565(); function and replace your RGB code.
In this template, We created a function which accepts numbers as input and displays them as a pie chart. We just use draw arc and filled circle functions.
while (a < b) { Serial.println(a); j = 80 * (sin(PI * a / 2000)); i = 80 * (cos(PI * a / 2000)); j2 = 50 * (sin(PI * a / 2000)); i2 = 50 * (cos(PI * a / 2000)); tft.drawLine(i2 + 235, j2 + 169, i + 235, j + 169, tft.color565(0, 255, 255)); tft.fillRect(200, 153, 75, 33, 0x0000); tft.setTextSize(3); tft.setTextColor(0xffff); if ((a/20)>99)
while (b < a) { j = 80 * (sin(PI * a / 2000)); i = 80 * (cos(PI * a / 2000)); j2 = 50 * (sin(PI * a / 2000)); i2 = 50 * (cos(PI * a / 2000)); tft.drawLine(i2 + 235, j2 + 169, i + 235, j + 169, tft.color565(0, 0, 0)); tft.fillRect(200, 153, 75, 33, 0x0000); tft.setTextSize(3); tft.setTextColor(0xffff); if ((a/20)>99)

A thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display (TFT LCD) is a variant of a liquid-crystal display that uses thin-film-transistor technologyactive matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven (i.e. with segments directly connected to electronics outside the LCD) LCDs with a few segments.
In February 1957, John Wallmark of RCA filed a patent for a thin film MOSFET. Paul K. Weimer, also of RCA implemented Wallmark"s ideas and developed the thin-film transistor (TFT) in 1962, a type of MOSFET distinct from the standard bulk MOSFET. It was made with thin films of cadmium selenide and cadmium sulfide. The idea of a TFT-based liquid-crystal displ




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey